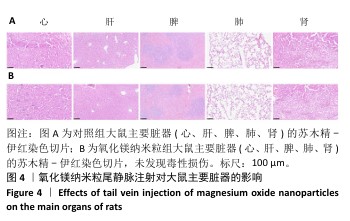
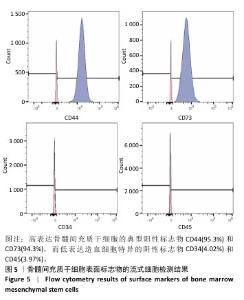
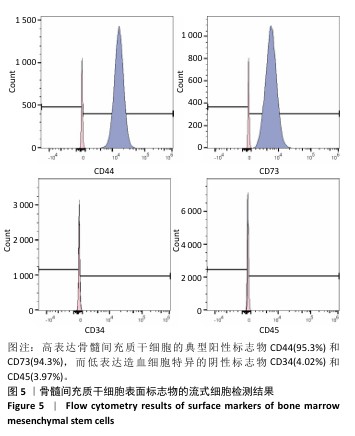
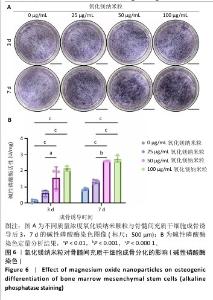
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (8): 1885-1895.doi: 10.12307/2026.030
Previous Articles Next Articles
Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing
Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng
- West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-22Accepted:2025-02-07Online:2026-03-18Published:2025-07-14 -
Contact:Li Yu, Professor, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China Liao Jinfeng, Professor, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wu Yanting, West China Hospital of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 32171354 (to LJF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

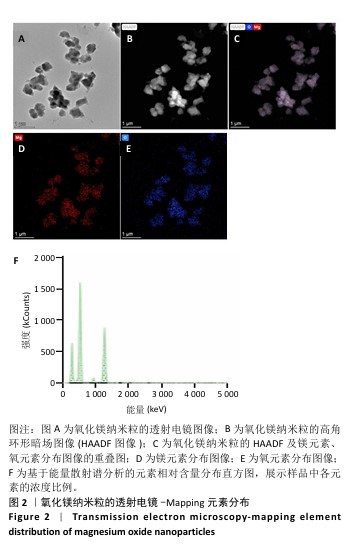
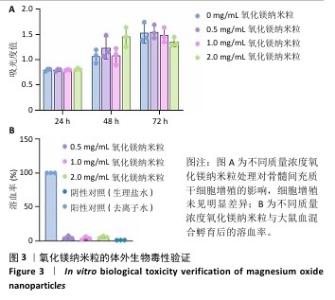
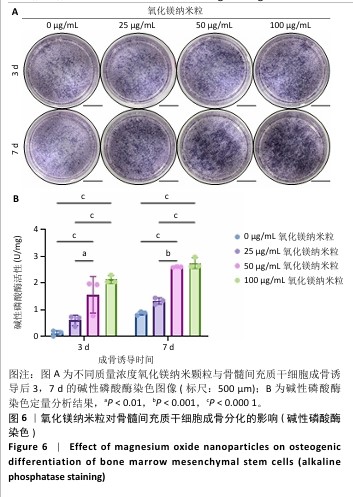
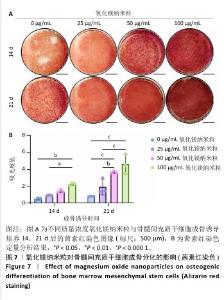
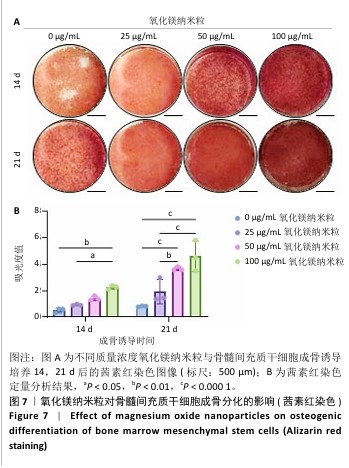
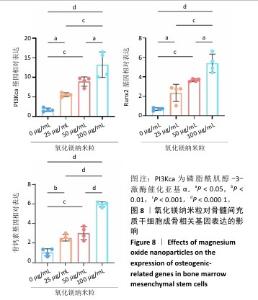
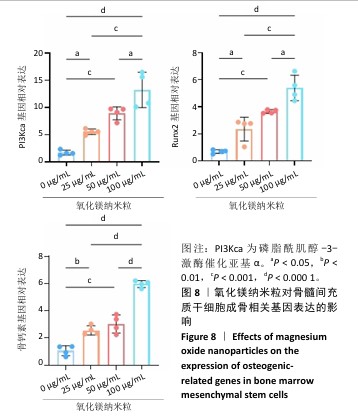
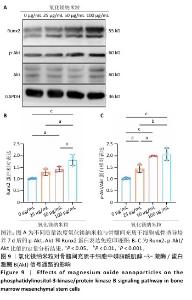
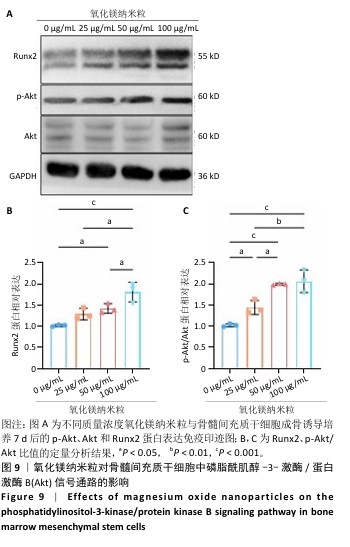
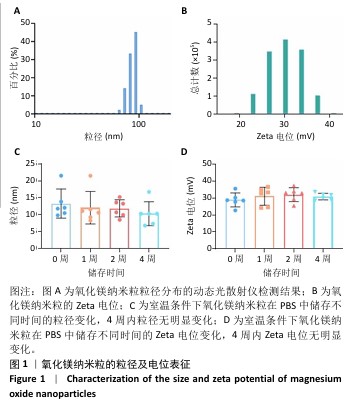
2.1 氧化镁纳米粒的表征结果 氧化镁纳米粒的水合粒径为(80±20) nm(图1A),多分散指数为0.129,表明氧化镁纳米粒的粒径分布均匀。Zeta 电位测试结果显示氧化镁纳米粒表面电位为(30.29±2.10) mV(图1B),Zeta电位绝对值在30 mV以上为纳米粒在水溶液中具有良好的稳定性,结果表明氧化镁纳米粒在水溶液中具有良好的稳定性。进一步检测发现,在室温条件下储存1个月后,氧化镁纳米粒的粒径和Zeta电位均未出现显著变化(图1C,D),表现出良好的储存稳定性。透射电镜图像显示氧化镁纳米粒呈类球形,粒径分布在50-100 nm 范围内,颗粒分散性良好,与动态光散射仪检测数据基本一致;元素分布图像显示 Mg和O元素均匀分布(图2),证实该纳米粒的化学成分为氧化镁且纯度较高。综上,制备的氧化镁纳米粒具备均一的粒径分布、优异的稳定性和高纯度。"
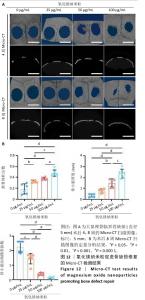
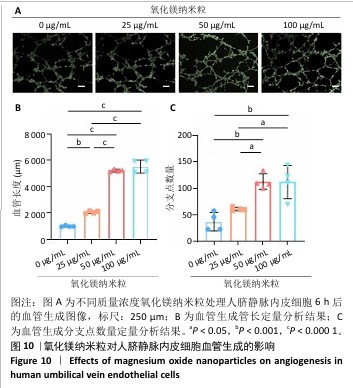
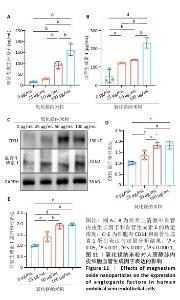
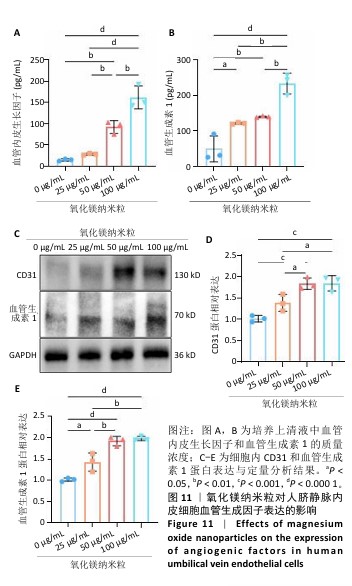
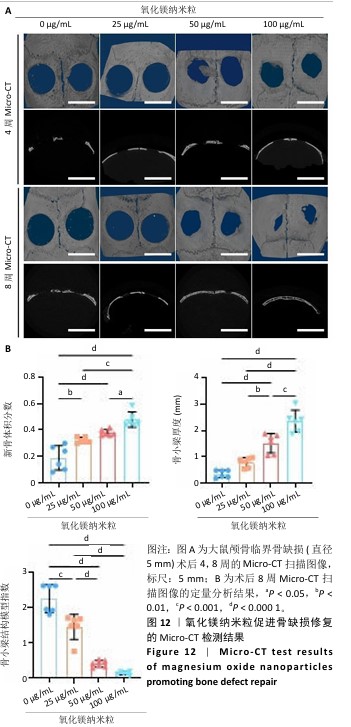
2.5 氧化镁纳米粒修复大鼠颅骨缺损实验结果 为了评估氧化镁纳米粒在体内的促骨再生效果,此次实验建立了大鼠颅骨临界骨缺损模型(直径5 mm)[11],然后将不同质量浓度的氧化镁纳米粒悬浮液注射到骨缺损部位。 2.5.1 实验动物数量分析 24只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.5.2 骨缺损部位Micro-CT检测 术后4,8周,氧化镁纳米粒处理组骨缺损区域新骨形成显著高于对照组,并且新骨密度随着氧化镁纳米粒质量浓度的增加而逐渐提高(图12A)。定量分析结果显示,随着氧化镁纳米粒质量浓度的增加,骨缺损部位的新骨体积分数和骨小梁厚度升高,骨小梁结构模型指数降低(图12B)。表明氧化镁纳米粒可通过增强骨小梁质量促进新骨形成。"
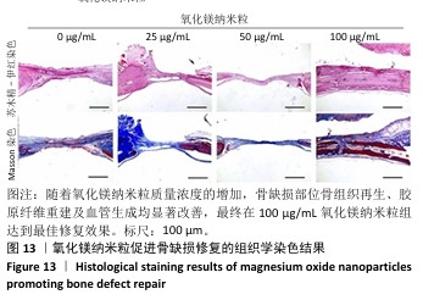
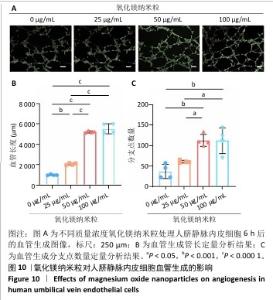
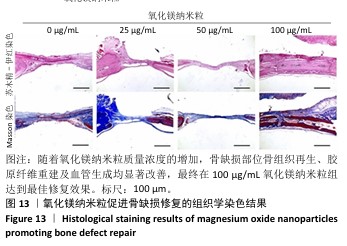
2.5.3 骨缺损部位组织学分析 术后8周,苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,0 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组骨缺损区域主要被纤维结缔组织填充,未见新骨形成;25 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组可见新骨生成,主要为结构松散的编织骨;50 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组可见明显的新骨形成,编织骨逐渐转变为更加成熟的板层骨;100 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组新骨生成最为明显,骨缺损区域几乎被板层骨完全填充,骨组织排列规则,修复效果最佳,见图13。 术后8周,Masson染色结果显示,0 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组胶原纤维稀疏且无序,缺乏新骨结构特征;25 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组胶原纤维稍显增加,但排列仍较为松散;50 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组胶原纤维显著增多,呈现出较为有序的排列,同时血管生成明显;100 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组胶原纤维排列最为致密有序,并伴随大量血管生成,见图13,为骨再生提供了理想的环境。 结果表明,随着氧化镁纳米粒质量浓度的增加,骨缺损部位骨组织再生、胶原纤维重建及血管生成均显著改善,最终在100 μg/mL氧化镁纳米粒组达到最佳修复效果。"
| [1] WU Y, ZHANG X, ZHAO Q, et al. Role of Hydrogels in Bone Tissue Engineering: How Properties Shape Regeneration. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2020;16(12):1667-1686. [2] YANG Y, CHU L, YANG S, et al. Dual-functional 3D-printed composite scaffold for inhibiting bacterial infection and promoting bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:265-275. [3] PENG Z, WANG C, LIU C, et al. 3D printed polycaprolactone/beta-tricalcium phosphate/magnesium peroxide oxygen releasing scaffold enhances osteogenesis and implanted BMSCs survival in repairing the large bone defect. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(28):5698-5710. [4] FAN J, PARK H, LEE MK, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and BMP-2 Delivery in Chitosan-Based 3D Constructs to Enhance Bone Regeneration in a Rat Mandibular Defect Model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(15-16):2169-2179. [5] YAO H, ZOU Y, YANG K, et al. TGFβ1 induces bone formation from BMP9-activated Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with possible involvement of non-canonical pathways. Int J Med Sci. 2020;17(12):1692-1703. [6] XIAO X, XU M, YU H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles mitigate oxidative stress-induced senescence in endothelial cells via regulation of miR-146a/Src. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):354. [7] FENG Y, HAN Z, JIANG W, et al. Promotion of osteogenesis in BMSC under hypoxia by ATF4 via the PERK–eIF2α signaling pathway. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022;58(10):886-897. [8] ZHAO Y, MENG L, ZHANG K, et al. Ultra-small nanodots coated with oligopeptides providing highly negative charges to enhance osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs better than osteogenic induction medium. Chin Chem Lett. 2021;32(1):266-270. [9] DIAS AM, DO NASCIMENTO CANHAS I, BRUZIQUESI CGO, et al. Magnesium (Mg2 +), Strontium (Sr2 +), and Zinc (Zn2 +) Co-substituted Bone Cements Based on Nano-hydroxyapatite/Monetite for Bone Regeneration. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023;201(6):2963-2981. [10] FU M, YANG C, SUN G. Recent advances in immunomodulatory hydrogels biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration. Mol Immunol. 2023;163:48-62. [11] LV Z, HU T, BIAN Y, et al. A MgFe-LDH Nanosheet-Incorporated Smart Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel with Controllable Growth Factor Releasing Capability for Bone Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2023;35(5):e2206545. [12] LU X, SHI S, LI H, et al. Magnesium oxide-crosslinked low-swelling citrate-based mussel-inspired tissue adhesives. Biomaterials. 2020;232:119719. [13] KANG Y, XU C, MENG L, et al. Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:26-41. [14] TARAFDER S, DERNELL WS, BANDYOPADHYAY A, et al. SrO- and MgO-doped microwave sintered 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds: mechanical properties and in vivo osteogenesis in a rabbit model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(3):679-690. [15] XIONG Y, LIN Z, BU P, et al. A Whole-Course-Repair System Based on Neurogenesis-Angiogenesis Crosstalk and Macrophage Reprogramming Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Mater. 2023;35(19):e2212300. [16] DAI Y, WU J, WANG J, et al. Magnesium Ions Promote the Induction of Immunosuppressive Bone Microenvironment and Bone Repair through HIF-1α-TGF-β Axis in Dendritic Cells. Small. 2024;20(33):e2311344. [17] HU X, CHEN J, YANG S, et al. 3D Printed Multifunctional Biomimetic Bone Scaffold Combined with TP-Mg Nanoparticles for the Infectious Bone Defects Repair. Small. 2024;20(40):e2403681. [18] MAO J, SUN Z, WANG S, et al. Multifunctional Bionic Periosteum with Ion Sustained-Release for Bone Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(39): e2403976. [19] LI J, WU J, LIU F, et al. Magnesium-Organic Framework-Loaded Bisphosphonate-Functionalized Gel Scaffolds for Enhanced Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(12):6849-6859. [20] LIU L, WANG F, SONG W, et al. Magnesium promotes vascularization and osseointegration in diabetic states. Int J Oral Sci. 2024;16(1):10. [21] SHU M, WANG J, XU Z, et al. Targeting nanoplatform synergistic glutathione depletion-enhanced chemodynamic, microwave dynamic, and selective-microwave thermal to treat lung cancer bone metastasis. Bioact Mater. 2024;39:544-561. [22] GAO G, JIANG YW, JIA HR, et al. Near-infrared light-controllable on-demand antibiotics release using thermo-sensitive hydrogel-based drug reservoir for combating bacterial infection. Biomaterials. 2019;188:83-95. [23] FENTON OS, OLAFSON KN, PILLAI PS, et al. Advances in Biomaterials for Drug Delivery. Adv Mater. 2018;30(29):1705328. [24] LI J, WEI G, LIU G, et al. Regulating Type H Vessel Formation and Bone Metabolism via Bone-Targeting Oral Micro/Nano-Hydrogel Microspheres to Prevent Bone Loss. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(15):e2207381. [25] ZOU D, ZHANG Z, HE J, et al. Blood vessel formation in the tissue-engineered bone with the constitutively active form of HIF-1α mediated BMSCs. Biomaterials. 2012;33(7):2097-2108. [26] MEURY T, VERRIER S, ALINI M. Human endothelial cells inhibit BMSC differentiation into mature osteoblasts in vitro by interfering with osterix expression. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(4):992-1006. [27] QIN Q, LEE S, PATEL N, et al. Neurovascular coupling in bone regeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(11):1844-1849. [28] ALAIZERI ZM, ALHADLAQ HA, ALDAWOOD S, et al. Facile Synthesis, Characterization, Photocatalytic Activity, and Cytotoxicity of Ag-Doped MgO Nanoparticles. Nanomater Basel Switz. 2021;11(11):2915. [29] HE L, HE T, XING J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):276. [30] DZAMUKOVA M, BRUNNER TM, MIOTLA-ZAREBSKA J, et al. Mechanical forces couple bone matrix mineralization with inhibition of angiogenesis to limit adolescent bone growth. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3059. [31] RIBATTI D, D’AMATI A. Bone angiocrine factors. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023; 11:1244372. [32] DARVISHI B, DINARVAND R, MOHAMMADPOUR H, et al. Dual l-Carnosine/Aloe vera Nanophytosomes with Synergistically Enhanced Protective Effects against Methylglyoxal-Induced Angiogenesis Impairment. Mol Pharm. 2021;8(9):3302-3325. [33] VEIS A. Mineral-matrix interactions in bone and dentin. J Bone Miner Res. 1993;8 Suppl 2:S493-497. [34] ZHENG L, ZHAO S, LI Y, et al. Engineered MgO nanoparticles for cartilage-bone synergistic therapy. Sci Adv. 2024;10(10):eadk6084. [35] ZHENG G, XIE J, YAO Y, et al. MgO@polydopamine Nanoparticle-Loaded Photothermal Microneedle Patches Combined with Chitosan Gel Dressings for the Treatment of Infectious Wounds. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024; 16(10):12202-12216. [36] GAO Y, WANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Advancing neural regeneration via adaptable hydrogels: Enriched with Mg2+ and silk fibroin to facilitate endogenous cell infiltration and macrophage polarization. Bioact Mater. 2024;33:100-113. [37] ZHANG B, LI KY, JIANG LC, et al. Rib Composite Flap With Intercostal Nerve and Internal Thoracic Vessels for Mandibular Reconstruction. J Craniofac Surg. 2016;27(7):1815-1818. [38] XU J, HE SJ, XIA TT, et al. Targeting type H vessels in bone-related diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(4):e18123. [39] LIU Z, HUANG L, QI L, et al. Activating Angiogenesis and Immunoregulation to Propel Bone Regeneration via Deferoxamine-Laden Mg-Mediated Tantalum Oxide Nanoplatform. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(19): 24384-24397. [40] LI Q, LIU W, HOU W, et al. Micropatterned photothermal double-layer periosteum with angiogenesis-neurogenesis coupling effect for bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;18:100536. [41] SARKER M, IZADIFAR M, SCHREYER D, et al. Influence of ionic crosslinkers (Ca2+/Ba2+/Zn2+) on the mechanical and biological properties of 3D Bioplotted Hydrogel Scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2018;29(10): 1126-1154. [42] YAN C, ZHANG P, QIN Q, et al. 3D-printed bone regeneration scaffolds modulate bone metabolic homeostasis through vascularization for osteoporotic bone defects. Biomaterials. 2024;311:122699. [43] LIAO P, CHEN L, ZHOU H, et al. Osteocyte mitochondria regulate angiogenesis of transcortical vessels. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2529. [44] LIU M, WANG R, LIU J, et al. Incorporation of magnesium oxide nanoparticles into electrospun membranes improves pro-angiogenic activity and promotes diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112609. [45] ASKAR MA, THABET NM, EL-SAYYAD GS, et al. Dual Hyaluronic Acid and Folic Acid Targeting pH-Sensitive Multifunctional 2DG@DCA@MgO-Nano-Core-Shell-Radiosensitizer for Breast Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2021;13(21):5571. [46] LI X, COATES DE. Hollow channels scaffold in bone regenerative: a review. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2023;34(12):1702-1715. [47] LIU M, WANG R, LIU J, et al. Incorporation of magnesium oxide nanoparticles into electrospun membranes improves pro-angiogenic activity and promotes diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112609. [48] SUN TW, YU WL, ZHU YJ, et al. Hydroxyapatite Nanowire@Magnesium Silicate Core-Shell Hierarchical Nanocomposite: Synthesis and Application in Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(19):16435-16447. [49] YOSHIZAWA S, BROWN A, BARCHOWSKY A, et al. Magnesium ion stimulation of bone marrow stromal cells enhances osteogenic activity, simulating the effect of magnesium alloy degradation. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(6): 2834-2842. [50] HONG X, YANG Y, LI X, et al. Enhanced anti-Escherichia coli properties of Fe-doping in MgO nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2021;11(5):2892-2897. |
| [1] | Jiang Xinghai, Song Yulin, Li Dejin, Shao Jianmin, Xu Junzhi, Liu Huakai, Wu Yingguo, Shen Yuehui, Feng Sicheng. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 genes transfected into bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct a vascularized amphiphilic peptide gel module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [2] | Yuan Qian, Zhang Hao, Pang Jie. Characterization and biological properties of naringin-loaded chitosan/beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
| [3] | Zhang Junwei, Chen Lingling, Ma Zhenyuan, Nie Weizhi, Li Chaohui, Wang Haitao, Duan Laibao, Hou Jinyong, Bi Hongzheng. Three-dimensional displacement and risk factors of midshaft clavicle fractures treated with titanium elastic intramedullary nailing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 269-277. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||