Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (5): 1236-1246.doi: 10.12307/2026.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Schwann cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration: retrospect and prospect
Fu Zhenyi, Li Junhao, Zhang Yating, He Yunkai, Liu Junyu, Wei Yunhao, Liu Jiaxin
- Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-04Accepted:2025-02-06Online:2026-02-18Published:2025-06-26 -
Contact:Liu Jiaxin, PhD, Lecturer, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Fu Zhenyi, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fu Zhenyi, Li Junhao, Zhang Yating, He Yunkai, Liu Junyu, Wei Yunhao, Liu Jiaxin. Schwann cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration: retrospect and prospect[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1236-1246.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
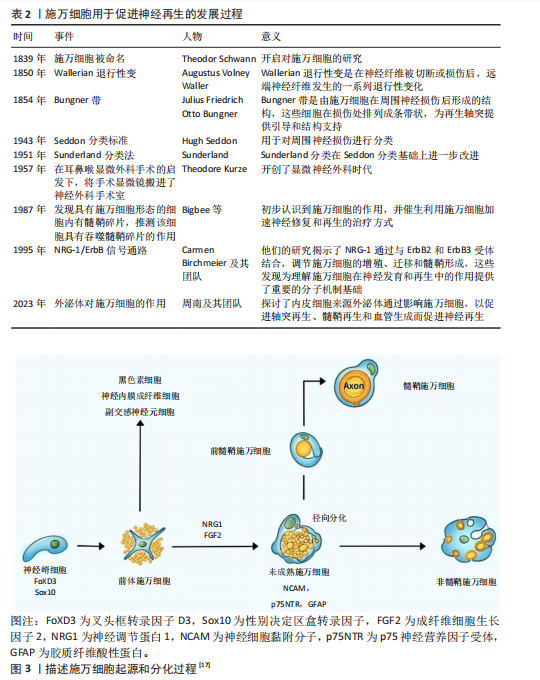
2.1 施万细胞与外周神经损伤研究现状 通过检索相关文献,将施万细胞与外周神经损伤的研究发展进行总结,自1839年Theodor Schwann发现施万细胞之后,神经再生开始得到深入研究,包括施万细胞在神经损伤中吞噬碎片、促进神经再生的机制以及移植治疗等,施万细胞的深入研究为神经治疗提供新的方向,见表2。 2.2 施万细胞的起源和分化 施万细胞的发育过程分为施万细胞前体、不成熟施万细胞、成熟施万细胞3个阶段[15]。施万细胞起源于胚胎发育早期的神经嵴细胞[16],神经嵴细胞是一种多能干细胞,能够在胚胎发育过程中迁移到不同的部位,分化成多种细胞类型,包括神经内膜成纤维细胞、副交感神经元细胞、黑色素细胞以及施万细胞等。神经嵴干细胞表达FoxD3(Forkhead box D3)和Sox10(SRY-box10)基因[17],在施万细胞分化成熟过程中至关重要。在胚胎发育过程中,神经嵴细胞从神经管的背侧迁移出来,向周围组织迁移分化成前体施万细胞,在神经胶质生长因子[18]、成纤维细胞生长因子2(fibroblast growth factor,FGF2)[19]、Notch信号转导下分化为未成熟的施万细胞[20],并表达一些特定的分子标记,如NCAM、p75NTR和GFAP等。未成熟施万细胞通过径向分选过程与直径大于1 μm的轴突结合时才最终分化为成熟的髓鞘施万细胞,而另一部分分化成非髓鞘施万细胞,支持无髓鞘的神经纤维[17-21],如图3所示。 2.3 施万细胞的功能 施万细胞具有支持和保护神经元的作用[22],施万细胞包裹着周围神经的轴突,为神经元提供结构上的支持,防止轴突受到外界的物理损伤。施万细胞修复外周神经系统的主要机制:施万细胞通过表达多种细胞因子和趋化因子[23],如白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α和单核细胞趋化因子1,启动免"
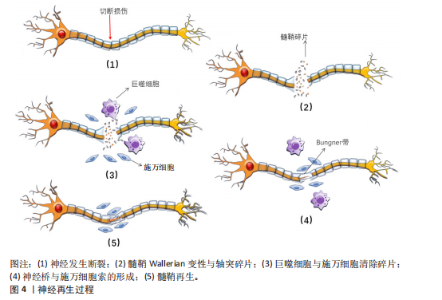
疫反应,募集巨噬细胞向损伤部位迁移、侵入并激活。巨噬细胞清除退化的髓鞘碎片以及促进血管生成和髓鞘分解[24-25],为轴突再生创造有利环境。 施万细胞分泌营养因子,如胶质细胞源性神经营养因子、脑源性神经营养因子和神经生长因子等。胶质细胞源性神经营养因子能够促进施万细胞的增殖和迁移,从而有助于周围神经的修复和再生[26]。脑源性神经营养因子在海马和皮质中含量最为丰富,与其特异性受体结合后能激活下游多条信号通路,发挥促进神经元生长、发育、分化,轴突和树突生长,调节突触可塑性以及神经损伤后的再生修复等功能[27]。神经生长因子通过与对应的高亲和酪氨酸激酶受体结合并激活下游信号通路,具有维持神经元存活与促进神经生长的作用[28]。在神经完全断裂的情况下,施万细胞的基板围成神经膜管,增生的施万细胞延伸出长的平行突起,排列成束状,在神经膜管内有序排列,形成施万细胞索,即Bungner带,如图4所示。此外施万细胞与成纤维细胞、巨噬细胞和血管内皮细胞一起,形成连接近端和远端神经残端的神经桥,为轴突再生提供物理支持[20],引导再生的轴突重新支配其原先的效应器[29]。 2.4 周围神经轴突断裂病理生理学机制 周围神经轴突断裂是一种严重的周围神经损伤类型,通常由切割伤、牵拉、压迫等引起。这些外力直接作用于神经,导致轴突的连续性中断,使神经冲动传导无法正常传递,损伤部位以远的神经支配区域出现感觉丧失、运动功能障碍等临床症状[30]。 根据Seddon分类标准将轴突断裂分为3类:神经失用型、轴索断裂型和神经断裂型。①神经失用型,通常由神经的轻微压迫或牵拉引起,主要特点为仅涉及神经纤维的髓鞘损伤,神经轴突和结缔组织(包括神经内膜、神经束膜和神经外膜)保持完整,表现为神经传导减慢或消失。②轴索断裂型,此类损伤中神经轴索发生断裂,但神经"
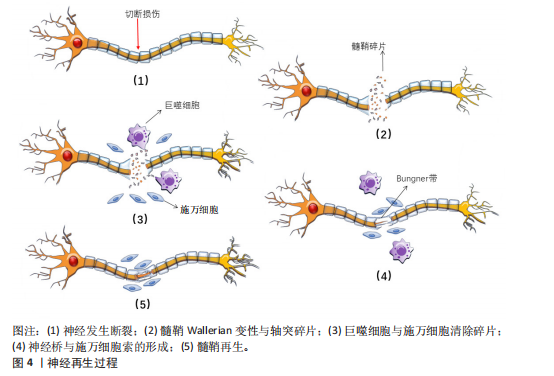
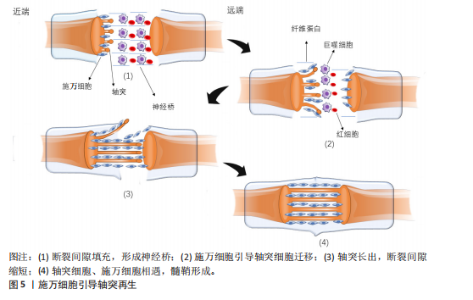
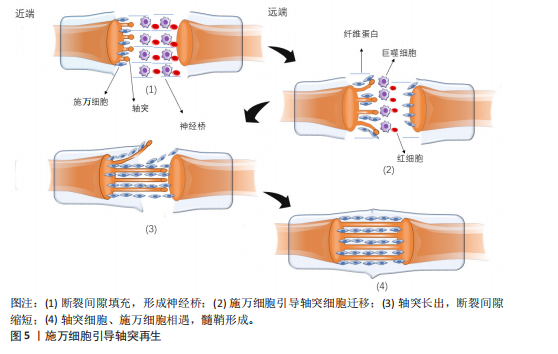
的结缔组织保持完整。一般在损伤后三四天损伤远端会发生Wallerian退行性变,损伤远端的神经传导功能丧失,患者出现感觉和运动功能障碍。③神经断裂型,是Seddon分类中最严重的神经损伤类型,神经轴索和结缔组织完全横断,神经的连续性中断,损伤远端会发生Wallerian退行性变,感觉、运动功能和自主神经功能障碍严重[31]。Sunderland的分类方法在Seddon提出的3种神经损伤类型基础上,进一步细化为5个不同的严重程度等级。第一级损伤和第二级损伤分别与Seddon的神经失用型、轴索断裂型相对应,第三级损伤发生在轴突断裂且内膜部分受损时,定位在Seddon的轴索断裂和神经完全断裂之间。Sunderland将Seddon的神经完全断裂细分为第四级和第五级损伤。在第四级损伤中,除了神经外膜以外,神经的所有结构都已断裂,没有外科手术干预则无法恢复。第五级损伤则涉及到神经的彻底断裂[32]。 Wallerian退行性变是周围神经轴突断裂过程中的关键变化。Wallerian变性是一种由钙离子触发的神经损伤后的变化[33],包括轴突和髓鞘的断裂,形成大量髓鞘碎片,这些碎片大量积累会破坏神经再生的环境,从而阻碍神经的修复。因此,清除这些髓鞘碎片对于促进神经再生是关键的[29]。施万细胞在损伤后的24 h内变得活跃,细胞核和细胞质增大,分裂速度加快,迅速增殖并激活多种分子的基因表达,释放单核细胞趋化因子1,巨噬细胞穿过高通透性的毛细血管壁到达损伤区域,与施万细胞共同吞噬髓鞘碎片。肥大细胞在损伤后的第1周内数量显著增加,释放组胺和血清素,增加了毛细血管的通透性,从而促进巨噬细胞的迁移[32-34]。此外,施万细胞会迅速激活,沿着未碎裂的远端切割轴突形成收缩的肌动蛋白球,以加速碎片分解[35]。 在上述反应发生同时启动再生程序,合成和释放神经生长因子等促进轴突再生的物质。损伤后的数天内,损伤部位近侧的轴突开始长出芽生支,沿着神经内膜管向远端生长,试图重新连接到原来的靶器官或组织,但轴突再生速度相对较慢,通常每天生长1.0-2.0 mm且需要正确的定向生长[24],再生过程依赖于神经生长因子的引导,若再生方向错误,可能导致神经功能恢复不完全或出现异常连接。 2.5 施万细胞修复外周神经系统的机制 2.5.1 施万细胞促进外周神经系统再生的过程 神经细胞在出生前从外胚层逐渐迁移到脑组织的特定未成熟部位,增殖分化为成熟的神经细胞,一旦受损就无法再生。与中枢神经系统相比,外周神经系统具有更大的再生潜力,这主要是因为施万细胞具有高度的可塑性[26]。再生过程涉及多种细胞反应与分子反应,如下所示。 轴突与髓鞘的再生过程主要涉及神经桥的形成、Bungner带的形成以及髓鞘的压实。清除碎片后,神经桥是轴突穿过神经间隙的基础。神经发生断裂后,断裂间隙会被纤维蛋白网填充,包含红细胞和巨噬细胞等细胞。施万细胞与成纤维细胞、巨噬细胞和血管内皮细胞共同形成神经桥,连接近端和远端神经残端。近端断端轴突细胞在施万细胞的引导下沿着纤维蛋白网迁移,更多的轴突从近端断端长出,逐渐减少近端与远端轴突细胞的间隙,最终两侧的轴突细胞、施万细胞相遇,形成髓鞘,完成神经的修复。如图5所示。 在神经桥形成的过程中,施万细胞形成Bungner带,为再生的轴突提供生长支架,引导轴突正确地穿过神经桥。再生的轴突沿着Bungner带生长,寻找目标肌肉进行再支配。随着轴突再生,施万细胞再次分化为髓鞘形成细胞,开始形成新的髓鞘。随着髓鞘的形成和轴突的再支配,神经功能逐渐恢复[36]。若没有施万细胞的引导,轴突再生时将会沿着异常的方向生长。在这个过程中,施万细胞不仅提供了物理的路径,还通过分泌神经营养因子和激活局部间充质干细胞来促进轴突的生长和再生[37]。 在修复的晚期,新生的轴突被未成熟的髓鞘包裹,未成熟的髓鞘经压实形成成熟的髓鞘。成熟的髓鞘形成与致密线、髓鞘碱性蛋白以及O-GlcNAcylation、组蛋白脱乙酰酶等密切相关。髓鞘碱性蛋白与髓鞘的压实有关,其位于细胞膜内表面,呈正电荷并具有疏水性,与对侧细胞膜脂质负电荷相互吸引,使施万细胞的两侧细胞膜相互靠近,中间间隔由细胞质填充,构成髓鞘的结构单位——致密线[38]。O-GlcNAcylation"
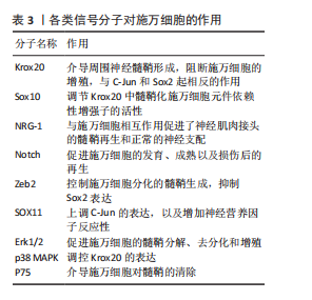
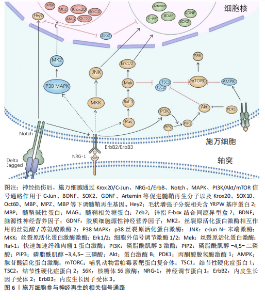
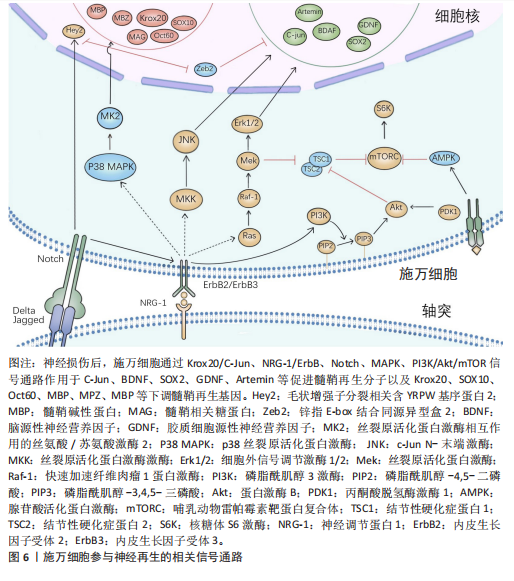
是核蛋白质和胞质中的O连接N-乙酰葡萄糖胺的翻译修饰产物,由 O连接N-乙酰葡萄糖胺转移酶催化,对施万细胞缺失O连接N-乙酰葡萄糖胺转移酶的小鼠进行坐骨神经挤压,会导致神经髓鞘再生缺陷[39]。抑制组蛋白脱乙酰酶在损伤后周围神经髓鞘形成和髓鞘再生中起到重要作用,敲除或者使用组蛋白脱乙酰酶抑制剂,可以促进髓鞘再生;组蛋白脱乙酰酶3抑制剂可促进施万细胞的功能恢复,增强髓鞘再生[40]。 2.5.2 施万细胞的信号通路 (1) Krox20/C-Jun信号通路:Krox20是调节施万细胞髓鞘形成和分化的关键因子,通过调节与髓鞘相关的多种因子,如SOX2与C-Jun转录因子,抑制这两种因子的表达进而抑制神经再生。而Krox20参与髓鞘蛋白MBP、P0和MPZ的转录[41],在转录过程中C-Jun和SOX2可以抑制Krox20。在周围神经损伤后,编码Krox20 的基因表达降低,SOX2与C-Jun被激活,启动施万细胞修复损伤神经的功能。C-Jun可以通过促进再生相关基因如Arpc3、Spro1a以及转录因子Atf3的表达来促进轴突生长。C-Jun 还能够直接上调神经营养因子,如胶质细胞源性神经营养因子和Artemin,从而促进轴突延伸和神经再生[42]。C-Jun受p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase,p38 MAPK)、细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK)和Jun N末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)信号通路的调节[43]。在C-Jun/JNK/MKK信号通路中,JNK是丝裂原活化蛋白激酶激酶7(mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase,MKK7)的专属下游底物,MKK7被激活时上调JNK,进而上调C-Jun。此外,C-Jun/JNK/MKK信号通路中MKK4还可激活p38 MAPK信号通路[44],见图6,表3。"
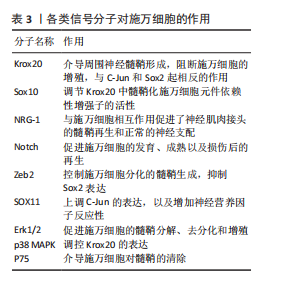
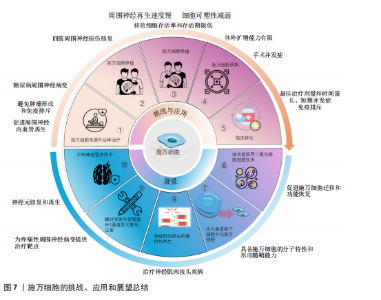
再生中起重要作用[28]。在周围神经损伤后,轴突NRG-1驱动再生,它与施万细胞的相互作用促进了神经肌肉接头的髓鞘再生和正常的再生神经支配[45]。神经元上的NRG-1配体与施万细胞上的ErbB受体结合来控制髓鞘厚度,从而诱导髓鞘蛋白的表达,使轴突髓鞘化。过量的葡萄糖以糖原的形式储存施万细胞中,当环境中葡萄糖浓度降低或神经元活动增加,糖原分解成乳酸供应轴突能量,而神经元上的NRG-1信号受损时,施万细胞无法有效地为神经元提供能量[46]。该通路还可以上调C-Jun,进而通过Krox20/C-Jun信号通路促进神经再生[43],见图6,表3。 (3) Notch信号通路:Notch信号通路在施万细胞的发育、成熟以及损伤后的再生过程中发挥作用,其主要是通过影响前体施万细胞的增殖和分化。在周围神经系统中,Notch信号和转录因子Hairy2之间的相互作用对神经嵴细胞的发育十分重要[47]。PIOVESANA等[48]实验表明,槟榔丙炔酯激活M2毒蕈碱受体,可以下调Notch活性,从而间接抑制ErbB2受体表达,进而抑制施万细胞对NRG-1的反应能力。BACE1是一种膜锚定的天冬氨酰蛋白酶,并且还是阿尔茨海默症的β-分泌酶,BACE1缺失可以通过调节Notch分子的膜锚定配体Jagged-1和Delta1,激活Notch信号通路[48]。Notch靶基因Hes1还能通过抑制Mash1间接支持Sox10表达,以促进神经发生[49]。Zeb2控制施万细胞分化的髓鞘生成程序,Zeb2缺失的施万细胞无法在周围神经中生成髓鞘;在神经再生过程中,Zeb2缺失的施万细胞中Krox20阳性率显著减少,且Zeb2能够抑制SOX2表达,但不影响C-Jun。Hey2是 Notch 的Hes相关家族碱性螺旋-环-螺旋(bHLH)效应子,抑制施万细胞的分化过程,Zeb2通过抑制Hey2驱动施万细胞分化[50],见图6,表3。 (4) MAPK信号通路:MAPK信号通路包括ERK1/2、p38和JNK分支,对施万细胞的去分化、增殖、迁移和髓鞘形成有影响。在这里介绍ERK1/2与p38分支。 ERK1/2分支:神经损伤导致轴突膜破裂,钙离子迅速从细胞外流入受损的轴突内,激活ERK1/2 MAPK信号通路。钙离子内流激活钙调蛋白依赖的蛋白激酶,激活RAS,进而激活Raf-1,这是ERK1/2 MAPK信号通路的上游激酶。Raf-1激活MEK1/2,进而激活ERK1/2。ERK1/2的激活促使施万细胞从成熟状态去分化为具有增殖能力的修复细胞,在去分化过程中,髓鞘碱性蛋白的表达下调。ERK1/2通过磷酸化和激活转录因子C-Jun,促进施万细胞进入细胞周期并增殖,具有增殖能力的施万细胞产生胶质细胞源性神经营养因子和Artemin等神经营养因子,支持轴突再生和神经元存活[36],见图6,表3。 为了维持细胞状态的平衡,ERK1/2 MAPK信号通路通过负反馈机制进行自我调节,包括激活磷酸酶如MKPs,以及诱导负反馈调节因子如Spry蛋白和DUSPs的表达[51],负反馈调节保证了ERK1/2 MAPK信号通路的变化和输出更具有稳定性。 p38分支:在神经损伤后,p38 MAPK通过下游激酶MK2和MSK-1/CREB途径调控Krox20的表达,其中p38α亚型调节Krox20的表达。p38调节转录因子SCIP(suppressed cAMP-inducible protein)和Sox10 (SRY-box10)的表达,但不调节Sox2的表达,Sox10是Krox20的拮抗剂。SCIP调节髓鞘基因的表达,进而调节周围髓鞘的形成[52],见图6,表3。 (5) 磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,Akt)/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路:PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路在施万细胞的生长、存活、迁移和髓鞘形成中起调控作用。通常该通路的激活始于细胞表面受体(如生长因子受体)的激活,然后激活PI3K,引起磷脂酰肌醇-4,5-二磷酸[phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate,PIP2]转化为磷脂酰肌醇-3,4,5-三磷酸(phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate,PIP3),PIP3作为第二信使,招募Akt蛋白到细胞膜上并被激活,通过PH结构域与PIP3结合后,由磷脂依赖性激酶1磷酸化激活,磷酸化并抑制磷酸酶和张力蛋白同源物(phosphatase and tensin homolog,PTEN)表达,从而增加PIP3的水平,进一步激活PI3K/Akt通路。Akt还通过磷酸化结节性硬化症蛋白2(tuberous sclerosis complex 2,TSC2),从而抑制TSC1/TSC2复合体,导致mTOR复合体的激活[41]。 mTORC1通过p70S6激酶和真核起始因子4E结合蛋白1等磷酸化其底物,促进蛋白质的合成。mTORC1可以通过磷酸化胰岛素受体底物1来抑制PI3K/Akt通路的进一步激活;MAPK和Wnt/β-catenin通路也可以影响PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路的活性。PTEN将PIP3去磷酸化为PIP2,从而关闭信号,使信号通路终止[53]。神经生长因子与施万细胞的P75NTR结合,激活AMP活化蛋白激酶,进而抑制mTOR,介导施万细胞对髓鞘的清除[29],见图6,表3[54-55]。 2.6 动物实验和临床应用 施万细胞在外周神经系统中具有巨大修复潜能和促进神经元再生能力[21]。近年来,临床应用施万细胞促进外周神经元再生的治疗方法已经取得了初步成果。这些治疗方法为外周神经系统疾病患者带来了新的希望,也极大地推动了再生医学领域的发展。 施万细胞来源外泌体在促进轴突再生[56]、抗炎和免疫调节、促进血管生成以及分泌营养因子方面均发挥作用[57]。SUN等[58]研究表明,缺氧施万细胞来源外泌体(H-SCs-Exos)比常氧施万细胞来源外泌体(N-SCs-Exos)更能促进周围神经损伤后的神经内血管再生,这是因为含有更多的可以使细胞糖酵解比例上调的miR-21-5p,这为更好地修复周围神经损伤提供了潜在的、有效的治疗靶点。糖尿病周围神经病变与施万细胞密切相关[59],WANG等[60]实验使用20周龄的2型糖尿病db/db小鼠模型,通过尾静脉注射施万细胞来源外泌体,每2周1次,连续8周,发现施万细胞来源外泌体治疗显著改善了db/db小鼠的周围神经病变症状,包括提高坐骨神经传导速度和热、机械敏感性等,增加糖尿病小鼠表皮神经纤维和坐骨神经的再髓鞘化,施万细胞来源外泌体还逆转了糖尿病引起的miRNA(如miR-21、miR-27a和miR-146a)的减少,以及SEMA6A、RhoA、PTEN和NF-κB的增加。由此可见施万细胞来源外泌体对糖尿病周围神经病变具有治疗效果,可能通过调节miRNA和相关蛋白来实现[61]。而外泌体作为无细胞治疗方法的一部分,避免了直接使用干细胞可能带来如肿瘤形成或免疫排斥反应等风险[62],见图7①。 臂丛神经损伤和坐骨神经损伤是常见的周围神经损伤类型[63-64],施万细胞移植有助于这些损伤后的神经和肌肉功能的恢复。此外,施万细胞与其他治疗方法如细胞注射技术、干细胞疗法[65]、细胞封装技术、基因编辑技术以及3D打印生物工程支架技术相结合[66],可进一步提高治疗效果,模拟和改善受损神经的微环境,促进轴突的定向生长和髓鞘化,见图7②。 施万细胞移植并非在临床实践中没有成功应用的案例,LEVI等[67]和GERSEY等[68]临床研究表明,从腓肠神经活检和创伤的坐骨神经残端中分离出施万细胞,经过纯化和增殖后,将细胞与腓肠神经移植物结合,成功修复了1例 7.5 cm 缺损(病例1:坐骨神经被船螺旋桨损伤完全横断)和1例5 cm缺损(病例2:坐骨神经胫骨部分损伤,腿部枪伤)。病例1术后随访36个月,患者恢复了近端感觉以及运动功能[69],而病例2术后12个月表现出完整的运动功能和胫骨表面皮肤的部分感觉恢复。另外1例挤压伤患者,同样是坐骨神经断裂,由FDA批准进行了施万细胞自体移植治疗,并进行了超过48个月的随访,也力证了施万细胞在周围神经损伤的临床应用中具有很大的潜力[70]。因此,施万细胞功能的深入研究对于推动神经再生医学的进步和提高患者的生活质量具有重要意义,见图7②。"
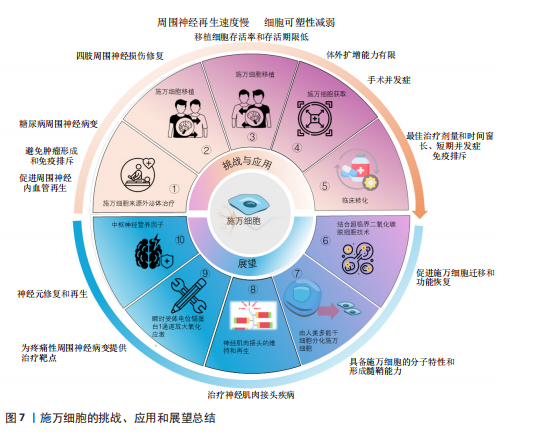

尽管如此,细胞移植的临床应用仍面临着一些挑战,外周神经系统神经再生的速度每天大约只有1 mm,且这个速度还会受到损伤位置的影响[71],且随着时间的推移,施万细胞的可塑性会逐渐减弱,外周神经系统的环境也会逐渐变得不利于神经再生。因此,影响施万细胞可塑性因素对于促进神经修复急需深入研究,见图7③。其次,施万细胞的获取通常需要通过神经活检的方式,这是一种侵入性手术,可能会给患者带来额外的风险和不适[72],并可能导致手术相关的并发症,因此这种侵入性操作限制了施万细胞在临床治疗中的广泛应用,见图7④。此外,即使成功从患者体内获取了施万细胞,这些细胞在体外的扩增能力比较有限[73],这意味着在实验室中培养足够数量的施万细胞以用于治疗尚有困难,这种有限的扩增能力限制了施万细胞在大量需求时的应用(图7④),特别是在需要大量细胞以修复严重神经损伤的情况下,在将施万细胞疗法从实验室研究转化为临床应用的过程中,尚未有进行大量的临床试验结果和数据来支持这些治疗方法的安全性和有效性。优化细胞培养和移植技术、监测短期和长期的并发症以及确定最佳的治疗剂量和时间点、免疫排斥反应、提高移植细胞的存活率和存活期限、治疗效果的持久性,可能伴随的不良反应等均为施万细胞治疗外周神经元再生的重大挑战[26],见图7⑤。因此,未来的研究致力于克服这些障碍,需要更多的跨学科合作交流,更深的多学科交叉融合,整合不同领域的技术和知识,以充分推动施万细胞应用的发展,实现细胞移植技术治疗外周神经系统疾病[74]。 2.7 未来展望 施万细胞促进轴突再生能力强,施万细胞移植技术是周围神经系统修复的基石,而组织工程技术的革新——超临界二氧化碳(scCO2)脱细胞技术为施万细胞的研究和应用提供了新的机遇,其制备的神经移植物在保留细胞外基质成分和促进神经再生方面优于传统的化学脱细胞方法,能够更好地模拟天然神经环境,提高神经再生的效率,有利于施万细胞的迁移、功能的恢复和髓鞘形成[75],见图7⑥。同时从新生儿和成人的周围神经中分离出施万细胞,或将干细胞诱导为施万细胞的技术日渐成熟,如使用人类牙髓干细胞分化成的施万细胞来构建神经组织[76],这为细胞自体移植提供了可能性。这两种技术的应用,有望改善周围以及中枢神经系统损伤修复的治疗结果,为患者提供更有效的治疗策略。此外,MAJD等[77]已经开发出一种从人类多能干细胞分化得到施万细胞的高效策略,不仅能够模拟原发性施万细胞的分子特性,还具备形成髓鞘的能力,这无疑增加了施万细胞来源的途径,有望解决施万细胞移植供体细胞不足的难题,见图7⑦。 存在神经肌肉接头中的突触型施万细胞,包裹突触附近的神经末梢和肌肉表面,神经轻微损伤后,受损的神经肌肉接头中的突触型施万细胞增殖形成施万细胞桥[21],引导新形成的神经到受损的突触进而阻止乙酰胆碱受体簇的丢失并且形成新的乙酰胆碱受体簇[78]。此外,BARIK等[79]实验表明,突触型施万细胞在神经肌肉接头形成前被去除时,乙酰胆碱受体簇的大小和密度均降低,而在神经肌肉接头形成后,去除突触型施万细胞则乙酰胆碱受体簇的大小降低,密度不变,神经肌肉接头碎片化。在神经肌肉接头成熟后杀死突触型施万细胞,神经肌肉接头碎片化,神经肌肉的突触传递过程受损。因此,突触型施万细胞在神经肌肉接头再生和功能维持方面有着重要作用。这一发现为重症肌无力、肌萎缩侧索硬化症等神经肌肉接头疾病治疗提供了新的研究方向,见图7⑧。肿瘤化疗引起的周围神经病变是一种常见的肿瘤治疗不良反应[80],而施万细胞与疼痛性周围神经病变密切相关,BELLANTONI等[81]发现施万细胞表达的瞬时受体电位锚蛋白1(transient receptor potential ankyrin 1,TRPA1)对斑马鱼幼体的周围神经病变模型具有放大氧化应激,并向相邻神经纤维发出机械异常性疼痛信号以维持类似疼痛的作用,为治疗疼痛性周围神经病变提供了药物设计的靶点,见图7⑨。尽管目前还没有直接的人类临床试验专注于施万细胞移植治疗周围神经病变,但已有的研究表明施万细胞移植在其他类型的周围神经病变治疗中是安全有效的,这为施万细胞在周围神经病变治疗中的应用提供了初步的科学依据。 施万细胞不仅在周围神经系统修复中富有潜力,在中枢神经系统修复能力也不容忽视。中枢神经系统的再生过程比外周神经系统更为困难,其损伤修复不理想一直是临床上的难题。然而,研究发现,施万细胞也是多种中枢神经营养因子的来源,能够提供对轴突生长和存活的营养支持,包括神经生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子和睫状神经营养因子等神经营养因子[82-83]。脑源性神经营养因子在神经元的保护、修复和再生中起着核心作用[84],特别是在海马体皮质区域[85]。此外,脑源性神经营养因子可增强神经可塑性[86],促进突触的形成和强化[87],睫状神经营养因子能调节神经胶质细胞(如星形胶质细胞和小胶质细胞)的活性,影响它们的免疫功能和对损伤的反应,减少炎症引起的神经损伤[88]。施万细胞还能修复中枢神经系统的脱髓鞘区域,使中枢神经系统再髓鞘化,恢复神经冲动的传导[89]。因此,施万细胞未来可能在中枢神经系统脱髓鞘疾病(如肌萎缩侧索硬化症、多发性硬化症等神经病变)的治疗中发挥重大作用,见图7⑩[90-91]。 综上所述,施万细胞在神经系统中的应用前景广阔,研究涉及神经科学、分子生物学、免疫学等多个领域。目前已经对施万细胞形态变化、表观遗传学机制、转录因子和信号通路等在神经修复中起重要作用的因素进行了研究。然而,如何对这些因素进行激活、激活的时间和强度,以及它们之间的相关性还尚未明确。未来的研究将会关注如何提高细胞体外扩增能力和修复能力,以及如何延长作用时间,以满足临床治疗中轴突再生的长期需求[35]。"

| [1] MENORCA RM, FUSSELL TS, ELFAR JC. Nerve physiology: mechanisms of injury and recovery. Hand Clin. 2013;29(3):317-330. [2] PERLMUTTER GS. Axillary nerve injury. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(368):28-36. [3] CALLAGHAN BC, CHENG HT, STABLES CL, et al. Diabetic neuropathy: clinical manifestations and current treatments. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(6):521-534. [4] RøIKJER J, EJSKJAER N. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022; 274:309-328. [5] PADOVANO WM, DENGLER J, PATTERSON MM, et al. Incidence of Nerve Injury After Extremity Trauma in the United States. Hand (N Y). 2022;17(4):615-623. [6] LI R, LIU Z, PAN Y, et al. Peripheral nerve injuries treatment: a systematic review. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;68(3):449-454. [7] LANS J, EBERLIN KR, EVANS PJ, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Nerve Gap Repair: Comparative Effectiveness of Allografts, Autografts, and Conduits. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023; 151(5):814e-827e. [8] PANAGOPOULOS GN, MEGALOIKONOMOS PD, MAVROGENIS AF. The Present and Future for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Orthopedics. 2017;40(1):e141-e156. [9] ROBALLO KCS, GIGLEY JP, SMITH TA, et al. Functional and immunological peculiarities of peripheral nerve allografts. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(4):721-727. [10] TANG P, CHAUHAN A. Decellular Nerve Allografts. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015; 23(11):641647. [11] LAN D, WU B, ZHANG H, et al. Novel Bioinspired Nerve Scaffold with High Synchrony between Biodegradation and Nerve Regeneration for Repair of Peripheral Nerve Injury. Biomacromolecules. 2023; 24(11):5451-5466. [12] AQEL S, AL-THANI N, HAIDER MZ, et al. Biomaterials in Traumatic Brain Injury: Perspectives and Challenges. Biology (Basel). 2023;13(1):21. [13] 肖雨,翁秋燕,邵磊,等.周围神经损伤后再生与修复机制研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2022,49(7):1243-1250. [14] 王乐禹, 邱小忠, 王璞玥,等.组织工程研究的现状及应关注的重要基础科学问题[J].中国科学基金,2020,34(2):213-220. [15] JESSEN KR, MIRSKY R. Origin and early development of Schwann cells. Microsc Res Tech. 1998;41(5):393-402. [16] TAVEGGIA C, FELTRI ML. Beyond Wrapping: Canonical and Noncanonical Functions of Schwann Cells. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2022; 45:561-580. [17] JESSEN KR, MIRSKY R, LLOYD AC. Schwann Cells: Development and Role in Nerve Repair. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2015;7(7):a020487. [18] 刘莉.施旺细胞源性Sema3b调节周围神经轴突径向排序[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2020. [19] 苏新豪,石长坚,黄大元.富血小板血浆在周围神经损伤再生修复的研究进展[J].临床医学进展,2023,13(5):8313-8318. [20] 王海燕,徐如祥,姜晓丹.Notch信号转导通路对神经干细胞的调控[J].生命的化学,2003,23(3):167-169. [21] BOSCH-QUERALT M, FLEDRICH R, STASSART RM. Schwann cell functions in peripheral nerve development and repair. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;176:105952. [22] 高曌,骆天炯,宣思,等.施万细胞在周围神经疾病中的免疫调节研究进展[J].现代医药卫生,2023,39(2):313-319. [23] 徐晓明.SCHWANN细胞在中枢神经系统损伤修复及再生中的作用[J].神经解剖学杂志,1996(4):302,291-302,429. [24] WANG K, QIN B. Research progress of peripheral nerve mismatch regeneration. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(3):387-391. [25] ROTSHENKER S. Wallerian degeneration: the innate-immune response to traumatic nerve injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2011; 8:109. [26] WEI C, GUO Y, CI Z, et al. Advances of Schwann cells in peripheral nerve regeneration: From mechanism to cell therapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024;175: 116645. [27] 杨恩璐,孙秉贵.BDNF及其下游通路与GABA能神经元发育相关性的研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(6):544-550. [28] 项捷.神经营养因子在神经发育及神经退行性疾病中作用机制研究[D].西安: 空军军医大学,2019. [29] LI R, LI D, WU C, et al. Nerve growth factor activates autophagy in Schwann cells to enhance myelin debris clearance and to expedite nerve regeneration. Theranostics. 2020;10(4):1649-1677. [30] 张守萍,关晋东,孙诚,等.激酶与外周神经损伤修复研究进展[J].生物过程, 2021,11(4):99-108. [31] KAMBLE N, SHUKLA D, BHAT D. Peripheral Nerve Injuries: Electrophysiology for the Neurosurgeon. Neurol India. 2019;67(6): 1419-1422. [32] BURNETT MG, ZAGER EL. Pathophysiology of peripheral nerve injury: a brief review. Neurosurg Focus. 2004;16(5):E1. [33] VARGAS ME, BARRES BA. Why is Wallerian degeneration in the CNS so slow? Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:153-179. [34] GORDON T. Peripheral Nerve Regeneration and Muscle Reinnervation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8652. [35] NOCERA G, JACOB C. Mechanisms of Schwann cell plasticity involved in peripheral nerve repair after injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(20):3977-3989. [36] KIM HA, MINDOS T, PARKINSON DB. Plastic fantastic: Schwann cells and repair of the peripheral nervous system. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(8):553-557. [37] MIN Q, PARKINSON DB, DUN XP. Migrating Schwann cells direct axon regeneration within the peripheral nerve bridge. Glia. 2021;69(2):235-254. [38] LIU B, XIN W, TAN JR, et al. Myelin sheath structure and regeneration in peripheral nerve injury repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(44):22347-22352. [39] KIM S, MAYNARD JC, STRICKLAND A, et al. Schwann cell O-GlcNAcylation promotes peripheral nerve remyelination via attenuation of the AP-1 transcription factor JUN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; 115(31):8019-8024. [40] GOMEZ-SANCHEZ JA, PATEL N, MARTIRENA F, et al. Emerging Role of HDACs in Regeneration and Ageing in the Peripheral Nervous System: Repair Schwann Cells as Pivotal Targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(6): 2996. [41] FIGLIA G, GERBER D, SUTER U. Myelination and mTOR. Glia. 2018;66(4):693-707. [42] ZHANG Y, ZHAO Q, CHEN Q, et al. Transcriptional Control of Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Mol Neurobiol. 2023; 60(1):329-341. [43] XU X, SONG L, LI Y, et al. Neurotrophin-3 promotes peripheral nerve regeneration by maintaining a repair state of Schwann cells after chronic denervation via the TrkC/ERK/c-Jun pathway. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):733. [44] HAEUSGEN W, HERDEGEN T, WAETZIG V. The bottleneck of JNK signaling: molecular and functional characteristics of MKK4 and MKK7. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011;90(6-7):536-544. [45] PELLEGATTA M, TAVEGGIA C. The Complex Work of Proteases and Secretases in Wallerian Degeneration: Beyond Neuregulin-1. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:93. [46] HU X, HOU H, BASTIAN C, et al. BACE1 regulates the proliferation and cellular functions of Schwann cells. Glia. 2017;65(5): 712-726. [47] ZHOU B, LIN W, LONG Y, et al. Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):95. [48] PIOVESANA R, PISANO A, LORETI S, et al. Notch Signal Mediates the Cross-Interaction between M2 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor and Neuregulin/ErbB Pathway: Effects on Schwann Cell Proliferation. Biomolecules. 2022;12(2):239. [49] PAWOLSKI V, SCHMIDT MHH. Neuron-Glia Interaction in the Developing and Adult Enteric Nervous System. Cells. 2020;10(1):47. [50] WU LM, WANG J, CONIDI A, et al. Zeb2 recruits HDAC-NuRD to inhibit Notch and controls Schwann cell differentiation and remyelination. Nat Neurosci. 2016; 19(8):1060-1072. [51] LAKE D, CORRÊA SA, MÜLLER J. Negative feedback regulation of the ERK1/2 MAPK pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(23): 4397-4413. [52] HOSSAIN S, DE LA CRUZ-MORCILLO MA, SANCHEZ-PRIETO R, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 regulates Krox-20 to direct Schwann cell differentiation and peripheral myelination. Glia. 2012; 60(7):1130-1144. [53] ISHII A, FURUSHO M, BANSAL R. Mek/ERK1/2-MAPK and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling plays both independent and cooperative roles in Schwann cell differentiation, myelination and dysmyelination. Glia. 2021;69(10):2429-2446. [54] YI S, XU L, GU X. Scaffolds for peripheral nerve repair and reconstruction. Exp Neurol. 2019;319:112761. [55] JANKOWSKI MP, MILLER L, KOERBER HR. Increased Expression of Transcription Factor SRY-box-Containing Gene 11 (Sox11) Enhances Neurite Growth by Regulating Neurotrophic Factor Responsiveness. Neuroscience. 2018;382:93-104. [56] WANG H, JIA Y, LI J, et al. Schwann cell‑derived exosomes induce bone marrow‑derived mesenchymal stem cells to express Schwann cell markers in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(3):1640-1646. [57] LOPEZ-VERRILLI MA, PICOU F, COURT FA. Schwann cell-derived exosomes enhance axonal regeneration in the peripheral nervous system. Glia. 2013;61(11):1795-1806. [58] SUN J, ZENG Q, WU Z, et al. Enhancing intraneural revascularization following peripheral nerve injury through hypoxic Schwann-cell-derived exosomes: an insight into endothelial glycolysis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):283. [59] WU L, WANG XJ, LUO X, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on Schwann cell injury: mechanisms of cell death regulation and therapeutic perspectives. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024;15:1427679. [60] WANG L, CHOPP M, SZALAD A, et al. Exosomes Derived From Schwann Cells Ameliorate Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Diabetes. 2020;69(4):749-759. [61] LAM TC, LEUNG YY. Innovations in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024;11(5):444. [62] PAN W, LI S, LI K, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential in Organ Transplantation. Stem Cells Int. 2024;2024:2043550. [63] CHEN JN, YANG XJ, CONG M, et al. Promotive effect of skin precursor-derived Schwann cells on brachial plexus neurotomy and motor neuron damage repair through milieu-regulating secretome. Regen Ther. 2024;27:365-380. [64] CHEN W, CHANG S, YANG C, et al. Schwann cell‑like cells derived from human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells promote sciatic nerve repair through an exosome‑induced SOX2/FN1 pathway in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 2022;49(6):80. [65] SVENDSEN SP, SVENDSEN CN. Cell therapy for neurological disorders. Nat Med. 2024; 30(10):2756-2770. [66] YAO K, HONG G, YUAN X, et al. 3D Printing of Tough Hydrogel Scaffolds with Functional Surface Structures for Tissue Regeneration. Nanomicro Lett. 2024;17(1):27. [67] LEVI AD, BURKS SS, ANDERSON KD, et al. The Use of Autologous Schwann Cells to Supplement Sciatic Nerve Repair With a Large Gap: First in Human Experience. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(7):1395-1403. [68] GERSEY ZC, BURKS SS, ANDERSON KD, et al. First human experience with autologous Schwann cells to supplement sciatic nerve repair: report of 2 cases with long-term follow-up. Neurosurg Focus. 2017;42(3):E2. [69] WANG Q, CHEN FY, LING ZM, et al. The Effect of Schwann Cells/Schwann Cell-Like Cells on Cell Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022;16:836931. [70] XU J, RUAN X. Schwann cell autotransplantation for the treatment of peripheral nerve injury. Life Sci. 2024;358: 123129. [71] STASSART RM, GOMEZ-SANCHEZ JA, LLOYD AC. Schwann Cells as Orchestrators of Nerve Repair: Implications for Tissue Regeneration and Pathologies. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2024;16(6):a041363. [72] MATHIS S, MAGY L, LE MASSON G, et al. Value of nerve biopsy in the management of peripheral neuropathies. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018;18(7):589-602. [73] MONJE PV. The properties of human Schwann cells: Lessons from in vitro culture and transplantation studies. Glia. 2020;68(4):797-810. [74] MODRAK M, TALUKDER MAH, GURGENASHVILI K, et al. Peripheral nerve injury and myelination: Potential therapeutic strategies. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(5):780-795. [75] CHOI SJ, HAN J, SHIN YH, et al. Increased efficiency of peripheral nerve regeneration using supercritical carbon dioxide-based decellularization in acellular nerve graft. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):23696. [76] SANEN K, MARTENS W, GEORGIOU M, et al. Engineered neural tissue with Schwann cell differentiated human dental pulp stem cells: potential for peripheral nerve repair? J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(12):3362-3372. [77] MAJD H, AMIN S, GHAZIZADEH Z, et al. Deriving Schwann cells from hPSCs enables disease modeling and drug discovery for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Cell Stem Cell. 2023;30(5):632-647.e10. [78] HOFFMAN DB, BASTEN AM, SORENSEN JR, et al. Response of terminal Schwann cells following volumetric muscle loss injury. Exp Neurol. 2023;365:114431. [79] BARIK A, LI L, SATHYAMURTHY A, et al. Schwann Cells in Neuromuscular Junction Formation and Maintenance. J Neurosci. 2016;36(38):9770-9781. [80] KACEM H, CIMINI A, D’ANGELO M, et al. Molecular and Cellular Involvement in CIPN. Biomedicines. 2024;12(4):751. [81] BELLANTONI E, MARINI M, CHIECA M, et al. Schwann cell transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) ortholog in zebrafish larvae mediates chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Br J Pharmacol. 2024;181(23):4859-4873. [82] FLETCHER JL, MURRAY SS, XIAO J. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Central Nervous System Myelination: A New Mechanism to Promote Myelin Plasticity and Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(12):4131. [83] JI-WEI S, ZI-YING L, XIANG T, et al. CNTF induces Clcf1 in astrocytes to promote the differentiation of oligodendrocyte precursor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022; 636(Pt 1):170-177. [84] PALASZ E, WYSOCKA A, GASIOROWSKA A, et al. BDNF as a Promising Therapeutic Agent in Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):1170. [85] ZHANG K, WANG F, ZHAI M, et al. Hyperactive neuronal autophagy depletes BDNF and impairs adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a corticosterone-induced mouse model of depression. Theranostics. 2023;13(3):1059-1075. [86] COLUCCI-D’AMATO L, SPERANZA L, VOLPICELLI F. Neurotrophic Factor BDNF, Physiological Functions and Therapeutic Potential in Depression, Neurodegeneration and Brain Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20): 7777. [87] MATTHIES C, RAMPELTSHAMMER E, BREUN M. Neurofibromatosis. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2023;91(5):213-232. [88] HU Z, DENG N, LIU K, et al. CNTF-STAT3-IL-6 Axis Mediates Neuroinflammatory Cascade across Schwann Cell-Neuron-Microglia. Cell Rep. 2020;31(7):107657. [89] CERQUEIRA SR, LEE YS, CORNELISON RC, et al. Decellularized peripheral nerve supports Schwann cell transplants and axon growth following spinal cord injury. Biomaterials. 2018;177:176-185. [90] CABEZA-FERNÁNDEZ S, HERNÁNDEZ-ROJAS R, CASILLAS-BAJO A, et al. Schwann cell JUN expression worsens motor performance in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. Glia. 2024;72(12): 2178-2189. [91] CHRISTODOULOU MV, PETKOU E, ATZEMOGLOU N, et al. Cell replacement therapy with stem cells in multiple sclerosis, a systematic review. Hum Cell. 2024;37(1):9-53. [92] 张佳琪,刘俊华,马洁,等.基于单细胞转录组数据解析大鼠背根神经节在出生后发育中非神经元细胞变化特征[J].生物工程学报,2023,39(9):3772-3786. [93] OKAMOTO Y, TAKASHIMA H. The Current State of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Treatment. Genes (Basel). 2023; 14(7):1391. [94] MCCULLOCH MK, MEHRYAB F, RASHNONEJAD A. Navigating the Landscape of CMT1B: Understanding Genetic Pathways, Disease Models, and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(17):9227. [95] CAO W, ZHANG R. Research advance of underlying pathogenesis and target therapies in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2020;37(5):578-583. |
| [1] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [2] | Yan Laijun, Ge Haiya, Wang Zhengming, Yang Zongrui, Niu Lifeng, Zhan Hongsheng. Mechanism by which Tongdu Huoxue Decoction inhibits macrophage inflammation to delay intervertebral disc degeneration in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6851-6857. |
| [3] | Shalayiding·Aierxiding, Aikebaierjiang·Aisaiti, Kutiluke·Shoukeer, Gulimire·Yilihamu, Aikeremujiang·Muheremu. Cellular biomechanisms of Wallerian degeneration in peripheral nerve axon injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5688-5694. |
| [4] | Fang Jun, Wei Wei, Xue Yating, Cui Chenlong, Wei Jiasheng, Shi Xiao, Yang Lijuan, Yang Baozhong. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote microglia M2-type polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5320-5327. |
| [5] | Wang Zengshun, Suonan Angxiu, Liu Limin, Zhou Jingyuan. Role and mechanism of miR-155/leptin receptor/adenosine phosphate-dependent protein kinase axis in tuberculin-induced osteoclast formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3190-3195. |
| [6] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [7] | Tan Xu, Liang Yu, Liang Yan, Liao Jian. Hypoxia-treated dental pulp stem cell exosomes induce M2 macrophage polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3961-3967. |
| [8] | Shan Shuai, Dong Yi, Liu Jialin, Han Xiangzhen, He Huiyu. Effects of red deer horn powder extract on the biological behavior of bone marrow derived macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3840-3845. |
| [9] | Zhao Jiling, Peng Yi, Peng Zhiyong, Yu Guolong. Effects of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells secreting tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulating gene-6 protein on conversion of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophage subtypes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2012-2019. |
| [10] | Zhao Yanrui, Zhou Junlin. Effect of surface hardness of biomaterials in the phagocytosis of E. coli biofilm cells by macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1551-1554. |
| [11] | Qin Jianfang, Wang Huan, Wu Bingbing, Ma Xiaojing. Effect of GOLM1 gene knockout on renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(26): 4162-4167. |
| [12] | Li Li, Zhuo Jin, Zheng Ling, Zhou Ling, Wang Qisong, Luo Lan, Luo Kai. Effects of different induced polarization methods on the proliferation, apoptosis and phagocytosis of rat bone marrow-derived macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4032-4037. |
| [13] | Mao Xin, Yu Limei, Wang Feng. Important role of mesenchymal stem cells in immune tolerance induction in heart transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2070-2078. |
| [14] | Li Junqi, Tian Guangzhao, Chen Mingxue, Wang Hao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Li Ming, Guo Quanyi. Regulatory effect of acellular cartilage extracellular matrix on phenotype of mouse macrophage line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1512-1516. |
| [15] | Cao Jiangang, Chen Desheng. Synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis: roles and features [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4731-4736. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||