Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 2269-2277.doi: 10.12307/2026.105
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and validation of a prediction model for axial symptoms after laminectomy with lateral mass screw fixation
Shi Yaozhou1, Jia Fanglin1, Zhang Heling1, Song Hanlin1, Gao Haoran1, Gao Xiao2, Sun Wei2, Feng Hu2
- 1Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2025-02-14Accepted:2025-04-12Online:2026-03-28Published:2025-09-28 -
Contact:Feng Hu, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Shi Yaozhou, Master candidate, Physician, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:cervical compressive myelopathy; laminectomy with lateral mass screw fixation; axial symptom; risk factor; nomogram; prediction model
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shi Yaozhou, Jia Fanglin, Zhang Heling, Song Hanlin, Gao Haoran, Gao Xiao, Sun Wei, Feng Hu. Establishment and validation of a prediction model for axial symptoms after laminectomy with lateral mass screw fixation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2269-2277.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
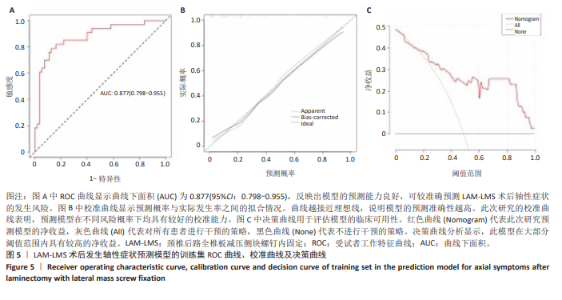
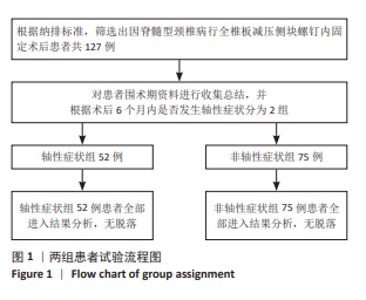
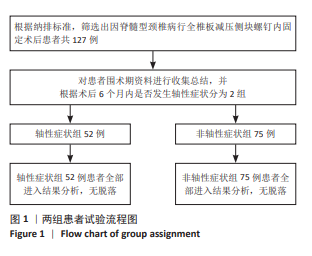
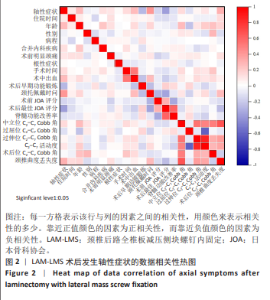
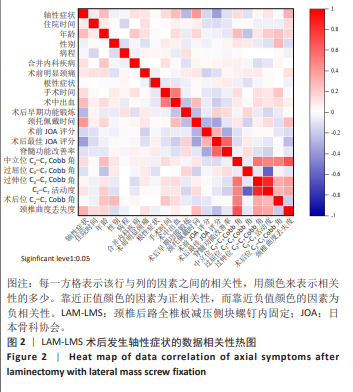
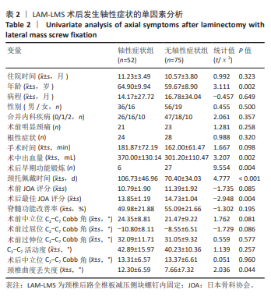
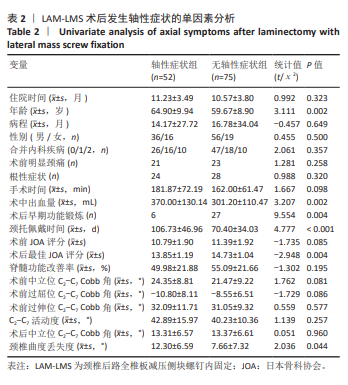
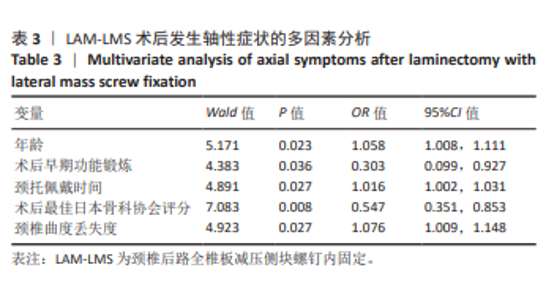
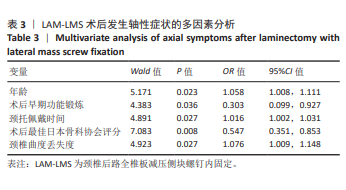
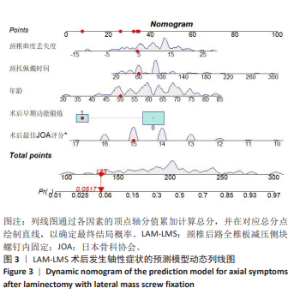
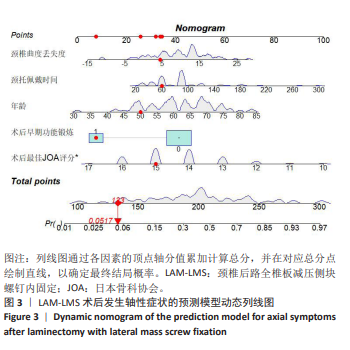
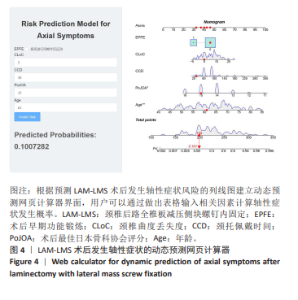
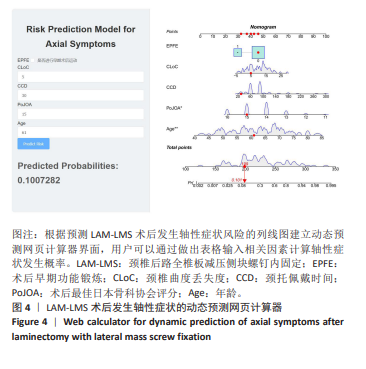
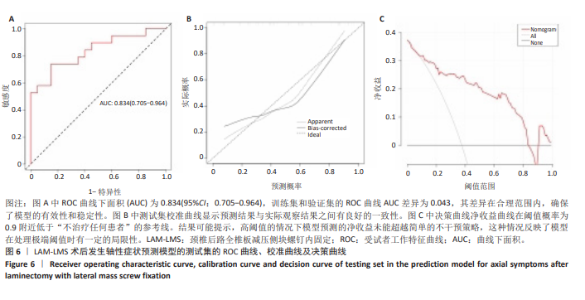
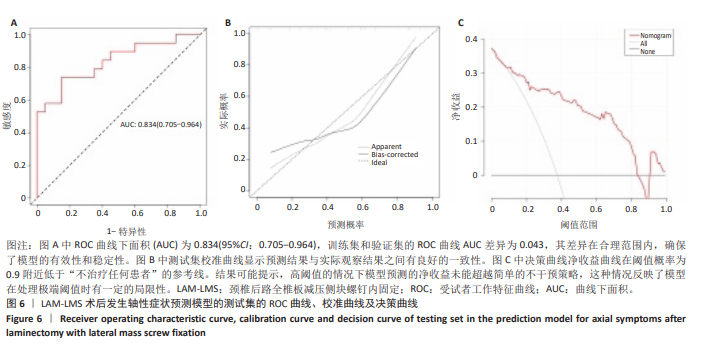
2.7 预测模型的验证 此次研究构建的轴性症状预测模型在验证队列中展现出良好的风险分层能力,该模型在校准曲线上表现出接近参考线的良好性能,在决策曲线分析中显示其具有较高的临床净收益,见图5。训练集中ROC曲线下面积为0.877(95%CI:0.798-0.955),根据COOK[15]提出的临床模型判别标准,该值超过0.85提示具有高水平风险识别效能。模型敏感度(78.8%)与特异度(87.3%)的均衡性满足FRITZ等[16]提出的优化诊断阈值要求,其阳性似然比6.19,达到美国临床病理学会推荐的临床决策价值阈值[17](阳性似然比> 5具有重要诊断意义)。Kappa一致性系数0.661(95%CI:0.498-0.823)符合Landis-Koch分级标准中的“显著一致性”等级(0.61-0.80)[18],表明预测结果与金标准具有临床可接受的吻合度。且模型的阴性预测值达87.3%(95%CI:0.785-0.961),这意味着对于术后预测低风险患者可减少23.7%的过度影像学复查(参照NICE指南CT检查适应证[19])。图6中可见,测试集中ROC曲线下面积为0.834(95%CI:0.705-0.964),训练集和验证集的ROC曲线的曲线下面积差异为0.043,验证集中曲线下面积较训练集略有下降,提示模型可能存在一定程度的过拟合。为进一步提升泛化能力,后续将尝试引入外部数据库进行验证,并优化变量筛选过程,增强模型稳定性与临床适用性,但差异在合理范围内,确保了模型的有效性和稳定性。测试集校准曲线显示预测结果与实际观察结果之间有良好的一致性;但决策曲线净收益曲线在阈值概率为0.9附近低于“不治疗任何患者”的参考线。结果提示,高阈值下模型预测的净收益未能超越简单的不干预策略,这种情况可能反映了模型在处理极端阈值时的局限性。"
| [1] 王远征,冷辉,吴景山,等. 脊髓型颈椎病病因学研究概况[J]. 中国医疗前沿,2013,8(1):9-10. [2] 陈亮,王冲,高峰,等. 脊髓型颈椎病的研究进展[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(8):875-881. [3] FEHLINGS MG, WILSON JR, KOPJAR B, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Surgical Decompression in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Results of the AOSpine North America Prospective Multi-Center Study. J Bone Joint Surg. 2013;95A(18):1651-1658. [4] FEHLINGS MG, TETREAULT LA, RIEW KD, et al. A Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy: Introduction, Rationale, and Scope. Glob Spine J. 2017;7:S21-S27. [5] RHEE JM, SHAMJI MF, ERWIN WM, et al. Nonoperative management of cervical myelopathy: a systematic review. Spine. 2013;38(22S):S55-S67. [6] BERLIN C, MARINO AC, MUMMANENI PV, et al. Determining the time frame of maximum clinical improvement in surgical decompression for cervical spondylotic myelopathy when stratified by preoperative myelopathy severity: a cervical Quality Outcomes Database study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2022;37(5):758-766. [7] 刘忠军. 对脊髓型颈椎病手术入路与术式的思考[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009,19(7):481-482. [8] JOAQUIM AF, MURAR J, SAVAGE JW, et al. Dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a systematic review of potential preventative measures. Spine J. 2014;14(9):2246-2260. [9] LAO LF, ZHONG GB, LI XF, et al. Laminoplasty versus laminectomy for multi-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a systematic review of the literature. J Orthop Surg Res. 2013;8:9. [10] KAWAGUCHI Y, MATSUI H, ISHIHARA H, et al. Axial symptoms after en bloc cervical laminoplasty. J Spinal Disord. 1999;12(5):392-395. [11] 潘胜发,孙宇,朱振军,等. 单开门颈椎管扩大椎板成形术后轴性症状与颈椎稳定性的相关观察[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2003,13(10):29-32. [12] KOTANI Y, ABUMI K, ITO M, et al. Impact of deep extensor muscle-preserving approach on clinical outcome of laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: comparative cohort study. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(8):1536-1544. [13] 李玉伟, 严晓云, 王海蛟, 等. 保留C2、3棘突肌肉附着点的改良颈椎管扩大成形术[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(1):30-34. [14] 何心愉, 周红海, 曾禹铭,等. 颈椎病术后并发轴性症状的研究进展[J]. 局解手术学杂志,2022,31(10):912-916. [15] COOK NR. Use and misuse of the receiver operating characteristic curve in risk prediction. Circulation. 2007;115(7):928-935. [16] FRITZ CO, MORRIS PE, RICHLER JJ. Effect size estimates: current use, calculations, and interpretation. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2012;141(1):2-18. [17] MCGEE S. Simplifying likelihood ratios. J Gen Intern Med. 2002;17(8):646-649. [18] LANDIS JR, KOCH GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1):159-174. [19] National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Routine preoperative tests for elective surgery[NG123]. 2021. [20] 曹俊明,张英泽,申勇,等 全椎板减压侧块螺钉内固定治疗颈椎后纵韧带骨化症的疗效分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(10):844-849. [21] RUAN CY, JIANG WY, LU WJ, et al. Incidence and risk factors for the development of axial symptoms following posterior single-door laminoplasty: a retrospective analysis. World Neurosurg. 2024;183:E603-612. [22] LARSSON L, GRIMBY G, KARLSSON J. Muscle strength and speed of movement in relation to age and muscle morphology. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979;46(3):451-456. [23] MANNION AF, KÄSER L, WEBER E, et al. Influence of age and duration of symptoms on fibre type distribution and size of the back muscles in chronic low back pain patients. Eur Spine J. 2000;9(4):273-281. [24] 王琪, 毛敏, 孙威, 等. 老年人本体感觉、足底触觉和肌肉力量与姿势稳定性的关系[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2022,28(4):373-378. [25] APPELL HJ. Muscular atrophy following immobilisation. A review. Sports Med. 1990;10(1):42-58. [26] MENSE S. How do muscle lesions such as latent and active trigger points influence central nociceptive neurons? J Musculoskelet Pain. 2010;18(4): 348-353. [27] BARBOSA TP, RAPOSO AR, CUNHA PD, et al. Rehabilitation after cervical and lumbar spine surgery. EFORT Open Rev. 2023;8(8):626-638. [28] KATZ EA, KATZ SB, FREEMAN MD. Non-surgical management of upper cervical instability via improved cervical lordosis: a case series of adult patients. J Clin Med. 2023;12(5):10. [29] YOON SY, MOON HI, LEE SC, et al. Association between cervical lordotic curvature and cervical muscle cross-sectional area in patients with loss of cervical lordosis. Clin Anat. 2018;31(5):710-715. [30] PHILLIPS CA, PETROFSKY JS. Neck muscle loading and fatigue: systematic variation of headgear weight and center-of-gravity. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1983;54(10):901-905. [31] BAO XT, ZHANG JH, HUANG GM, et al. The crosstalk between HIFs and mitochondrial dysfunctions in cancer development. Cell Death Dis. 2021; 12(2):13. [32] HALL JK, BANKS GB, CHAMBERLAIN JS, et al. Prevention of muscle aging by myofiber-associated satellite cell transplantation. Sci Transl Med. 2010; 2(57):8. [33] MOHAPATRA S, KRISHNAN V, ARUIN AS. Postural control in response to an external perturbation: effect of altered proprioceptive information. Exp Brain Res. 2012;217(2):197-208. [34] CURT A, VAN HEDEL HJA, KLAUS D, et al. Recovery from a spinal cord injury: significance of compensation, neural plasticity, and repair. J Neurotrauma. 2008;25(6):677-685. [35] 周非非, 孙宇, 张凤山, 等. 颈椎前路椎间盘切除、植骨融合内固定术治疗脊髓型颈椎病术后轴性症状的前瞻性研究[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014,24(6):505-509. [36] SUN PF, WANG ZP, JIA LY, et al. SMOTE-kTLNN: A hybrid re-sampling method based on SMOTE and a two-layer nearest neighbor classifier. Expert Syst Appl. 2024;238:23. [37] TURCOTTE K, HOLTZMAN S. Does a diagnosis of depression influence observer ratings of pain severity? The mediating role of causal attributions of pain and pain genuineness. Br J Pain. 2024;18(2):128-136. [38] CHIANCA V, VINCENZO B, CUOCOLO R, et al. MRI quantitative evaluation of muscle fatty infiltration. Magnetochemistry. 2023;9(4):11. [39] ANDREWS AE, DICKINSON H, HAGUE JP. Rapid prediction of lab-grown tissue properties using deep learning. Phys Biol. 2023;20(6):22. [40] 美国化学文摘社(CAS). 未来健康:新兴生物材料[R]. 哥伦布(美国): 美国化学文摘社,2023. |
| [1] | Zhang Zizheng, Luo Wang, Liu Changlu. Application value of finite element analysis on unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial knee compartmental osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2313-2322. |
| [2] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. Risk factors and coping strategies of internal fixation failure in treatment of intertrochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2323-2333. |
| [3] | Li Qingbin, Lin Jianhui, Huang Wenjie, Wang Mingshuang, Du Jiankai, Lao Yongqiang. Bone cement filling after enlarged curettage of giant cell tumor around the knee joint: a comparison of subchondral bone grafting and non-grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1896-1902. |
| [4] | Li Guangzheng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Ding Haoqin, Zhou Zhongqi, Li Gang, Liang Xuezhen. A prediction model for sarcopenia in postmenopausal women: information analysis based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 849-857. |
| [5] | Liao Long, Zhao Zepeng, Li Zongyuan, Yu Qinglong, Zhang Tao, Tang Jinyuan, Ye Nan, Xu Han, Shi Bo. Establishment and validation of a model for femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture using logistic regression and SHAP analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 626-633. |
| [6] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Shang Qisong Song Xinghua. Analysis of factors for recurrent fractures of vertebral and adjacent vertebrae after osteoporotic compression fracture in the elderly patients with underlying diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 642-651. |
| [7] | Yang Peng, Xu Chenghan, Zhou Yingjie, Chai Xubin, Zhuo Hanjie, Li Lin, Shi Jinyu. A meta-analysis of risk factors for residual back pain after vertebral augmentation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 731-739. |
| [8] | Wang Zhipeng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Hongwei, Zhao Xiyun, Li Yuanzhen, Guo Chenglong, Qin Daping, Ren Zhen. A systematic review of application value of machine learning to prognostic prediction models for patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [9] | Yu Weijie, Cao Dongdong, Guo Tianci, Niu Puyu, Yang Jialin, Wang Simin, Liu Aifeng. Risk prediction models of recurrence after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 749-759. |
| [10] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [11] | Zhang Junwei, Chen Lingling, Ma Zhenyuan, Nie Weizhi, Li Chaohui, Wang Haitao, Duan Laibao, Hou Jinyong, Bi Hongzheng. Three-dimensional displacement and risk factors of midshaft clavicle fractures treated with titanium elastic intramedullary nailing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 269-277. |
| [12] | Li Jie, Zhao Xiaofeng, Zeng Qi, Zhou Runtian, Chen Rong, Hu Xijian, Zhao Bin. Influencing factors of spine deformity progression in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis and construction of a joint prediction model and nomogram [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2727-2735. |
| [13] | Yan Wenjian, Li Yinghui, Zhang Yong. Daily diet and structural damage of the knee joint: a large-scale genetic analysis based on UK and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2877-2885. |
| [14] | Huang Fengqin, Hu Yalin, Yang Boyin, Luo Xingmei. Constructing a risk prediction nomogram model for cognitive impairment in hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2466-2474. |
| [15] | Jiang Kai, Rong Yifa, Jia Haifeng, Li Hanzheng, Lu Bowen, Liang Xuezhen, Li Gang. Relationship between inflammatory factors and rheumatoid arthritis: a large-sample analysis based on the FinnGen R10 database and genome-wide association studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2629-2640. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||