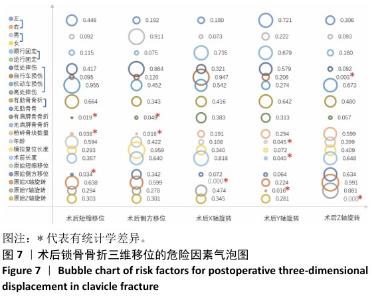
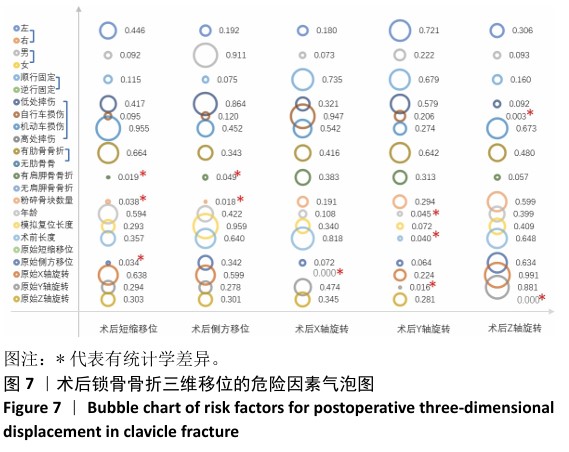
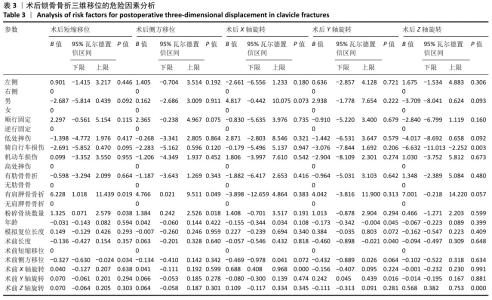
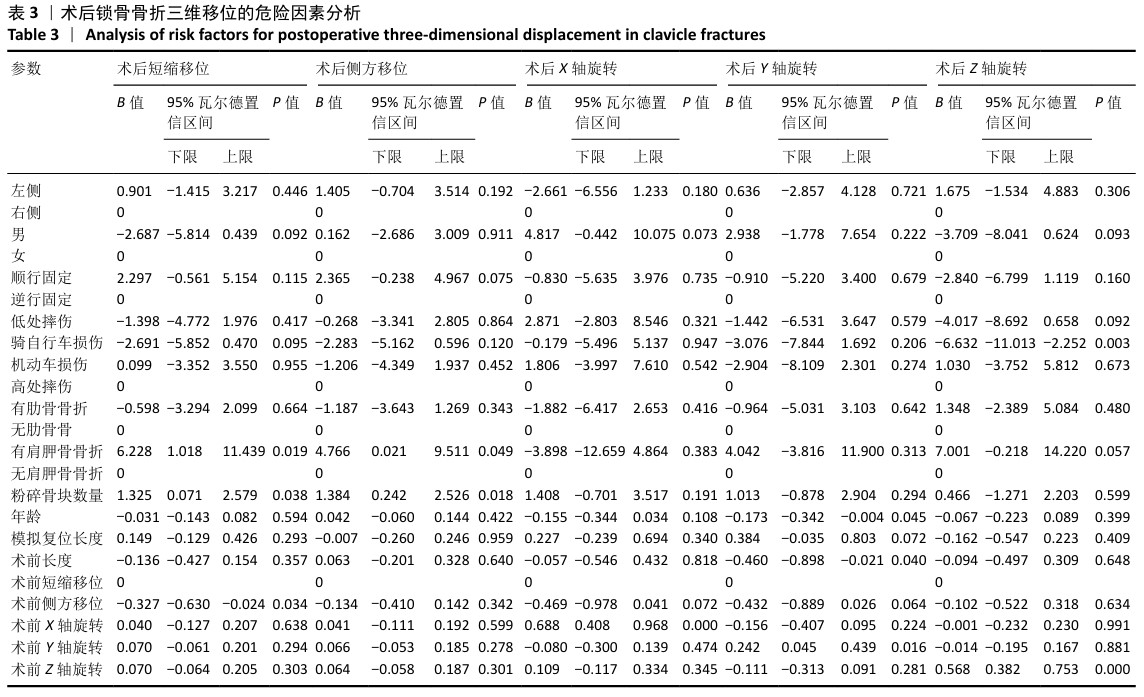
[1] HUNG LW, LU HY, CHANG CH, et al. Effects of Internal Fixation for Mid-Shaft Clavicle Fractures on Shoulder Kinematics During Humeral Elevations. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:710787.
[2] KIM JH, GWAK HC, KIM CW, et al. Three-dimensional clavicle displacement analysis and its effect on scapular position in acute clavicle midshaft fracture. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2019;28(10): 1877-1885.
[3] WRIGHT M, DELLA ROCCA GJ. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Clinical Practice Guideline Summary on the Treatment of Clavicle Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31(18):977-983.
[4] PRADEL S, BRUNAUD M, COULOMB R, et al. Less than 1.5cm shortening in clavicle midshaft fracture has long-term functional impact. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023;109(5):103590.
[5] LEE GB, KIM H, JEON IH, et al. Long-term outcomes of initially conservatively treated midshaft clavicle fractures. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2021;24(1):9-14.
[6] JUBEL A, KNOPF M, JUBEL JM, et al. Clavicle nonunion. Unfallchirurgie (Heidelb). 2024;127(11):776-782.
[7] VON RüDEN C, REHME-RÖHRL J, AUGAT P, et al. Evidence on treatment of clavicle fractures. Injury. 2023;54:110818.
[8] NICHOLSON JA, MAKARAM N, SIMPSON A, et al. Fracture nonunion in long bones: A literature review of risk factors and surgical management. Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 2:S3-S11.
[9] JERAY KJ, BRODERICK JS, MULLIS BH, et al. Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Study of Nonoperative Versus Operative Treatment for High-Energy Midshaft Clavicle Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2024; 38(7):345-350.
[10] TRIVELLAS M, WITTSTEIN J. Midshaft Clavicle Fractures: When Is Surgical Management Indicated and Which Fixation Method Should Be Used? Clin Sports Med. 2023;42(4):633-647.
[11] QVIST AH, JENSEN SL. Minimal early functional gains after operative treatment of midshaft clavicular fractures: a meta-analysis of 10 randomized controlled trials including 1333 patients. JSES Int. 2024; 8(3):400-406.
[12] BIZ C, POZZUOLI A, BELLUZZI E, et al. An Institutional Standardised Protocol for the Treatment of Acute Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures (ADMCFs): Conservative or Surgical Management for Active Patients? Healthcare (Basel). 2023;11(13):1883.
[13] KUMAR AV, RAMACHANDRA KAMATH K, SALIAN PRV, et al. Operative stabilisation versus non-operative management of mid-shaft clavicle fractures. Sicot J. 2022;8:45.
[14] RING D, HOLOVACS T. Brachial plexus palsy after intramedullary fixation of a clavicular fracture. A report of three cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(8):1834-1837.
[15] Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89(1):1-10.
[16] ASSOBHI JE. Reconstruction plate versus minimal invasive retrograde titanium elastic nail fixation for displaced midclavicular fractures. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(4):185-192.
[17] DONNELLY TD, MACFARLANE RJ, NAGY MT, et al. Fractures of the clavicle: an overview. Open Orthop J. 2013;7:329-233.
[18] DHODAPKAR MM, MODRAK M, HALPERIN SJ, et al. Trends in and Factors Associated With Surgical Management for Closed Clavicle Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2023;7(12):e23.00226.
[19] ANNICCHIARICO N, LATTA A, SANTOLINI E. Plate osteosynthesis for mid-shaft clavicle fractures: An update. Injury. 2023;54 Suppl 1:S53-S57.
[20] LU M, QIU H, LIU Y, et al. Intramedullary fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Surg. 2023;10:1194050.
[21] HAGAN D, BURNETT A, PAZIK M, et al. Outcomes of young active patients with displaced clavicle fractures treated with Rockwood pin. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(7):3037-3042.
[22] KUNKLE BF, DESJARDINS JD, CAMPBELL JR, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of an intramedullary clavicle screw in simple oblique and butterfly wedge fractures. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2021;235(11): 1257-1264.
[23] BENTS RT, BENTS EJ. Intramedullary Screw Fixation for Midshaft Clavicle Fractures. Arthrosc Tech. 2024;13(3):102884.
[24] HOOGERVORST P, VAN DAM T, VERDONSCHOT N, et al. Functional outcomes and complications of intramedullary fixation devices for Midshaft clavicle fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):395.
[25] YADAV S, PHALAK MO, SHEVATE I, et al. Comparative Study of Postoperative Outcomes of Clavicle Midshaft Fracture Treated by Nailing vs. Plating. Cureus. 2022;14(3):e22862.
[26] WIJDICKS FJ, HOUWERT M, DIJKGRAAF M, et al. Complications after plate fixation and elastic stable intramedullary nailing of dislocated midshaft clavicle fractures: a retrospective comparison. Int Orthop. 2012;36(10):2139-2145.
[27] BRAUN KF, SIEBENLIST S, SANDMANN GH, et al. Functional results following titanium elastic-stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) of mid-shaft clavicle fractures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2014;81(2): 118-121.
[28] NARSARIA N, SINGH AK, ARUN GR, et al. Surgical fixation of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: elastic intramedullary nailing versus precontoured plating. J Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15(3):165-171.
[29] OMID R, KIDD C, YI A, et al. Measurement of Clavicle Fracture Shortening Using Computed Tomography and Chest Radiography. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8(4):367-372.
[30] HOOGERVORST P, CHOPRA A, WORKING ZM, et al. Measurement of midshaft clavicle vertical displacement is not influenced by radiographic projection. JSES Int. 2020;4(2):251-255.
[31] STEGEMAN SA, DE WITTE PB, BOONSTRA S, et al. Measurement of clavicular length and shortening after a midshaft clavicular fracture: Spatial digitization versus planar roentgen photogrammetry. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2016;29:74-80.
[32] LIMA GV, LA BANCA V, MURACHOVSKY J, et al. Assessment of the measurement methods in midshaft clavicle fracture. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):992.
[33] CHAO YH, CHOU YC, LIN CL. The deformities of acute diaphyseal clavicular fractures: a three-dimensional analysis. Biomed Eng Online. 2023;22(1):42.
[34] ÖZTüRK M, PAULIN E, CHARBONNIER C, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction and virtual reposition of fragments compared to two dimensional measurements of midshaft clavicle fracture shortening. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):216.
[35] OKI S, MATSUMURA N, KIRIYAMA Y, et al. Three-Dimensional Deformities of Nonoperative Midshaft Clavicle Fractures: A Surface Matching Analysis. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(11): e385-e389.
[36] HILLEN RJ, BOLSTERLEE B, VEEGER D. The biomechanical effect of clavicular shortening on shoulder muscle function, a simulation study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2016;37:141-146.
[37] SU WR, CHEN WL, CHEN RH, et al. Evaluation of three-dimensional scapular kinematics and shoulder function in patients with short malunion of clavicle fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21(6):739-744.
[38] HUNG LW, LU HY, CHEN TY, et al. Residual kinematic deviations of the shoulder during humeral elevation after conservative treatment for mid-shaft clavicle fractures. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1413679.
[39] LEDGER M, LEEKS N, ACKLAND T, et al. Short malunions of the clavicle: an anatomic and functional study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2005;14(4): 349-354.
[40] KIM D, LEE D, JANG Y, et al. Effects of short malunion of the clavicle on in vivo scapular kinematics. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2017;26(9): e286-e292.
[41] RISTEVSKI B, HALL JA, PEARCE D, et al. The radiographic quantification of scapular malalignment after malunion of displaced clavicular shaft fractures. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2013;22(2):240-246.
[42] BIZ C, SCUCCHIARI D, POZZUOLI A, et al. Management of Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures with Figure-of-Eight Bandage: The Impact of Residual Shortening on Shoulder Function. J Pers Med. 2022;12(5):759.
[43] TAGLIAPIETRA J, BELLUZZI E, BIZ C, et al. Midshaft Clavicle Fractures Treated Nonoperatively Using Figure-of-Eight Bandage: Are Fracture Type, Shortening, and Displacement Radiographic Predictors of Failure? Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(10):788.
[44] ANDERMAHR J, JUBEL A, ELSNER A, et al. Malunion of the clavicle causes significant glenoid malposition: a quantitative anatomic investigation. Surg Radiol Anat. 2006;28(5):447-456.
[45] HOOGERVORST P, APPALSAMY A, FRANKEN S, et al. Quantifying shortening of the fractured clavicle assuming clavicular symmetry is unreliable. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(6):803-807.
[46] RIBAS GGO, DAU L, GONçALVES FF, et al. Measurement of Clavicular Symmetry in Healthy Subjects Using Tomographic Database of Public Hospitals. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2023;58(4):e617-e624.
[47] ERGIŞI Y, ÖZDEMIR E, TıKMAN M, et al. Revisiting the surgical indication of mid-shaft clavicle fractures: Clavicle asymmetry. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2023;34(1):63-68.
[48] HERMAN A, WHITESELL R, STEWART RL, et al. The impact of upright radiographs of midshaft clavicle fractures on treatment recommendations. Acta Orthop Belg. 2019;85(3):289-296.
[49] BACKUS JD, MERRIMAN DJ, MCANDREW CM, et al. Upright versus supine radiographs of clavicle fractures: does positioning matter? J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(11):636-641. |