Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 626-633.doi: 10.12307/2025.866
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment and validation of a model for femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture using logistic regression and SHAP analysis
Liao Long1, Zhao Zepeng2, Li Zongyuan1, Yu Qinglong2, Zhang Tao2, Tang Jinyuan2, Ye Nan1, Xu Han1, Shi Bo1
- 1Department of Orthopedics of Mianyang Central Hospital, Mianyang Hospital Affiliated to School of Medicine of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Chengdu Medical College, Chengdu 610500, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-09Accepted:2024-12-18Online:2026-01-28Published:2025-07-04 -
Contact:Shi Bo, MS, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics of Mianyang Central Hospital, Mianyang Hospital Affiliated to School of Medicine of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Liao Long, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics of Mianyang Central Hospital, Mianyang Hospital Affiliated to School of Medicine of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liao Long, Zhao Zepeng, Li Zongyuan, Yu Qinglong, Zhang Tao, Tang Jinyuan, Ye Nan, Xu Han, Shi Bo. Establishment and validation of a model for femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture using logistic regression and SHAP analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 626-633.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
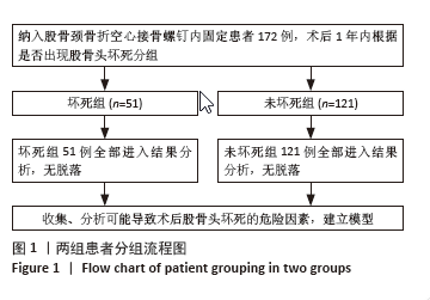
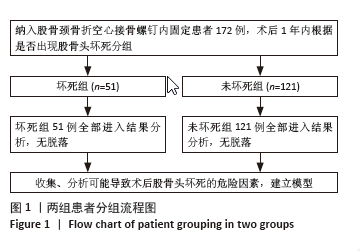
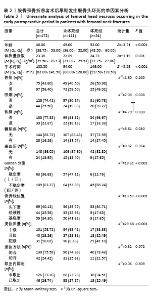
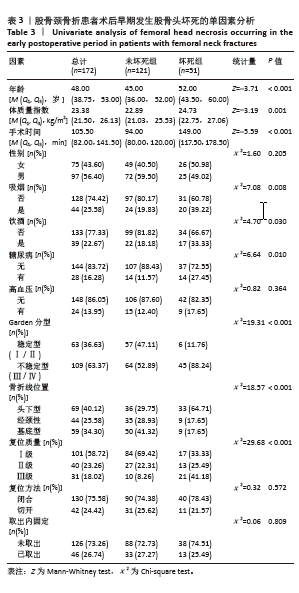
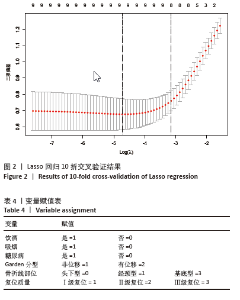
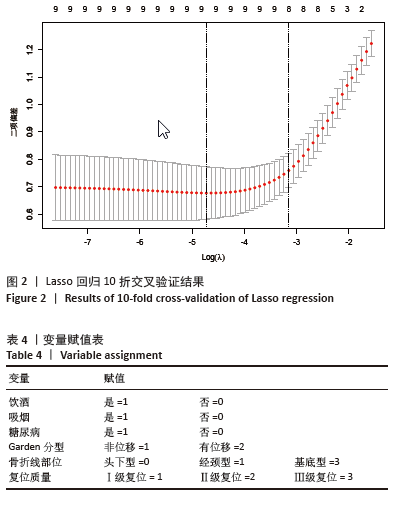
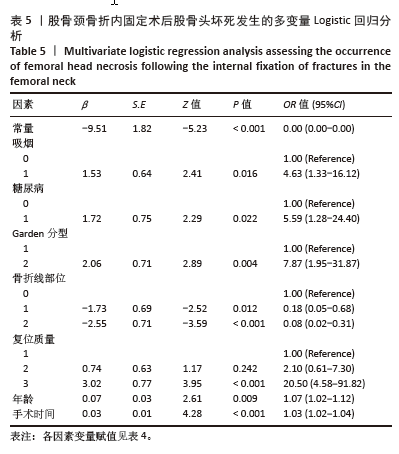
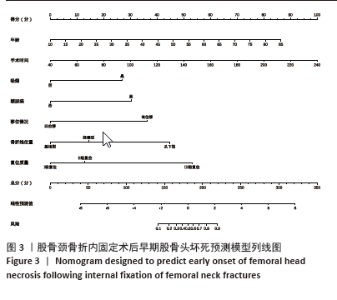
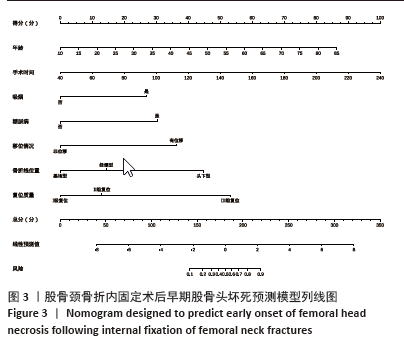
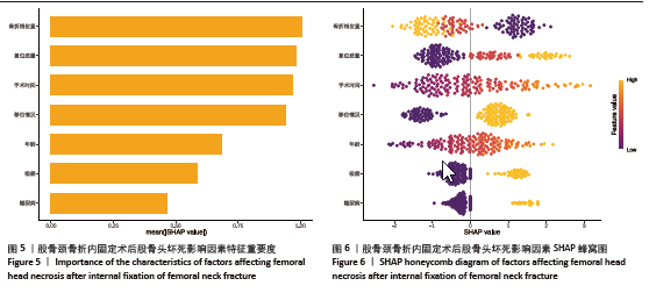
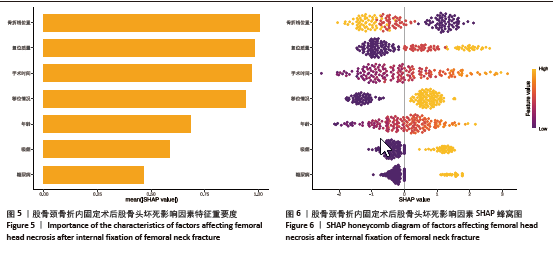
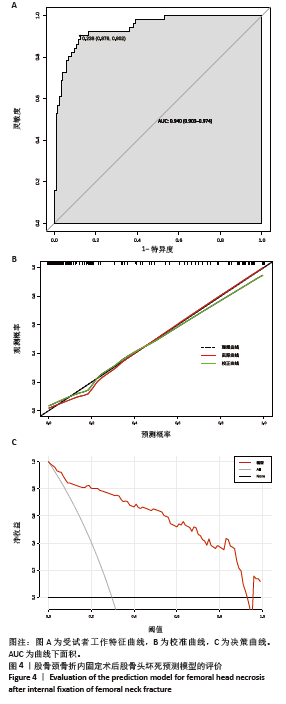
2.6 预测模型的评价及内部验证 使用受试者工作特征曲线分析和Hosmer-Lemeshow测试来评估模型的判别能力和校准能力。预测模型的AUC为0.940(95%CI:0.903-0.977),灵敏度为90.2%,特异度为87.6%,证明模型区分度良好(图4A);H-L检验显示,χ2=6.59,P=0.581 > 0.05,说明模型校准度良好;通过绘制校准曲线来评估列线图的准确性,该模型与理想模型的重合程度良好(图4B)。结果显示,决策曲线分析法通过直观方式证实了风险预测模型在临床实践中的有效性。预测模型的最大净收益阈值概率范围为1%-92%(图4C)。采用Bootstrap法重抽样1 000次,对模型进行内部验证,重抽样后,预测模型的AUC为0.939,模型鉴别效能依然良好。 2.7 SHAP分析 为了进一步研究股骨颈骨折内固定术后股骨头坏死的主要影响因素,此次研究通过SHAP方法对数据集特征进行分析,其成果展示于图5中,详细说明了各特征的重要性。骨折线位置、复位质量、手术时间以及移位情况是影响内固定术后股骨头坏死的重要因素,其中以骨折线位置最为重要。对于划分好的数据,此文借助Python中的SHAP库计算了模型的SHAP值,如图6所示,每个点对应数据集的一个样本。x轴上的位置、即实际的SHAP值,表示该特征对特定样本的模型输出、即对特定样本的相对患病风险的影响。换言之,较高SHAP值的样本相对于较低SHAP值的样本具有较高的股骨头坏死风险。此外,各个特征按其重要性沿y轴排列,其重要性由其绝对SHAP值的平均值给出,特征位置越高,说明重要性越高。"
| 1] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组,中国医师协会骨科医师分会创伤专家工作委员会.成人股骨颈骨折诊治指南[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018, 20(11):921-928. [2] 张文彬,周琴,吕良友,等.股骨颈动力交叉钉系统和空心螺钉内固定治疗中青年股骨颈骨折的早期疗效对比[J].骨科,2024,15(4):357-361. [3] EHLINGER M, MOSER T, ADAM P, et al. Early prediction of femoral head avascular necrosis following neck fracture. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011;97(1):79-88. [4] 周咏辉,李磊,李冲,等.空心螺钉双平面垂直固定与倒三角固定治疗中青年PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的临床疗效分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2024,38(8):961-967. [5] BI ZG, WANG XM. Reviewing the surgery strategy for fracture neck of femur. Zhonghuawaikezazhi. 2019;57(11):804-806. [6] 梁浩然,周新,杨彦飞,等.青壮年股骨颈骨折内固定后股骨头坏死的发病机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(3):456-460. [7] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Complications following young femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2015;46(3):484-491. [8] 李志鹏,环大维,袁兆丰,等.老年股骨颈骨折患者术后死亡的危险因素及预测列线图的构建[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21): 3361-3366. [9] WOJCIECH K, TOMASZ P, ANDRZEJ Ś, et al. Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head—Overview and Current State of the Art. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(12):7348. [10] XIA W, ZHANG A, QIU B, et al. Femoral neck fracture after femoral head necrosis: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1). doi:10.1186/s12891-023-06992-9. [11] PAPAKOSTIDIS C, PANAGIOTOPOULOS A, PICCIOLI A, et al.Timing ofinternal fixation of femoral neck fractures. A systematic review andmeta-analysis of the final outcome. Injury. 2015;46(3): 459-466. [12] TANI T, ANDO W, FUKUSHIMA W, et al. Geographic distribution of the incidence of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan and its relation to smoking prevalence. Mod Rheumatol. 2022;32(1):186-192. [13] LAI SW, LIN CL, LIAO KF. Real-World Database Examining the Association Between Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head and Diabetes in Taiwan. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(1):39. [14] WONGWAI T, WAJANAVISIT W, WORATANARAT P. Non-union and avascular necrosis of delayed reduction and screw fixation in displaced femoral neck fracture in young adults. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012;95 Suppl 10(95 Suppl 10):S120-S127. [15] PERUMAL V, WOODLEY SJ, NICHOLSON HD. Neurovascular structures of the ligament of the head of femur. J Anat. 2019;234(6):778-786. [16] 薛晨曦,荆珏华,徐杰,等.选择性血管造影评价股骨颈骨折后股骨头血供变化[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(2):149-151+154. [17] LIU Y, LI MH, ZHANG M, et al. Femoral neck fractures: prognosis based on a new classification after superselective angiography. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(3):443-450. [18] KUMAR MN, BELEHALLI P, RAMACHANDRA P. PET/CT study of temporal variations in blood flow to the femoral head following low-energy fracture of the femoral neck. Orthopedics. 2014;37(6):e563-5e70. [19] GADINSKY NE, KLINGER CE, SCULCO PK, et al. Femoral Head Vascularity: Implications Following Trauma and Surgery About the Hip. Orthopedics. 2019; 42(5):250-257. [20] SEELEY MA, GEORGIADIS AG, SANKAR WN. Hip Vascularity: A Review of the Anatomy and Clinical Implications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(8):515-526. [21] WANG Y, MA JX, YIN T, et al. Correlation Between ReductionQuality of Femoral Neck Fracture and Femoral Head Necrosis Based on Biomechanics. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):318-324. [22] CELIK B, KOSE A, MILCAN A, et al. Relation of femur fractures location with clinical outcomes in elderly patients. Acta Ortop Bras. 2023;31(spe1):e239997. [23] WANG H, WU W, HAN C, et al. Prediction model of osteonecrosis of the femoral head after femoral neck fracture: machine learning–based development and validation study. JMIR Med Inform. 2021; 9(11):e30079. [24] HU Y, YANG Q, ZHANG J, et al. Methods to predict osteonecrosis of femoral head after femoral neck fracture: a systematic review of the literature. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):377. [25] CONG B, ZHANG H. The association between three-dimensional measurement of posterior tilt angle in impacted femoral neck fractures and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):758. [26] TANG Z, LI R, LU C, et al. Risk factors for avascular necrosis of the femoral head after developmental hip dislocation reduction surgery and construction of Nomogram prediction model. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):464. [27] RANDELLI F, VIGANÒ M, LICCARDI A, et al. Femoral neck fractures: Key points to consider for fixation or replacement a narrative review of recent literature. Injury. 2023;54:S70-S77. [28] LIN G, YANG D, SUI W. Clinical Effect of Open Reduction and Internal Fixation for Femoral Neck Fracture in Young Adults and Related Factors of Femoral Head Necrosis. J Environ Public Health. 2022;2022(1):2974830. [29] YANG TJ, SUN SY, ZHANG L, et al. A delphi-based model for prognosis of femoral head collapse in osteonecrosis: a multi-factorial approach. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):762. [30] KONARSKI W, POBOŻY T, ŚLIWCZYŃSKI A, et al. Avascular necrosis of femoral head—overview and current state of the art. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(12):7348. [31] LIU Y, SONG W, LIANG H, et al. Comparison of femoral mechanics before and after internal fixation removal and the effect of sclerosis on femoral stress: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):930. [32] LIU B, HOU G, YANG Z, et al. Machine learning models to predict osteonecrosis in patients with femoral neck fractures undergoing internal fixation. Injury. 2024;55(11):111830. [33] QI BH, WANG XW, WANG XM, et al. Risk factors related with avascular necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1188179. [34] MEI J, LIU S, JIA G, et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of cannulated screw placement and drilling frequency on femoral neck fracture fixation. Injury. 2014;45(12):2045-2050. [35] WANG W, LI Y, XIONG Z, et al. Effect of the number, size, and location of cannulated screws on the incidence of avascular necrosis of the femoral head in pediatric femoral neck fractures: a review of 153 cases. J Pediatr Orthop. 2022;42(3):149-157. [36] MOON JK, LEE JI, HWANG KT, et al. Biomechanical comparison of the femoral neck system and the dynamic hip screw in basicervical femoral neck fractures. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):7915. [37] DE FRANCO S, IPPONI E, RUINATO AD, et al. Femoral neck fractures treated with cannulated screws: can surgeons predict functional outcomes and minimize the risk of necrosis? Acta Biomed. 2023;94(1):e2023013. [38] ALSAYED MA, ALQHTANI MM, ALKHAMMASH ZM, et al. Hip Fracture, Causes, Classification, and Management: A Literature Review. World J Environ Biosci. 2021;10(2-2021):49-55. [39] KOABAN S, ALATASSI R, ALHARBI S, et al. The relationship between femoral neck fracture in adult and avascular necrosis and nonunion: a retrospective study. Ann Med Surg. 2019;39:5-9. [40] RANDELLI F, VIGANÒ M, LICCARDI A, et al. Femoral neck fractures: Key points to consider for fixation or replacement a narrative review of recent literature. Injury. 2023;54:S70-S77. |
| [1] | Liao Guangtao, Feng Ziyu, Fu Xiaoyong, Zhao Qinglan, Chen Chao, Hong Jinsong. Subtalar arthroereisis for treatment of pediatric flexible flatfoot: relationship between radiographic indicators and clinical efficacy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 661-670. |
| [2] | Wang Peng, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Wu Yimin. Intervertebral disc rehydration after posterior lumbar dynamic internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 711-720. |
| [3] | Wang Zhipeng, Zhang Xiaogang, Zhang Hongwei, Zhao Xiyun, Li Yuanzhen, Guo Chenglong, Qin Daping, Ren Zhen. A systematic review of application value of machine learning to prognostic prediction models for patients with lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 740-748. |
| [4] | Yu Weijie, Cao Dongdong, Guo Tianci, Niu Puyu, Yang Jialin, Wang Simin, Liu Aifeng. Risk prediction models of recurrence after percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 749-759. |
| [5] | Yu Xinlin, Chen Huiyu, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Feng Bin Lin Chengshou, Lin Wang. Finite element analysis of internal fixation with new retrograde intramedullary nail on lateral femur condyle for distal type A2 femur fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 546-552. |
| [6] | Wang Meng, Lu Tan, Li Minjie, Liu Zhicheng, Guo Xiaoyong. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of anchors at different implantation depths under different bone density conditions in rotator cuff tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 561-569. |
| [7] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Wang Chaolu. High tibial osteotomy on a single plane: femorofibular angle as a reference marker for mechanical axis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 570-576. |
| [8] | Jia Yingao, Gao Shitao, Wang Fei. Application of 3D printed titanium cage cutting model in anterior cervical vertebrae subtotal decompression and bone graft fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 604-611. |
| [9] | Wang Jiangjing, Zhao Na, Hu Xiaona, Zhao Na . Safety of 3D printed titanium alloy bone trabecular cup prosthesis combined with modified Kidney Tonifying and Blood Activating Decoction for elderly hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 612-619. |
| [10] | Xu Xinbao, Chen Feiyang, Chen Yinbing, Zhang Feixiang, Lyu Shujun, Cui Haidong, Chen Zhigang. Univariate and multivariate regression analysis of femoral neck shortening after cannulated screw fixation in femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 620-625. |
| [11] | Zhang Hao, Wang Qing, Zhang Jian, Li Guangzhou, Wang Gaoju. Comparison of posterior C2-3 fixation combined with bucking bar technique and posterior C2-3 fixation alone in treatment of unstable Hangman fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1848-1854. |
| [12] | Su Lintao, Jiang Jianfeng, Ma Jun, Huang Liangliang, Lei Changyu, Han Yaozheng, Kang Hui. Precise application of O-arm navigation system in thoracolumbar fractures with developmental pedicle stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1855-1862. |
| [13] | Gao Zhenyang, Zeng Xiuan, Yang Qibing, Kou Xianshuai, Wang Kejing, Li Meng. Computer-simulated repositioning combined with pelvic reduction frame for treatment of anteroposterior compression-III pelvic fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1870-1875. |
| [14] | Chen Xi, Tang Tao, Chen Tongbing, Li Qing, Zhang Wen. Mechanical stability of intertrochanteric fracture of femur with different internal fixation systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1783-1788. |
| [15] | Huang Haobo, Liang Xinyuan, Ye Guozhong, Xie Qingxiang, Su Boyuan. Suture tape and headless compression screws in treatment of Lisfranc injury with comminuted fractures of the first and second proximal metatarsal bones [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1803-1809. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||