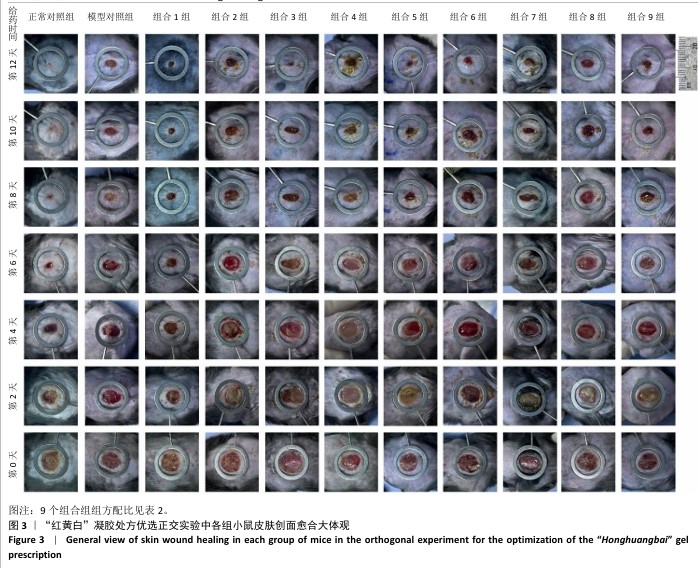
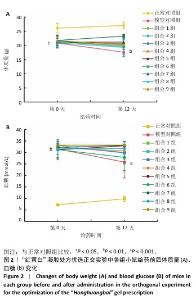
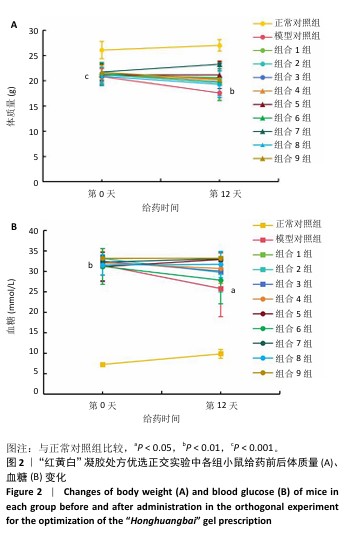
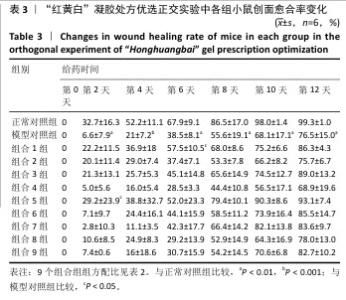
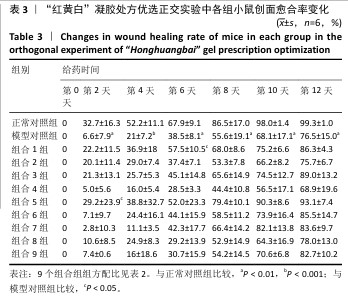
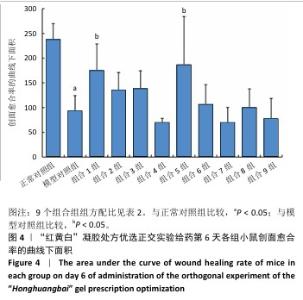
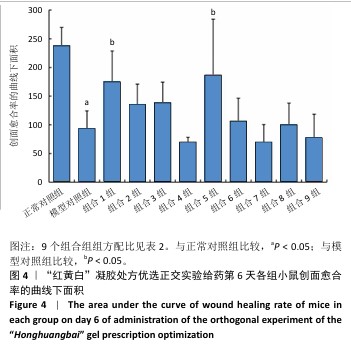
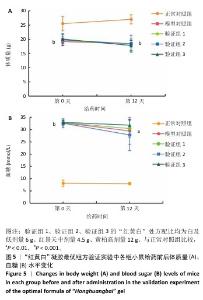
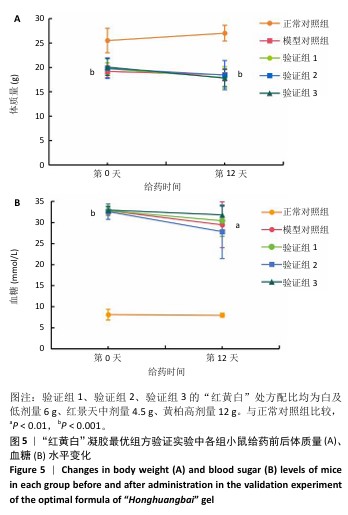
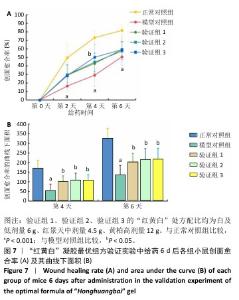
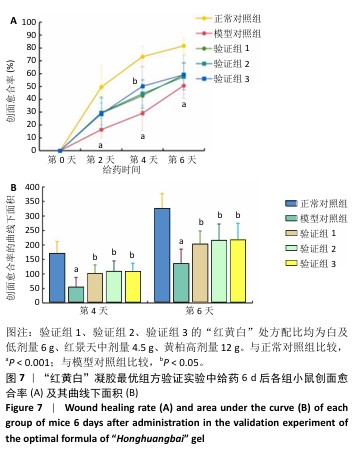
[1] REHMAN ZU, KHAN J, NOORDIN S. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: Contemporary Assessment And Management. J Pak Med Assoc. 2023;73(7):1480-1487.
[2] MCDERMOTT K, FANG M, BOULTON AJM, et al. Etiology, Epidemiology, and Disparities in the Burden of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(1):209-221.
[3] DOGRUEL H, AYDEMIR M, BALCI MK. Management of diabetic foot ulcers and the challenging points: An endocrine view. World J Diabetes. 2022;13(1): 27-36.
[4] PATEL M, PATEL V, SHAH U, et al. Molecular pathology and therapeutics of the diabetic foot ulcer; comprehensive reviews. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2024;130(5):591-598.
[5] ARMSTRONG DG, TAN TW, BOULTON AJM, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(1):62-75.
[6] BOLTON L. Diabetic foot ulcer: treatment challenges. Wounds. 2022; 34(6):175-177.
[7] VU NB, NGUYEN HT, PALUMBO R, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes for wound healing: current status and promising directions. Minerva Med. 2021;112(3):384-400.
[8] LI P, HONG G, ZHAN W, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell derived exosomes mediated miR-182-5p delivery accelerate diabetic wound healing via down-regulating PPARG. Int J Med Sci. 2023;20(4):468-481.
[9] 杜明威,朱信霖,廖万清,等.中西医治疗糖尿病足溃疡的研究现状[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2024,38(2):128-133.
[10] 叶全,刘馨琪,王栋先,等.王新陆临证运用红景天经验[J].中医杂志,2024,65(9):887-891.
[11] 路舜,崔红倩,申远.黄柏与关黄柏化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J].新乡医学院学报,2023,40(5):478-482.
[12] JIANG S, WANG M, JIANG L, et al. The medicinal uses of the genus Bletilla in traditional Chinese medicine: A phytochemical and pharmacological review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;280:114263.
[13] ZHAO Y, WANG Q, YAN S, et al. Bletilla striata Polysaccharide Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing Through Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:659215.
[14] 韩雪,刘海,张烨珊,等.白及多糖创面敷料及交联方式的研究进展[J].中药材,2024,47(2):519-525.
[15] MIRZA RE, FANG MM, WEINHEIMER-HAUS EM, et al. Sustained inflammasome activity in macrophages impairs wound healing in type 2 diabetic humans and mice. Diabetes. 2014;63(3):1103-1114.
[16] TANAKA R, VAYNRUB M, MASUDA H, et al. Quality-control culture system restores diabetic endothelial progenitor cell vasculogenesis and accelerates wound closure. Diabetes. 2013;62(9):3207-3217.
[17] 梅凌,严绪华,黄中强,等.醉鱼草凝胶制剂成型性工艺研究[J].时珍国医国药,2024,35(5):1152-1155.
[18] 蔡建峰,杨真真.正骨消肿止痛凝胶的制备工艺研究[J].临床合理用药,2024,17(20):160-162.
[19] GUO Y, BIAN Z, XU Q, et al. Novel tissue-engineered skin equivalent from recombinant human collagen hydrogel and fibroblasts facilitated full-thickness skin defect repair in a mouse model. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;130:112469.
[20] BAHMAD HF, POPPITI R, ALEXIS J. Nanotherapeutic approach to treat diabetic foot ulcers using tissue-engineered nanofiber skin substitutes: A review. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021;15(2):487-491.
[21] 张广静,王正想,刘杰,等.组织工程皮肤在糖尿病皮肤溃疡模型大鼠创面修复中的应用研究[J]. 临床皮肤科杂志,2024,53(12):715-720.
[22] EJIUGWO M, ROCHEV Y, GETHIN G, et al. Toward Developing Immunocompetent Diabetic Foot Ulcer-on-a-Chip Models for Drug Testing. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2021;27(2):77-88.
[23] SUNG JH, KIM JJ. Recent advances in in vitro skin-on-a-chip models for drug testing. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2023;19(5):249-267.
[24] NAHAK BK, MISHRA A, PREETAM S, et al. Advances in Organ-on-a-Chip Materials and Devices. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022;5(8):3576-3607.
[25] 郑红波,周伟,李永文,等.糖尿病足的中医外治法研究进展[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2021,30(1):103-107.
[26] 胡锦庆,巴元明,丁霑,等.基于络病理论探讨糖尿病足溃疡的中医病机及治疗[J].辽宁中医杂志,2017,44(1):51-53.
[27] ZHENG T, WANG Q, BIAN F, et al. Salidroside alleviates diabetic neuropathic pain through regulation of the AMPK-NLRP3 inflammasome axis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021;416:115468.
[28] 景亮,祁永章.红景天苷对糖尿病足溃疡大鼠Nrf2/Keap1信号通路及伤口愈合的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2021,31(8):48-54.
[29] ARIYANTI AD, SISJAYAWAN J, ZHANG J, et al. Elevating VEGF-A and PDGF-BB secretion by salidroside enhances neoangiogenesis in diabetic hind-limb ischemia. Oncotarget. 2017;8(57):97187-97205.
[30] ARIYANTI AD, ZHANG J, MARCELINA O, et al. Salidroside-Pretreated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhance Diabetic Wound Healing by Promoting Paracrine Function and Survival of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Under Hyperglycemia. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(4):404-414.
[31] 王洪瑾,李毅,冯艳萍,等.红景天苷对慢性低氧后冻伤大鼠血管内皮细胞的保护作用[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2022,38(6):664-669.
[32] 李越,吴中宝,杨艳玲,等.Box-Behnken响应面法优选红景天苷乳剂凝胶处方工艺并研究其对烫伤的治疗作用[J].中国现代中药, 2020,22(4):609-614,635.
[33] 龙世棋,周祝兴,杨黎,等.红景天对皮肤创伤治疗的作用及机制[J].贵州医科大学学报,2016,41(10):1181-1184.
[34] 邹超.外用中药制剂治疗EGFRIs相关皮肤干燥的临床研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2013.
[35] YIN MC, CHANG CH, SU CH, et al. Pteris multifida, Cortex phellodendri, and probiotics attenuated inflammatory status and immunity in mice with a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2018;82(5):836-847.
[36] LI C, XIE J, CHEN X, et al. Comparison of Helicobacter pylori Urease Inhibition by Rhizoma Coptidis, Cortex Phellodendri and Berberine: Mechanisms of Interaction with the Sulfhydryl Group. Planta Med. 2016;82(4):305-311.
[37] CHENG H, LIU J, TAN Y, et al. Interactions between gut microbiota and berberine, a necessary procedure to understand the mechanisms of berberine. J Pharm Anal. 2022;12(4):541-555.
[38] ZHANG JJ, ZHOU R, DENG LJ, et al. Huangbai liniment and berberine promoted wound healing in high-fat diet/Streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;150:112948.
[39] 王艮一,范琦琛,张筱茜,等.黄柏及其有效成分促进创面愈合机制研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2023,25(9):151-155.
[40] 赵艳,王启斌,郝新才,等.白及促创面愈合作用研究进展[J].中药材,2020,43(4):1027-1031.
[41] XU D, PAN Y, CHEN J. Chemical Constituents, Pharmacologic Properties, and Clinical Applications of Bletilla striata. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10: 1168. |