Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (35): 7511-7518.doi: 10.12307/2026.533
Previous Articles Next Articles
Improvements in automatic diagnosis methods for knee osteoarthritis based on deep learning
Fang Ying1, Zhang Yanwei2, Li Xi3, Yan Peidong4, Bi Miao1#br#
- 1The Third Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510403, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Imaging, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Radiology, Second Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510260, Guangdong Province, China; 4Zhuhai School of Clinical Medicine, Jinan University, Zhuhai 519009, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-29Accepted:2024-12-31Online:2025-12-18Published:2025-04-30 -
Contact:Zhang Yanwei, PhD, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Imaging, the Third Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510378, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Fang Ying, Master candidate, The Third Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510403, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fang Ying, Zhang Yanwei, Li Xi, Yan Peidong, Bi Miao. Improvements in automatic diagnosis methods for knee osteoarthritis based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7511-7518.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
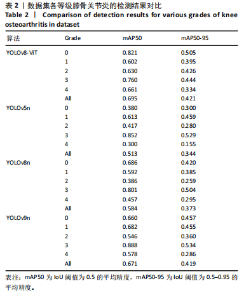
3 试验与结果 Testing and results 3.1 数据集 采集筛选了2013-2023年广州中医药大学第三附属医院收治的5 078例膝骨关节炎患者的X射线影像数据,年龄5-92岁,全部为2D图像,包含正位和侧位X射线片。实验方案得到广州中医药大学第三附属医院伦理委员会批准(伦理批件号:PJ-XS-20241226-001,审批时间:2024-12-26),并申请免除了患者知情同意。 将上述X射线影像数据按照COCO数据集的格式分为3个子数据集train,test,val,比例为7∶2∶1。由3个专业影像医师根据K-L分级标准采用labelme软件来标注膝骨关节炎部位并进行分类:0级,正常的膝关节,无骨关节炎的影像学特征;1级,存在关节间隙狭窄和怀疑存在骨赘;2级,存在明显的骨赘和关节间隙狭窄;3级,多发性骨赘,明显的关节间隙狭窄,骨质硬化,并怀疑存在骨畸形;4级,存在大骨赘,明显关节间隙狭窄,严重骨硬化,明显骨畸形。采用并集方式确定最后分级结果。 3.2 实验设备及评价指标 此模型的开发语言主要是Python,使用PyTorch作为网络框架。训练时,将输入图像设置为 384×384,使用 SGD 作为优化函数对模型进行训练。模型训练周期(epoch)为500,批量大小为16,初始学习速率为0.1。此次实验采用与原YOLOv8算法相同的数据增强算法。此文使用的评价指标有F1分数、mean average precision(mAP)、Recall(召回率)、val/box_loss(边框损失)、val/cls_loss(分类损失)和val/dfl_loss (分布拟合损失)。其中以正确率和查全率作为基本指标,根据正确率和查全率计算的 F1分数和 mAP作为最终评价指标,衡量模型的识别正确率。召回率和损失函数作为分类模型评估中的另一个重要指标,前者用于衡量一个模型在识别正样本方面的能力,后者用以判断模型的性能和泛化能力。 3.3 实际应用检测评价 此次实验数据集中检测到5种类型的膝骨关节炎,0级为正常的膝关节,无膝关节炎影像学特征,1级为关节间隙狭窄和疑似存在骨赘下垂,2级为明显的骨赘和关节间隙狭窄,3级为多发骨赘、明显的关节间隙狭窄、硬化症以及疑似存在骨畸形,4级为大骨赘、明显的关节间隙狭窄、严重硬化以及明显的骨畸形。图6显示了YOLOv8-ViT模型在此次数据集上的检测效果。结果表明,改进后的YOLOv8-ViT模型能够有效检测出膝关节炎目标,并且准确地识别它们的位置和类别,表现出较强的鲁棒性和准确性。 为了进一步验证不同模型对膝骨关节炎的检测效果,表2展示了YOLOv8-ViT模型和YOLOv5n、YOLOv8n、YOLOv9n模型在0-4分级的膝骨关节炎上表现的性能。实验数据表明,YOLOv8-ViT模型在0,1,2,4,all这几个类别上的检测精度均高于其余模型,其中类别3(多发骨赘、明显的关节间隙狭窄、硬化症以及疑似存在骨畸形)的检测精度低于其他模型,这是因为类别3目标特征较多且训练样本数量较少,与类别4较难区别,模型难以学习到更多的特征。特别提出的是与YOLOv5n、YOLOv8n、"


YOLOv9n模型相比,YOLOv8-ViT模型的所有类别平均mAP50(IoU阈值为0.5的平均精度)和mAP50-90(IoU阈值为0.5-0.95的平均精度)分别提升了18.2%和7.7%,11.1%和4.8%,2.4%和0.2%,其检测精度是最全面稳定的,体现了该模型良好的性能。 3.4 与不同算法的检测结果比较 为了进一步测试算法的性能,此次研究对YOLO系列中的YOLOv5n、YOLOv8n、YOLOv9n轻量级网络与YOLOv8-ViT进行了比较,具体结果见表3。从表3可以观察到,YOLOv8-ViT在确保运行速度的同时,其准确率相较于这些轻量级网络分别提升了37.1%,36%和29%,mAP50分别提高了31.7%,28.6%和24.5%,mAP50-95则提升了25%,23%和20.6%。实验结果表明,YOLOv8-ViT在与其他YOLO系列轻量级网络算法的比较中,以最小的模型体积取得了极高的检测精度,"

| [1] DESHPANDE BR, KATZ JN, SOLOMON DH, et al. Number of Persons With Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis in the US: Impact of Race and Ethnicity, Age, Sex, and Obesity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016;68(12):1743-1750. [2] XIE F, KOVIC B, JIN X, et al. Economic and Humanistic Burden of Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review of Large Sample Studies. Pharmacoeconomics. 2016;34(11): 1087-1100. [3] LIU M, JIN F, YAO X, et al. Disease burden of osteoarthritis of the knee and hip due to a high body mass index in China and the USA: 1990-2019 findings from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):63. [4] KELLGREN JH, LAWRENCE JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4):494-502. [5] OLSSON S, AKBARIAN E, LIND A, et al. Automating classification of osteoarthritis according to Kellgren-Lawrence in the knee using deep learning in an unfiltered adult population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):844. [6] KÖSE Ö, ACAR B, ÇAY F, et al. Inter- and Intraobserver Reliabilities of Four Different Radiographic Grading Scales of Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(3):247-253. [7] TEOH YX, LAI KW, USMAN J, et al. Discovering Knee Osteoarthritis Imaging Features for Diagnosis and Prognosis: Review of Manual Imaging Grading and Machine Learning Approaches. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:4138666. [8] 李松, 史涛, 井方科. 改进YOLOv8的道路损伤检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用,2023,59(23):165-174. [9] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016:779-788. [10] LIU X, PENG H, ZHENG N, et al. EfficientViT: Memory Efficient Vision Transformer with Cascaded Group Attention. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2023:14420-14430. [11] CAI H, LI J, HU M, et al. EfficientViT: Lightweight Multi-Scale Attention for High-Resolution Dense Prediction, 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2023:17256-17267. [12] WU TH, WANG TW. Real-Time Vehicle and Distance Detection Based on Improved Yolo v5 Network. 2021 3rd World Symposium on Artificial Intelligence (WSAI), Guangzhou, China, 2021:24-28. [13] JIAO L, ZHANG F, LIU F, et al. A Survey of Deep Learning-Based Object Detection. IEEE Access. 2019;7:128837-128868. [14] CAI W, NING X, ZHOU G, et al. A Novel Hyperspectral Image Classification Model Using Bole Convolution With Three-Direction Attention Mechanism: Small Sample and Unbalanced Learning. IEEE Trans Geosci Rem Sens. 2023;61:1-17. [15] LI J, LI B, JIANG Y, et al. MrFDDGAN: Multireceptive Field Feature Transfer and Dual Discriminator-Driven Generative Adversarial Network for Infrared and Color Visible Image Fusion. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas. 2023;72:1-28. [16] KANG J, TARIQ S, OH H, et al. A Survey of Deep Learning-Based Object Detection Methods and Datasets for Overhead Imagery. IEEE Access. 2022;10:20118-20134. [17] ABDULGHANI AM, ABDULGHANI MM, WALTERS WL, et al. Data Augmentation with Noise and Blur to Enhance the Performance of YOLO7 Object Detection Algorithm. 2023 Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering, & Applied Computing (CSCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2023:180-185. [18] RAGAB MG. A Comprehensive Systematic Review of YOLO for Medical Object Detection (2018 to 2023). IEEE Access. 2024;12:57815-57836. [19] Romero-González JTC. A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: From yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas. Mach Learn Knowl Extra. 2023;(5):1680-1716. [20] VARGHESE R, SAMBATH M. YOLOv8: A Novel Object Detection Algorithm with Enhanced Performance and Robustness, 2024 International Conference on Advances in Data Engineering and Intelligent Computing Systems (ADICS), Chennai, India, 2024:1-6. [21] Liu X, Peng H, Zheng N, et al. EfficientViT: Memory Efficient Vision Transformer with Cascaded Group Attention. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2023:14420-14430. [22] FU R, CUI S, FENG X. Mixed Global and Local Attention Alleviates Domain Shift Between Terahertz Image Datasets. 2024 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing (ICSPCC), Bali, Indonesia, 2024:1-5. [23] LUO G, ZHOU Y, JI R, et al. Cascade Grouped Attention Network for Referring Expression Segmentation. New York, NY, USA: ACM. 2020. [24] 冯晓晴, 蔡道章,余星磊,等.基于GBD大数据中国膝骨关节炎疾病负担现状与趋势分析[J].现代预防医学,2022,49(10):1753-1760. [25] Tiulpin A, Melekhov I, Saarakkala S. KNEEL: Knee Anatomical Landmark Localization Using Hourglass Networks. in 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). 2019. [26] LEUNG K, ZHANG B, TAN J, et al. Prediction of Total Knee Replacement and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis by Using Deep Learning on Knee Radiographs: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Radiology. 2020;296(3):584-593. [27] PIERSON E, CUTLER DM, LESKOVEC J, et al. An algorithmic approach to reducing unexplained pain disparities in underserved populations. Nat Med. 2021;27(1): 136-140. [28] GUAN B, LIU F, MIZAIAN AH, et al. Deep learning approach to predict pain progression in knee osteoarthritis. Skeletal Radiol. 2022;51(2):363-373. [29] CHEUNG JC, TAM AY, CHAN LC, et al. Superiority of Multiple-Joint Space Width over Minimum-Joint Space Width Approach in the Machine Learning for Radiographic Severity and Knee Osteoarthritis Progression. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(11):1107. [30] TAN JS, TIPPAYA S, BINNIE T, et al. Predicting Knee Joint Kinematics from Wearable Sensor Data in People with Knee Osteoarthritis and Clinical Considerations for Future Machine Learning Models. Sensors (Basel). 2022;22(2):446. [31] ABDULLAH SS, RAJASEKARAN MP. Rajasekaran. Automatic detection and classification of knee osteoarthritis using deep learning approach. Radiol Med. 2022;127(4):398-406. [32] BAYRAMOGLU N, ENGLUND M, HAUGEN IK, et al. Deep Learning for Predicting Progression of Patellofemoral Osteoarthritis Based on Lateral Knee Radiographs, Demographic Data, and Symptomatic Assessments. Methods Inf Med. 2024; 63(1-02):1-10. [33] HILL BG, BYRUM T, ZHOU A, et al. An Algorithmic Approach to Understanding Osteoarthritic Knee Pain. JB JS Open Access. 2023;8(4):e23.00039. [34] 王昕, 刘爽, 周长才, 基于深度学习和磁共振图像的膝骨关节炎分类[J]. 长春工业大学学报,2023,44(1):45-51. [35] 庾广文,谢俊杰,梁嘉健,等.深度学习对膝骨关节炎MRI图像智能分割和测量分析的作用及意义[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,33(33):5382-5387. [36] 马明昌, 李永杰,徐国胜,等.膝骨关节炎X线辅助诊断模型建立的临床应用初探[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(2):152-158. [37] 王佳妮, LEUNG K, ZHANG B, 等. 通过对膝关节X线摄影影像深度学习预测膝关节骨性关节炎的诊断和全膝关节置换:来自膝关节骨性关节炎初始数据[J].国际医学放射学杂志,2020,43(6):734. [38] 杨丽, 王欢,王婷婷, 等. 基于深度学习算法从X线图像识别手关节炎的诊断研究[J]. 现代医学,2024,52(7):1043-1049. [39] 许超,王云健, 刘洋,等. 基于改进Swin Transformer的膝骨关节炎X光影像自动诊断[J].电子测量技术,2024,47(19):155-163. [40] 高瑞婷, 林强, 满正行,等. 基于深度学习的SPECT图像关节炎病灶分割[J]. 西北民族大学学报(自然科学版),2021,42(1):22-30,37. [41] 姜斌. X线、MRI影像对膝骨关节炎的诊断价值分析[J]. 航空航天医学杂志, 2020,31(11):1338-1339. |
| [1] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [2] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [3] | Wang Simin, Zhang Dezhou, Zhao Jing, Wang Chaoqun, Li Kun, Chen Jie, Bai Xue, Zhao Hailong, Zhang Shaojie, Ma Yuan, Hao Yunteng, Yang Yang, Li Zhijun, Shi Jun, Wang Xing. Artificial intelligence and cervical spine image recognition: application prospects and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7231-7240. |
| [4] | Song Haoran, Zhang Yuqiang, Gu Na, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Visualization analysis of artificial intelligence in bone trauma research based on Citespace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 493-502. |
| [5] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [6] | Shaban Amiri Nzelekela, Yang Lianbo, Li Peng. Objective accuracy of six degree of freedom gait analysis system in evaluating the severity of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5890-5896. |
| [7] | Chen Yixin, Lu Yan, Zhang Xuan, Chen Xiaoli, Tan Liangyuan, Xu Zhangjie, Chen Wanglong, Su Shaoting, Liang Jiyao, Zhou Honghai. Mechanism by which Tongan Decoction regulates synovial macrophage polarization in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5621-5631. |
| [8] | Liu Yantong, Wang Shixuan, Zhao Shuangli, Wei Wei, Wang Donghai, Jiang Zongkun, Liu Hongfei. Transcriptional profiling and experimental validation of acupotomy for knee osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4239-4248. |
| [9] | Wei Mengli, Zhong Yaping, Gui Huixian, Zhou Yiwen, Guan Yeming, Yu Shaohua. Sports injury prediction model based on machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(2): 409-418. |
| [10] | Tang Xiran, Chen Weijian, Jiang Tao, Tan Xianyun, Liu Wengang . Types and contents of fatty acids and the risk of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(17): 3724-3731. |
| [11] | Liao Qing, Zeng Jing, Chen Jun, Yuan Lixia, Liu Gang. Moxibustion alleviates cartilage lesions in rats with knee osteoarthritis through regulating the circPan3/miR-667-5p/Ghrelin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2475-2483. |
| [12] | Hu Xiaoshen, Li Huijing, Lyu Junling, Xiao Xianjun, Li Juan, Li Xiang, Liu Ling, Jin Rongjiang. Pathological changes in the total knee joint during spontaneous knee osteoarthritis in guinea pigs at different months of age [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2218-2224. |
| [13] | Shen Xuyu, Luo Chengnuo, Zhang Xiaoyun, Jiang Zhouying, Chai Yuan . Role and mechanism of alkaloid components of traditional Chinese medicine against knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2368-2376. |
| [14] | Yang Yuxuan, Tan Jingyi, Zhou Lili, Bian Zirui, Chen Yifan, Wu Yanmin. Application of deep learning in oral imaging analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2385-2393. |
| [15] | Yu Weijie, Liu Aifeng, Chen Jixin, Guo Tianci, Jia Yizhen, Feng Huichuan, Yang Jialin. Advantages and application strategies of machine learning in diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||









