Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (13): 2054-2060.doi: 10.12307/2024.133
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hypoxic postconditioning protects myocardium by regulating autophagy in aging cardiomyocytes through piRNA-005854
Chi Hongyang1, 2, Yang Huixia1, 2, Hao Yinju3, Yang Anning2, 4, Bai Zhigang2, 5, Jiao Yun2, 6, Xiong Jiantuan2, 4, Ma Shengchao2, 4, Jiang Yideng2, 4
- 1School of Clinical Medicine, 2National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Disease Research, 3School of Pharmacy, 4School of Basic Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 5People’s Hospital of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China; 6Department of Infection, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2023-01-28Accepted:2023-04-07Online:2024-05-08Published:2023-08-28 -
Contact:Jiang Yideng, MD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Disease Research; School of Basic Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China Ma Shengchao, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Disease Research; School of Basic Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Chi Hongyang, Master candidate, School of Clinical Medicine; National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Metabolic Cardiovascular Diseases Research, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Key Project of Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2022BFH02013 (to HYJ); Key Project of Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2020BFH02003 (to YAN); Key Project of Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2021BEG02033 (to XJT); Key Project of Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2020BEG03005 (to JY); Key Project of Key Research and Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, No. 2020BFH02001 (to BZG); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U21A20343 (to JYD); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160049 (to XJT); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81900273 (to MSC); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82060412 (to JY); Fundamental Research Funds for Central Public Welfare Scientific Research Institutes of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, No. 2019PT330002 (to JYD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chi Hongyang, Yang Huixia, Hao Yinju, Yang Anning, Bai Zhigang, Jiao Yun, Xiong Jiantuan, Ma Shengchao, Jiang Yideng. Hypoxic postconditioning protects myocardium by regulating autophagy in aging cardiomyocytes through piRNA-005854[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(13): 2054-2060.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
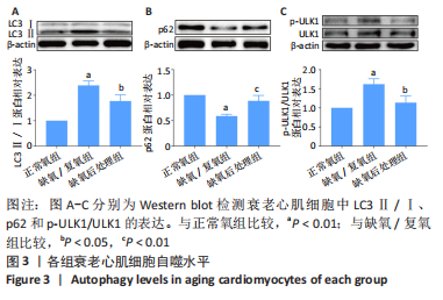
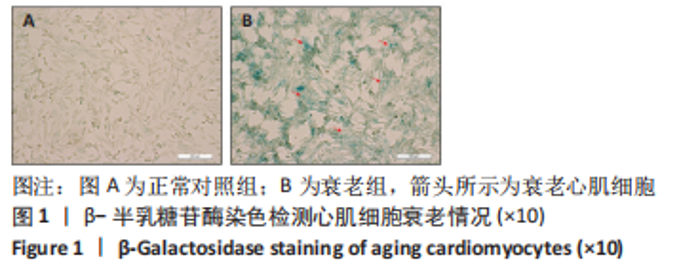
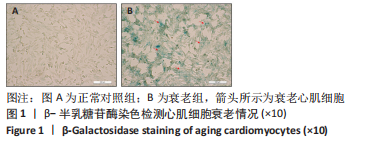
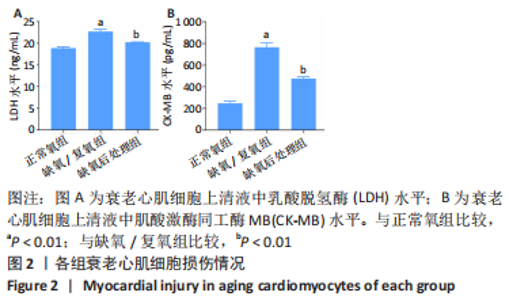
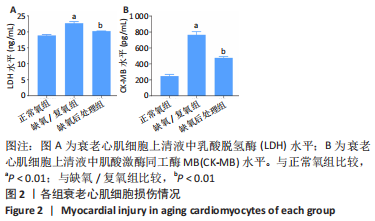
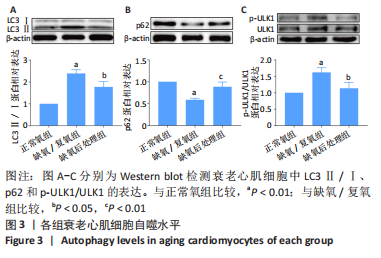
2.3 LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ、p62、ULK1以及p-ULK1在衰老心肌细胞中的表达 采用Western blot检测正常氧组、缺氧/复氧组、缺氧后处理组衰老心肌细胞LC3Ⅱ/LC3Ⅰ、p62、ULK1以及p-ULK1蛋白的表达。实验结果显示:与正常氧组相比,缺氧/复氧组LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ显著升高,p62表达水平显著降低,ULK1总蛋白表达水平基本不变,但ULK1磷酸化水平显著升高,表明衰老心肌细胞经缺氧/复氧处理后自噬水平升高;与缺氧/复氧组相比,缺氧后处理组LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ显著降低,p62表达水平显著升高,ULK1总蛋白表达水平基本不变,但ULK1磷酸化水平显著降低,提示缺氧后处理可抑制衰老心肌细胞自噬,见图3。"
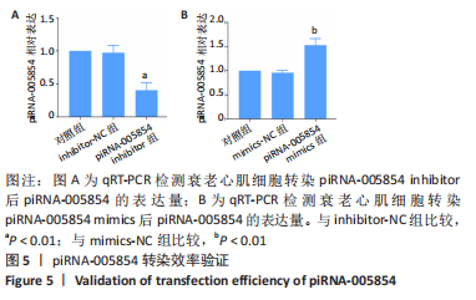
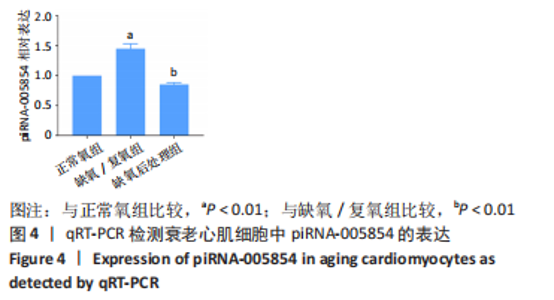
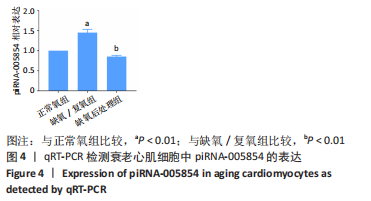
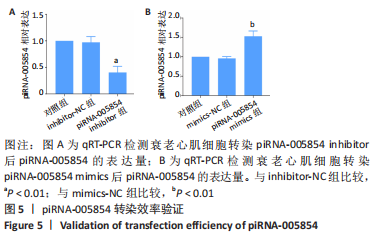
2.5 干扰和过表达piRNA-005854在衰老心肌细胞中的验证 为了明确piRNA-005854对缺氧后处理衰老心肌细胞自噬的作用,分别将piRNA-005854 inhibitor和piRNA-005854 mimics转染至衰老心肌细胞,采用qRT-PCR检测piRNA-005854的表达。实验结果显示,与inhibitor-NC组相比,piRNA-005854 inhibitor组piRNA-005854的表达显著降低;而与mimics-NC组相比,piRNA-005854 mimics组piRNA-005854的表达明显升高;表明piRNA-005854干扰和过表达片段转染成功,并能在衰老心肌细胞中稳定表达,见图5。"
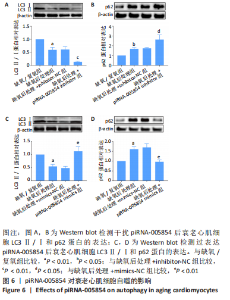
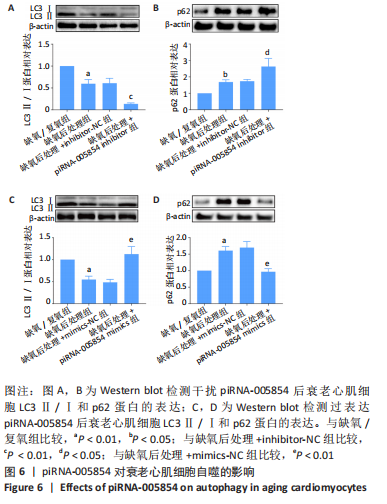
2.6 piRNA-005854对衰老心肌细胞自噬的影响 为了进一步探讨piRNA-005854对缺氧后处理衰老心肌细胞自噬的作用,将piRNA-005854 inhibitor及inhibitor-NC转染至衰老心肌细胞后,给予缺氧后处理,然后采用Western blot检测自噬相关蛋白LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ和p62的蛋白表达。实验结果显示,与inhibitor-NC组相比,piRNA-005854 inhibitor组LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ水平明显降低,而p62的蛋白表达显著升高,见图6A,B。同时,将piRNA-005854 mimics及mimics-NC转染至衰老心肌细胞后,给予缺氧后处理。Western blot结果显示,与mimics-NC组相比,piRNA-005854 mimics组LC3Ⅱ/Ⅰ水平显著升高,而p62的蛋白表达水平降低,见图6C,D,表明缺氧后处理通过piRNA-005854调控衰老心肌细胞自噬。"
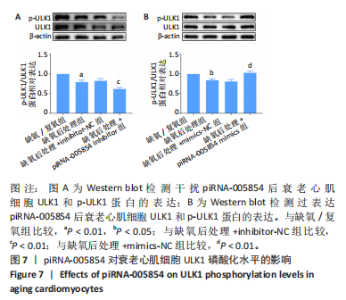
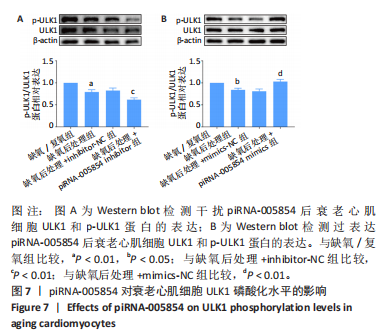
2.7 piRNA-005854对衰老心肌细胞内ULK1磷酸化修饰的影响 进一步探讨piRNA-005854在自噬中发挥的调控作用,将piRNA-005854 inhibitor及piRNA-005854 mimics转染衰老心肌细胞,给予缺氧后处理,采用Western blot检测衰老心肌细胞中ULK1蛋白的表达变化。实验结果显示,与inhibitor-NC组相比,piRNA-005854 inhibitor 组ULK1总蛋白表达水平基本不变,但ULK1磷酸化水平显著降低,见图7A。与mimics-NC组相比,转染piRNA-005854 mimics组ULK1总蛋白表达水平基本不变,但ULK1磷酸化水平明显升高,见图7B,表明piRNA-005854通过调控ULK1磷酸化来调控缺氧后处理的衰老心肌细胞自噬。"
| [1] SARROPOULOS I, MARIN R, CARDOSO-MOREIRA M, et al. Developmental dynamics of lncRNAs across mammalian organs and species. Nature. 2019;571(7766):510-514. [2] DÍAZ-VESGA MC, ZÚÑIGA-CUEVAS Ú, RAMÍREZ-REYES A, et al. Potential Therapies to Protect the Aging Heart Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:770421. [3] LIU D, XU L, ZHANG X, et al. Snapshot: Implications for mTOR in Aging-related Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Aging Dis. 2019;10(1):116-133. [4] MA W, ZHU K, YIN L, et al. Effects of ischemic postconditioning and long non-coding RNAs in ischemic stroke. Bioengineered. 2022;13(6): 14799-14814. [5] BRAVO-SAN PEDRO JM, KROEMER G, GALLUZZI L. Autophagy and Mitophagy in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2017;120(11):1812-1824. [6] DONG Y, CHEN H, GAO J, et al. Molecular machinery and interplay of apoptosis and autophagy in coronary heart disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;136:27-41. [7] WANG Y, ZHOU L, SU W, et al. Selective Inhibition of PKCβ2 Restores Ischemic Postconditioning-Mediated Cardioprotection by Modulating Autophagy in Diabetic Rats. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:2408240. [8] CHEN Z, HU Z, LU Z, et al. Differential microRNA profiling in a cellular hypoxia reoxygenation model upon posthypoxic propofol treatment reveals alterations in autophagy signaling network. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:378484. [9] ZHANG J, CHEN S, LIU K. Structural insights into piRNA biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2022;1865(2):194799. [10] ANZELON TA, CHOWDHURY S, HUGHES SM, et al. Structural basis for piRNA targeting. Nature. 2021;597(7875):285-289. [11] CZECH B, MUNAFÒ M, CIABRELLI F, et al. piRNA-Guided Genome Defense: From Biogenesis to Silencing. Annu Rev Genet. 2018;52: 131-157. [12] YANG Q, LI R, LYU Q, et al. Single-cell CAS-seq reveals a class of short PIWI-interacting RNAs in human oocytes. Nat Commun. 2019; 10(1):3389. [13] WANG K, ZHOU LY, LIU F, et al. PIWI-Interacting RNA HAAPIR Regulates Cardiomyocyte Death After Myocardial Infarction by Promoting NAT10-Mediated ac4 C Acetylation of Tfec mRNA. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(8):e2106058. [14] 王琳,丁秀云,刘谟焓,等.D-半乳糖对幼鼠心肌细胞拟衰老作用的实验 [J].中国临床康复,2005,9(39):25-27,193. [15] 徐灵博,郝银菊,丁宁,等.衰老心肌细胞缺氧后处理中miR-204的作用 [J].广东医学,2017,38(18):2764-2767. [16] 胡大一,韩雅玲,宁光,等. 中国心血管病一级预防指南 [J].中华心血管病杂志,2020,48(12):1000-1038. [17] IBÁÑEZ B, HEUSCH G, OVIZE M, et al. Evolving therapies for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(14):1454-1471. [18] BIRNBACH B, HÖPNER J, MIKOLAJCZYK R. Cardiac symptom attribution and knowledge of the symptoms of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020;20(1):445. [19] 盛菽洋, 程江.生化标志物检测对急性心肌梗死再灌注的临床应用 [J]. 农垦医学,2021,43(3):248-251. [20] PIRZEH L, BABAPOUR V, BADALZADEH R, et al. Pretreatment with vildagliptin boosts ischemic-postconditioning effects on cardioprotection and expression profile of genes regulating autophagy and mitochondrial fission/fusion in diabetic heart with reperfusion injury. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019;392(11): 1371-1382. [21] HEUSCH G. Molecular basis of cardioprotection: signal transduction in ischemic pre-, post-, and remote conditioning. Circ Res. 2015;116(4): 674-699. [22] HUMMITZSCH L, ZITTA K, BERNDT R, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning attenuates intestinal mucosal damage: insight from a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):136. [23] BALLIN M, NORDSTRÖM P, NIKLASSON J, et al. Associations of Visceral Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Density With Incident Stroke, Myocardial Infarction, and All-Cause Mortality in Community-Dwelling 70-Year-Old Individuals: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(9):e020065. [24] MA Y, MOUTON AJ, LINDSEY ML. Cardiac macrophage biology in the steady-state heart, the aging heart, and following myocardial infarction. Transl Res. 2018;191:15-28. [25] AMAN Y, SCHMAUCK-MEDINA T, HANSEN M, et al. Autophagy in healthy aging and disease. Nat Aging. 2021;1(8):634-650. [26] SU X, SHEN Y, JIN Y, et al. Aging-Associated Differences in Epitranscriptomic m6A Regulation in Response to Acute Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Female Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12:654316. [27] DE LUCIA C, PIEDEPALUMBO M, WANG L, et al. Effects of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury on plasma metabolomic profile during aging. Aging Cell. 2021;20(1):e13284. [28] SAHA S, PANIGRAHI DP, PATIL S, et al. Autophagy in health and disease: A comprehensive review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;104:485-495. [29] WU X, LIU Z, YU XY, et al. Autophagy and cardiac diseases: Therapeutic potential of natural products. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(1):314-341. [30] JUNG S, CHOE S, WOO H, et al. Autophagic death of neural stem cells mediates chronic stress-induced decline of adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive deficits. Autophagy. 2020;16(3):512-530. [31] WANG X, GUO Z, DING Z, et al. Inflammation, Autophagy, and Apoptosis After Myocardial Infarction. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(9):e008024. [32] HEUSCH G. Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(12):773-789. [33] DU J, LI Y, ZHAO W. Autophagy and Myocardial Ischemia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1207:217-222. [34] LI G, DING N, XIONG J, et al. Ischemic Postconditioning Protects against Aged Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Transcriptional and Epigenetic Regulation of miR-181a-2-3p. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:9635674. [35] LI Y, CHEN Y. AMPK and Autophagy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1206:85-108. [36] TONG M, SAITO T, ZHAI P, et al. Alternative Mitophagy Protects the Heart Against Obesity-Associated Cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2021; 129(12):1105-1121. [37] KOBAYASHI S, XU X, CHEN K, et al. Suppression of autophagy is protective in high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte injury. Autophagy. 2012;8(4):577-592. [38] SIOMI H, SIOMI MC. On the road to reading the RNA-interference code. Nature. 2009;457(7228):396-404. [39] YANG J, XUE FT, LI YY, et al. Exosomal piRNA sequencing reveals differences between heart failure and healthy patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(22):7952-7961. [41] PERERA BPU, TSAI ZT, COLWELL ML, et al. Somatic expression of piRNA and associated machinery in the mouse identifies short, tissue-specific piRNA. Epigenetics. 2019;14(5):504-521. [41] RAJAN KS, VELMURUGAN G, GOPAL P, et al. Abundant and Altered Expression of PIWI-Interacting RNAs during Cardiac Hypertrophy. Heart Lung Circ. 2016;25(10):1013-1020. [42] 滕增光. piRNA-DQ765261/Bcl-xL和AMPK/ULK在镉诱导生精细胞自噬中的作用 [D].武汉:武汉科技大学,2021. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [3] | Sheng Siqi, Xie Lin, Zhao Xiangyu, Jiang Yideng, Wu Kai, Xiong Jiantuan, Yang Anning, Hao Yinju, Jiao Yun. Involvement of miR-144-3p in Cbs+/- mouse hepatocyte autophagy induced by high-methionine diet [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1289-1294. |
| [4] | Yue Yun, Wang Peipei, Yuan Zhaohe, He Shengcun, Jia Xusheng, Liu Qian, Li Zhantao, Fu Huiling, Song Fei, Jia Menghui. Effects of croton cream on JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathway and neuronal apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1186-1192. |
| [5] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Li Wenbo, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. Effect of aerobic exercise on glycolipid metabolism, skeletal muscle inflammation and autophagy in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [6] | Zhou Bangyu, Li Jie, Ruan Yushang, Geng Funeng, Li Shaobo. Effects of Periplaneta americana powder on motor function and autophagic protein Beclin-1 in rats undergoing spinal cord hemisection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [7] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [8] | Huang Yuxin, Liang Wenzi, Chen Xiuwen, Ni Na, Zhao Yinglin, Lin Changmin. Role of autophagy in hair regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1112-1117. |
| [9] | Liu Qiwei, Zhang Junhui, Yang Yuan, Wang Jinjuan. Role and mechanism of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1015-1020. |
| [10] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [11] | Xue Jingwen, Wang Fangfang, Zhang Xin, Pang Ruifeng, Wang Xiaoye, Ma Xiaoru. Effect of ganoderma spore on mitochondrial autophagy and apoptosis in testicular tissue of diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 562-568. |
| [12] | Yan Binghan, Li Zhichao, Su Hui, Xue Haipeng, Xu Zhanwang, Tan Guoqing. Mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine monomers in the treatment of osteoarthritis by targeting autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 627-632. |
| [13] | Wang Jingfeng, Wen Dengtai, Wang Shijie, Gao Yinghui. Atg-mediated autophagy, exercise and skeletal muscle aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 295-301. |
| [14] | Zhao Kui, Pan Runsang, Lan Fengjun, Deng Jin, Chen Houping. Molecular mechanisms of autophagy-apoptosis interactions in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2912-2917. |
| [15] | Luo Fu, Shu Xiangzhong, Liu Danni, Tan Jinqu, Peng Ting, Huang Xiarong, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Wang Jinling, Zhou Jun. Electroacupuncture reduces inflammatory factor expression by suppressing Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2186-2190. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||