Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1294-1301.doi: 10.12307/2026.043
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis
Wen Xiaolong1, 2, Weng Xiquan2, Feng Yao2, Cao Wenyan2, Liu Yuqian1, 3, Wang Haitao1, 3
- 1Institute of Exercise and Health Promotion, 3School of Physical Sciences, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang 524048, Guangdong Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Exercise Biochemistry, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou 510500, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-31Accepted:2025-03-01Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-27 -
Contact:Wang Haitao, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Exercise and Health Promotion, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang 524048, Guangdong Province, China; School of Physical Sciences, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang 524048. Guangdong Province, China Co-corresponding author: Liu Yuqian, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Institute of Exercise and Health Promotion, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang 524048, Guangdong Province, China; School of Physical Sciences, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang 524048. Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wen Xiaolong, Master candidate, Institute of Exercise and Health Promotion, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang 524048, Guangdong Province, China; Key Laboratory of Exercise Biochemistry, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou 510500, Guangdong Province, China Chen Xinmin, dong Province, China -
Supported by:Humanities and Social Sciences Research Fund Project of the Ministry of Education, No. 23YJAZH088 (to LYQ); Guangdong Province Education Science Project, No. 2023GXJK371 (to LYQ); Philosophy and social Science Project of Guangdong Province, No. GD23XTY39 (to WHT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

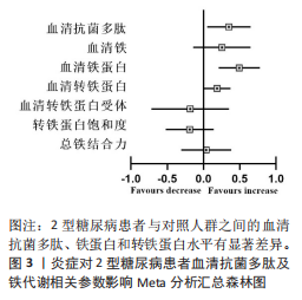
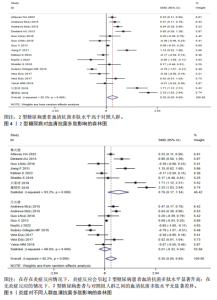
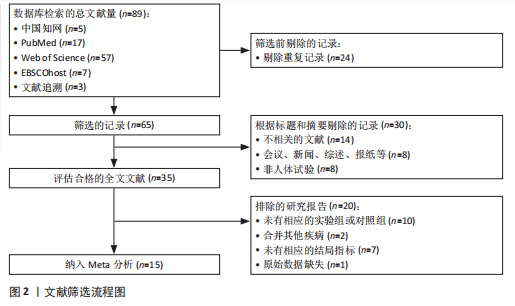
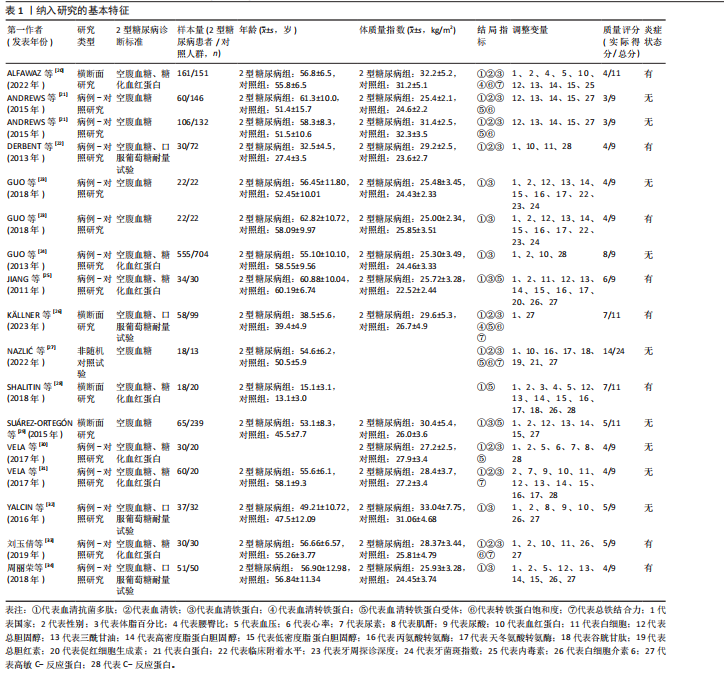
2.1 文献筛选 初检得到了89篇文献,其中中文文献5篇、英文文献81篇、文献追溯3篇。经逐层筛选后,最终纳入15篇文献[20-34],共3 314名参与者(病例组1 472人,对照组1 842人)。文献筛选流程及结果见图2。 2.2 纳入研究的基本特征 15篇文献共包括17项研究,包括12项病例-对照研究、4项横断面研究和1项非随机对照试验;总样本量3 159名受试者,包括病例组1 357人、对照组1 802人;高质量研究1篇,中等质量研究8篇,低质量研究6篇。 纳入研究的基本特征见表1。 2.3 Meta分析结果 图3总结了2型糖尿病组与对照组参与者之间每个结局指标的差异,以95%CI的标准化均数差表示,中或高异质性(I2≥50%)研究采用随机效应模型进行汇总分析,低异质性研究采用固定效应模型汇总"
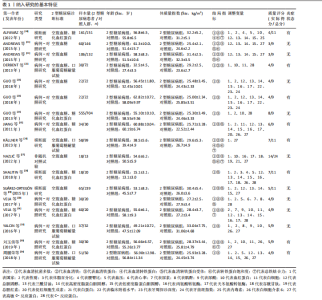
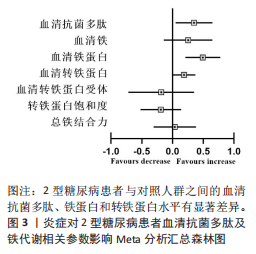
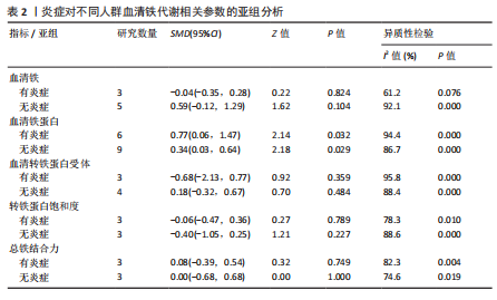
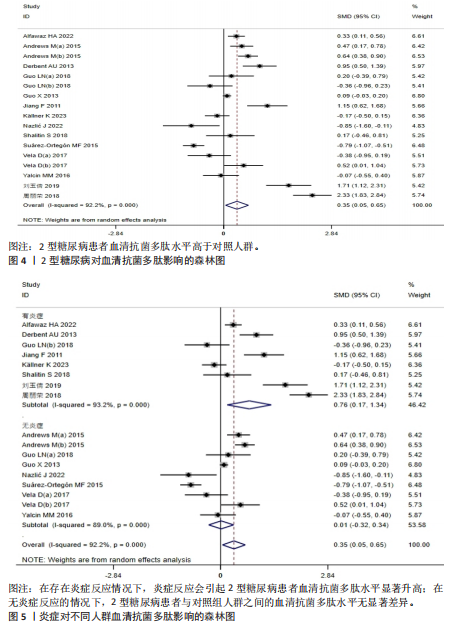
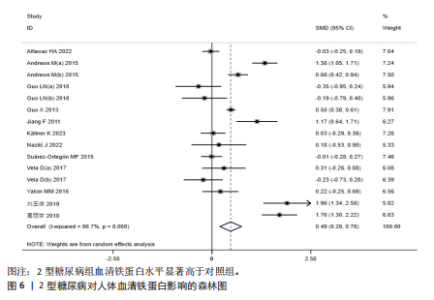
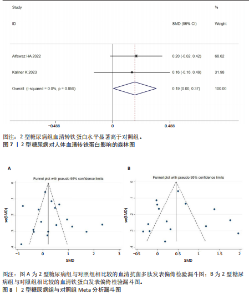
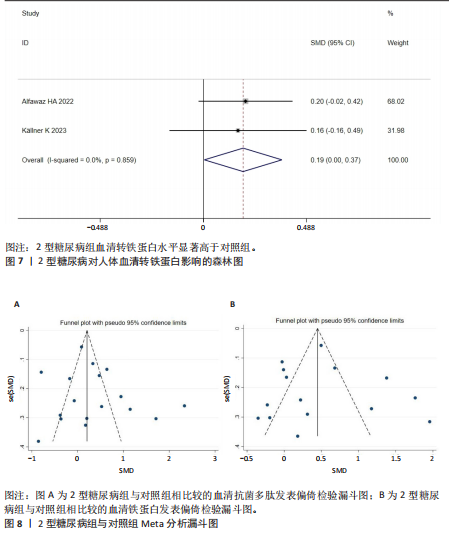
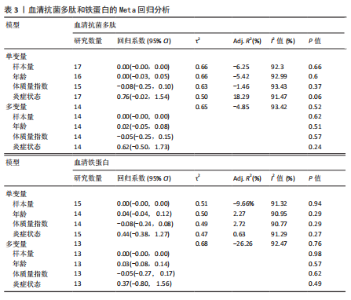
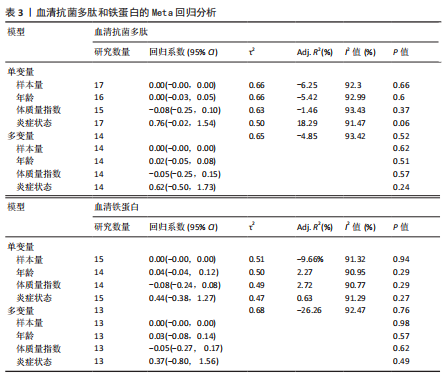
分析。从整体上看,2型糖尿病患者与对照人群之间的血清抗菌多肽、铁蛋白和转铁蛋白水平有显著差异。 2.3.1 2型糖尿病组与对照组参与者之间的血清抗菌多肽差异 共纳入12项病例-对照研究、4项横断面研究、1项非随机对照试验,共涉及3 159名参与者。汇总结果显示,2型糖尿病的影响较大且具有高度异质性(P=0.000,I2=92.2%),2型糖尿病患者血清抗菌多肽水平高于对照人群[SMD=0.35,95%CI(0.05,0.65),P=0.023],合并结果稳健,见图4所示。 2.3.2 炎症水平对不同人群血清抗菌多肽的影响 以是否存在炎症反应作为亚组进行分析,结果显示:在参与者均存在炎症反应的情况下,2型糖尿病患者与对照人群之间的血清抗菌多肽水平比较差异有显著性意义,炎症反应会引起2型糖尿病患者血清抗菌多肽水平显著升高[SMD=0.76,95%CI(0.17,1.34),P=0.01];在无炎症反应的情况下,2型糖尿病患者与对照组人群之间的血清抗菌多肽水平无显著差异[SMD=0.01,95%CI(-0.32,0.34),P=0.95],见图5所示。 2.3.3 次要结局指标 次要结局指标包括铁代谢相关参数如血清铁、铁蛋白、转铁蛋白、转铁蛋白受体、转铁蛋白饱和度及总铁结合力。Meta分析汇总表明,大多数铁代谢相关参数在2型糖尿病患者与对照人群中的差异较小(P > 0.05),仅有血清铁蛋白(共纳入15项研究,共涉及3 019名参与者)和转铁蛋白(共纳入2项研究,共涉及469名参与者)在2型糖尿病组和对照组中有显著差异,2型糖尿病组血清铁蛋白[SMD=0.49,95%CI(0.20,0.78),P=0.001]和转铁蛋白[SMD=0.19,95%CI(0.00,0.37),P=0.045]水平显著高于对照组,详见图6,7。 亚组分析结果表明,当存在炎症反应的情况下,2型糖尿病患者血清铁蛋白水平显著高于对照人群[SMD=0.77,95%CI(0.06,1.47),P=0.032];无论个体是否存在炎症水平,2型糖尿病组与对照组参与者间血清铁、转铁蛋白受体、转铁蛋白饱和度、总铁结合力水平均无显著差异,见表2。 2.4 发表偏倚 当纳入的研究数量≥10时采用漏斗图判断发表偏倚,因此,仅对血清抗菌多肽和血清铁蛋白进行分析,漏斗图中均显示主观判断的对称性,见图8。其中两项指标的Egger检验结果显示无显著发表偏倚(P抗菌多肽=0.331,P铁蛋白=0.375)。 2.5 Meta回归分析结果 将上述Meta分析中存在的统计学上高度异质性及纳入研究数≥10进行Meta回归,以找到异质性的可能来源,协变量包括样本量、年龄、体质量指数、炎症状态,然而,单变量回归并没有发现任何显著的协变量(P > 0.05),同时这些协变量的多元回归也无法解释Meta分析的高异质性来源(P > 0.05),见表3。高异质性的原因可能是由于统计异质性(如不同的研究设计、测量方式等因素)或未被此次研究考虑的协变量之外其他潜在变量所引起。"
| [1] PRÁ D, FRANKE SIR, HENRIQUES JAP, et al. Iron and genome stability: an update. Mutat Res. 2012;733(1-2):92-99. [2] MOON DO. NADPH dynamics: Linking insulin resistance and β-Cells ferroptosis in diabetes mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;25(1):342. [3] MIAO R, FANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Iron metabolism and ferroptosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus and complications: mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(3):186. [4] CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity. J Exp Med. 2021;218(6):e20210518. [5] CHAND SK, SINGH RG, PENDHARKAR SA, et al. Iron: a strong element in the pathogenesis of chronic hyperglycaemia after acute pancreatitis. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018;183: 71-79. [6] KALI A, CHARLES MVP, SEETHARAM RSK. Hepcidin-A novel biomarker with changing trends. Pharmacogn Rev. 2015;9(17):35. [7] NEMETH E, GANZ T. Hepcidin-ferroportin interaction controls systemic iron homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6493. [8] NEMETH E, GANZ T. Hepcidin and iron in health and disease. Annu Rev Med. 2023;74(1):261-277. [9] HAN Y, HUANG W, MENG H, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6-induced hepcidin, a key mediator of periodontitis-related anemia of inflammation. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(4):690-701. [10] NEMETH E, RIVERA S, GABAYAN V, et al. IL-6 mediates hypoferremia of inflammation by inducing the synthesis of the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. J Clin Invest. 2004;113(9): 1271-1276. [11] LIU J, LI Q, YANG Y, et al. Iron metabolism and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta‐analysis and systematic review. J Diabetes Investig. 2020;11(4):946-955. [12] ELLULU MS, SAMOUDA H. Clinical and biological risk factors associated with inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022;22(1):16. [13] RIDKER PM. A Test in Context: High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; 67(6):712-723. [14] WAN X, WANG W, LIU J, et al. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:1-13. [15] 曾宪涛,刘慧,陈曦,等.Meta分析系列之四:观察性研究的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(4):297-299. [16] SLIM K, NINI E, FORESTIER D, et al. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73(9): 712-716. [17] STANG A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25:603-605. [18] 唐萍,王佳琳,谢婉青,等.中国老年人述情障碍发生现状的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志,2021,21(7):779-786. [19] CHA SM. Mobile Application Applied for Cognitive Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review. Life (Basel). 2024;14(7):891. [20] ALFAWAZ HA, ALFAIFI AA, YAKOUT SM, et al. Circulating hepcidin and its associations with low-grade inflammation and iron indices among Arab adults with and without T2DM. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(10):7520. [21] ANDREWS M, SOTO N, ARREDONDO-OLGUÍN M. Association between ferritin and hepcidin levels and inflammatory status in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Nutrition. 2015;31(1):51-57. [22] DERBENT AU, SIMAVLI SA, KAYGUSUZ I, et al. Serum hepcidin is associated with parameters of glucose metabolism in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013;26(11):1112-1115. [23] GUO LN, YANG YZ, FENG YZ. Serum and salivary ferritin and Hepcidin levels in patients with chronic periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health. 2018;18:1-9. [24] GUO X, ZHOU D, AN P, et al. Associations between serum hepcidin, ferritin and Hb concentrations and type 2 diabetes risks in a Han Chinese population. Br J Nutr. 2013; 110(12):2180-2185. [25] JIANG F, SUN ZZ, TANG YT, et al. Hepcidin expression and iron parameters change in Type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;93(1):43-48. [26] KÄLLNER K, KROOK R, SANDBERG AS, et al. Interaction of Iron Homeostasis and Fatty Acid Metabolism in the Development of Glucose Intolerance in Women with Previous Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients. 2023; 15(14):3214. [27] NAZLIĆ J, JURIĆ D, MUDNIĆ I, et al. Effects of moderate consumption of red wine on hepcidin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Foods. 2022;11(13):1881. [28] SHALITIN S, DEUTSCH V, TAUMAN R. Hepcidin, soluble transferrin receptor and IL-6 levels in obese children and adolescents with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus/impaired glucose tolerance and their association with obstructive sleep apnea. J Endocrinol Invest. 2018;41: 969-975. [29] SUÁREZ‐ORTEGÓN MF, MORENO M, ARBELÁEZ A, et al. Circulating hepcidin in type 2 diabetes: A multivariate analysis and double blind evaluation of metformin effects. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59(12):2460-2470. [30] VELA D, LESHOSKI J, VELA Z, et al. Insulin treatment corrects hepcidin but not YKL-40 levels in persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus matched by body mass index, waist-to-height ratio, C-reactive protein and Creatinine. BMC Endocr Disord. 2017;17:1-9. [31] VELA D, LESHOSKI J, GJORGIEVSKA ES, et al. The role of insulin therapy in correcting hepcidin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Oman Med J. 2017; 32(3):195. [32] YALCIN MM, ALTINOVA AE, AKTURK M, et al. GDF‐15 and Hepcidin Levels in Nonanemic Patients with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016(1):1240843. [33] 刘玉倩,郑梅,张静,等.铁调素(Hepcidin)在2型糖尿病发生中的作用研究[J].现代预防医学,2019,46(15):2851-2855. [34] 周丽荣,郭昆全,杨坤,等.初诊2型糖尿病患者铁调素水平的变化[J].湖北医药学院学报,2018,37(4):341-345. [35] SONG JX, AN JR, CHEN Q, et al. Liraglutide attenuates hepatic iron levels and ferroptosis in db/db mice. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):8334-8348. [36] 刘玉倩,杨雯茜,王海涛.Nrf2/FPN1介导的铁稳态通路在有氧运动预防小鼠肝胰岛素抵抗中的作用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2023, 42(4):294-302. [37] KEMNA E, PICKKERS P, NEMETH E, et al. Time-course analysis of hepcidin, serum iron, and plasma cytokine levels in humans injected with LPS. Blood. 2005; 106(5):1864-1866. [38] PECHLANER R, WEISS G, BANSAL S, et al. Inadequate hepcidin serum concentrations predict incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2016;32(2):187-192. [39] KAUTZ L, JUNG G, VALORE EV, et al. Identification of erythroferrone as an erythroid regulator of iron metabolism. Nat Genet. 2014;46(7):678-684. [40] VELA D, SOPI RB, MLADENOV M. Low hepcidin in type 2 diabetes mellitus: examining the molecular links and their clinical implications. Can J Diabetes. 2018;42(2):179-187. [41] LEE BK, KIM Y, KIM YI. Association of serum ferritin with metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus in the South Korean general population according to the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008. Metabolism. 2011;60(10):1416-1424. [42] FENERCIOGLU AK, GONEN MS, UZUN H, et al. The association between Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and pro-inflammatory markers in new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and prediabetes. Biomolecules. 2023;13(12):1778. |
| [1] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [2] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [3] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [4] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [5] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [6] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [7] | Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235. |
| [8] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [9] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [10] | Chen Qiang, Wu Wenjuan, Jiang Shuhua, Huang Da. Physical exercise improves physical function in burn patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1269-1281. |
| [11] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [12] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [13] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [14] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [15] | Zhang Jiuxuan, Zhang Jinnan, Sui Xiaofan, Pei Xiaxia, Wei Jianhong, Su Qiang, Li Tian. Effects of ammonia poisoning on cognitive behavior and hippocampal synaptic damage in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1122-1128. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||