Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 661-670.doi: 10.12307/2026.511
Previous Articles Next Articles
Subtalar arthroereisis for treatment of pediatric flexible flatfoot: relationship between radiographic indicators and clinical efficacy
Liao Guangtao1, 2, Feng Ziyu3, Fu Xiaoyong2, Zhao Qinglan1, 2, Chen Chao3, Hong Jinsong1, 4
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Guangzhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guangzhou 510045, Guangdong Province, China; 3School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China; 4First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-08-05Accepted:2024-10-22Online:2026-01-28Published:2025-07-05 -
Contact:Hong Jinsong, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China Co-corresponding author: Chen Chao, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Liao Guangtao, MS, Physician, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; Guangzhou Orthopedic Hospital, Guangzhou 510045, Guangdong Province, China Feng Ziyu, MD, Physician, School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China Liao Guangtao and Feng Ziyu contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China - General Project, No. 82374605 (to CC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liao Guangtao, Feng Ziyu, Fu Xiaoyong, Zhao Qinglan, Chen Chao, Hong Jinsong. Subtalar arthroereisis for treatment of pediatric flexible flatfoot: relationship between radiographic indicators and clinical efficacy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 661-670.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

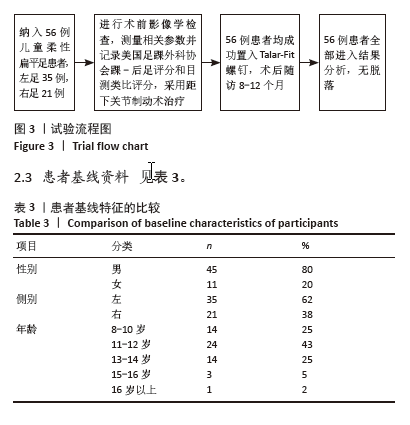
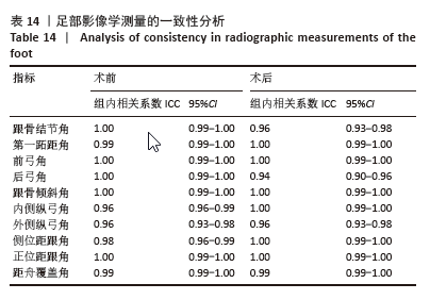
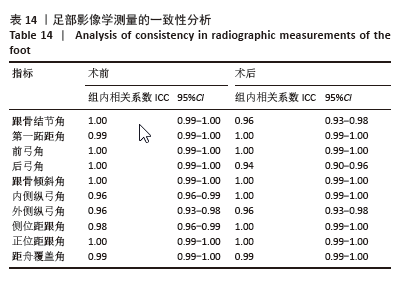
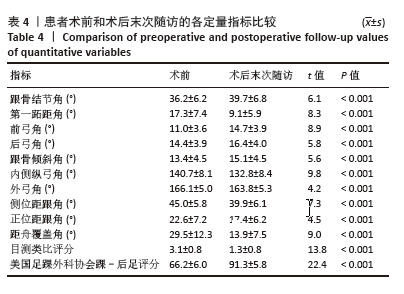
表3显示,参与者性别方面,男性所占比例为80%,女性所占比例为20%。男性比例明显高于女性比例。在参与者年龄方面,主要集中在11-12岁年龄段,占比为43%;8-10岁和13-14岁年龄段的比例均相当,占25%;15-16岁和16岁以上年龄段的比例分别为5%和2%。在参与者侧别方面,左侧所占比例为62%,右侧为38%。通过对上述结果的分析,可以看出此次研究的样本在性别和年龄分布上存在一定的集中趋势,尤其是在11-12岁年龄段和男性参与者中占比较大。左侧平足的发生率较右侧更高。 2.4 影像学与临床疗效的定量分析 与术前相比,术后末次随访时的各足部角度参数、目测类比评分、美国足踝外科协会踝-后足评分均显著改善,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.001),见表4。"
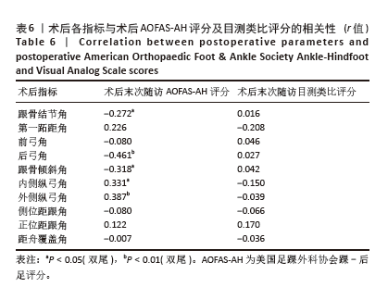
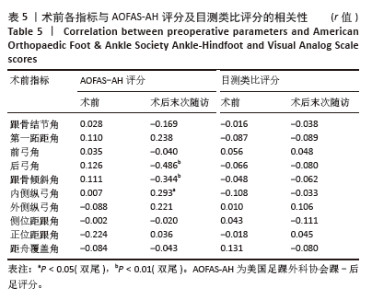
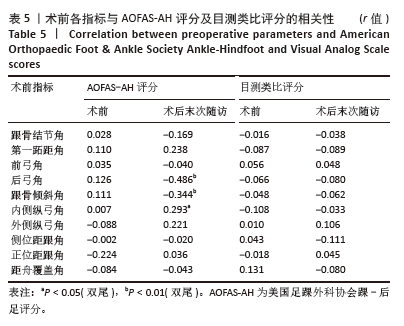
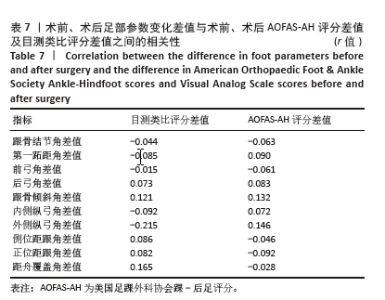
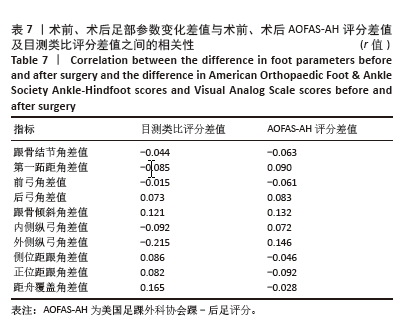
此次研究进一步分析术后足部各指标与术后AOFAS-AH评分及目测类比评分之间的相关性。Pearson 相关性分析结果显示:术后跟骨结节角与术后AOFAS-AH评分之间存在显著负相关(r=-0.272,P < 0.05);术后后弓角与术后AOFAS-AH评分之间存在显著负相关(r=-0.461,P < 0.01);术后跟骨倾斜角与术后AOFAS-AH评分之间也存在显著负相关(r=-0.318,P < 0.05);术后内侧纵弓角与术后AOFAS-AH评分之间存在显著正相关(r=0.331,P < 0.05);术后外侧纵弓角与术后AOFAS-AH评分之间存在显著正相关(r=0.387,P < 0.01)。见表 6。"


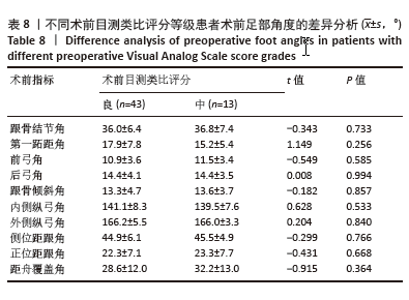
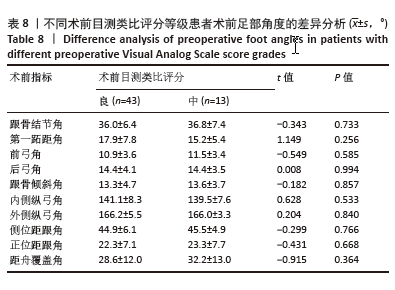
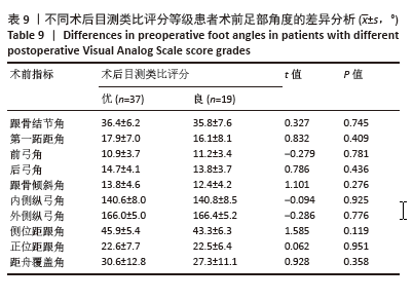
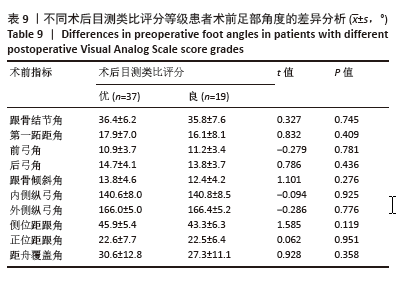
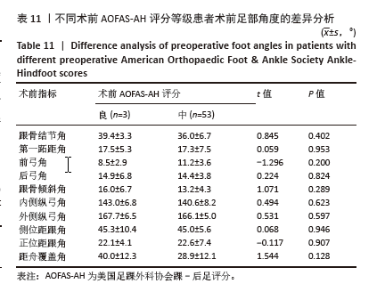
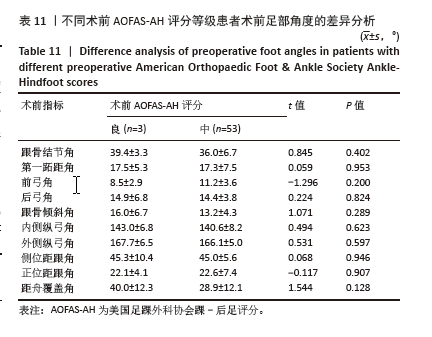
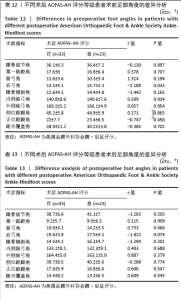
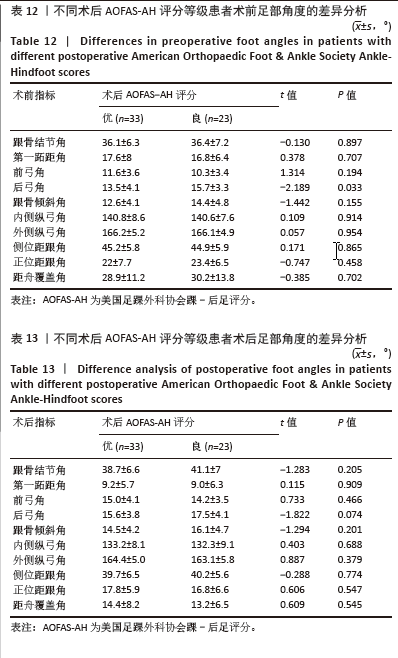
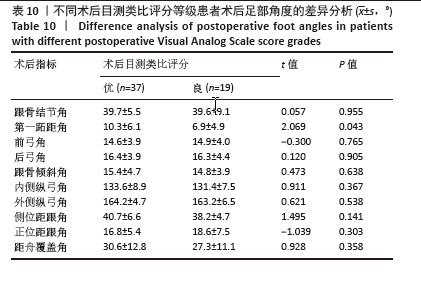
为了探讨术后各足部角度参数在术后目测类比评分等级“优”和“良”两组间的差异,进行了独立t检验,结果显示术后第一跖距角在术后目测类比评分等级为“优”和“良”的两组患者间差异有显著性意义(P=0.043),表明术后第一跖距角角度与目测类比评分等级之间具有统计学关联。其他术后足部角度参数在两组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。见表10。 2.7 术前、术后足部角度与AOFAS-AH评分的关系 同样地,经独立样本t检验发现,术前各足部角度参数在术前AOFAS-AH评分等级为“良”和“中”的两组患者间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),表明术前角度测量值与术前AOFAS-AH评分等级无显著统计学关联。见表 11。"
| [1] BOBIŃSKI A, TOMCZYK Ł, REICHERT P, et al. Short-term and medium-term radiological and clinical assessment of patients with symptomatic flexible flatfoot following subtalar arthroereisis with Spherus screw. J Clin Med. 2023;12(15):5038. [2] UEKI Y, SAKUMA E, WADA I. Pathology and management of flexible flat foot in children. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(1):9-13. [3] YAMASHITA T, SATO M, ATA S, et al. Predictors of flatfoot in 11-12-year olds: a longitudinal cohort study. Biomed Eng Online. 2024;23(1):83. [4] PAVONE V, TESTA G, VESCIO A, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of flexible flatfoot: results of 2019 flexible flatfoot survey from the European Paediatric Orthopedic Society. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics Part B. 2021;30(5):450-457. [5] LI B, HE W, YU G, et al. Treatment for flexible flatfoot in children with subtalar arthroereisis and soft tissue procedures. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:656178. [6] SMITH C, ZAIDI R, BHAMRA J, et al. Subtalar arthroereisis for the treatment of the symptomatic paediatric flexible pes planus: a systematic review. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6(2):118-129. [7] HEGAZY FA, ABOELNASR EA, SALEM Y, et al. Validity and diagnostic accuracy of foot posture index-6 using radiographic findings as the gold standard to determine paediatric flexible flatfoot between ages of 6-18 years: a cross-sectional study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;46:102107. [8] 邓明明,孙广超,杜瑞,等.两种术式治疗儿童柔韧性平足合并痛性副舟骨疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(10):1225-1229. [9] 潘旭月,魏芳远,陈卫衡.青少年柔韧性扁平足距下关节制动术长期疗效与韧带松弛程度的相关性[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2024,17(4):347-353. [10] METCALFE SA, BOWLING FL, REEVES ND. Subtalar joint arthroereisis in the management of pediatric flexible flatfoot: a critical review of the literature. Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(12):1127-1139. [11] SHI C, LI M, ZENG Q, et al. Subtalar arthroereisis combined with medial soft tissue reconstruction in treating pediatric flexible flatfoot with accessory navicular. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):55. [12] SOLTANOLKOTABI M, MALLORY C, ALLEN H, et al. Postoperative findings of common foot and ankle surgeries: an imaging review. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022; 12(5):1090. [13] 严广斌.AOFAS踝-后足评分系统[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014,8(4):557. [14] 万丽,赵晴,陈军,等.疼痛评估量表应用的中国专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中华疼痛学杂志,2020,16(3):177-187. [15] MURLEY GS, MENZ HB, LANDORF KB. A protocol for classifying normal- and flat-arched foot posture for research studies using clinical and radiographic measurements. J Foot Ankle Res. 2009;2:22. [16] DAGNEAUX L, MORONEY P, MAESTRO M. Reliability of hindfoot alignment measurements from standard radiographs using the methods of Meary and Saltzman. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;25(2):237-241. [17] GIANNINI S, CADOSSI M, MAZZOTTI A, et al. Bioabsorbable Calcaneo-Stop implant for the treatment of flexible flatfoot: a retrospective cohort study at a minimum follow-up of 4 years. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(4):776-782. [18] NEEDLEMAN RL. Current topic review: subtalar arthroereisis for the correction of flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(4):336-346. [19] LI B, HE W, YU G, et al. Treatment for flexible flatfoot in children with subtalar arthroereisis and soft tissue procedures. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:656178. [20] WONG DW, WANG Y, NIU W, et al. Finite element analysis of subtalar joint arthroereisis on adult-acquired flexible flatfoot deformity using customised sinus tarsi implant. J Orthop Translat. 2020;27:139-145. [21] DE PELLEGRIN M, MOHARAMZADEH D. Subtalar arthroereisis for surgical treatment of flexible flatfoot. Foot Ankle Clin. 2021;26(4):765-805. [22] BERNASCONI A, ARGYROPOULOS M, PATEL S, et al. Subtalar arthroereisis as an adjunct procedure improves forefoot abduction in stage IIb adult-acquired flatfoot deformity. Foot Ankle Spec. 2022; 15(3):209-220. [23] XIE HG, CHEN L, GENG X, et al. Mid-term assessment of subtalar arthroereisis with Talar-Fit implant in pediatric patients with flexible flatfoot and comparing the difference between different sizes and exploring the position of the inserted implant. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1258835. [24] HAGEN L, KOSTAKEV M, PAPE JP, et al. Are there benefits of a 2D gait analysis in the evaluation of the subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis? Short-term investigation in children. Clin Biomechanics (Bristol, Avon). 2019;63:73-78. [25] GRAHAM ME, JAWRANI NT, CHIKKA A. Extraosseous talotarsal stabilization using HyProCure® in adults: a 5-year retrospective follow-up. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2012;51(1):23-29. [26] DE PELLEGRIN M, MOHARAMZADEH D, STROBL WM, et al. Subtalar extra-articular screw arthroereisis (SESA) for the treatment of flexible flatfoot in children. J Child Orthop. 2014;8(6):479-487. [27] 曹洪,赵飞,Sauro Angelici,等.经跗骨窦HyProCure螺钉治疗儿童柔韧性平足症[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(11): 1038-1041. [28] HERDEA A, NECULAI AG, ULICI A. The role of arthroereisis in improving sports performance, foot aesthetics and quality of life in children and adolescents with flexible flatfoot. Children (Basel). 2022;9(7):973. [29] 刘冠杰,韩煜,赵康成,等.距下关节制动术治疗柔韧性扁平足的历史与现状[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(1):52-55. [30] SINHA S, SONG HR, KIM HJ, et al. Medial arch orthosis for paediatric flatfoot. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery (Hong Kong). 2013;21(1): 37-43. [31] NILSSON MK, FRIIS R, MICHAELSEN MS, et al. Classification of the height and flexibility of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot. J Foot Ankle Res. 2012;5:3. [32] SU Y, CHEN W, ZHANG T, et al. Bohler’s angle’s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2013;13:40. [33] 黄立本,林小永,叶琳,等.跗骨窦螺钉联合软组织手术治疗儿童柔韧性平足症12例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2022,30(7):70-74. [34] 赵廷虎,陈汉鑫,郑挺渠,等.距下关节制动术治疗成人柔性平足症28例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023,31(2):70-74. [35] 徐军奎,赵炼,屈福锋,等.距下关节稳定器治疗儿童柔韧性平足的中期疗效分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(2): 106-110+114. [36] 丰波,邹英财,王永军,等.HyProcure距下关节稳定器治疗儿童柔韧性平足症的中期疗效[J].足踝外科电子杂志,2020,7(2):9-14. [37] 李兵,俞光荣,杨云峰,等. 距下关节制动联合软组织手术治疗大龄儿童柔性平足症[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,2020,41(4):356-360. [38] XIE HG, CHEN L, GENG X, et al. Mid-term assessment of subtalar arthroereisis with Talar-Fit implant in pediatric patients with flexible flatfoot and comparing the difference between different sizes and exploring the position of the inserted implant. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1258835. [39] DE CESAR NETTO C, SHAKOOR D, ROBERTS L, et al. Hindfoot alignment of adult acquired flatfoot deformity: a comparison of clinical assessment and weightbearing cone beam CT examinations. Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;25(6):790-797. [40] MCKEON PO, HERTEL J, BRAMBLE D, et al. The foot core system: a new paradigm for understanding intrinsic foot muscle function. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(5):290. [41] BUDIMAN-MAK E, CONRAD KJ, MAZZA J, et al. A review of the foot function index and the foot function index - revised. J Foot Ankle Res. 2013;6(1):5. [42] VARNI JW, SEID M, RODE CA. The PedsQL: measurement model for the pediatric quality of life inventory. Med Care. 1999;37(2):126-139. |
| [1] | Liao Long, Zhao Zepeng, Li Zongyuan, Yu Qinglong, Zhang Tao, Tang Jinyuan, Ye Nan, Xu Han, Shi Bo. Establishment and validation of a model for femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture using logistic regression and SHAP analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 626-633. |
| [2] | Wang Yalei, Wang Xuezhi, Zhou Tao, Shen Xinxin, Fang Ding, Chen Hongliang. Effect of sacroiliac joint ankylosis on outcomes of L5/S1 transforminal lumbar interbody fusion and lumbar sagittal parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 634-641. |
| [3] | Wang Meng, Lu Tan, Li Minjie, Liu Zhicheng, Guo Xiaoyong. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of anchors at different implantation depths under different bone density conditions in rotator cuff tears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 561-569. |
| [4] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Wang Chaolu. High tibial osteotomy on a single plane: femorofibular angle as a reference marker for mechanical axis correction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 570-576. |
| [5] | Jia Yingao, Gao Shitao, Wang Fei. Application of 3D printed titanium cage cutting model in anterior cervical vertebrae subtotal decompression and bone graft fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 604-611. |
| [6] | Wang Jiangjing, Zhao Na, Hu Xiaona, Zhao Na . Safety of 3D printed titanium alloy bone trabecular cup prosthesis combined with modified Kidney Tonifying and Blood Activating Decoction for elderly hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 612-619. |
| [7] | Xu Xinbao, Chen Feiyang, Chen Yinbing, Zhang Feixiang, Lyu Shujun, Cui Haidong, Chen Zhigang. Univariate and multivariate regression analysis of femoral neck shortening after cannulated screw fixation in femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 620-625. |
| [8] | Zhang Junwei, Chen Lingling, Ma Zhenyuan, Nie Weizhi, Li Chaohui, Wang Haitao, Duan Laibao, Hou Jinyong, Bi Hongzheng. Three-dimensional displacement and risk factors of midshaft clavicle fractures treated with titanium elastic intramedullary nailing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 269-277. |
| [9] | Ao Xiaojing, Li Kun, Liu Yuhang, Yang Xiaoxuan, Wang Xing, Li Zhijun, Ren Xiaoyan, Zhang Shaojie. Development and application of a three-dimensional digital visualization system for children’s neck acupoints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1834-1840. |
| [10] | Sun Xiaojun, Wang Huaming, Zhang Dehong, Song Xuewen, Huang Jin, Zhang Chen, Pei Shengtai. Effect of finite element method in treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip in children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1897-1904. |
| [11] | Wang Lei, Li Chengsong, Zhang Shenshen, Wang Qing. Finite element analysis of biomechanical characteristics of three internal fixation methods in treatment of inferior patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7048-7054. |
| [12] | Abuduainijiang·Abulimiti, Alimu·Mamuti, Li Simi. Artificial femoral head replacement for femoral neck fracture in the elderly: validation of a risk prediction model for hip dysfunction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7143-7149. |
| [13] | Liu Ning, Sun Yingjin, Huang Long, Feng Shuo, Chen Xiangyang. Optimal rotational alignment of the tibial component during Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7158-7164. |
| [14] | Yang Wanzhong, Ma Rong, Guo Wei, Wang Zhiqiang, Yang Wei, Chen Zhen, Wang Zemin, Zhang Honglai, Ge Zhaohui. One-stage posterior hemivertebra resection and pedicle screw fixation in treatment of congenital scoliosis: a 2-year follow-up of correction effect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7173-7180. |
| [15] | Jiang Zehua, Du Wenjun, Ren Zhishuai, Cui Haojun, Zhu Rusen. Percutaneous vertebroplasty via Kambin's triangle for treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures: evaluation of safety and effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7181-7188. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||