Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (36): 5758-5763.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.36.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interleukin-6 expression in rhesus monkey models with acute rejection after liver transplantation
Ran Jiang-hua, Zhang Xi-bing, Liu Jing, Zhang Sheng-ning, Li Lai-bang, Gao Yang, Chen Yi-ming, Li Wang, Li Li
- Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, the Affiliated Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Liver Transplantation Center of Organ Transplantation Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Revised:2014-06-26Online:2014-08-30Published:2014-08-30 -
Contact:Li Li, M.D., Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, the Affiliated Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Liver Transplantation Center of Organ Transplantation Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Ran Jiang-hua, M.D., Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Surgery, the Affiliated Ganmei Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Liver Transplantation Center of Organ Transplantation Institute of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the Major Project of Kunming Science and Technology Bureau, No. 08S100304
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ran Jiang-hua, Zhang Xi-bing, Liu Jing, Zhang Sheng-ning, Li Lai-bang, Gao Yang, Chen Yi-ming, Li Wang, Li Li . Interleukin-6 expression in rhesus monkey models with acute rejection after liver transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(36): 5758-5763.
share this article
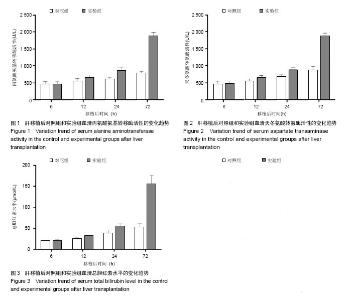
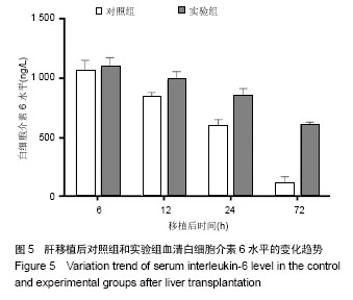
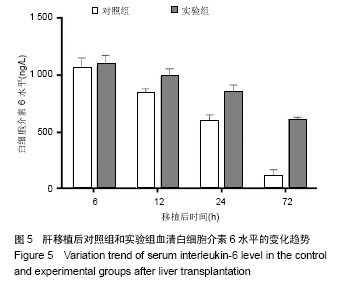
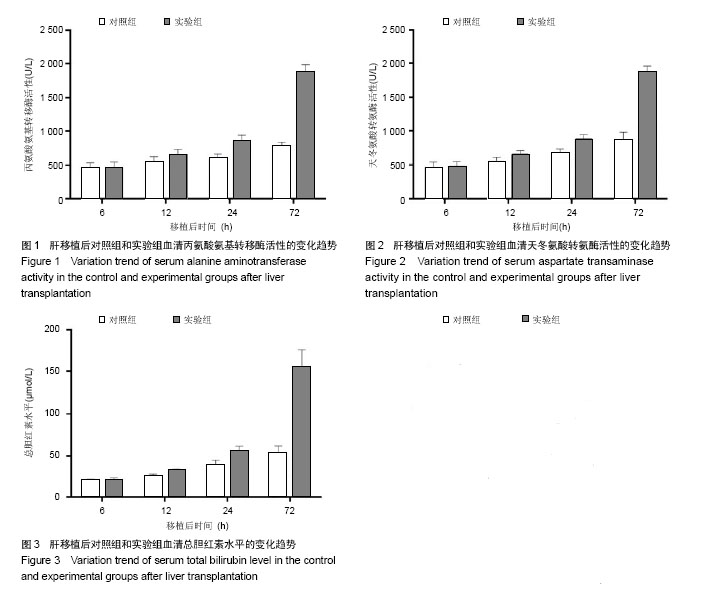
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验组和对照组分别建立恒河猴同种异体原位肝移植模型各4只,其中实验组术后缺失2只,对照组术后缺失1只,主要原因为移植后腹腔出血和呼吸循环功能衰竭所致,缺失恒河猴均及时予以补齐。 2.2 恒河猴肝移植后肝功能的变化 随着时间的延长,两组移植后血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶、天冬氨酸转氨酶及血清总胆红素水平均呈增加趋势,其中6 h和12 h时3个指标水平比较接近,两组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。但移植后24 h和72 h时血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶、天冬氨酸转氨酶及血清总胆红素水平明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),可见实验组肝细胞受到机体炎性细胞的攻击损伤较对照组明显(图1-3)。"
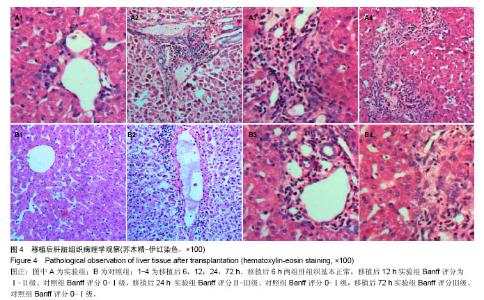
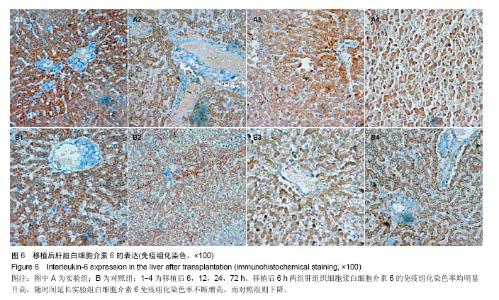
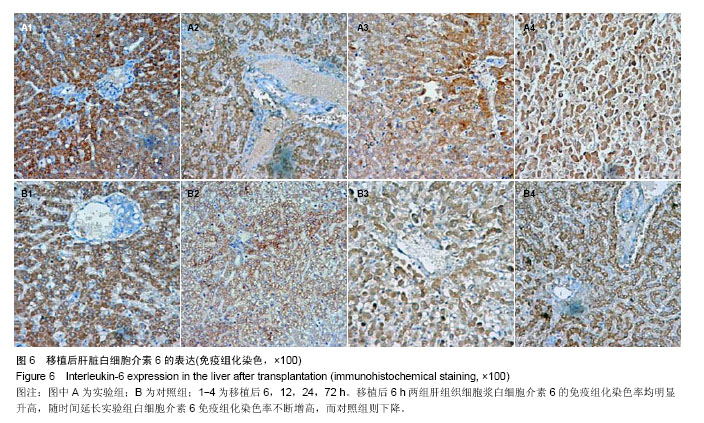
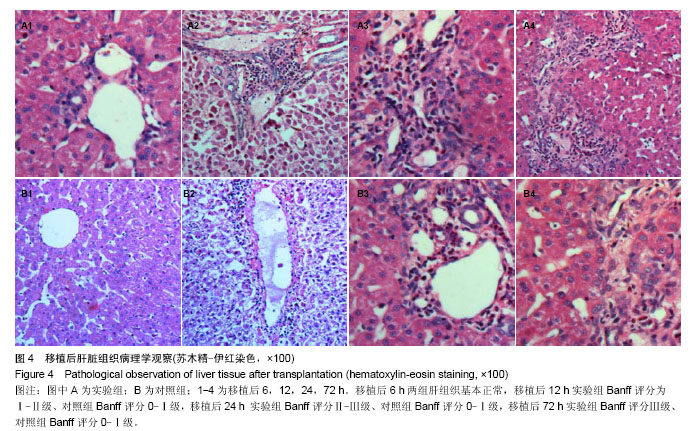
2.3 恒河猴肝移植后肝脏组织病理学观察 实验组和对照组在移植后6 h镜下观察:肝组织基本正常,未见排斥反应(图4A1,B1)。移植后12 h,苏木精-伊红染色镜下观察:实验组有轻度的排斥反应,Banff评分Ⅰ-Ⅱ级;而对照组Banff评分0-Ⅰ级(图4A2,B2)。移植后24 h,苏木精-伊红染色镜下观察:实验组有中度至重度排斥反应,Banff评分Ⅱ-Ⅲ级,而对照组有轻度急性排斥反应,Banff评分0-Ⅰ级(图4A3,B3)。移植后72 h,苏木精-伊红染色镜下观察:实验组有重度排斥反应,Banff评分Ⅲ级,而对照组有轻度急性排斥反应,Banff评分0-Ⅰ级,实验组排斥反应程度重于对照组,且该时点两组Banff评分比较,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05,图4A4,B4)。"
| [1] Xie XJ, Ye YF, Zhou L,et al. Th17 promotes acute rejection following liver transplantation in rats. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010;11(11):819-827. [2] Casas-Melley AT, Falkenstein KP, Flynn LM,et al. Improvement in renal function and rejection control in pediatric liver transplant recipients with the introduction of sirolimus. Pediatr Transplant. 2004;8(4):362-366. [3] Mas VR, Fisher RA, Maluf DG,et al. Polymorphisms in cytokines and growth factor genes and their association with acute rejection and recurrence of hepatitis C virus disease in liver transplantation.Clin Genet. 2004;65(3): 191-201. [4] Cueto-Manzano AM, Morales-Buenrostro LE, González-Espinoza L,et al. Markers of inflammation before and after renal transplantation.Transplantation. 2005;80(1): 47-51. [5] Boniface K, Lecron JC, Bernard FX,et al. Keratinocytes as targets for interleukin-10-related cytokines: a putative role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2005;16(4): 309-319. [6] Murano M, Maemura K, Hirata I,et al. Therapeutic effect of intracolonically administered nuclear factor kappa B (p65) antisense oligonucleotide on mouse dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000; 120(1):51-58. [7] 冉江华,张升宁,刘静,等.恒河猴同种异体原位肝移模型的改进[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2010,17(7):694-698. [8] 冉江华,李铸,刘静,等.二袖套法建立恒河猴原位肝移植的稳定模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(5):762-768. [9] Busuttil RW, Lake JR. Role of tacrolimus in the evolution of liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2004;77(9 Suppl): S44-51. [10] Solez K. History of the Banff classification of allograft pathology as it approaches its 20th year.Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010;15(1):49-51. [11] Racusen LC, Halloran PF, Solez K. Banff 2003 meeting report: new diagnostic insights and standards.Am J Transplant. 2004; 4(10):1562-1566. [12] Girnita DM, Burckart G, Zeevi A. Effect of cytokine and pharmacogenomic genetic polymorphisms in transplantation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008;20(5):614-625. [13] Cordero-Pérez P, Torres-González L, Muñoz-Espinosa LE. Cytokines expression in peripheral blood cells of patients with orthotopic liver transplant: preliminary results. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2011;76(2):108-112. [14] Yao J, Feng XW, Yu XB,et al. Recipient IL-6-572C/G genotype is associated with reduced incidence of acute rejection following liver transplantation.J Int Med Res. 2013; 41(2):356-364. [15] Ravaglia G, Forti P, Maioli F, et al. Associations of the -174 G/C interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism with serum interleukin 6 and mortality in the elderly.Biogerontology. 2005;6(6):415-423. [16] Tono T, Monden M, Yoshizaki K,et al. Biliary interleukin 6 levels as indicators of hepatic allograft rejection in rats. Transplantation. 1992;53(6):1195-1201. [17] Kita Y, Iwaki Y, Demetris AJ,et al. Evaluation of sequential serum interleukin-6 levels in liver allograft recipients. Transplantation. 1994;57(7):1037-1041. [18] Kunz D, Pross M, König W,et al. Diagnostic relevance of procalcitonin, IL-6 and cellular immune status in the early phase after liver transplantation.Transplant Proc. 1998;30(5): 2398-2399. [19] Boros P, Suehiro T, Curtiss S,et al. Differential contribution of graft and recipient to perioperative TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6 and IL-8 levels and correlation with early graft function in clinical liver transplantation.Clin Transplant. 1997;11(6): 588-592. [20] Afzali B, Lombardi G, Lechler RI,et al. The role of T helper 17 (Th17) and regulatory T cells (Treg) in human organ transplantation and autoimmune disease.Clin Exp Immunol. 2007;148(1):32-46. [21] Függer R, Hamilton G, Steininger R,et al. Intraoperative estimation of endotoxin, TNF alpha, and IL-6 in orthotopic liver transplantation and their relation to rejection and postoperative infection.Transplantation. 1991;52(2): 302-306. [22] Ohzato H, Yoshizaki K, Nishimoto N,et al. Interleukin-6 as a new indicator of inflammatory status: detection of serum levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein after surgery. Surgery. 1992;111(2):201-209. [23] Tilg H, Nordberg J, Vogel W,et al.Circulating serum levels of interleukin 6 and C-reactive protein after liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1992;54(1):142-146. [24] Debonera F, Aldeguer X, Shen X,et al. Activation of interleukin-6/STAT3 and liver regeneration following transplantation.J Surg Res. 2001;96(2):289-295. [25] Kutukculer N, Clark K, Rigg KM,et al. The value of posttransplant monitoring of interleukin (IL)-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and soluble CD23 in the plasma of renal allograft recipients.Transplantation. 1995;59(3):333-340. [26] Gorczynski RM, Adams RB, Levy GA,et al. Correlation of peripheral blood lymphocyte and intragraft cytokine mRNA expression with rejection in orthotopic liver transplantation.Surgery. 1996;120(3):496-502. [27] Takai Y, Wong GG, Clark SC,et al. B cell stimulatory factor-2 is involved in the differentiation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes.J Immunol. 1988;140(2):508-512. [28] Brouckaert P, Spriggs DR, Demetri G,et al. Circulating interleukin 6 during a continuous infusion of tumor necrosis factor and interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1989;169(6):2257- 2262. [29] Cho KA, Lim GW, Joo SY, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow cells reduces CCl4 -induced liver fibrosis in mice. Liver Int. 2011;31(7):932-939. [30] Ren X, Hogaboam C, Carpenter A,et al. Stem cell factor restores hepatocyte proliferation in IL-6 knockout mice following 70% hepatectomy.J Clin Invest. 2003;112(9):1407- 1418. |
| [1] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [2] | Li Liqiang, Jiao Longxing, Zhang Wu, Yan Wentao, Li Jian, Li Minghao. Effect of immature dendritic cells derived from bone marrow on rejection of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2025-2029. |
| [3] | Yang Feng, Chang Lipu, Huang Changshan, Gong Xiaoguang, Chang Shunwu. Macrolide antibiotics protects against ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4176-4182. |
| [4] | Yang Fan, Liu Baoyi, Cao Meng, Zhu Xiaoshu, Zhang Yu, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Basic fibroblast growth factors protect chondrocytes by antagonizing extracellular inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3621-3626. |
| [5] |
Li Qinxuan, Wang Yizhi, Xu Yan, Zhang Huayang, Lü Qixuan, Zhang Cheng, He Zhengyun, Zhang Xiao, Yang Zheng.
Effects of dexamethasone combined with estrogen on the
expression of interleukin-6, Caspase3 and Bcl-2 after spinal cord contusion in
rats |
| [6] | Liu Ting, Yang Tingting, Ma Xiaona, Ma Haibin, Jin Yiran, Liang Xueyun. Immunoregulation of allograft rejection: a role played by human CD200+ sub-population from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(13): 2068-2073. |
| [7] | Liu Mengyuan1, Fang Fang2. Risk factors for multi-drug resistant organisms infection after liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1109-1114. |
| [8] | Li Peng, Yang Shuye, Zhang Kai, Jia Long, Du Gangqiang, Liu Dong, Zhang Xinjun, Zhang Degang, Wang Zhigang. Influence of different wear particles on human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 894-900. |
| [9] | Chen Peng, Shi Xiaotian, Guo Yu, Qiu Xunyong, Wang Yan. Longbie capsule combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 797-802. |
| [10] | Zhao Hongshun, A Jiancuo, Gao Shunhong, Li Yonggang, Guo Liping. Intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 after local application of tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 493-498. |
| [11] | Wu Xingyuan, Zhang Guoru, Liu Tang, Zhou Caisheng. Intravenous and intraarticular tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and inflammatory response during cemented posterior cruciate ligament-retaining unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5753-5759. |
| [12] | Meng Qingxi1, Wang Weiheng2, Sun Aijun3, Xi Yanhai1, Ye Xiaojian1. Protective effects of methane saturated saline on endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 396-403. |
| [13] | Gao Hongqiang, Liu Jing, Li Zhiqiang, Wang Hailei, Zhao Xiongqi, Zhang Shengning, Ran Jianghua, Li Li . Ulinastatin improves rat liver metabolism after reduced-size liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 435-440. |
| [14] | Gao Hua1, 2, Li Yanxia1, Wang Dan1, Yang Xinling1 . Protective effects and the mechanism of lipoic acid on cell model of Parkinson’s disease induced by lipopolysaccharide [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 447-452. |
| [15] | Chen Jun1, Lin Jie2, Zhao Zhongsheng2, Huang Yanfeng2, Wu Guangwen3. Effect of Wutou Decoction on TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in synovial tissue of rat models with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4381-4386. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||