Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7519-7528.doi: 10.12307/2025.961
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells
Fang Yuan1, 2, Qian Zhiyong3, He Yuanhada3, Wang Haiyan3, Sha Lirong1, Li Xiaohe3, Liu Jing4, He Yachao4, Zhang Kai5, Temribagen6
- 1Graduate School, 3Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, 4Bayannur Clinical College of Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Bayannur Hospital, Bayannur 015000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 5Department of Orthopedics, The Second Hospital of Ulanqab, Ulanqab 012000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 6Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Hohhot TCM Mongolian Hospital, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-10-09Accepted:2024-12-12Online:2025-12-18Published:2025-04-30 -
Contact:Wang Haiyan, Master, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Co-corresponding author: Li Xiaohe, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Fang Yuan, Master candidate, Attending physician, Graduate School, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; Bayannur Hospital, Bayannur 015000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Inner Mongolia Health Science and Technology Project, No. 202201188 (to WHY); Inner Mongolia Higher Education Innovation Team Development Plan, Nos. NMGIRT2419 (to WHY) and NMGIRT2227 (to LXH); Scientific Research Project of Mongolian Medicine Collaborative Innovation Center of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in 2021, No. MYYXTYB202104 (to LXH); Key Research Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University in 2021, No. YKD2021ZD001 (to LXH); 2021 Ulanqab Science and Technology Basic Research Project, No. 2021JC321 (to ZK); Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 2022MS08051 (to Temribagen)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Yuan, Qian Zhiyong, He Yuanhada, Wang Haiyan, Sha Lirong, Li Xiaohe, Liu Jing, He Yachao, Zhang Kai, Temribagen. Mechanism of Mongolian medicine Echinops sphaerocephalus L. in proliferation and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7519-7528.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
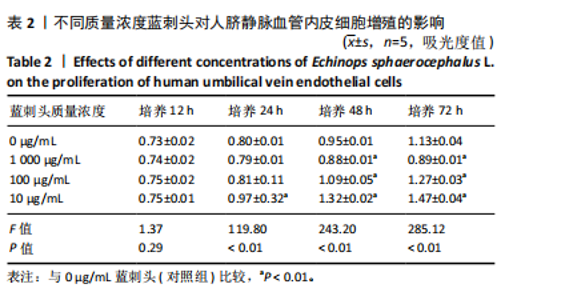
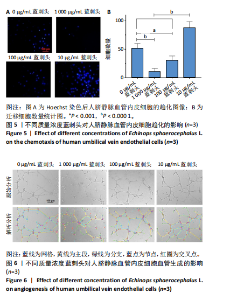
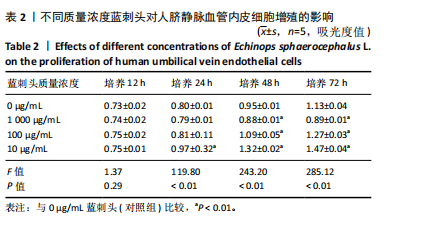
2.1 蓝刺头冻干粉性状及人脐静脉血管内皮细胞形态学观察 蓝刺头冻干粉大体观呈黄褐色粉状;将50 mg冻干粉加入10 mL纯水中,振荡摇匀后可见溶液呈棕色悬浊液,静置后底部可见部分不溶性物质;过滤后溶液呈棕色(图1)。 原代人脐静脉血管内皮细胞生长方式为贴壁生长,细胞形态呈扁平多角形,细胞边界清楚,整体呈铺路石状镶嵌排列(图2)。 2.2 不同质量浓度蓝刺头对于人脐静脉血管内皮细胞增殖的影响 表2为不同质量浓度蓝刺头培养基培养后人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的吸光度值。培养12 h,各组A值比较无明显差异(P > 0.05);培养24,48,72 h后,10 μg/mL蓝刺头组A值大于对照组(P < 0.01);培养48,72 h后,100 μg/mL蓝刺头组A值大于对照组(P < 0.01),1 000 μg/mL蓝刺头组A值小于对照组(P < 0.01)。"

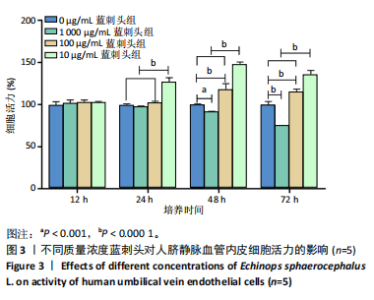
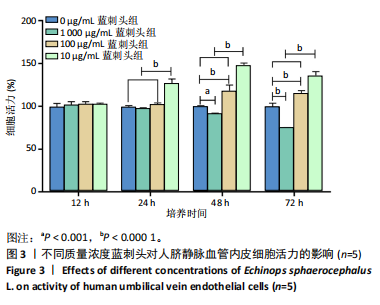
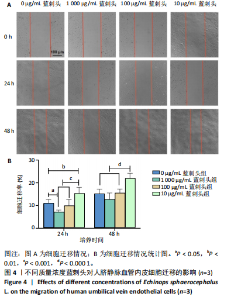
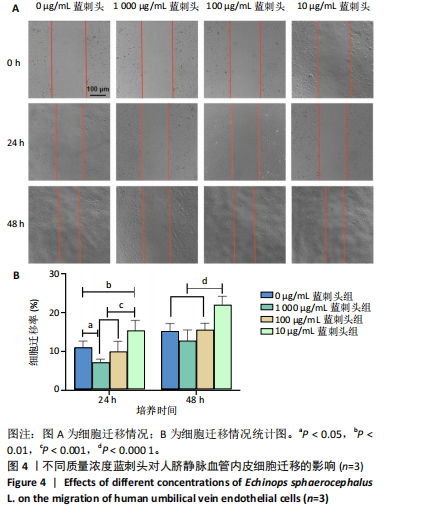
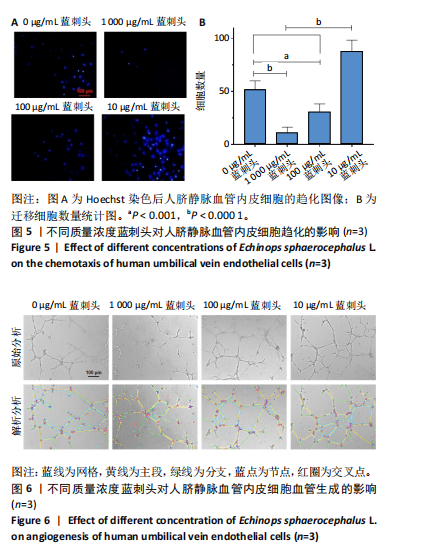
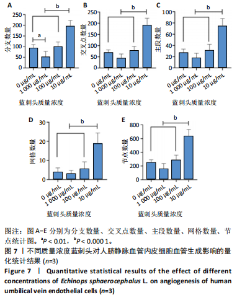
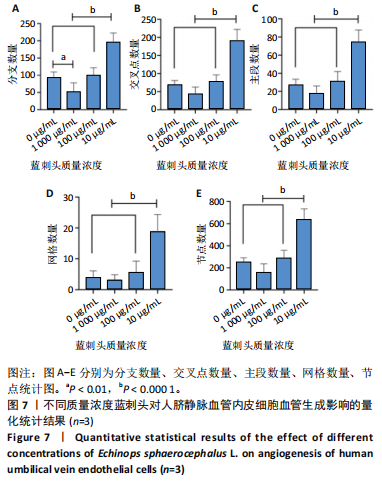
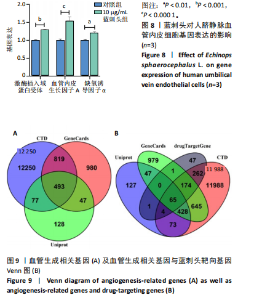
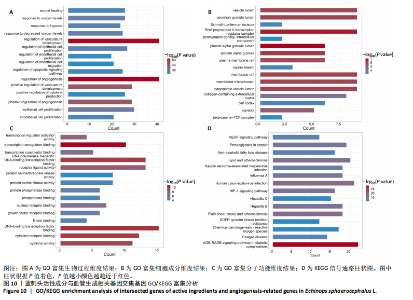
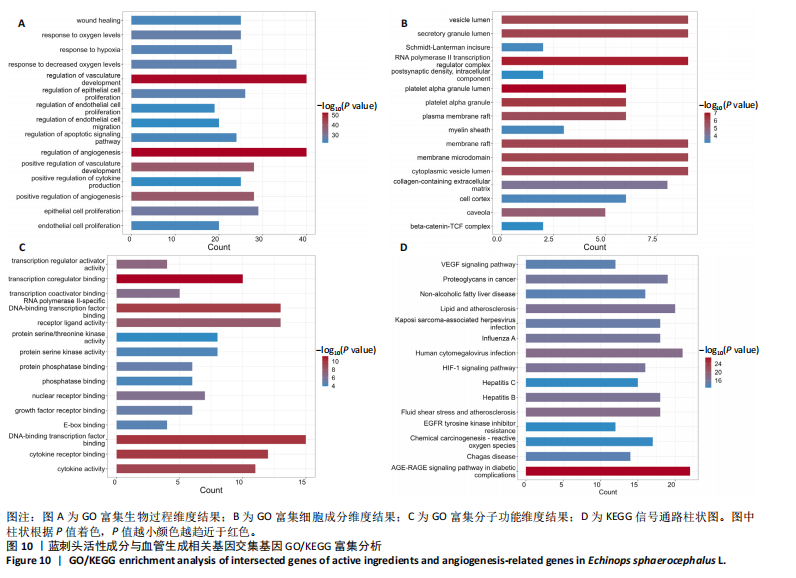
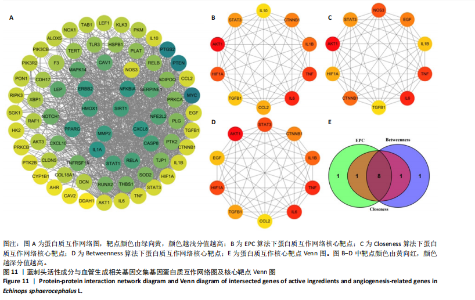
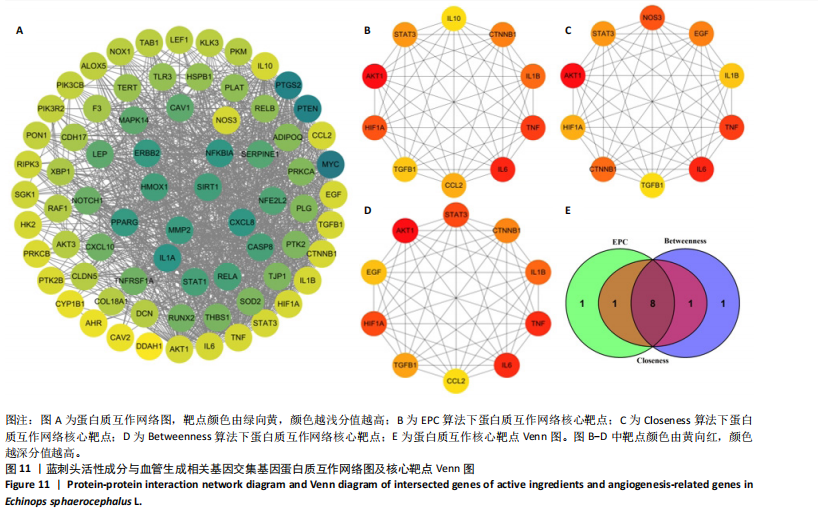
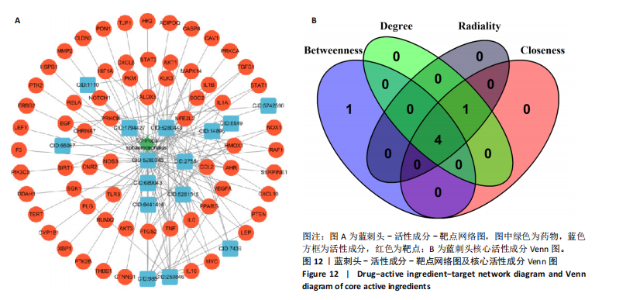
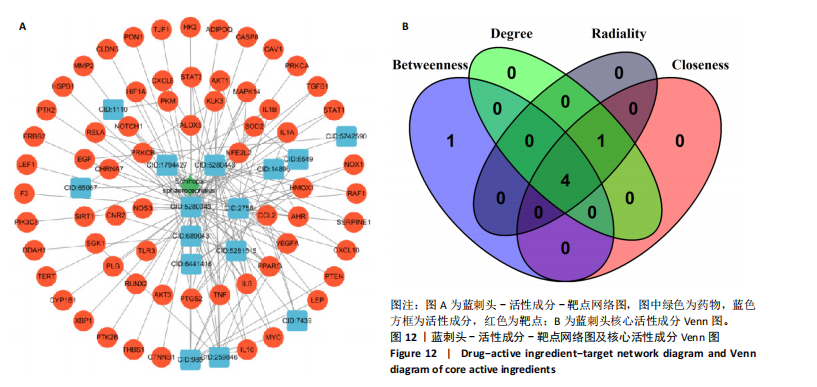
进一步比较各组的细胞活力,结果显示:培养12 h后,各组细胞活力相比无明显差异(P > 0.05);培养24 h后,10 μg/mL蓝刺头组细胞活力高于其他3组(P < 0.000 1);培养48,72 h后,10 μg/mL蓝刺头组、100 μg/mL蓝刺头组活力高于对照组(P < 0.000 1),以10 μg/mL蓝刺头组细胞活力最佳,1 000 μg/mL蓝刺头组细胞活力低于对照组(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1),见图3。结果表明,10 μg/mL蓝刺头作用24 h后即可提高人脐静脉血管内皮细胞活力,并且随时间延长细胞活力进一步提高;100 μg/mL蓝刺头作用48 h后人脐静脉血管内皮细胞活力提高;1 000 μg/mL蓝刺头作用48 h后可降低人脐静脉血管内皮细胞活力,并且随时间增加细胞活力进一步降低。 2.3 不同质量浓度蓝刺头富集人脐静脉血管内皮细胞迁移的影响 细胞划痕实验是体外研究细胞迁移运动的方法。图4A是各组人脐静脉血管内皮细胞划痕24 h和48 h后的迁移情况,图中可观察到各组细胞出现不同程度的迁移。图4B为各组人脐静脉血管内皮细胞迁移实验定量分析结果,划痕24 h后,10 μg/mL蓝刺头组细胞迁移率高于对照组(P < 0.01),1 000 μg/mL蓝刺头组细胞迁移率低于对照组(P < 0.05);划痕48 h后,10 μg/mL蓝刺头组细胞迁移率高于其他3组(P < 0.000 1)。结果表明,10 μg/mL 蓝刺头可促进人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的迁移。 2.4 不同质量浓度蓝刺头对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞趋化的影响 不同质量浓度蓝刺头对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞趋化作用的显微镜下图片,见图5A。进一步的定量统计分析表明,与对照组相比,10 μg/mL蓝刺头组人脐静脉血管内皮细胞迁移数量显著增加(P < 0.000 1),1 000 μg/mL和100 μg/mL处理组的人脐静脉血管内皮细胞迁移数量显著减少(P < 0.000 1,P < 0.001),见图5B。结果表明,10 μg/mL蓝刺头对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的趋化活性最强,1 000,100 μg/mL蓝刺头抑制人脐静脉血管内皮细胞的趋化。 2.5 不同质量浓度蓝刺头对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞血管生成的影响 采用基质胶模拟体外血管生成微环境,诱导血管生成并模拟血管网络构建及早期血管发生的过程。图6为各组人脐静脉血管内皮细胞在基质胶上培养4 h后的网格数量、主段、分支数量、节点、交叉点形成情况,实验组上述指标明显优于对照组。血管形成定量分析结果显示,10 μg/mL蓝刺头组网格数量、主段、分支数量、节点、交叉点形成均多于其他3组(P < 0.000 1),1 000 μg/mL蓝刺头组分支数量少于对照组(P < 0.01),见图7。结果表明10 μg/mL蓝刺头可促进早期血管生成。 2.6 蓝刺头(10 μg/mL)对人脐静脉血管内皮细胞基因表达的影响 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,实验组细胞内激酶插入域蛋白受体、血管内皮生长因子A和缺氧诱导因子α mRNA表达均高于对照组(P < 0.001,P < 0.000 1,P < 0.01),见图8。 2.7 蓝刺头活性成分及靶基因预测 经文献检索共获得35个蓝刺头相关活性成分,使用Python中rdkit模块对活性成分QED和DL进行计算及筛选,共得到31个活性成分。使用蓝刺头活性成分的Pubchem_ID在HIT、CTD 2个数据库中进行靶基因预测,共得到554个靶基因。 2.8 血管生成相关基因预测 经筛选,Gene Cards获得2 339个疾病基因,Uniprot获得745个疾病基因,CTD获得13 639个疾病基因。将3个数据库所得疾病基因取交集,最终得到493个疾病相关基因(图9A),而后与554个药靶基因取交集后得到65个交集基因(图9B)。 2.9 蓝刺头活性成分与血管生成相关基因交集基因GO/KEGG富集分析 对65个交集基因进行GO富集分析,通过筛选显著富集到2 154条GO结果,在生物过程维度共富集2 054个相关术语,细胞成分维度共富集29个相关术语,分子功能维度共富集了71个相关术语。根据P值对生物过程、细胞成分、分子功能进行排序并取前15进行绘图(图10A-C)。其中,生物过程主要涉及脉管系统尤其是血管系统的生成及发育的调控、上皮细胞及内皮细胞增殖和迁移的调控、低氧环境的调控以及相关细胞因子的调控等,细胞成分涉及RNA聚合酶Ⅱ转录调控复合物、血小板α颗粒管腔、膜筏及膜微域、囊泡腔、含胶原蛋白的细胞外基质细胞皮层、髓鞘、施-兰切迹、突触后致密区等,分子功能涉及细胞因子、核受体、转录因子等的结合,以及激活受配体、蛋白激酶、蛋白磷酸酶和RNA聚合酶的活性。 对65个交集基因进行KEGG信号通路富集分析,共计得到161条信号通路。根据P值对KEGG排序并取前15进行绘图(图10D),主要信号通路包括血管生成相关信号通路、动脉粥样硬化相关信号通路、病毒感染(甲、乙、丙型肝炎病毒、卡波西肉瘤相关疱疹病毒等)相关信号通路及肿瘤血管生成相关信号通路。 2.10 蛋白质互作网络构建结果 通过STRING数据库预测交集靶点的互作蛋白,并对蛋白互作关系进行网络拓扑分析,依据分值标注靶点颜色,构建蛋白质互作网络图(图11A)。筛选后共得到1 106对互作关系。利用Cytohubba软件中的EPC(图11B)、Closeness(图11C)、Betweenness(图11D)3个算法对核心靶点进行筛选,并将3种算法中排名前10的核心靶点取交集并绘图(图11E),共得到8个核心靶点,分别为TGFB1、TNF、IL-6、STAT3、CTNNB1、IL-1B、AKT1、HIF-1A。 2.11 蓝刺头核心活性成分筛选 基于65个交集基因构建了药物-活性成分-靶基因的互作关系网络(图12A),对辐射力、间接中心性、紧密中心性和度中心性4种算法前5的活性成分取交集(图12B),共得到4个核心活性成分,分别为芹菜素、咖啡酸、槲皮素、绿原酸(表3)。"

| [1] 国家卫生健康委员会.中国卫生健康统计年鉴(2022)[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社,2022:148-152 [2] 那生桑.内蒙古蒙药饮片炮制规范(2020年版)[M].呼和浩特:内蒙古人民出版社,2020:456. [3] 刘岩,裴艳春,王雄耀,等.蒙药蓝刺头对去卵巢大鼠骨组织雌激素受体mRNA表达影响的实验研究[J]. 内蒙古医科大学学报, 2017,39(3):249-253. [4] 高小明,常虹,丁超华.蒙药蓝刺头对去卵巢大鼠离体骨骨密度及骨最大变形挠度的影响[J].中医药导报,2016,22(24):16-19. [5] 巴音额古乐,金鸿宾.蒙药蓝刺头对骨折愈合过程中BMP-2及VEGF表达影响[J].中国民族医药杂志,2017,23(6):53-56. [6] ZHI J, YIN L, ZHANG Z, et al. Network pharmacology-based analysis of Jin-Si-Wei on thetreatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;319(Pt 3):117291. [7] BERGH C, MÖLLER M, EKELUND J, et al. Mortality after Sustaining Skeletal Fractures in Relation to Age. J Clin Med. 2022;11(9):2313. [8] DUCHAMP DE LAGENESTE O, JULIEN A, ABOU-KHALIL R, et al. Periosteum contains skeletal stem cells with high bone regenerative potential controlled by Periostin. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):773. [9] SAUL D, KHOSLA S. Fracture Healing in the Setting of Endocrine Diseases, Aging, and Cellular Senescence. Endocr Rev. 2022;43(6): 984-1002. [10] MAHAPATRA C, KUMAR P, PAUL MK, et al. Angiogenic stimulation strategies in bone tissue regeneration. Tissue Cell. 2022;79:101908. [11] LI J, MA J, FENG Q, et al. Building Osteogenic Microenvironments with a Double-Network Composite Hydrogel for Bone Repair. Research(Wash D C). 2023;6:0021. [12] 内蒙古植物志编辑委员会.内蒙古植物志[M]. 4卷.呼和浩特:内蒙古人民出版社,1985:69. [13] 王宇,郝光,张晶.蒙药蓝刺头中微量元素测定与分析[J].内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(3):1-3. [14] 赵磊,姜大成,王丹彧,等.HPLC法测定蒙药蓝刺头中7种有机酸的含量[J].特产研究,2023,45(1):131-135. [15] 王佳琪,高建萍,杨楠,等.蒙药蓝刺头的化学成分研究Ⅱ[J].中南药学,2018,16(12):1713-1716. [16] 薛培凤,波拉提•马卡比力,杨雷,等.蒙药蓝刺头的化学成分研究[J].中草药,2017,48(19):3921-3926. [17] 谢友良,赖小平,易智彪.蒙药蓝刺头研究进展[J].亚太传统医药, 2019,15(12):22-24. [18] ZULKEFLI N, CHE ZAHARI CNM, SAYUTI NH, et al. Flavonoids as Potential Wound-Healing Molecules: Emphasis on Pathways Perspective. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4607. [19] HUANG HC, CHEN Y, HU J, et al. Quercetin and its derivatives for wound healing in rats/mice: Evidence from animal studies and insight into molecular mechanisms. Int Wound J. 2023;21(2):e14389. [20] ZHU D, CHEN B, XIANG Z, et al. Apigenin enhances viability of random skin flaps by activating autophagy. Phytother Res. 2021;35(7):3848-3860. [21] ORTEGA-LLAMAS L, QUIÑONES-VICO MI, GARCÍA-VALDIVIA M, et al. Cytotoxicity and Wound Closure Evaluation in Skin Cell Lines after Treatment with Common Antiseptics for Clinical Use. Cells. 2022; 11(9):1395. [22] AUERBACH R, LEWIS R, SHINNERS B, et al Angiogenesis assays: a critical overview. Clin Chem. 2003;49(1):32-40. [23] DUDLEY AC, GRIFFIOEN AW. The modes of angiogenesis: an updated perspective. Angiogenesis. 2023;26(4):477-480. [24] LASCHKE MW, GU Y, MENGER MD. Replacement in angiogenesis research: Studying mechanisms of blood vessel development by animal-free in vitro, in vivo and in silico approaches. Front Physiol. 2022;13:981161. [25] NUSSDORFER P, PETROVIČ D, ALIBEGOVIĆ A, et al. The KDR Gene rs2071559 and the VEGF Gene rs6921438 May Be Associated with Diabetic Nephropathy in Caucasians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(17):9439. [26] TAO J, MIAO R, LIU G, et al. Spatiotemporal correlation between HIF-1α and bone regeneration. FASEB J. 2022;36(10):e22520. [27] ZHANG XY, XIA KR, WANG YN, et al. Unraveling the pharmacodynamic substances and possible mechanism of Trichosanthis Pericarpium in the treatment of coronary heart disease based on plasma pharmacochemistry, network pharmacology and experimental validation. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;325:117869. [28] HUANG HC, CHEN Y, HU J, et al. Quercetin and its derivatives for wound healing in rats/mice: Evidence from animal studies and insight into molecular mechanisms. Int Wound J. 2023;21(2):e14389. [29] HE S, CHEN R, PENG L, et al. Differential action of pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic components of Danhong injection in ischemic vascular disease or tumor models. Chin Med. 2022;17(1):4. [30] FAN Y, LI Y, YANG Y, et al. Chlorogenic acid promotes angiogenesis and attenuates apoptosis following cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion injury by regulating the PI3K-Akt signalling. Pharm Biol. 2022;60(1):1646-1655. |
| [1] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [3] | Chi Wenxin, Zhang Cunxin, Gao Kai, Lyu Chaoliang, Zhang Kefeng. Mechanism by which nobiletin inhibits inflammatory response of BV2 microglia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1321-1327. |
| [4] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [5] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [6] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [7] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [8] | Li Chen, Liu Ye, Ni Xindi, Zhang Yuang. Simulation analysis of real-time continuous stiffness in muscle fibers and tendons of the triceps surae during multi-joint movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7529-7536. |
| [9] | Yang Bo, Pan Xinfang, Chang Liuhui, Ni Yong. Correlation of echocardiographic parameters with disability at 3 months after acute ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7544-7551. |
| [10] | Jiang Qiyu, Zeng Huiyan. A novel analysis and prediction method for potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on artificial intelligence and omics data-driven approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7552-7561. |
| [11] | Liu Xuan, Ding Yuqing, Xia Ruohan, Wang Xianwang, Hu Shujuan. Exercise prevention and treatment of insulin resistance: role and molecular mechanism of Keap1/nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7578-7588. |
| [12] | Wang Tong, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Yang Hu, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Action mechanism of Gegenmaqi prescription in treatment of periarthritis of shoulder combined with type 2 diabetes based on TCMSP database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7669-7678. |
| [13] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [14] | Han Jie, Pan Chengzhen, Shang Yuzhi, Zhang Chi. Identification of immunodiagnostic biomarkers and drug screening for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7690-7700. |
| [15] | Liu Chengyuan, Guo Qianping. Differential effects of kartogenin on chondrogenic and osteogenic differentiation of rat and rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7490-7498. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||