Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1225-1235.doi: 10.12307/2026.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes
Wen Fan1, Xiang Yang1, Zhu Huan1, Tuo Yanfang1, Li Feng2
- 1School of Physical Education, Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China; 2School of Physical Education, Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-11-04Accepted:2025-01-06Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-26 -
Contact:Li Feng, PhD, Associate professor, School of Physical Education, Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Wen Fan, Master candidate, School of Physical Education, Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:2024 Hubei University for Nationalities Graduate Student Research and Innovation Project, No. MYK2024016 (to WF); 2024 Hubei University for Nationalities Graduate Student Education Reform Project, No. MYG2024006 (to ZH); 2025 Hubei Provincial Natural Science Foundation for Sport Innovation and Development, No. JCZRLH202500954 (to ZH); Guangxi University of Science and Technology PhD Fund Project, No. 20S07 (to LF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wen Fan, Xiang Yang, Zhu Huan, Tuo Yanfang, Li Feng. Exercise improves microvascular function in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1225-1235.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
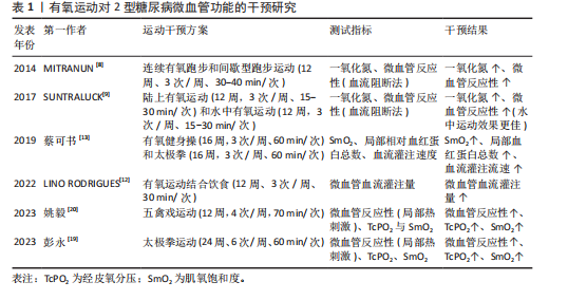
2.1 运动类型对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 2.1.1 有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 (1)陆上有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 基于运动强度适中、运动风险低等优点,有氧运动是2型糖尿病患者常采用的运动干预方式,该运动方式对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能具有积极的干预效果。内皮细胞功能障碍是心血管疾病发生的早期事件,在血管舒缩因子失衡、炎症、氧化应激及血栓等因素作用下,2型糖尿病患者微血管内皮细胞常出现功能障碍,其最为显著的特征是内皮依赖性血管舒张功能下降。研究发现,有氧跑步运动(12周,3次/周、30-40 min/次)能显著提高2型糖尿病患者的微血管内皮依赖性舒张功能,改善血糖水平[9]。动物实验得出类似结论,有氧跑步运动(12周、3次/周、30 min/次)能改善2型糖尿病小鼠微血管血流灌注量,其原因与抑制晚期糖基化终产物-细胞表面受体-糖基化终产物受体信号通路激活以及提高抗氧化酶的活性有关[12]。作为常见的有氧运动方式,有氧健身操(16周,3次/周、60 min/次)和太极拳(16周,3次/周、60 min/次)均能通过提高足底组织肌氧饱和度、局部血红蛋白总数、血流灌注流速等途径改善2型糖尿病患者微血管的血流灌注能力,且太极拳运动干预效果更佳[13]。虽然有氧健身操和太极拳两者均属于有氧运动,但太极拳运动过程中足底肌肉间歇性等张和等长收缩的运动方式更有利于提高组织的血流量和供氧水平,因此对足底微血管功能显示出更佳的干预效果。提示对于有足部微血管功能障碍的2型糖尿病患者,建议采取太极拳等对足部血管有特异性运动刺激的运动方式,以获得针对性和特异性的干预效果。 但该研究中关于2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的评价存在局限性。微血管血流灌注量是评价微循环功能的常用指标,但血管血流量基线值(未进行刺激)并不能科学评价微血管功能。当机体处于微循环功能障碍的早期阶段时,微血管血流量可能不会发生明显变化或者通过代偿反应使微血管血流量达到甚至超出正常值,以满足机体的物质能量代谢需求[14]。另外,正常静息状态下微血管的血流呈动态变化,微血管扩张和收缩程度不同,所测得的血流量可能有较大差异,因此不能仅通过微血管血流灌注量的基线值评价微循环功能,常用外部刺激后微血管血流量的变化(微血管反应性)消除这种差异,进而精准评估微血管功能的变化。 目前,局部皮肤热刺激、血流阻断、离子渗透以及运动负荷等是常用的刺激方式,其中局部热刺激的测量结果重复性和依从性最好,在临床上已广泛用于糖尿病等患者微血管反应性的评估,并成为临床替代指标[15]。当局部皮肤加热到42-44 ℃,会诱导微血管达到最大的舒张状态,此时微血管血流量将达到最大值,该值能客观评价微血管最大血流储备能力和血管舒张能力的大小[15-16]。研究指出,2型糖尿病患者皮肤微血管对局部热刺激的舒张反应能力下降以及对热刺激的响应有相位滞后[17]。FUCHS等[18]得出相似结论,2型糖尿病患者微血管血流量的基础值与健康受试者无显著差异,但皮肤微血管对局部热刺激的反应性明显下降。 有氧运动是改善2型糖尿病患者微血管反应性(局部热刺激)的有效方式。彭永等[19]研究指出,太极拳运动(24周、6次/周、60 min/次)能通过调节内源性一氧化氮、内皮素1、血管内皮生长因子等因子水平改善2型糖尿病患者足部微血管反应性,提高经皮氧分压和肌氧饱和度。此外,五禽戏运动(12周,4次/周,70 min/次)也能通过调节内源性一氧化氮、前列环素、血管内皮生长因子水平及降低内皮素1、血栓素等因子水平,提高2型糖尿病患者微血管反应性、经皮氧分压和肌氧饱和度[20]。 肌氧饱和度是评价2型糖尿病患者微血管功能和机体供氧能力的重要指标,能反映肌肉需氧-供氧平衡及肌肉代谢的情况,其取决于毛细血管向肌肉细胞输送氧的能力,因此肌氧饱和度能在经皮氧分压的基础上进一步评价微血管向肌肉细胞输送氧气的能力[21]。综上,有氧运动通过调节内源性一氧化氮、内皮素1、血管内皮生长因子等血管因子水平改善2型糖尿病患者的微血管反应性,提高微血管和肌肉组织的氧合能力,这些可能是引起2型糖尿病患者微血管功能变化的重要机制;同时有氧运动还能通过调节血管内皮生长因子的表达有效防止足部毛细血管消退并降低骨骼肌线粒体的氧化能力,从而对微血管内皮细胞产生保护作用[20]。 文献综合分析见表1。 (2)水中有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 近年来,随着水中疗法在慢性病康复中的应用,有研究显示水中有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能也能产生积极的效果。研究指出,陆上有氧运动(12周,3次/周、15-30 min/次)和水中有氧运动(方案同陆上有氧运动)均能提高2型糖尿病患者血浆的一氧化氮浓度,但水中运动在提高患者微血管反应性方面效果更好[9]。水中有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的干预效果与水刺激对血管的压力作用和更高的能量消耗有关,水中运动对血管产生的压力能降低交感血管收缩功能,抑制肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统活性,促进利钠肽的释放,提高微血管舒张功能;同时水对血管的压力刺激还能促进内皮细胞释放一氧化氮,提高血管舒张功能。另外,由于水的阻力远大于空气的阻力,在水中和陆上以相同的速度运动时,需要更大的骨骼肌收缩力量来推动身体去克服阻力,消耗更高的能量。此外,水的导热性显著高于空气,在水中完成相同运动量的运动所消耗的热量也显著高于空气且降低运动风险。因此对2型糖尿病患者尤其是超重或肥胖患者,水中运动可能是更好的运动选择。由于水中运动对2型糖尿病患者有着更高的能量消耗,肥胖型2型糖尿病患者在水中运动能消耗更多脂肪,改善血脂代谢因子水平,提高微血管功能。 血脂代谢因子对微血管舒张反应有着重要的影响:首先,氧化型低"
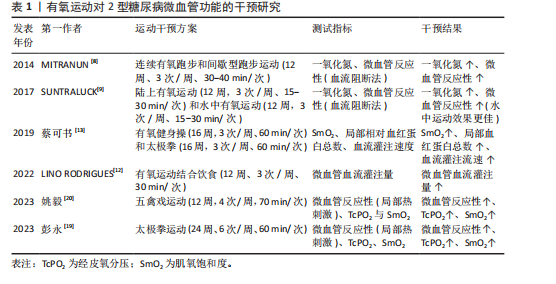
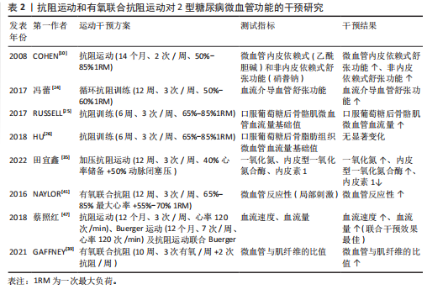
密度脂蛋白能直接损伤血管内皮细胞,导致内皮细胞脱落、诱发炎症反应并抑制一氧化氮的释放,同时氧化型低密度脂蛋白通过氧化应激促进一氧化氮降解,降低血管的舒张反应能力;其次,氧化型低密度脂蛋白具有细胞毒性作用,能诱发内皮细胞功能紊乱,促进血管硬化发生;此外,高密度脂蛋白对内皮细胞具有保护作用并能促进微血管增生。当高密度脂蛋白降低后,血管内皮细胞的修复功能和血管生成随之下降[22]。运动能通过腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶等促进过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体的表达,而过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体通过调控下游相关酶的活性、调控葡萄糖转运体4的表达等增强脂肪代谢及提高胰岛素的敏感性,对内皮细胞产生保护作用,促进内源性一氧化氮的生成,提高微血管功能。因此,基于水的浮力、压力以及高能量消耗等特点,水中运动会对2型糖尿病患者的血管产生更深的刺激,且能降低运动风险,适合具有下肢血管病变无法承受陆上运动负荷的2型糖尿病患者,故水中运动是调控2型糖尿病患者血糖和增强微血管功能的较佳选择。此外,不同水温对患者微血管的功能干预效果也可能存在较大差异。相比于冷水,温水能更有效地促进血液循环,动员更多肌纤维参与收缩,消耗更多的能量,从而对微血管产生更佳的干预效果[23]。因此,建议围绕不同水温设计改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的水中疗法,并对两者的剂量效应进行深入探究,从而为2型糖尿病患者提供更加精准的水中干预方案。 综上,持续12-24周、3-5次/周、单次运动时间> 30 min的有氧运动能显著改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能,且水中有氧运动可能是更具潜力的干预方式。但对于微血管功能的评价,不能仅以微血管血流量的基线值为评价指标,应通过微血管反应性科学评价微血管功能的变化,并在此基础上进一步联合经皮氧分压、肌氧饱和度等指标判断微血管和肌细胞的氧合情况。 2.1.2 抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 (1)传统抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响:抗阻运动是肌肉克服外来阻力进行的阻力运动,已广泛用于2型糖尿病的干预治疗,其中常用一次最大负荷(one repetition maximum,1RM)的百分比来设置运动强度。研究发现,抗阻运动(14个月、2次/周、50%-85%1RM)能显著提高2型糖尿病患者前臂皮肤微血管内皮细胞依赖式和非内皮依赖式舒张功能,且与糖化血红蛋白的变化高度相关[10]。血管舒张有内皮依赖式和非内皮依赖式两种,虽然两种方式均能评价内皮细胞的舒张功能,但其作用机制不同。前者需要依赖完整的内皮细胞产生一氧化氮发挥舒血管作用,而后者则是由一氧化氮供药体直接产生一氧化氮。2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的变化以内皮细胞依赖式舒张下降为主,内皮依赖式舒张功能受损并不明显,但该研究中患者的非内皮依赖式舒张功能也得到显著提高,说明运动不仅能提高2型糖尿病患者微血管内皮细胞的功能,且能提高一氧化氮供药体对微血管的扩张作用。提示,当使用外源性一氧化氮供药体改善2型糖尿病患者微血管舒张功能时,联合运动干预可能具有更好的效果。 另外,循环抗阻训练(12周,3次/周、50%-60%1RM)能改善2型糖尿病妇女血流介导的血管舒张功能[24]。此外,抗阻运动还能提高2型糖尿病患者骨骼肌微血管功能。抗阻训练(6周,3次/周、65%-85%1RM)能显著增加2型糖尿病患者口服葡萄糖后骨骼肌微血管血流量,且微血管血流量的变化与空腹血糖、糖化血红蛋白和糖耐量有关[25]。骨骼肌质量占人体总质量的45%左右,是消耗血糖的主要部位,抗阻运动提高2型糖尿病患者骨骼肌微血管血流量有助于增强肌肉的能量代谢水平,进而消耗更多的血糖,改善患者病情。但抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者脂肪组织中的微血管血流量无显著影响。研究表明,抗阻运动能降低2型糖尿病患者空腹血糖、体脂、三酰甘油水平,但脂肪组织中的微血管血容量、血流量均无显著变化[26];相比于有氧运动,抗阻运动能增大肌肉体积和肌肉质量,但对脂肪组织的影响较小;虽然该研究中患者体脂和三酰甘油水平在干预后下降,但脂肪组织的体积可能未出现明显的变化,减掉的脂肪组织不足以引起微血管结构的重塑。但进一步研究发现,微血管基线血流高的患者空腹三酰甘油水平较低,表明三酰甘油水平的变化与脂肪组织微血管血流量有着密切的关系[27]。对于2型糖尿病患者,脂肪组织中微血管功能受损可能与全身炎症无直接关系,但与血脂异常、高血糖以及胰岛素抵抗等因素直接相关。因此,即使抗阻运动不能显著提高脂肪组织微血管血流量,但三酰甘油等血脂因子的改善也能在一定程度上逆转微血管功能的下降。 综上,抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能也有积极干预效果,是改善患者微血管功能的有效方式,建议具有一定力量基础的患者定期进行抗阻力量锻炼,并以全身性抗阻运动为主。虽然局部抗阻运动能提高局部血流灌注量,但对整体血流量的贡献相对较小,因此血管内皮细胞的剪切应力刺激相对较小且模式较为单一,干预效果自然不如全身性抗阻运动。此外,抗阻运动引起2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的显著变化存在个体运动量阈值,需达到相应的阈值才能显著改善微血管功能。因此,建议在设计抗阻运动的方案时丰富动作形式、适当增大运动强度和延长运动周期,以达到运动量阈值。 (2)加压抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响:作为新型抗阻运动手段,加压抗阻训练(也称血流限制抗阻训练)也是改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的有效方式,且较传统抗阻运动可能更具潜力。加压抗阻训练作为一种新的训练方式,是指将血流限制带(或袖带)放置在四肢(手臂或腿部)近端,使用加压空气泵来限制静脉从骨骼肌流出,同时保持动脉流入,达到限制血流的目的[28]。基于抗阻强度低、运动损伤风险低以及特殊的生理效应,加压抗阻训练也用于2型糖尿病患者血糖的调控,并显示出良好的干预效果[29-30]。此外,加压抗阻训练能对微血管产生针对性、特异性的干预效果。加压抗阻训练期间产生的CO2、乳酸及腺苷等代谢物质透过细胞膜弥散到细胞间隙,作用于阻力血管平滑肌,产生强烈的舒血管效应,提高血流灌注量;在反复缺血和再灌注的刺激下,会使微血管静脉顺应性、壁张力以及内皮细胞剪切应力,促进血管内皮生长因子表达以及调节一氧化氮/内皮素1水平[31-34]。有研究得出,低强度血流限制训练能显著改善2型糖尿病患者血管内皮生长因子、内皮型一氧化氮合酶、内皮素1、一氧化氮等血管因子水平,且较单纯的低强度有氧运动的干预效果更佳[35]。作者的相关研究也得出,加压抗阻运动和高强度抗阻运动均能通过调节内皮型一氧化氮合酶、血管内皮生长因子、内皮素1等血管因子的分泌提高微血管功能,但前者对微血管血流灌注量、血细胞移动速度的干预效果更佳,说明低负荷血流限制运动较高强度抗阻运动在提高微循环功能方面更具优势[14]。虽然已有研究证实加压抗阻训练能对2型糖尿病血管内皮功能产生积极影响,但加压设备的袖带宽度、加压部位以及加压量等因素可能会影响干预效果。 加压设备袖带宽度对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响:袖带宽度是影响加压抗阻训练效果的重要因素,会对微血管功能产生不同影响。目前,加压抗阻设备的上肢袖带宽度为3-5 cm,下肢为5-18 cm[36-37]。但多数研究未在加压抗阻训练方案中对袖带宽度进行说明,这在一定程度上影响了加压抗阻训练方案的推广应用以及相互之间的比较。相关研究指出,袖带宽度越大,受试者主观疲劳感觉(rating of perceived exertion,RPE)更深、疼痛评分更高,动脉闭塞率更高[36-37]。对于微血管,较高的动脉闭塞率可以带来更加显著的缺血再灌注水平,增大血管内皮细胞的剪切应力,促进血管内皮细胞释放更多的血管因子,进而对微血管产生更加显著的干预效果。但对于2型糖尿病患者,微血管功能已出现功能障碍,较高的动脉闭塞率会加深血管的缺血缺氧程度,造成更深的疲劳状态和不适感觉,不仅会降低患者的运动依从性,且会增大运动安全风险。因此,建议2型糖尿病患者在进行加压抗阻运动时,根据自身的血管功能选择适宜的袖带宽度,或根据训练效果逐步增大袖带宽度。 加压位置对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响:加压位置也是影响加压抗阻训练效果的重要因素。目前,对于2型糖尿病加压抗阻部位主要为大腿根部[30,35,38],这与加压抗阻运动的干预效果有关。下肢肌肉量要明显高于上肢,运动时可以募集更多的肌纤维参与工作,因此下肢加压抗阻运动可以产生更高的运动量,进而对微血管产生更加显著的干预效果。有研究指出,对受试者上肢和下肢进行相同压力和剂量的加压抗阻运动干预后,下肢血管缺血再灌注损伤得到保护,而上肢血管内皮细胞未产生类似效益,认为加压抗阻运动对血管的影响与血流闭塞组织量有关[36]。血流闭塞组织量越大,血管内皮细胞的有益变化越大。另外,相比于上肢,下肢肌肉中的微血管数量更多,在运动刺激下可以使内皮细胞释放更多的血管内皮生长因子、一氧化氮等血管因子。此外,下肢加压抗阻训练对改善2型糖尿病患者足部微血管功能也能产生积极影响,有助于预防或治疗足溃疡并发症。糖尿病足溃疡是2型糖尿病典型的并发症,伤面愈合与微血管功能障碍有着密切关系。微血管功能障碍会加重溃疡部位的缺氧程度,提高慢性炎症和氧化应激水平,延缓伤面愈合。下肢加压抗阻训练过程中的缺血再灌注效益会加快下肢血管血流速度,这会间接提高足部微血管的血流速度,增大足部微血管内皮细胞的剪切应力,促使血管内皮生长因子、一氧化氮等血管因子释放,改善足部微血管功能,增强创伤组织的血流灌注和供氧能力,进而促进伤面愈合。综上,下肢加压抗阻训练能对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能产生更佳的干预效果,建议2型糖尿病患者多采用下肢加压抗阻运动。 加压量对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响:加压量(压力、加压时间、负荷强度等)是影响加压抗阻训练效果的另一重要因素,加压量过大不仅不能改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能,且会带来运动安全隐患。目前,2型糖尿病患者下肢加压抗阻运动的压力多为个体50%动脉闭塞压[36,38],该压力能对微血管内皮细胞产生积极影响,促进内皮细胞释放一氧化氮等血管舒张因子。但当压力过大时,可能会诱导内皮细胞严重的缺血-再灌注,使血流出现紊乱,促进逆行和震荡剪切应力的产生,使一氧化氮的表达出现下降,进而引起内皮细胞功能障碍。单次加压训练时间也会对干预效果产生影响。目前,一次加压抗阻训练的总时间一般介于15-20 min,包括训练时间和间歇时间。如果训练时间过短,可能不会对微血管产生足够的运动刺激,干预效果难以体现;但训练时间过长会造成细胞缺氧时间延长,对细胞产生不可逆的损伤,加重微血管功能障碍。因此,2型糖尿病患者应严格控制加压时间,避免带来不利影响。此外,加压抗阻训练负荷强度也是影响训练效果的重要因素。相关研究表明,比较安全有效的加压抗阻强度为20%-40%1RM[36]。另外,患者也可以采用弹力带加压抗阻运动方式。相比于器械抗阻,弹力带抗阻具有强度易调节、运动安全风险低、价格低等优点,是综合性价比较强的抗阻运动方式,更易推广应用。综上,加压压力、加压时间、负荷强度等是影响2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的重要因素,但尚未发现对上述因素的干预效果进行比较的研究,后续建议相关学者围绕上述因素系统研究加压量对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响,为加压抗阻训练在2型糖尿病患者中的应用提供可靠证据。 文献综合分析见表2。 2.1.3 有氧联合抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 有氧联合抗阻运动综合了有氧运动和抗阻运动两种运动方式,其对2型糖尿病患者胰岛素分泌以及提高胰岛素的舒血管效应有着重要的促进作用。GAFFNEY等[39]的研究发现,有氧联合抗阻运动(10周,3次有氧/周+2次抗阻/周)能显著提高2型糖尿病患者骨骼肌线粒体密度和微血管与肌纤维的比值,并能降低患者血压。此外,在运动干预的基础之上补充乳清蛋白能够进一步地提高2型糖尿病患者胰岛素对微血管的舒张功能[39]。一项对比研究显示,有氧运动(12周、3次/周、乳酸阈运动强度)、抗阻运动(3次/周、乳酸阈运动强度)及有氧结合抗阻运动(3次/周、乳酸阈运动强度)均能增加2型糖尿病患者胰岛素受体底物1的表达,其中抗阻运动组胰岛素受体底物1的表达增加了65%,联合组胰岛素受体底物1的表达增加了90%[40]。由此可见,有氧联合抗阻对2型糖尿病胰岛素的分泌具有更佳的干预效果。胰岛素与微血管舒张功能有着密切的关系,其能刺激微血管内皮细胞释放内皮型一氧化氮及减少内皮素1生成,增强血管内皮依赖式舒张功能,提高血管血流量,并增加骨骼肌毛细血管募集程度,增强骨骼肌对葡萄糖的摄取能力。 但另一研究指出,有氧结合抗阻运动(12周,3次/周、65%-85% 最大心率+55%-70% 1RM)能显著提高2型糖尿病青少年患者微血管反应性,但患者胰岛素敏感性未发生变化[41]。虽然提高胰岛素敏感性能增强2型糖尿病患者微血管反应性,但只是作用路径之一,改善患者氧化应激、线粒体功能等也会对微血管反应性产生积极影响。机体氧化应激与抗氧化系统功能是影响微血管舒张反应的重要因素。氧化应激会引起内皮细胞损伤,降低内皮型一氧化氮合酶活性,减少内源性一氧化氮的生成,同时降低一氧化氮的生物利用度,而提高机体抗氧化能力能加快自由基的消除,降低机体氧化应激水平,对内皮细胞产生保护作用。运动干预能通过激活过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α、Sirt3等途径提高抗氧化能力,对内皮细胞产生保护作用,提高微血管功能[42-44]。此外,线粒体分裂与微血管内皮细胞损伤有着密切的关系,线粒体过度分裂会导致线粒体碎裂,进而损伤内皮细胞,运动能促进线粒体融合过程,并抑制线粒体分裂来改善线粒体功能状态,对微血管内皮细胞产生保护作用[45-46]。 此外,抗阻运动(3次/周、靶心率为120次/min)、Buerger运动(7次/周、靶心率为120次/min)及抗阻运动联合Buerger(隔天1次、靶心率为120次/min)运动均能提高2型糖尿病合并下肢血管病变患者血流速"
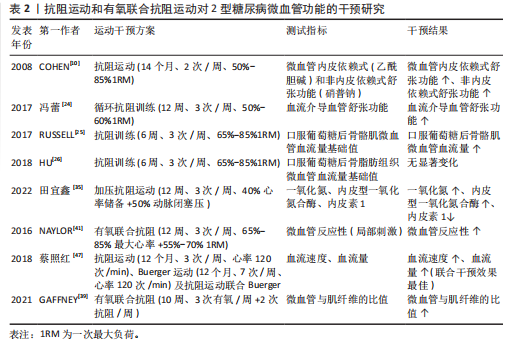
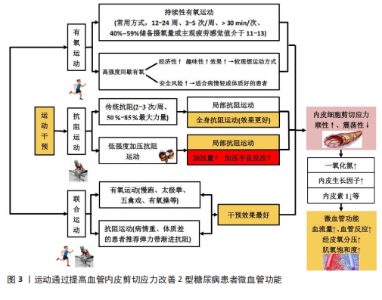
度和血流量,但抗阻运动联合Buerger运动效果最好[47]。不同运动方式对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能干预效果的差异,可能与运动对内皮细胞产生的剪切应力模式有关,进而产生不同的干预效果。相比于单一的抗阻运动和Buerger运动,抗阻运动联合Buerger运动可能会产生顺行/逆行的剪切应力模式,而前者主要以单一的顺行模式为主,因此后者对内皮细胞产生了更佳的刺激效果[48]。但作者的相关研究得出,太极拳运动和太极拳结合抗阻运动可显著改善2型糖尿病患者的足背微循环功能,但两种运动方式的干预效果无显著差异[19]。这可能与抗阻运动的次数较少和抗阻运动强度有关,在作者的研究中每周仅对2型糖尿病进行了2次干预,可能未能达到抗阻运动引起微血管功能显著变化的运动量阈值。提示在设计2型糖尿病患者的有氧联合抗阻运动方案时,建议抗阻运动次数应不低于2次/周。此外,作者早期研究中使用的弹力带抗阻方案的运动强度可能相对较小,虽然弹力带抗阻运动具有安全性好、简单易操作等优点,但其运动强度小于传统的抗阻力量运动,因此联合干预组未表现出更佳的干预效果。 综上所述,相比于单纯的抗阻运动,有氧联合抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的干预效果可能更佳,但抗阻运动次数和强度也会影响干预效果。此外,有氧联合抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的干预效果同样具有可逆性,需持久运动维持干预效果。NAYLOR等[41]的研究表明,有氧联合抗阻运动停训后12周2型糖尿病患者的微血管功能被逆转。针对有氧联合抗阻运动干预效应的可逆性变化,2型糖尿病患者也应坚持长久运动,以获得持续性的干预效应。 2.2 运动强度和运动量对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 2.2.1 运动强度对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 运动强度是影响运动干预效果的关键因素,中等强度的运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能有积极的干预效果,但高强度运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响存在不同的研究结果。MITRANUN等[8]的研究表明,等能耗的连续性有氧运动和高强度间歇性有氧运动均能提高2型糖尿病患者微血管内皮依赖式舒张能力,且高强度间歇性有氧运动干预效果更佳。在单次运动干预中也得出相似结论。10 min高强度有氧行走后2型糖尿病患者足底微血管血流量显著增加,但10 min低强度步行后足底微血管血流量无显著变化[49]。虽然在段艺杰等[49]的研究中,高强度步行和低强度步行均属于有氧运动,但未对低强度和高强度进行量化界定,因此该研究中的具体运动强度尚不明确,这也是其不足之处。另外,高强度(步频≥110步/min)的体育活动与2型糖尿病患者皮肤微血管反应性具有显著的正相关[50]。但也有研究报道,高强度运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能无显著影响。MORTENSEN等[51]研究表明,11周运动强度为50%峰值功率的自行车骑行运动(3次/周)能增大2型糖尿病患者的骨骼肌微血管密度以及管腔直径,但95%峰值功率的骑行运动对微血管密度、管腔直径无显著影响。高强度运动对1型糖尿病患者微血管功能的干预也得到相似结果。ZINN等[52]的研究表明,4周的高强度间歇性训练(RPE值≥18,≥95%最大心率)能显著提高1型糖尿病患者个体乳酸阈和自行车最大输出功率,但中心凹无血管区面积、血管密度、血管直径指数和浅丛、深丛及径向乳头周围毛细血管分形维数等微循环指数均无显著变化。提示高强度的运动能提高2型糖尿病患者的微血管舒张功能,但对于微血管结构无显著影响,这可能与高强度运动过程中较高的剪切应力以及较短的运动时间有关。 内源性一氧化氮是介导微血管内皮依赖式舒张反应的主要因子,而一氧化氮生成主要受血管流体剪切应力的影响。血流速度、血液特性以及血管形态是影响血管流体剪切应力的关键因素。正常范围内,较高的血管产生的剪切应力更有利于维持和提高血管内皮细胞功能[48]。高强度有氧运动期间,血管中的血流速度较快,对血管产生的剪切应力较大,引起机体蛋白激酶β含量增加,并通过蛋白激酶β/内皮型一氧化氮合酶通路诱导内皮型一氧化氮合酶磷酸化,提高内皮型一氧化氮合酶的活性,从而促进内源性一氧化氮的表达以及提高一氧化氮的生物利用度。但由于高强度运动的时间较短,患者运动期间整体运动量和能量代谢需求降低,对血管生成因子的刺激不足,不能诱导微血管增生。但ANDERSEN等[53]研究表明,24周运动强度为(83±2)%最大心率的足球运动使2型糖尿病患者Ⅰ型肌纤维周围毛细血管数量增加7%,而对照组中Ⅰ型肌纤维周围毛细血管数量减少5%,同时运动组患者血糖、脂肪量和峰值摄氧量显著改善。该研究中肌纤维周围毛细血管数量变化与足球运动的时间有关,受试者每次运动时间为1 h,跑动距离为(4.7±0.2) km,较长的运动时间使训练量和机体代谢需求显著增加,诱导血管内皮细胞增生因子表达,使微血管增生。提示当使用高强度运动干预2型糖尿病患者微血管时,在保证安全的情况下,应适当延长运动时间,促进血管内皮生长因子表达,诱导血管新生。 综上,不同运动强度均能提高2型糖尿病患者的微血管舒张功能,且高强度有氧间歇运动可能具有更佳的干预效果。因此,在保证安全的前提下,具有微血管功能障碍的2型糖尿病患者可适当提高有氧运动强度,以获得更佳的干预效果。但运动强度过大会改变血流剪切应力模式,使震荡剪切应力增大,促使机体释放活性氧,产生氧化应激反应,进而通过提高一氧化氮降解量、抑制一氧化氮生成等途径使内皮细胞功能下降。因此,建议2型糖尿病患者根据病情程度、运动耐受能力等选择针对性、个体化的运动强度,以获得最佳的干预效果。对于病情较重或运动耐受能力较差的患者,运动过程中应实时监控运动强度,避免不良心血管事件发生。 针对这一问题,建议将患者RPE水平作为重要的参考依据。虽然心率、肌氧饱和度等指标也可用于运动强度监控,但均需借助专业的测试设备,因此在应用过程中具有一定的局限性,不利于大群体推广应用。RPE测试不需要借助任何专业仪器设备,且能较好地弥补生理监控指标的缺陷。运动过程中,患者主观疲劳程度是衡量运动强度以及身体反应的重要指标,该指标有利于患者根据自身的身体反应和疲劳程度主动控制运动强度,因此其安全性较高。目前,RPE测量已在2型糖尿病患者的运动干预中得到应用,但未见其监控结果准确性和科学性的报道。为了提高RPE在2型糖尿病患者运动强度制定和运动强度监控中的准确性、科学性,未来应对RPE与心率、肌氧饱和度等指标的关联度进行比较研究,为RPE在运动干预中的应用提供可靠的证据支撑。另外,RPE的测量结果受患者主观意识的控制,患者能否真实给出评分将直接影响测量结果,因此在使用RPE值监控患者运动强度时应对患者正确引导,以获得真实数据。 2.2.2 运动量对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 运动量是运动强度、运动时间等因素的综合反映。生理范围之内,运动量越大,2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的改善幅度越大。研究指出,相比于连续性有氧运动,等能耗(运动过程中)的高强度间歇性有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管内皮依赖式舒张功能的干预效果更为显著[8]。相比持续性有氧运动,间歇性高强度有氧运动单次运动时间相对较长(存在休息期)以及运动强度偏大,虽然休息期内患者未进行运动,但由于运动后机体仍处于高强度的运转状态(等同于运动状态),机体仍需要消耗大量的氧气偿还运动过程中的过量氧耗,此时机体仍等同于运动状态。虽然运动过程中两组患者的能量消耗一致,但由于间歇运动组休息期内额外的能量消耗,使整体的能量消耗(运动量)更大,进而显示出更好的干预效果。基于间歇性运动的干预效果以及考虑运动干预的经济性、趣味性,认为高强度间歇性有氧运动可能是一种较好的运动替代形式。 另外,每周90 min的运动量对代谢综合征患者体质量和毛细血管密度无显著影响,每周150 min的运动量能减轻代谢综合征患者体质量和改善毛细血管密度,而每周300 min的运动量能显著减少体内脂肪堆积和增大毛细血管密度[54],这与2022年美国运动医学会《2型糖尿病患者的运动/身体活动指南》相符。根据指南建议,2型糖尿病患者每周运动量由原先150 min调整到至少运动150-300 min,甚至超过300 min,这样才能取得显著的身体收益[55]。此外,对于超重或肥胖2型糖尿病患者,根据2型糖尿病患者体质量管理专家共识(2024年版),每周有氧运动量至少为300 min或者比150 min更高强度的有氧运动[56]。 综上,运动改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能具有“正向剂量-效应”关系,在一定范围内运动量越高,2型糖尿病患者微血管功能改善越明显。一项研究显示,当2型糖尿病患者运动时间相同时,运动量越大足底微血管血流量增加越明显[49]。因此,在保障安全的前提下,患者可以通过提高运动量获得更佳的干预效果。此外,血流剪切应力对内皮细胞功能的影响不仅取决于模式,还与剪切应力的作用时间有关,见图3。因此,对于体质或运动能力偏差的2型糖尿病患者可通过延长单次运动时间提高运动量,以获得更高水平的剪切应力,而体质或运动能力相对较好的患者可通过适当增大运动强度提高运动量。提示运动量是影响2型糖尿病患者微血管功能干预效果的重要因素,为了制定更加精准的运动处方,建议从能量消耗的角度研究不同运动方式改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的运动量阈值,明确二者的“剂量-效应”关系,寻求有氧运动改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的最佳运动量。 2.2.3 运动频率对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的影响 运动频率是影响运动干预效果的重要因素之一。当运动频率较低时,运动干预的痕迹可能在下次运动时完全消失,导致运动干预效应无法累计。但运动频率过高时可能会造成患者运动量过大,诱导运动性疲劳的产生,使下次运动时身体功能仍未完全恢复。长期疲劳堆积会损害患者的身体健康,甚至造成严重的后果。以有氧运动为主要运动类型的临床研究中,3次/周、隔天进行的运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能具有较佳的干预效应。另外,作者的一项研究表明,持续12周、每周≥3次的有氧运动对微血管功能有积极的干预效应,但每周一两次的"
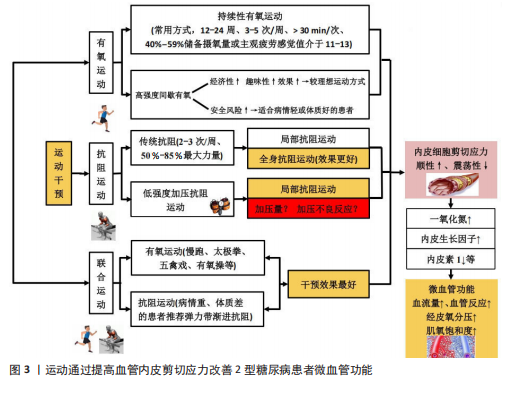

有氧运动对微血管舒张功能无显著影响[57]。此外,BORGES等[58-59]的研究也表明持续6个月、每周低于2次的运动干预(个体通气阈强度)不仅不能改善微血管功能,且会进一步加重微血管稀疏的发生。此外,每周6次的24式太极拳运动能显著提高2型糖尿病患者的微血管功能[19]。 综合相关研究,认为每周3次及以上的有氧运动能显著改善2型糖尿病患者的微血管功能。此外,以抗阻运动和有氧联合抗阻运动为主要运动类型的临床研究中,抗阻运动部分应以3次/周为宜,但应隔天进行,这与“2022年美国运动医学会《2型糖尿病患者的运动/身体活动指南》”中有关抗阻运动间隔时间相符[55]。依据指南,2次抗阻训练至少间隔48 h[55] 。虽然相关研究表明,3次/周或以上的联合运动干预对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能有积极作用,但缺乏不同运动频率的比较研究,高频率的运动干预是否具有更佳的干预效应有待于进一步验证,建议细化运动频率对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的干预研究,设计1-2次/周、3次/周、3-5次/周以及5次/周以上等运动频率对2型糖尿病微血管功能的影响,为运动频率的制定提供精准的证据参考。 2.3 运动改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的处方建议 基于以上研究结果,针对运动形式、运动强度、运动频率、运动周期等提出改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的运动处方建议。 2.3.1 运动类型与强度 对于运动类型,有氧运动是提高2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的有效方式,优先推荐太极拳、五禽戏、健身操以及慢跑等项目,其运动强度以40%-59%储备摄氧量或RPE值介于11-13为宜[60]。在保证安全的前提下,高强度间歇性有氧运动的干预效果可能更佳。在有氧运动基础上联合全身性抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的干预效果最佳,其中抗阻运动强度以50%-85%1RM为宜。对于病情较重或者体质较差的患者,建议采取渐进式弹力带抗阻锻炼。此外,加压抗阻运动可能是改善2型糖尿病患者微血管功能的更为有效的方式,能对微血管产生针对性和特异性的干预效果。 2.3.2 运动时间、频率、运动周期及运动量 基于上述学者的研究结果,认为持续12-24周、3-5次/周、单次运动时间> 30 min的有氧运动对2型糖尿病患者微血管功能具有较佳的干预效果。若2型糖尿病患者无抗阻运动禁忌证,建议每周再进行两三次的抗阻运动,以改善骨骼肌的微血管功能。另外,当患者无法进行规律性运动时,应保障每周总体有氧运动量不低于300 min或高强度有氧运动量不低于150 min。"

| [1] SABARI SS, BALASUBRAMANI K, IYER M, et al. Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and parkinson’s disease (PD):a mechanistic approach. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(8):4547-4573. [2] 糖尿病微循环障碍临床用药专家共识(2021年版)[J].中国医学前沿杂志,2021, 13(4):49-57. [3] 朱欢,庹艳芳,文凡,等.常见代谢性疾病微循环功能变化及有氧运动干预效应[J].湖北体育科技,2024,43(3):87-93. [4] 陈凯帆,林佳钏,王平.超声造影研究2型糖尿病骨骼肌微循环进展[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2022,19(10):661-664. [5] ZHANG X, DUAN Y, ZHANG X, et al. Adipsin alleviates cardiac microvascular injury in diabetic cardiomyopathy through Csk-dependent signaling mechanism. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):197-218. [6] FUJJJ N, MCGARR GW, AMANO T, et al. Type 2 diabetes impairs vascular responsiveness to nitric oxide, but not the venoarteriolar reflex or post-occlusive reactive hyperaemia in forearm skin. Exp Dermatol. 2021; 30(12):1807-1813. [7] RUSSELL RD, ROBERTS-THOMSON KM, HU D, et al. Impaired postprandial skeletal muscle vascular responses to a mixed meal challenge in normoglycaemic people with a parent with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2022;65(1):216-225. [8] MITRANUN W, DEEROCHANAWONG C, TANAKA H, et al. Continuous vs interval training on glycemic control and macro-and microvascular reactivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014;24(2):e69-e76. [9] SUNTRALUCK S, TANAKA H, SUKSOM D, et al. The relative efficacy of land-based and water-based exercise training on macro- and micro-vascular functions in older patients with type 2 diabetes. J Aging Physical Acti. 2017; 25(3):446-452. [10] COHEN ND, DUNSTAN DW, ROBINSON C, et al. Improved endothelial function following a 14-month resistance exercise training program in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes ResClin Pract. 2008; 79(3):405-411. [11] GAFFNEY K, LUCERO A, MACARTNEY-COXSON D, et al. Effects of whey protein on skeletal muscle microvascular and mitochondrial plasticity following 10 weeks of exercise training in men with type 2 diabetes. Applied Physiology, Nutrition. And Metabolism. 2021;46(8):915-924. [12] LINO RODRIGUES K, VIEIRA DIAS DA SILVA V, NUNES GOULART DA SILVA PEREIRA E, et al. Aerobic exercise training improves microvascular function and oxidative stress parameters in diet-induced type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022;15: 2991-3005. [13] 蔡可书. 健身操和太极拳运动对中老年2型糖尿病患者下肢循环功能的影响[D].南京:南京体育学院,2019. [14] 彭永,胡江平,朱欢.低负荷血流限制和高强度抗阻运动对男性运动青年大腿微循环功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(2):393-401. [15] 朱欢,高炳宏.微血管反应性在耐力性运动员训练中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(10):907-914. [16] 朱欢,高炳宏.有氧运动对人体微血管反应性的作用及机制研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(8):855-863. [17] 陈友强,程瑞豪,贺缨,等.基于皮肤温度信号的糖尿病患者血管舒张功能评价[J].医用生物力学,2023,38(2):368-374. [18] FUCHS D, DUPON PP, SCHAAP LA, et al. The association between diabetes and dermal microvascular dysfunction non-invasively assessed by laser Doppler with local thermal hyperemia: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017;16(1):11-22. [19] 彭永,朱欢,刘尧峰,等.24周太极拳结合弹力带抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者足背微循环功能的影响[J].首都体育学院学报, 2023,35(1):77-85. [20] 姚毅. 12周五禽戏运动对2型糖尿病患者微循环功能的影响及可能机制研究[D].恩施:湖北民族大学,2023. [21] 肖哲,朱欢,胡江平,等.10周有氧运动和有氧结合抗阻运动对肥胖大学生微循环功能的影响及机制研究[J].中国全科医学, 2022,25(19):2349-2355+2362. [22] PRIMER KR, PSALTIS PJ, TAN JTM, et al. The role of high-density lipoproteins in endothelial cell metabolism and diabetes-impaired angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(10):3633-3653. [23] 文凡,朱欢,王康锋,等.水中运动疗法对常见慢性病干预效果的研究进展[J].体育科技文献通报,2024,32(2): 236-241. [24] 冯蕾,周素珍,赵占胜,等.循环运动训练对2型糖尿病妇女心肺适能及血流介导的血管舒张功能的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(6):680-685. [25] RUSSELL RD, HU D, GREENAWAY T, et al. Skeletal muscle microvascular-linked improve ments in glycemic control from resistance training in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(9): 1256 -1263. [26] HU D, RUSSELL RD, REMASH D, et al. Are the metabolic benefits of resistance training in type 2 diabetes linked to improvements in adipose tissue microvascular blood flow. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018;315(6): E1242-E1250. [27] HU D, REMASH D, RUSSELL RD, et al. Impairments in adipose tissue microcirculation in type 2 diabetes mellitus assessed by real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11(4): e007074-e007088. [28] KAMBIČ T. Blood flow restriction training: You can occlude your veins, but not your oxygen transport. J Physiol. 2020;598(18):3825-3826. [29] SAATMANN N, ZAHARIA OP, LOENNEKE JP, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction exercise and possible applications in type 2 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021;32(2):106-117. [30] ŞAHIN E, AYAZ T, SAGLAM M, et al. Acute effects of blood flow restricted aerobic exercise in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicine(Baltimore). 2024;103(31): e39031-e39037. [31] DA CUNHA NASCIMENTO D, SCHOENFELD BJ, PRESTES J, et al. Potential implications of blood flow restriction exercise on vascular health:a brief review. Sports Med. 2020;50(1):73-81. [32] MAGA M, WACHSMANN-MAGA A, BATKO K, et al. Impact of blood-flow-restricted training on arterial Functions and angiogenesis-a systematic review with meta-analysis. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1601-1619. [33] GARCIA NF, DE MORAES C, REBELO MA, et al. Low load strength training, associated with or without blood flow restriction increased no production and decreased production of reactive oxygen species in rats aorta. Life Sci. 2022;294:120350-120358. [34] 刘申,姬卫秀,唐佳福,等.加压训练对心血管系统的作用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(5):401-406. [35] 田宜鑫.血流限制训练对Ⅱ型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢指标和血管内皮因子的影响[D].南京:南京体育学院,2022. [36] 魏佳,李博,冯连世,等.血流限制训练的方法学因素及潜在安全性问题[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(3):3-12. [37] 范紫菡,吴迎.缺血处理在运动训练中的应用:效果、机制及问题[J].中国运动医学杂志,2024,43(9):753-766. [38] 逯莉莉.血流限制联合四肢联动训练对2型糖尿病患者干预效果的观察[D].天津: 天津体育学院,2022. [39] GAFFNEY K, LUCERO A, MACARTNEY-COXSON D, et al. Effects of whey protein on skeletal muscle microvascular and mitochondrial plasticity following 10 weeks of exercise training in men with type 2 diabetes. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, And Metabolism. 2021;46(8):915-924. [40] JORGE ML, DE OLIVEIRA VN, RESENDE NM, et al. The effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise on metabolic control, inflammatory markers, adipocytokines, and muscle insulin signaling in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus - ScienceDirect. Metabolism. 2011;60(9):1244-1252. [41] NAYLOR LH, DAVISEA, KALIC RJ, et al. Exercise training improves vascular function in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Physiol Rep. 2016;4(4):e12713-e12724. [42] ZHAO YC, GUO W, GAO BH, et al. Hypoxic training upregulates mitochondrial turnover and angiogenesis of skeletal muscle in mice. Life Sci. 2022;291:119340-119347. [43] MA C, ZHAO Y, DING X, et al. The role of Sirt3 in the changes of skeletal muscle mitophagy induced by hypoxic training. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2022;41(5):447-455. [44] MA C, ZHAO Y, DING X, et al. Hypoxic training ameliorates skeletal muscle microcirculation vascular function in a sirt3-dependentmanner. Frontiers in Phy. 2022;13:921763-921771. [45] SUN Q, JIA H, CHENG S, et al. Metformin alleviates epirubicin-induced endothelial impairment by restoring mitochondrial homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):343-357. [46] 林建健,宋洁.运动调控线粒体动力学变化的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(11):1767-1771. [47] 蔡照红,江培兰,鲍红丹,等.抗阻运动联合Buerger运动在2型糖尿病下肢血管病变治疗中的应用[J].中国基层医药,2018,25(18):2354-2358. [48] 时文霞,谢军,何玉凤,等.血管内皮功能障碍运动干预的血流剪切力作用机制研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2024, 60(3):51-64. [49] 段艺杰,任韦燕,叶文强,等.日常运动对行走刺激下糖尿病足部微循环响应的影响[J].医用生物力学,2021, 36(S1):133. [50] SÖRENSEN BM, VAN DER HEIDE FCT, HOUBEN AJHM, et al. Higher levels of daily physical activity are associated with better skin microvascular function in type 2 diabetes-The Maastricht Study. Microcirculation. 2020;27(4): e12611-e12623. [51] MORTENSEN SP, WINDING KM, IEPSEN UW, et al. The effect of two exercise modalities on skeletal muscle capillary ultrastructure in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2019;29(3):360-368. [52] ZINN S, NELIS P, MINNEBECK K, et al. Effect of high-intensity interval training in patients with type 1 diabetes on physical fitness and retinal microvascular perfusion determined by optical coherence tomography angiography. Microvasc Res. 2020;132: 104057-104065. [53] ANDERSEN TR, SCHMIDT JF, THOMASSEN M, et al. A preliminary study: effects of football training on glucose control, body composition, and performance in men with type 2 diabetes. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014; 24(Supplement):43-56. [54] MACHADO MV, VIEIRA AB, DA CONCEIÇÃO F, et al. Exercise training dose differentially alters muscle and heart capillary density and metabolic functions in an obese rat with metabolic syndrome. Exp Physiol. 2017; 102(12):1716-1728. [55] 胥祉涵,王世强,李丹,等.2022年美国运动医学会《2型糖尿病患者的运动/身体活动指南》解读及启示[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(25):3083-3088. [56] 《2型糖尿病患者体重管理专家共识》专家组.2型糖尿病患者体重管理专家共识(2024年版)[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2024, 44(5):359-370. [57] 周术锋,肖哲,朱欢,等.12周有氧运动对习惯久坐大学生微循环功能的影响[J].中国学校卫生,2021,42(9):1332-1335+1339. [58] BORGES JP, NASCIMENT AR, LOPES GO, et al. The impact of exercise frequency upon microvascular endothelium function and oxidative stress among patients with coronary artery disease. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2018;38(5):840-846. [59] BORGES JP, LOPES GO, VERRI V, et al. A novel effective method for the assessment of microva-scular function in male patients with coronary artery disease: a pilot studyusing laser speck-le contrast imaging. Braz JMed Biol Res. 2016;49(10): e5541-e5547. [60] KANALEY JA, COLBERG SR, CORCORAN MH, et al. Exercise/Physical activity in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a consensus statement from the american college of sports medicine. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022;54(2):353-368. |
| [1] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [2] | Yin Yongcheng, Zhao Xiangrui, Yang Zhijie, Li Zheng, Li Fang, Ning Bin. Effect and mechanism of peroxiredoxin 1 in microglial inflammation after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1106-1113. |
| [3] | Zhang Jiuxuan, Zhang Jinnan, Sui Xiaofan, Pei Xiaxia, Wei Jianhong, Su Qiang, Li Tian. Effects of ammonia poisoning on cognitive behavior and hippocampal synaptic damage in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1122-1128. |
| [4] | Sun Yajie, Zhao Xinchen, Bo Shuangling. Spatiotemporal expression of bone morphologic protein 7 in mouse kidney development [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1156-1161. |
| [5] | Li Haojing, Wang Xin, Song Chenglin, Zhang Shengnan, Chen Yunxin. Therapeutic efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in the upper trapezius muscle area combined with exercise control training in patients with chronic non-specific neck pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1162-1170. |
| [6] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [7] | Yu Huifen, Mo Licun, Cheng Leping. The position and role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the repair of tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1196-1206. |
| [8] | Wang Zhengye, Liu Wanlin, Zhao Zhenqun. Advance in the mechanisms underlying miRNAs in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1207-1214. |
| [9] | Bu Yangyang, Ning Xinli, Zhao Chen. Intra-articular injections for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the temporomandibular joint: different drugs with multiple combined treatment options [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1215-1224. |
| [10] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [11] | Leng Xiaoxuan, Zhao Yuxin, Liu Xihua. Effects of different neuromodulatory stimulation modalities on non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s patients: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1282-1293. |
| [12] | Wen Xiaolong, Weng Xiquan, Feng Yao, Cao Wenyan, Liu Yuqian, Wang Haitao. Effects of inflammation on serum hepcidin and iron metabolism related parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1294-1301. |
| [13] | Yang Zeyu, Zhi Liang, Wang Jia, Zhang Jingyi, Zhang Qingfang, Wang Yulong, Long Jianjun. A visualized analysis of research hotspots in high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation from the macroscopic perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1320-1330. |
| [14] | Chen Yixian, Chen Chen, Lu Liheng, Tang Jinpeng, Yu Xiaowei. Triptolide in the treatment of osteoarthritis: network pharmacology analysis and animal model validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 805-815. |
| [15] | Yan Chengbo, Luo Qiuchi, Fan Jiabing, Gu Yeting, Deng Qian, Zhang Junmei. Effect of type 2 diabetes mellitus on orthodontic tooth movement and bone microstructure parameters on the tension side in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 824-831. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||