Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1199-1207.doi: 10.12307/2025.318
Previous Articles Next Articles
Impact of graft thickness on corneal endothelial decompensation following simple Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty
Ba Yanhong, Gao Minghong, Chen Yingxin
- General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2024-03-15Accepted:2024-04-13Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-21 -
Contact:Chen Yingxin, MD, Associate chief physician, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Ba Yanhong, Master, Physician, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ba Yanhong, Gao Minghong, Chen Yingxin. Impact of graft thickness on corneal endothelial decompensation following simple Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1199-1207.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
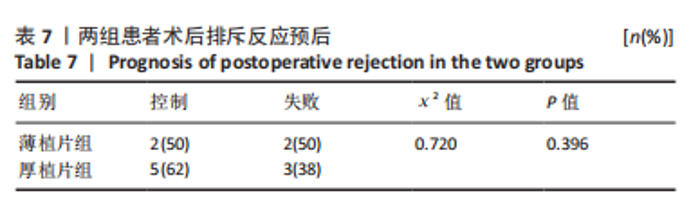
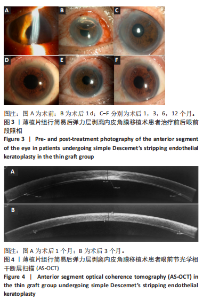
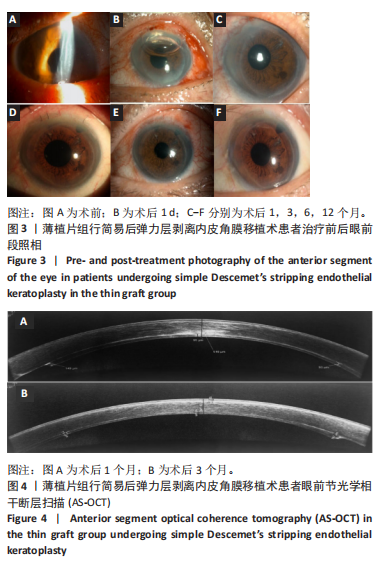
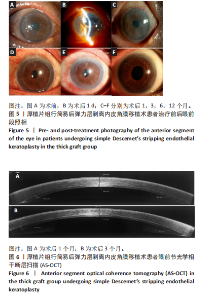
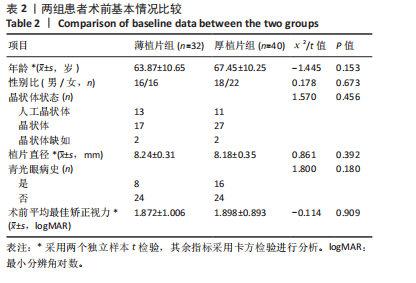
2.1 参与者数量分析 纳入行简易DSEK术的72例角膜内皮功能失代偿患者,2例最终行穿透性角膜移植术治疗,1例拒绝再次手术。 2.2 基线资料对比 两组患者之间在年龄、性别、晶状体状态、植片直径、青光眼病史及术前最佳矫正视力方面比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。 2.3 术后平均最佳矫正视力(以logMAR表示) 术后3个月,薄植片组患者术后最佳矫正视力为0.856±0.393,厚植片组为1.159±0.489,可见薄植片组视力明显优于厚植片组(P=0.006 < 0.05);术后1,6和12个月,平均最佳矫正视力(以logMAR表示):薄植片组(分别为:1.347±0.502,0.634±0.336,0.509±0.279),厚植片组(分别为:1.487±0.622,0.650±0.332,0.547±0.285),两组"
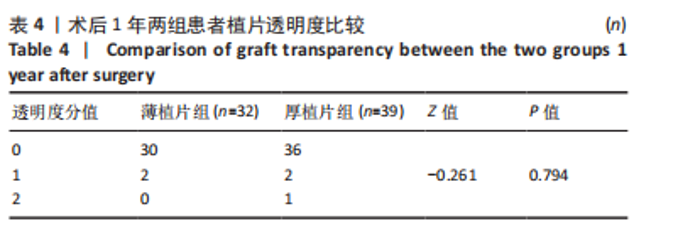
2.4 术后1年角膜内皮细胞数 由于角膜混浊水肿,大部分患者术前角膜内皮细胞数无法测量,患者术前内皮细胞计数未纳入统计。术后1年,薄植片组数量为(1 468±382)个/mm2,厚植片组为(1 445±397)个/mm2,两组术后1年时角膜内皮细胞数相近(P > 0.05)。 2.5 角膜植片透明度 随访1年时,绝大多数植片透明度较好,均未见3,4,5级案例出现,其中薄植片组术后32眼中30例角膜透明度为0级,2例眼角膜透明度为1级;厚植片组排除原发性移植失败1例,术后39眼中36例角膜透明度为0级,2例眼角膜透明度为1级,1例眼角膜透明度为2级,经统计学分析,两组间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05,为0.794),见表4。"

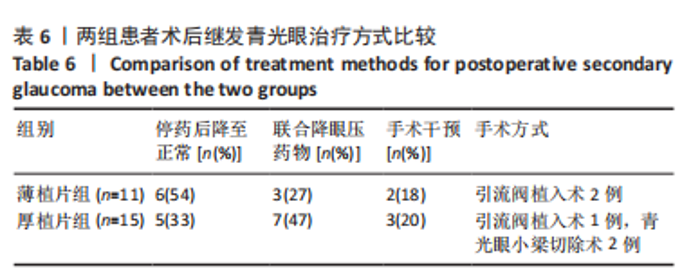
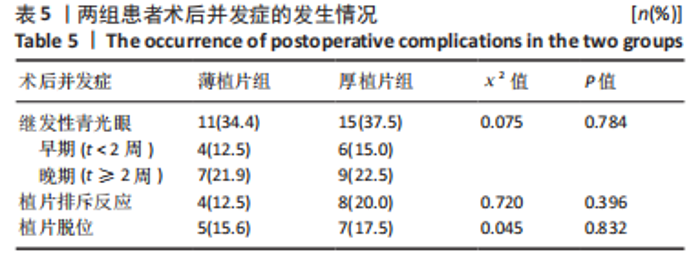
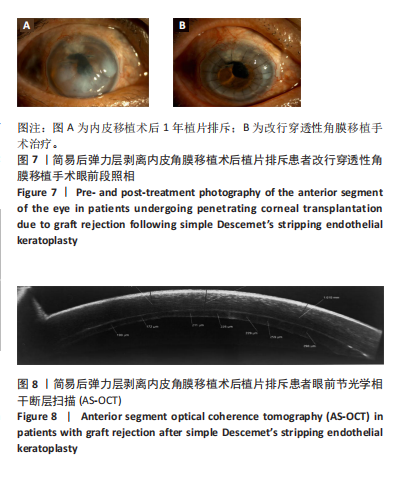
2.6.1 继发青光眼 薄植片组11眼,厚植片组15眼。按其发生时间分为早期青光眼(< 2周)和晚期青光眼(> 2周),其中薄植片组中术后早期继发青光眼4眼,晚期7眼;厚植片组早期6眼,晚期9眼。在术后继发青光眼患者中,薄植片组有6眼、厚植片组有5眼,调整激素类滴眼液用量眼压恢复至正常水平;若减少激素用量后眼压仍高于正常水平,则需联合局部降眼压药物进行治疗,其中薄植片组3眼,厚植片组7眼;当眼压仍达不到正常范围时,则患者需接受手术治疗,其中薄植片组有2眼,均为青光眼引流阀植入术;厚植片组有3眼,为青光眼引流阀植入术1例及青光眼小梁切除术2例。结果显示,两组患者术后继发青光眼比较差异无显著性意义(χ2=0.075,P=0.784 > 0.05)。两组术后继发青光眼的具体治疗方式见表6。"
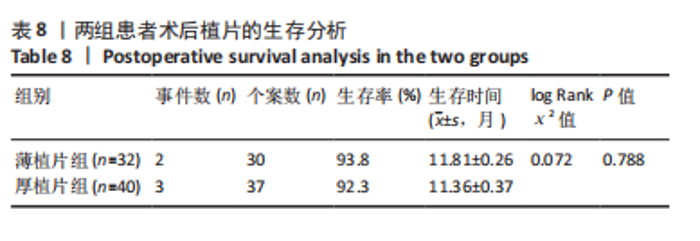
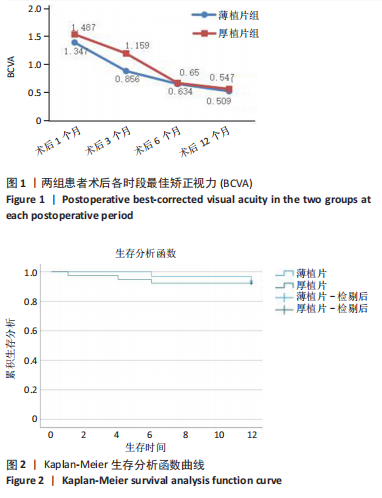
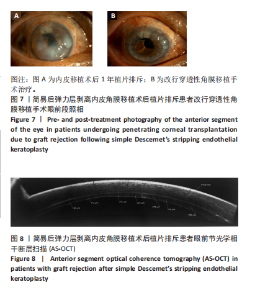
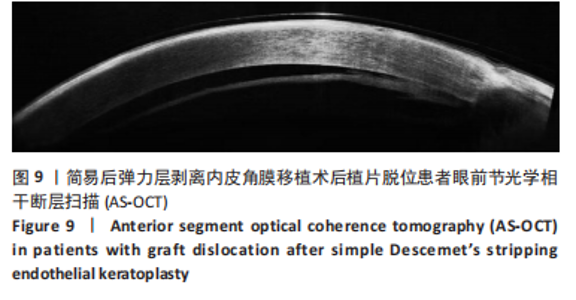
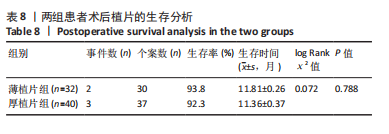
2.6.3 植片脱位 薄植片组5眼(15.6%),厚植片组7眼(17.5%),在术后24 h内发生植片移位,经再次前房注气后均贴附良好。两组患者植片脱位比较差异无显著性意义(χ2=0.045,P=0.832 > 0.05)。 2.7 原发移植失败 末次随访时,仅厚植片组中1例患者原发性移植失败,该患者2个月后再次行手术治疗,仍效果不佳,两组原发移植失败率比较差异无显著性意义(P=1.000 > 0.05)。 2.8 生存分析 在DSEK术后出现严重并发症并进行二次手术干预作为生存分析事件,薄植片组32例患者中有2例(6%)行二次手术,植片的生存率为93.8%。厚植片组40例排除1例因手术操作欠佳导致原发移植失败患者,在剩余39例患者中,共有3例(7.7%)行二次手术,植片的生存率为92.3%。两组总体植片生存率为93%,证明简易DSEK术治疗角膜内皮功能失代偿的植片生存率较高。log-Rank检验结果显示,两组间植片生存率比较差异无显著性意义(χ2=0.072,P=0.788 > 0.05,95%CI:11.45-12.17、10.67-12.07)。两组患者术后1年时累积植片生存曲线见表8及图2。"
| [1] ONG HS, ANG M, MEHTA JS. Evolution of therapies for the corneal endothelium: past, present and future approaches. Br J Ophthalmol. 2021;105(4):454-467. [2] VALLABH N A, KENNEDY S, VINCIGUERRA R, et al. Corneal Endothelial Cell Loss in Glaucoma and Glaucoma Surgery and the Utility of Management with Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK). J Ophthalmol. 2022;2022:1315299. [3] ALI M, CHO K, SRIKUMARAN D. Fuchs Dystrophy and Cataract: Diagnosis, Evaluation and Treatment. Ophthalmol Ther. 2023;12(2):691-704. [4] SINGH M, SINHA B P, MISHAR D, et al. Role of corneal collagen cross-linking in bullous keratopathy: A systematic review. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023;71(5):1706-1717. [5] TOURABALY M, CHETRIT Y, PROVOST J, et al. Influence of graft thickness and regularity on vision recovery after endothelial keratoplasty. Br J Ophthalmol.2020;104(9):1317-1323. [6] ANG MJ, CHAMBRELAIN W, LIN CC, et al. Effect of Unilateral Endothelial Keratoplasty on Vision-Related Quality-of-Life Outcomes in the Descemet Endothelial Thickness Comparison Trial (DETECT): A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2019;137(7):747-754. [7] BINESHFAR N, TAHVILDARI A, FEIZI S. Management of post-keratoplasty ametropia. Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2023;15:25158414231204717. [8] ADEMMER V, AGHA B, SHAJARI M, et al. Impact of DMEK on visual quality in patients with Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.2022;260(2):521-528. [9] GOLHAIT P, PESEYIE R.Persistent Epithelial Defect.2023//StatPearls [Internet].Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing.2024. [10] 中华医学会眼科学分会角膜病学组.中国人工角膜移植手术专家共识(2021年)[J]. 中华眼科杂志,2021,57(10):727-733. [11] SANDHU S, PETSOGLOU C, GRIGG J, et al. Elevated Intraocular Pressure in Patients Undergoing Penetrating Keratoplasty and Descemet Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty. J Glaucoma. 2016;25(4):390-396. [12] TILAK A, DORA J, TUDU KC, et al. A Comprehensive Investigation Into the Outcomes of Descemet’s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK) as a Treatment for Corneal Endothelial Disorders. Cureus. 2023;15(9): e46076. [13] GURNANI B, KAUR K, LALGUDI VG, et al. Risk Factors for Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty Rejection: Current Perspectives- Systematic Review. Clin Ophthalmol. 2023;17:421-440. [14] VIBERG A, SAMOLOV B, BYSTRÖM B. Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty versus Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty for Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: A National Registry-Based Comparison. Ophthalmology. 2023;130(12):1248-1257. [15] MELLES GR, WIJDH RH, NIEUWENDAAL CP. A technique to excise the descemet membrane from a recipient cornea (descemetorhexis). Cornea. 2004;23(3):286-288. [16] DAOUD YJ, MUNRO AD, DELMONTE DD, et al. Effect of cornea donor graft thickness on the outcome of Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156(5):860-866.e1. [17] VAN CLEYNENBREUGEL H, REMEIJER L, HILLENAAR T. Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty: effect of intraoperative lenticule thickness on visual outcome and endothelial cell density. Cornea. 2011;30(11):1195-1200. [18] SHETTY R, KAUSHIK J, KUMAR A, et al. Clinical study to estimate correlation between graft thickness as measured by anterior segment Optical Coherence Tomography and visual recovery after manual Descemet stripping endothelial keratoplasty. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2022; 66(2):118-124. [19] NEFF KD, BIBER JM, HOLLAND EJ. Comparison of central corneal graft thickness to visual acuity outcomes in endothelial keratoplasty. Cornea. 2011;30(4):388-391. [20] DENG SX, LEE WB, HAMMERSMITH KM, et al. Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty: Safety and Outcomes: A Report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2018;125(2): 295-310. [21] ROMANO D, AIELLO F, PAREKH M, et al. Incidence and management of early postoperative complications in lamellar corneal transplantation. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2023;261(11):3097-3111. [22] 顾绍峰,彭荣梅,肖格格,等. DSAEK手术植片厚度和大小对角膜内皮细胞密度的远期影响[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2022,40(12):1164-1169. [23] MOSKWA R, BLOCH F, VERMION JC, et al.Postoperative, but not preoperative, central corneal thickness correlates with the postoperative visual outcomes of Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty. PLoS One. 2023;18(3):e0282594. [24] 张莹莹.脱细胞猪角膜基质来源的超薄组织工程角膜内皮植片的构建[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2022. [25] KURJI KH, CHEUNG AY, ESLANI M, et al. Comparison of Visual Acuity Outcomes Between Nanothin Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty and Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty. Cornea. 2018;37(10):1226-1231. [26] ROSE-NUSSBAUMER J, LIN CC, AUSTIN A, et al. Descemet Endothelial Thickness Comparison Trial: Two-Year Results from a Randomized Trial Comparing Ultrathin Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty with Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty.Ophthalmology. 2021;128(8):1238-1240. [27] ROBERTS HW, MUKHERJEE A, AICHNER H, et al. Visual Outcomes and Graft Thickness in Microthin DSAEK--One-Year Results. Cornea. 2015;34(11):1345-1350. [28] DROUTSAS K, LAZARIDIS A, PAPACONSTANTINOU D, et al. Visual Outcomes After Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty Versus Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty-Comparison of Specific Matched Pairs. Cornea. 2016;35(6):765-771. [29] FU L, HOLLICK EJ. Comparison of Long-Term Outcomes of DSEK and DMEK in Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy. Cornea.2024;43(2):184-189. [30] PIOTROWIAK-SŁUPSKA I, KAŁUŻNY BJ, MALUKIEWICZ G. Corneal Optical Densitometry in the Evaluation of 2-Year Graft Function Following Endothelial Keratoplasty. J Clin Med. 2023;12(4):1552. [31] ANG M, SON Y, HTOON HM, et al. Five-Year Graft Survival Comparing Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty and Penetrating Keratoplasty. Ophthalmology. 2016;123(8):1646-1652. [32] LE B, BONNET C, YUNG M, et al. Descemet membrane endothelial keratoplasty in eyes with glaucoma. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2023;13(1): 13-20. [33] MAIER AK, KLAMANN MK, TORUN N, et al. Intraocular pressure elevation and post-DSEK glaucoma after Descemet`s stripping endothelial keratoplasty. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013; 251(4):1191-1198. [34] ESPANA EM, ROBRETSON ZM, HUANG B. Intraocular pressure changes following Descemet’s stripping with endothelial keratoplasty. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;248(2):237-242. [35] PRICE MO, JORDAN CS, MOORE G, et al. Graft rejection episodes after Descemet stripping with endothelial keratoplasty: part two: the statistical analysis of probability and risk factors. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009; 93(3):391-395. [36] ANSHU A, PRICE MO, PRICE FW, JR. Risk of corneal transplant rejection significantly reduced with Descemet’s membrane endothelial keratoplasty. Ophthalmology. 2012;119(3):536-540. [37] LEE WB, JACOBS DS, MUSCH DC, et al. Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty: safety and outcomes: a report by the American Academy of Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology. 2009;116(9):1818-1830. [38] WOO JH, ANG M, HTOON HM, et al. Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty Versus Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty and Penetrating Keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol. 2019;207: 288-303. [39] MANDAL S, MAHARANA PK, KAWERI L, et al. Management and prevention of corneal graft rejection. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2023;71(9): 3149-3159. [40] BASAK SK, BASAK S. Complications and management in Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty: analysis of consecutive 430 cases. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2014;62(2):209-218. [41] COVERT DJ, KOENIG SB.New triple procedure: Descemet’s stripping and automated endothelial keratoplasty combined with phacoemulsification and intraocular lens implantation. Ophthalmology. 2007;114(7):1272-1277. [42] ALDAVE AJ, CHEN JL, ZAMAN AS, et al. Outcomes after DSEK in 101 eyes with previous trabeculectomy and tube shunt implantation. Cornea. 2014;33(3):223-239. |
| [1] | Liu Ting, Yang Tingting, Ma Xiaona, Ma Haibin, Jin Yiran, Liang Xueyun. Immunoregulation of allograft rejection: a role played by human CD200+ sub-population from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2068-2073. |
| [2] | Gong Yu-bo1, Liu Yong2, Zhao Hong-wei1, Xu Qian-qian1, Guo Hui-ling1 . Expression levels of Foxp3 and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase in mouse corneal allograft rejection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4513-4517. |
| [3] | Tian Ying, Wu Jie, Wang Shuang-yong. Polyethylene glycol: an expert of cellular camouflage confusing the immune system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(10): 1625-1633. |
| [4] | Tu Ze-song, Liang Li-xue, Xing Ji-si. Reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament by allogeneic tendon graft: clinical curative effect and immune rejection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(15): 2190-2196. |
| [5] | Wang Heng, Lu Xiao-he, Zuo Wei. Effects of transforming growth factor-beta1 on tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression of corneal allografts during acute immunological rejection in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(5): 778-782. |
| [6] | Zhou Yu, Zheng Xue-yang, Lu Han-lan, Chen Yu, Fu Shang-xi, Wang Li-ming. Continuous monitoring of peripheral blood retinol blinding protein-4 in the early stage after renal transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(46): 7472-7477. |
| [7] | Yu Peng-cheng, Liu Yong-guang, Guo Ying, Li Min, Xiao Zong-yu, Hu Kong-he, Huang Jin-jun, Xin Jun, Wu Zhi-qiang, Zhao Ming. An experimental model of chronic renal allograft rejection in SD-Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(40): 6520-6525. |
| [8] | Sun Shu, Li Zhou-li, Cai Ming, Wang Qiang2 Jin Hai-long, Chen Chang-qing, Liu Zhi-jia, Kong Xiang-rui, Li Cong-ran, Shi Bing-yi. Expression and significance of interleukin-17 in rejection after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(51): 8275-8280. |
| [9] | Guo Cai-long, Mang Yuan-yi, Zhang Lei. A breakthrough in antibody-drug conjugates in anti-immune rejection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 773-778. |
| [10] | Cai Qiu-cheng. T lymphocytes and immune tolerance of liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 791-796. |
| [11] | Chen Chang-qing, Shi Bing-yi, Cai Ming, Zhao Yu-bo, Jin Bo-quan, Wang Chun-yan, Han Yong, Xiao Li, Zhou Wen-qiang, Li Zhou-li. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 in acute rejection after renal transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 730-735. |
| [12] | Yu Xiao-di, Wang Wei-zhong, Jiao Jie-ying, Zheng Jian-yong, Zhao Zheng-wei. Effect of artesunate on acute rejection after small intestine transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 761-766. |
| [13] | Ran Jiang-hua, Liu Jing, Zhang Xi-bing, Zhang Sheng-ning, Wu Shu-yuan, Li Lai-bang, Li Wang, Li Li. Variation of T cell subset during acute rejection after liver transplantation in rhesus monkeys [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 7948-7954. |
| [14] | Han Yong, Guo Hui, Cai Ming, Qian Ye-yong, Li Zhou-li, Zhou Wen-qiang, Wang Qiang, Xu Xiao-guang, Huang Hai-yan, Xiao Li, Wang Xin-ying, Shi Bing-yi. Expression of galectin-7 in acute antibody-mediated rejection after renal transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(42): 6884-6888. |
| [15] | Ran Jiang-hua, Zhang Xi-bing, Liu Jing, Zhang Sheng-ning, Li Lai-bang, Gao Yang, Chen Yi-ming, Li Wang, Li Li . Interleukin-6 expression in rhesus monkey models with acute rejection after liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(36): 5758-5763. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||