Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (6): 955-960.doi: 10.12307/2023.788
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty
Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin
- The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-11-21Accepted:2023-01-18Online:2024-02-28Published:2023-07-12 -
Contact:Huang Jian, MD, Chief physician, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Yang Yifeng, Master, Attending physician, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:Youth Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2022QN034 (to YYF); 2022 Health Science and Technology Project of Autonomous Region, No. 202201352 (to HJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
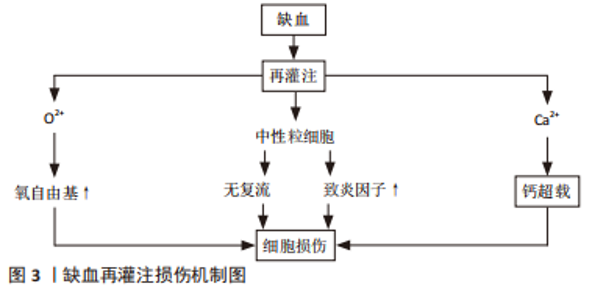
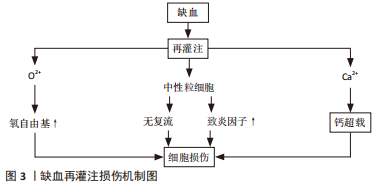
2.1 IRI的发生机制 2.1.1 氧自由基作用 氧自由基过多可能是IRI的重要机制之一。体内氧自由基与抗氧化剂之间失调,即发生氧化应激反应,发生蛋白质、核酸尤其是脂类的过氧化而引起组织细胞严重损伤[4]。最近有研究表明,在IRI的所有可能病理机制中,自由基损伤在该过程中起关键作用。自由基导致蛋白质功能障碍、DNA损伤和脂质过氧化,导致细胞死亡[5]。XIAMG等[6]研究发现,氧化应激是再灌注损伤中最重要的病理机制之一,它通过多种途径导致心肌细胞凋亡、自噬、炎症和其他一些损伤,从而导致不可逆的心肌细胞损伤和心脏功能障碍。 活性氧的过量产生作为再灌注损伤发生的关键因素受到持续关注。因此,目前更多的研究在关注缺血再灌注后过量活性氧产生的主要细胞和酶来源。迄今为止,黄嘌呤氧化酶、NADPH氧化酶、线粒体和未偶联的一氧化氮合酶被视为活性氧产生的主要酶来源[7]。 2.1.2 细胞内钙超载 钙超载指细胞内钙浓度显著增加导致细胞结构破坏和代谢失调,该现象在IRI中广泛存在。肌膜的Ca2+通道和肌浆网的Ca2+通道启动共同维持细胞内Ca2+浓度的上升,随后Ca2+、肌浆网、线粒体、肌丝和蛋白水解级联(即钙蛋白酶激活)之间的相互作用共同导致细胞损伤[8]。BODALIA等[9]在内质网Ca2+对脑缺血期间神经元细胞的影响研究中发现,当发生钙超载时氧自由基生成会增多,内质网应激、Ca2+流入增加、膜通透性增加,并最终导致细胞凋亡死亡,印证了钙超载会引起组织、细胞损伤。IRI的发病机制是多因素的,但线粒体Ca2+超载起着核心作用。一种新型Ca2+通道抑制剂——2-氨基乙氧基二苯基硼酸盐,可用于预防IRI。NICOUD等[10]实验表明,2-氨基乙氧基二苯基硼酸盐以剂量依赖性方式阻断离体肝线粒体中的Ca2+摄取,并减少Hep G2细胞中的细胞Ca2+积累,从而减轻肝IRI反应。该实验从侧面印证了降低钙超载可减轻IRI,表面钙超载在IRI中发挥重要作用。 2.1.3 中性粒细胞激活引起的组织损伤 近年来研究表明,中性粒细胞聚集、激活介导的微血管损伤在IRI中起着重要作用,IRI的另一个关键因素是中性粒细胞对梗死区域的激活和浸润。多项研究确定了中性粒细胞激活和其中涉及的物质,主要包括细胞黏附分子,特别是选择素和β2整合素,因为它们的拮抗剂反复被发现可以减少中性粒细胞活化和梗死面积[11]。KIKUCHI等[12]研究证实,IRI时机体局部会有大量中性粒细胞黏附及浸润,活化的中性粒细胞可通过细胞因子、核因子、内皮细胞、黏附分子、氧自由基、蛋白酶等相互作用,引起炎症反应失控及毛细血管堵塞,加重组织缺血缺氧状态,进而导致骨骼肌严重损伤。在IRI期间,肝脏会发生强烈的炎症过程,这种肝脏炎症由缺血期引发,但主要发生在再灌注阶段,其特征是大量中性粒细胞募集到肝脏,细胞因子、趋化因子和危险信号的产生导致常驻肝细胞、白细胞和库普弗细胞的激活。同样有研究表明,消除过多的中性粒细胞或抑制其功能可减少肝损伤和炎症[13]。 2.1.4 IRI的其他机制 一氧化氮损伤:研究认为,生理浓度的一氧化氮可作为内皮细胞衍生舒张因子扩张血管,阻止血小板的聚集;浓度降低时对机体有一定保护作用,浓度过高时可致细胞和组织损伤[14]。KHANNA等[15]针对骨骼肌IRI的研究表明,一氧化氮在再灌注损伤期间可以表现出保护作用或细胞毒性作用;使用转基因小鼠,无论是一氧化氮合酶基因敲除动物,还是过度表达一氧化氮合酶亚型的动物,通过直接测量一氧化氮或使用抑制剂,都证明了一氧化氮在骨骼肌再灌注损伤中的作用;在缺血的前20 min内刺激了一氧化氮的产生,随着早期再灌注一氧化氮含量逐渐下降,再灌注后期出现第二个更高的一氧化氮峰值。 无复流现象:当心肌、脑、肾和骨骼肌等全身器官组织局部缺血一段时间再恢复血流后部分缺血区未能充分复流,此现象称为无复流现象。动物实验发现,缺血大鼠再灌注过程中可见荧光染料缺失区,提示急性心肌缺血60 min再灌注120 min大鼠无复流现象,并伴有心脏微血管内皮结构和功能破坏[16]。无复流现象的特征在于缺血再灌注时微血管功能和微结构的损伤,微栓子是导致无复流的主要原因。 细胞凋亡:细胞凋亡是细胞程序性死亡形式之一,通过特定的基因调控完成,在肢体IRI中具有不可忽视的作用。HU等[17]研究认为,Bcl-2家族与凋亡密切相关,Bcl-2家族是一种重要的抗凋亡基因,Bcl-2可通过线粒体途径及P53基因依赖性途径发挥抗细胞凋亡作用。半胱氨酸天冬氨酸蛋白酶(caspase)家族是细胞凋亡的执行者,通过级联反应可以在细胞凋亡中发挥重要作用[18]。此外,还发现即刻早反应基因(IEG,如c-fos基因、c-jun基因)、核因子кB等,也在IRI中发挥重要作用[19]。 缺血再灌注部分损伤机制如图3所示。研究历程如图4所示。"
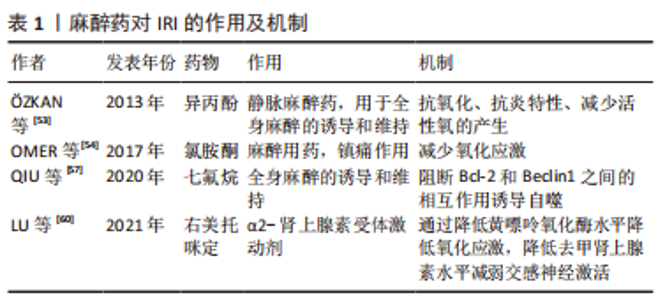
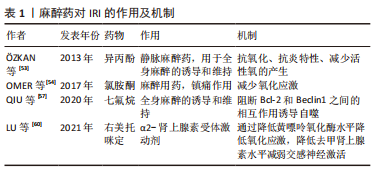
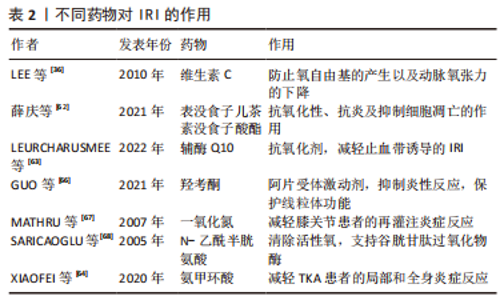
2.2 止血带诱导的IRI对局部骨骼肌的影响 肢体IRI后,由机体生理、生化和免疫学方面变化诱导的急性炎症反应可引起骨骼肌损伤。病理学检测发现肢体IRI后肌细胞水肿,形态改变,随后肌细胞核变大、数量增多,间质细胞增生,肌细胞功能下降或丧失,进而器官或肢体功能减弱甚至坏死[20]。再灌注会引发强烈的局部炎症,尤其是在再灌注的最初几个小时。从再灌注开始,时间上重叠的几种机制将导致IRI的发生:线粒体衰竭和活性氧的产生,坏死和损伤细胞释放内源性危险分子,趋化因子和促炎细胞因子的分泌,补体的激活和中性粒细胞的募集,这些非特异性信号导致血管扩张、内皮功能障碍、血管渗漏增加,随后是促炎途径的自放大网络,白细胞不断被招募和激活,这些变化会矛盾地加剧损伤和细胞死亡[21]。 已有研究证明在TKA中应用止血带通过触发细胞级联反应可导致骨骼肌中产生IRI。在缺血和再灌注早期,蛋白质合成的起始和延伸受到抑制,导致蛋白质合成减少[22]。止血带应用期间,在缺血60 min时,骨骼肌蛋白水解的主要途径泛素蛋白酶体系统上调,表明蛋白质降解增加[23]。IRI损伤导致的蛋白质代谢变化会进一步导致游离氨基酸的动员,进而导致股四头肌萎缩,有研究表明,TKA术后的肌肉萎缩以每天1%的速度发生,2周时损失14%,6周时为18% [24]。在对TKA术后基因表达谱的分析中发现,止血带释放后2 h,骨骼肌细胞中的72个基因显著上调,这些基因中有很大一部分调节细胞应激途径,这表明肌肉细胞在IRI时存在细胞应激途径中基因的上调,能够对细胞应激产生显著反应[25],与细胞应激途径相关的基因被改变,可能诱导细胞凋亡。 骨骼肌IRI的其他可能机制也有研究[26-27]。许多研究报道,血管活性物质包括内皮素1以及神经元和内皮型一氧化氮合酶的失衡导致内皮功能障碍,参与骨骼肌IRI[28-29]。内皮素1组织蛋白水平的升高发生在IRI期间,这是由于储存肽的释放增加或前体肽转化为内皮素1所致[26]。此外,一氧化氮合酶的上调发生在缺血后骨骼肌中,神经元一氧化氮合酶蛋白表达的增加受控于mRNA水平,而内皮型一氧化氮合酶蛋白的上调受到转录后过程的调控[27],蛋白水平以及一氧化氮含量的改变参与IRI。而这些发现提示,调节内皮素1和一氧化氮通路的药物,如内皮素拮抗剂,可能对这种情况有治疗效果。 在TKA手术骨骼肌发生IRI期间,细胞生物能量和线粒体得以保存,例如,ATP浓度和线粒体酶在缺血时间60-90 min和再灌注后24 h保持不变[30]。先前的研究显示,缺血15 min后,在电子显微镜下观察线粒体时,线粒体外观正常[31]。然而,在心肌发生IRI 情况下,线粒体呼吸链活性在缺血30 min后降低,在再灌注时恢复,这是一个双相过程[32]。这些结果表明,IRI引起的线粒体功能改变是组织特异性的,细胞损伤的严重程度取决于缺血时间的长短。然而,完全缺血导致线粒体损伤的实际时间和线粒体功能障碍的逆转时间尚未得到验证。 2.3 止血带诱导的IRI对远端器官的影响 下肢的IRI不仅影响局部结构,也影响远端器官,IRI的远程反应与微血管功能障碍相关[33]。激活的内皮细胞在再灌注开始时产生过多的活性氧,并导致微循环各节段中的超氧化物和一氧化氮之间的失衡,随后诱导全身炎症反应并导致多器官损伤。先前的一项研究报道了动物在经历3 h双侧后肢缺血后再灌注3 h,肝脏和肾脏功能障碍以及肺损伤[34]。在临床环境中,与止血带诱导的IRI相关的是,在TKA患者中使用N-乙酰半胱氨酸可能会增加远端肾损伤的风险,表明下肢止血带诱导的IRI可能会影响肾脏[35]。然而,单侧TKA手术后未发现明显的心肌、脑或肺损伤[36-37]。远处器官损伤的严重程度可能与局部组织损伤和全身炎症激活的程度有关。研究证实,与接受单侧TKA的患者相比,双侧TKA患者中影响多器官系统的术后并发症更高[38]。 2.4 止血带诱导的IRI对局部和全身循环的影响 止血带的使用及释放可导致缺血骨骼肌细胞和内皮中产生氧自由基并刺激炎症过程。内皮细胞中超氧化物和一氧化氮之间的失衡导致炎症递质(如血小板活化因子、肿瘤坏死因子)的产生和释放,并增强介导白细胞-内皮细胞黏附的黏附分子的生物合成[33]。TKA相关IRI模型中已经证实,在止血带通缩后局部和体循环氧化应激水平升高、炎症反应加重[39-40]。与全身循环相比,再灌注区血液中的变化更早、更强烈;由于次黄嘌呤在缺氧条件下积累,导致这些分子从受伤区域扩散到全身循环中,进而引起全身促氧化剂、次黄嘌呤水平以及黄嘌呤氧化酶活性的升高。止血带的应用已显示在再灌注期间对外周血白细胞产生基因毒性和细胞毒性作用,可能造成不可逆损伤[41]。尽管使用止血带会产生这些公认的有害影响,但手术创伤本身会产生手术应激,其特征是神经内分泌、免疫和血液系统的改变。有研究指出,与未应用止血带的手术相比,应用止血带的TKA患者术后24 h和7 d血浆白细胞介素6、C-反应蛋白、肌酸磷酸激酶和白细胞计数的增加没有差异,术后1年膝关节功能的改善与未应用止血带相比差异无显著性意义[42]。这些长期的全身反应可能源于手术损伤,在这种情况下,需要进一步研究区分手术应激反应和IRI反应。 2.5 缺血预处理对IRI的影响 缺血预处理是指组织暴露于一个或多个短暂的IRI,其产生少量自由基,从而对随后的长时间缺血应激和再灌注损伤产生适应性反应。实验表明,缺血预处理能将IRI降低高达75%[43],缺血预处理产生的保护,包括两个阶段,即早期阶段和晚期阶段[33,43]。早期影响离子通道的通透性、蛋白质的翻译后修饰以及自身活性物质的释放,如腺苷、缓激肽和一氧化氮等。后期取决于参与内皮功能、炎症反应和止血的基因表达以及蛋白质的从头合成。单侧TKA患者的下肢缺血预处理表现出保护性基因组反应,这导致即时早期反应基因、氧化应激防御基因和促生存基因的表达上调,这些发现表明,缺血预处理可能对膝关节置换术和其他肌肉骨骼状况有潜在益处[44]。有研究指出,缺血预处理在TKA患者中诱导了保护性基因组反应。缺血预处理的保护作用与参与神经系统过程的基因表达改变,和神经元凋亡的调节有关[45]。然而,经过1-3个5 min缺血和5 min再灌注周期的缺血预处理并没有抑制全身炎症信号[44,46]。研究发现,在应用止血带的TKA中,缺血预处理通过增强骨骼肌中的线粒体融合蛋白(Mfn2和Opa1蛋白),部分保护了术后股四头肌的力量,并预防了止血带诱导的IRI[47]。 远端缺血预处理是对远端组织或器官进行的预处理,目的是使后续持续缺血发作的组织抵抗IRI。在TKA手术中,对未手术大腿使用止血带导致的骨骼肌缺血进行了研究,在全麻下接受单侧TKA患者的早期再灌注期间,这种接受3个5 min缺血周期的远端缺血预处理改善了局部脑和肺氧合[37]。同样,在双侧TKA的情况下,在第一个手术膝关节上应用大腿止血带可以防止在随后的另一个膝关节缺血性手术过程中发生IRI[36,48]。在其他器官,陈彬等[49]研究发现,急性心肌梗死患者行急诊经皮冠状动脉介入治疗,术前及术后行肢体远端缺血预处理可减少心肌损伤,改善远期预后。远端缺血预处理的潜在机制由体液和神经两部分组成[50-51],这两种假说涉及到在远端缺血组织中产生内源性底物,如腺苷、缓激肽和降钙素基因相关肽,这些内源性介质进入血液,并通过其在其他组织中的受体启动保护作用,这些底物以不同的方式刺激传入神经纤维,并通过传出神经纤维将保护传递到远处的器官,因此,远程缺血预处理的完整信号传导需要完整的神经通路。值得注意的是,麻醉技术应该重点关注,因为脊髓麻醉可以阻断脊神经根的神经冲动,并可能干扰远端缺血预处理的神经通路。 2.6 麻醉药物对IRI损伤的影响 针对不同麻醉方式的研究发现,脊髓麻醉和全身麻醉均会使止血带诱导的IRI出现炎症反应,两组患者的炎症反应相似,表明不同的麻醉方式(脊髓麻醉和全身麻醉)不会对止血带诱导的IRI程度产生明显区别[52]。 麻醉干预以减少骨科手术病例中止血带相关IRI已被系统综述,经证实具有抗氧化作用的麻醉剂包括异丙酚、右美托咪定和氯胺酮。静脉注射异丙酚是镇静和维持麻醉的常用麻醉,其抗氧化性能源自其化学结构。在骨骼肌IRI中,在整个手术过程中输注小剂量的异丙酚显示出抗氧化和抗炎特性,小剂量异丙酚输注可减少止血带诱导的IRI中活性氧的产生[53]。在一项异丙酚和氯胺酮抗氧化作用的比较研究中发现,小剂量异丙酚和氯胺酮在脊髓麻醉下接受关节镜膝关节手术的患者中具有相似的潜力,可以减少止血带诱导IRI引起的氧化应激[54]。针对异丙酚对IRI保护机制的研究发现,异丙酚能上调PRR34AS1的表达,PRR34-SS1的上调可以通过靶向JAK1抑制JAS-STAT信号通路,降低细胞凋亡,潜在减轻异丙酚预处理小鼠TKA后的IRI[55]。七氟烷和其他卤化挥发性麻醉剂在心脏IRI后对心肌显示出保护作用[56]。有研究表明,七氟烷预处理能够使MicroRNA-153-3p表达上调,miR-153-3p通过阻断Bcl-2和Beclin1之间的相互作用诱导自噬,能够增强七氟烷预处理对TKA后IRI的保护[57]。也有研究发现,在骨骼肌缺血再灌注设置中,七氟醚和氟烷的抗氧化效果低于静脉注射异丙酚[58]。因此,针对TKA的合理麻醉技术是小剂量异丙酚输注联合脊髓麻醉[53,58-59]。 右美托咪定是一种α2-肾上腺素受体激动剂。有研究表明,老年患者术中使用右美托咪定可缓解下肢IRI后呼吸功能的恶化,并抑制老年患者的氧化应激反应[60]。右美托咪定可通过降低黄嘌呤氧化酶水平降低氧化应激,通过降低去甲肾上腺素水平减弱交感神经激活,并可能增加乙酰胆碱/去甲肾上腺素比值。右美托咪定还通过降低呼吸指数来减少呼吸功能的恶化。不同麻醉药物对IRI的作用及机制见表1所示。"
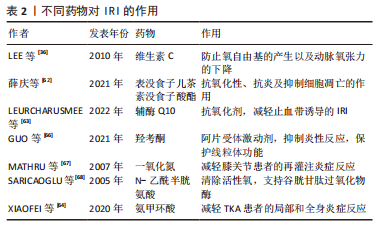
2.7 药物干预对IRI的影响 抗氧化剂可调节止血带相关IRI中产生的活性氧。抗氧化剂通过抑制活性氧的产生、增强抗氧化酶活性或与自由基中间体发生连锁反应来降低细胞中氧自由基的水平。除了抗氧化剂,预防线粒体功能障碍、干预局部或全身炎症过程的措施可能在骨骼肌IRI中发挥重要作用。 此前已有研究探讨了维生素C、甘露醇、N -乙酰半胱氨酸、吸入性一氧化氮和低浓度氧气对TKA术后IRI的预防作用[35-36,59,61]。维生素E和维生素C是天然的非酶促抗氧化剂,能有效清除脂质过氧化物自由基,终止脂质过氧化物酶连锁反应。止血带放气前10 min和再灌注后20 min,静脉大剂量维生素C能显著降低血清丙二醛水平,而丙二醛是一种脂质过氧化的有毒代谢物。此外,TKA期间与对照组相比,维生素C组在术后8 h显著降低肌钙蛋白Ⅰ水平,维生素C可以防止氧自由基的产生以及IRI引起的动脉氧张力和平均血压下降,从而显示出对心肌的保护作用[36]。表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯具有较强的抗氧化性、抗炎及抑制细胞凋亡的作用,在大鼠骨骼肌IRI的研究中发现,表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯组血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β水平降低,且与表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯剂量呈正相关性;肌纤维病理表现得到明显改善,细胞凋亡明显减少,提示表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯通过减轻炎症反应、抗氧化应激及抑制组织细胞凋亡保护大鼠骨骼肌IRI[62]。辅酶Q10是一种有效的抗氧化剂,它可能预防止血带诱导的IRI。有研究指出,辅酶Q10预处理的TKA患者能减轻止血带诱导的IRI;然而再灌注期初期,辅酶Q10预处理的益处不足,其真实的具体作用有待进一步研究[63]。 联合应用氨甲环酸可有效降低TKA患者IRI术后局部引流量和外周血清中白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,从而减轻局部和全身炎症反应[64]。同样有研究发现,半程应用止血带的血肿瘤坏死因子α、PTX3、CCL2、前列腺素E2、超氧化物歧化酶1和肌红蛋白低于全程组,半程组术后48 h膝关节活动度更好,提示半程应用止血带可能减轻止血带诱导的IRI[65]。羟考酮是阿片受体激动剂,羟考酮预处理通过抑制Toll样受体4/核因子κB依赖性炎症反应,降低了血清肿瘤坏死因子α水平,减轻骨骼肌急性IRI,并保护SIRT1/PGC-1α依赖性线粒体功能,同时其显著提高了血清ATP水平和骨骼肌的收缩力[66]。 外源性一氧化氮的使用减轻了全身麻醉膝关节手术患者的再灌注炎症反应[67]。然而,在脊髓麻醉时,止血带释放后2 h,均没有检测到局部及全身内皮细胞激活或炎症反应的迹象。因此,在这种情况下,外源性一氧化氮的存在未产生积极影响[61],提示一氧化氮减轻IRI的作用可能受麻醉方式影响,脊髓麻醉过程中氧张力降低可能是一种解释。关于N-乙酰半胱氨酸,它是谷胱甘肽的直接前体,直接清除活性氧并间接支持谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶。N-乙酰半胱氨酸对止血带相关缺血再灌注损伤的有益作用已有报道[68]。然而,高剂量N-乙酰半胱氨酸显著增加尿标记物,提示肾小管损伤[35]。因此,应在骨骼肌缺血再灌注模型中仔细验证给药技术,包括药物干预的最佳剂量、途径和时间。不同药物对IRI的作用见表2所示。"
| [1] BAKKER SMK, KOSSE NM, CMIC S, et al. Influence of a Tourniquet on Opioid Consumption After Local Infiltration Analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2019;47(2):107-111. [2] PARADIS S, CHARLES AL, MEYER A, et al. Chronology of mitochondrial and cellular events during skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(11):C968-C982. [3] KUMAR K, RAILTON C, TAWFIC Q. Tourniquet application during anesthesia: “What we need to know?”. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016;32(4):424-430. [4] JAGANJAC M, CIPAK A, SCHAUR RJ, et al. Pathophysiology of neutrophil-mediated extracellular redox reactions. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016;21(4):839-855. [5] SUN MS, JIN H, SUN X, et al. Free Radical Damage in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: An Obstacle in Acute Ischemic Stroke after Revascularization Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:3804979. [6] XIAMG M, LU Y, XIN L, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress in Reperfusion following Myocardial Ischemia and Its Treatments. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021: 6614009. [7] GRANGER DN, KVIETYS PR. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015;6:524-551. [8] BOMPOTIS GC, DEFTEREOS S, ANGELIDIS C, et al. Altered Calcium Handling in Reperfusion Injury. Med Chem. 2016;12(2):114-130. [9] BODALIA A, LI H, JACKSON MF. Loss of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ homeostasis: contribution to neuronal cell death during cerebral ischemia. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(1):49-59. [10] NICOUD IB, KNOX CD, JONES CM, et al. 2-APB protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing cellular and mitochondrial calcium uptake. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007;293(3): G623-G630. [11] KAMINSKI KA, BONDA TA, KORECKI J, et al. Oxidative stress and neutrophil activation--the two keystones of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 2002; 86(1):41-59. [12] KIKUCHI K, MIURA N, KAWAHARA KI, et al. Edaravone (Radicut), a free radical scavenger, is a potentially useful addition to thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Biomed Rep. 2013;1(1):7-12. [13] OLIVEIRA THC, MARQUES PE, PROOST P, et al. Neutrophils: a cornerstone of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Lab Invest. 2018;98(1):51-62. [14] JUNG JE, KIM GS, CHEN H, et al. Reperfusion and neurovascular dysfunction in stroke: from basic mechanisms to potential strategies for neuroprotection. Mol Neurobiol. 2010;41(2-3):172-179. [15] KHANNA A, COWLED PA, FITRIDGE RA. Nitric oxide and skeletal muscle reperfusion injury: current controversies (research review). J Surg Res. 2005; 128(1):98-107. [16] LIU X, TAO GZ. Effects of tirofiban on the reperfusion-related no-reflow in rats with acute myocardial infarction. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2013; 10(1):52-58. [17] HU H, BATTEUX F, CHEREAU C,et al. Clopidogrel protects from cell apoptosis and oxidative damage in a mouse model of renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Pathol. 2011;225(2):265-275. [18] KO JS, GWAK MS, KIM GS, et al. The protective effect of ischemic preconditioning against hepatic ischemic-reperfusion injury under isoflurane anesthesia in rats. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(5):1704-1707. [19] 李广罡,韩文斌,陈飞.即刻早期基因c-fos,c-jun在缺血再灌注大鼠肝脏中的表达[J].中国热带医学,2010,10(9):1048-1049. [20] GILLANI S, CAO J, SUZUKI T, et al. The effect of ischemia reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle. Injury. 2012;43(6):670-675. [21] BARNIG C, LUTZWEILER G, GIANNINI M, et al. Resolution of Inflammation after Skeletal Muscle Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Focus on the Lipid Mediators Lipoxins, Resolvins, Protectins and Maresins. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(6):1213. [22] RATCHFORD SM, BAILEY AN, SENESAC HA, et al. Proteins regulating cap-dependent translation are downregulated during total knee arthroplasty. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012;302(6): R702-R711. [23] JAWHAR A, HERMANNS S, PONELIES N, et al. Tourniquet-induced ischaemia during total knee arthroplasty results in higher proteolytic activities within vastus medialis cells: a randomized clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10):3313-3321. [24] DREYER HC. Tourniquet Use During Knee Replacement Surgery May Contribute to Muscle Atrophy in Older Adults. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2016;44(2):61-70. [25] MUYSKENS JB, HOCKER AD, TURNBULL DW, et al. Transcriptional profiling and muscle cross-section analysis reveal signs of ischemia reperfusion injury following total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Physiol Rep. 2016;4(1):e12671. [26] TSUI JC, BAKER DM, BIECKER E, et al. Altered endothelin-1 levels in acute lower limb ischemia and reperfusion. Angiology. 2004;55(5):533-539. [27] TSUI JC, BAKER DM, SHAW SG, et al. Alterations in nitric oxide synthase isoforms in acute lower limb ischemia and reperfusion. Angiology. 2007;58(5):586-592. [28] YANG Q, HE GW, UNDERWOOD MJ, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial ischemia/reperfusion injury: perspectives and implications for postischemic myocardial protection. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(2):765-777. [29] ABU-SALEH N, OVCHARENKO E, AWAD H, et al. Involvement of the endothelin and nitric oxide systems in the pathogenesis of renal ischemic damage in an experimental diabetic model. Life Sci. 2012;91(13-14):669-675. [30] JAWHAR A, PONELIES N, SCHILD L. Effect of limited ischemia time on the amount and function of mitochondria within human skeletal muscle cells. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2016;42(6):767-773. [31] APPELL HJ, GLOSER S, DUARTE JA, et al. Soares JM. Skeletal muscle damage during tourniquet-induced ischaemia. The initial step towards atrophy after orthopaedic surgery? Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1993;67(4):342-347. [32] LEE HL, CHEN CL, YEH ST, et al. Chen YR. Biphasic modulation of the mitochondrial electron transport chain in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;302(7):H1410-H1422. [33] SANCHEZ-HERNANDEZ CD, TORRES-ALARCON LA, GONZALEZ-CORTES A, et al. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Pathophysiology, Current Clinical Management, and Potential Preventive Approaches. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:8405370. [34] YASSIN MM, HARKIN DW, BARROS D’SA AA, et al. Lower limb ischemia-reperfusion injury triggers a systemic inflammatory response and multiple organ dysfunction. World J Surg. 2002;26(1):115-121. [35] LAISALMI-KOKKI M, PESONEN E, KOKKI H, et al. Potentially detrimental effects of N-acetylcysteine on renal function in knee arthroplasty. Free Radic Res. 2009; 43(7):691-696. [36] LEE JY, KIM CJ, CHUNG MY. Effect of high-dose vitamin C on oxygen free radical production and myocardial enzyme after tourniquet ischaemia-reperfusion injury during bilateral total knee replacement. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(4):1519-1529. [37] OH CS, KIM SH, LEE J, et al. Impact of remote ischaemic preconditioning on cerebral oxygenation during total knee arthroplasty. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(2): 115-122. [38] MEMTSOUDIS SG, GONZALEZ DELLA VALLE A, BESCULIDES MC, et al. In-hospital complications and mortality of unilateral, bilateral, and revision TKA: based on an estimate of 4,159,661 discharges. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2617-2627. [39] GARCIA-DE-LA-ASUNCION J, PEREZ-SOLAZ A, CARRAU M, et al. Different oxidative stress marker levels in blood from the operated knee or the antecubital vein in patients undergoing knee surgery: a tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion model. Redox Rep. 2012;17(5):194-199. [40] CLEMENTSEN T, REIKERAS O. Cytokine patterns after tourniquet-induced skeletal muscle ischaemia reperfusion in total knee replacement. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2008;68(2):154-159. [41] LIALIARIS T, KOUSKOUKIS A, TIAKA E, et al. Cytogenetic damage after ischemia and reperfusion. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2010;14(4):471-475. [42] TSUNODA K, SONOHATA M, KUGISAKI H, et al. The Effect of Air Tourniquet on Interleukin-6 Levels in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Open Orthop J. 2017;11:20-28. [43] PAC-SOO CK, MATHEW H, MA D. Ischaemic conditioning strategies reduce ischaemia/reperfusion-induced organ injury. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114(2):204-216. [44] MURPHY T, WALSH PM, DORAN PP, et al. Transcriptional responses in the adaptation to ischaemia-reperfusion injury: a study of the effect of ischaemic preconditioning in total knee arthroplasty patients. J Transl Med. 2010;8:46. [45] SHA Y, XU YQ, ZHAO WQ, et al. Protective effect of ischaemic preconditioning in total knee arthroplasty. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(10):1559-1566. [46] MEMTSOUDIS SG, STUNDNER O, YOO D, et al. Does limb preconditioning reduce pain after total knee arthroplasty? A randomized, double-blind study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(5):1467-1474. [47] LEURCHARUSMEE P, SAWADDIRUK P, PUNJASAWADWONG Y, et al. Ischemic preconditioning upregulates Mitofusin2 and preserves muscle strength in tourniquet-induced ischemia/reperfusion. J Orthop Translat. 2022;35:113-121. [48] AKTAS E, ATAY Ç, DEVECI MA, et al. Impact of oxidative stress on early postoperative knee function and muscle injury biochemical markers: Is it possible to create an ischemic preconditioning effect in sequential ischemic surgical procedures? Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(4):387-393. [49] 陈彬,胡雨,陶建平,等.远端肢体缺血预处理对AMI患者的心肌保护作用及对远期预后的影响[J].心血管康复医学杂志,2022,31(1):19-22. [50] HAUSENLOY DJ, YELLON DM. Ischaemic conditioning and reperfusion injury. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016;13(4):193-209. [51] GILL R, KURIAKOSE R, GERTZ ZM, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning for myocardial protection: update on mechanisms and clinical relevance. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;402(1-2):41-49. [52] GANJIFARD M, KOUZEGARAN S, ABDI R, et al. The Comparison of Inflammatory Cytokines between Spinal and General Anesthesia following Changes in Ischemic Reperfusion due to Tourniquet during Lower Limb Surgery. Adv Orthop. 2021; 2021:2027421. [53] ÖZKAN D, AKKAYA T, YALCINDAG A, et al. Propofol sedation in total knee replacement : effects on oxidative stress and ischemia-reperfusion damage. Anaesthesist. 2013;62(7):537-542. [54] OMER K, NERMIN G, ALI A, et al. Lesão de isquemia‐reperfusão induzida por torniquete: comparação dos efeitos antioxidantes de propofol e cetamina em doses baixas [Tourniquet-induced ischaemia-reperfusion injury: the comparison of antioxidative effects of small-dose propofol and ketamine]. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2017;67(3):246-250. [55] FANG H, ZHANG FX, LI HF, et al. PRR34-AS1 overexpression promotes protection of propofol pretreatment against ischemia/reperfusion injury in a mouse model after total knee arthroplasty via blockade of the JAK1-dependent JAK-STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3):2545-2556. [56] AGARWAL B, STOWE DF, DASH RK, et al. Mitochondrial targets for volatile anesthetics against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Physiol. 2014;5:341. [57] QIU S, LIU B, MO Y, et al. MicroRNA-153-3p increases autophagy in sevoflurane-preconditioned mice to protect against ischaemic/reperfusion injury after knee arthroplasty. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9): 5330-5340. [58] ARNAOUTOGLOU H, VRETZAKIS G, SOULIOTIS D, et al. The effects of propofol or sevoflurane on free radical production after tourniquet induced ischaemia-reperfusion injury during knee arthroplasty. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2007;58(1):3-6. [59] MAS E, BARDEN AE, CORCORAN TB, et al. Effects of spinal or general anesthesia on F₂-isoprostanes and isofurans during ischemia/reperfusion of the leg in patients undergoing knee replacement surgery. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;50(9): 1171-1176. [60] LU S, CHEN X, CHEN Q, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine on the function of distal organs and oxidative stress after lower limb ischaemia-reperfusion in elderly patients undergoing unilateral knee arthroplasty. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;87(11):4212-4220. [61] HALLSTROM L, FROSTELL C, HERRLIN A, et al. No signs of inflammation during knee surgery with ischemia: a study involving inhaled nitric oxide. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:620281. [62] 薛庆,童梁成,杨智伟,等.表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯可减轻大鼠骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(26):4145-4149. [63] LEURCHARUSMEE P, SAWADDIRUK P, PUNJASAWADWONG Y, et al. CoenzymeQ10 and Ischemic Preconditioning Potentially Prevent Tourniquet-Induced Ischemia/Reperfusion in Knee Arthroplasty, but Combined Pretreatment Possibly Neutralizes Their Beneficial Effects. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(2):419. [64] XIAOFEI L, XUAN W, JINLIANG W. Effect of tranexamic acid on ischemia-reperfusion injury caused by application of tourniquet in the surgery of total knee arthroplasty. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(9 suppl7):2325967120S00532. [65] CAO Q, HE Z, FAN Y, et al. Effects of tourniquet application on enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) and ischemia-reperfusion post-total knee arthroplasty: Full- versus second half-course application. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020;28(1): 2309499019896026. [66] GUO YX, WANG GY, CHENG WJ, et al. Activation of Opioid Receptors Attenuates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Skeletal Muscle Induced by Tourniquet Placement. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:6699499. [67] MATHRU M, HUDA R, SOLANKI DR, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide attenuates reperfusion inflammatory responses in humans. Anesthesiology. 2007;106(2):275-282. [68] SARICAOGLU F, DAL D, SALMAN AE, et al. Effect of low-dose N-acetyl-cysteine infusion on tourniquet-induced ischaemia-reperfusion injury in arthroscopic knee surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49(6):847-851. |
| [1] | Wang Tihui, Wang Xu, Wu Jinqing, Chen Jiliang, Wang Xiaolu, Miao Juan. Application of three-dimensional simulated osteotomy of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 905-910. |
| [2] | Xie Peng, Zhang Jiang, Deng Xiaolei, Wei Bo, Hou Decai. A systematic review of mouse model construction for sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 263-266. |
| [3] | Wang Jingfeng, Wen Dengtai, Wang Shijie, Gao Yinghui. Atg-mediated autophagy, exercise and skeletal muscle aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 295-301. |
| [4] | Long Yi, Yang Jiaming, Ye Hua, Zhong Yanbiao, Wang Maoyuan. Extracellular vesicles in sarcopenic obesity: roles and mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 315-320. |
| [5] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [6] | Zhang Lichuang, Gao Huali, Wang Jingchao, Lin Huijun, Wu Chonggui, Ma Yinghui, Huang Yunfei, Fang Xue, Zhai Weitao. Effect of tendon manipulation with equal emphasis on muscles and bones on accelerating the functional rehabilitation of quadriceps femoris after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1383-1389. |
| [7] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [8] | Jia Shengqi, Luo Wenlong, Tian Dingyuan, Zhang Xinhui, Cui Qian, Wang Chao, Pei Hanjun. Expression of mitochondrial sirtuin 3 in mice with acute renal ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1172-1178. |
| [9] | Zhang Yan, He Ruibo, Wang Qingbo, Pi Yihua, Lu Chunmin, Xu Chuanyi, Ma Gang, Peng Peng. Effects of aerobic exercises with different load volumes on inflammatory response and insulin signaling pathway of skeletal muscle in obese rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1237-1244. |
| [10] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [11] | Song Hehua, Wei Zairong. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285. |
| [12] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [13] | Liu Hongwen, Li Jiao, Xu Wenhao, Nie Hua, Liu Shaojiang, Xu Jie, Yin Li. Differential expression profiles of microRNAs in muscle tissue of denervated skeletal muscle atrophy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 732-737. |
| [14] | Wei Bo, Yao Qingqiang, Tang Cheng, Li Xuxiang, Xu Yan, Wang Liming. Advantage of medial pivot prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty via medial subvastus approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 552-557. |
| [15] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||