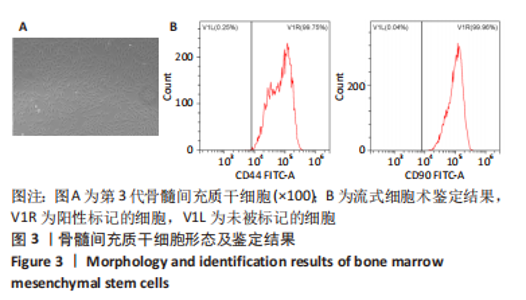
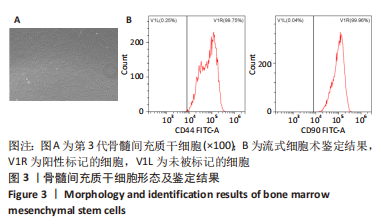
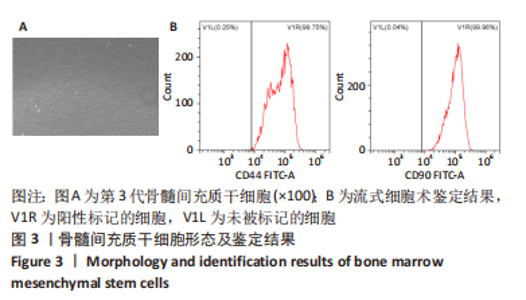
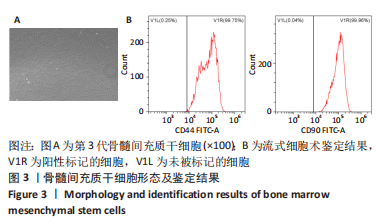
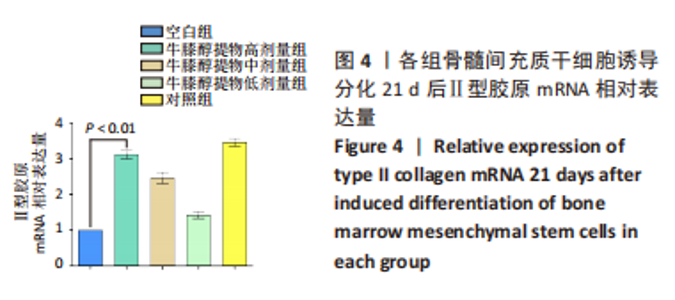
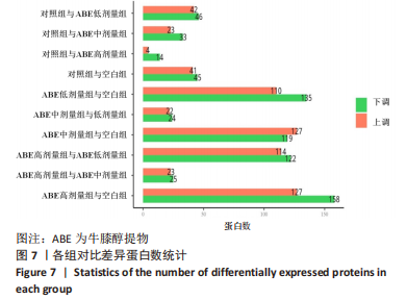
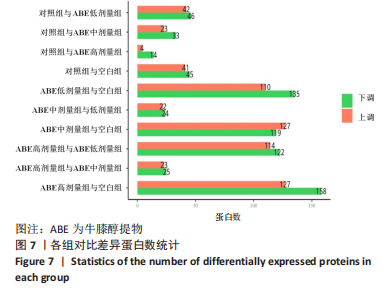
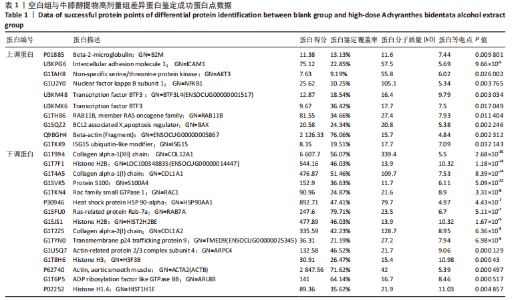
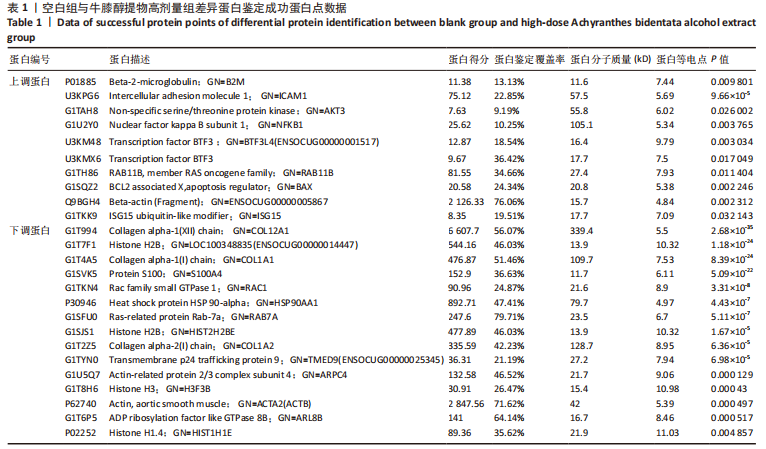
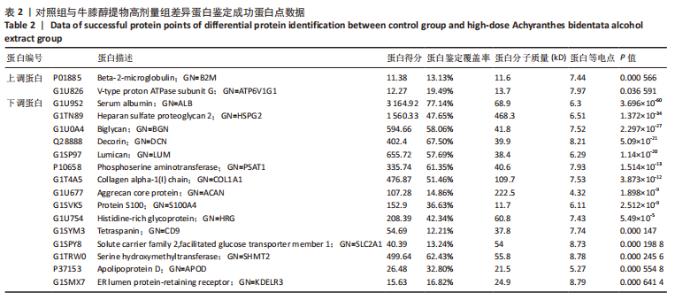
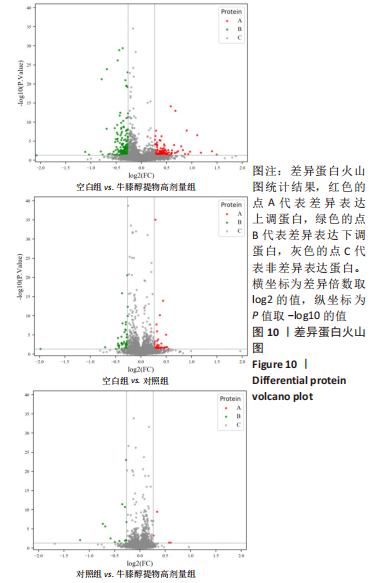
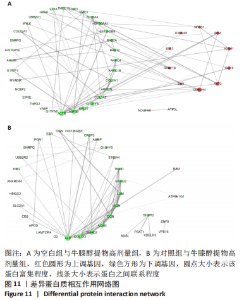
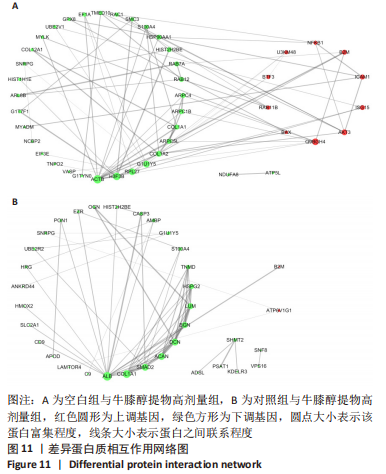
[1] 高子茏,李婷,吕政,等.补骨脂素联合转化生长因子β1诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(30):4884-4888.
[2] 田能,孔祥英,王荣田,等.不同引经药对股骨头坏死模型兔骨髓干细胞归巢的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2012,37(11):1624-1628.
[3] 黄勇,黄秀深,胡一梅,等.“左归丸”配伍规律对骨髓源成体干细胞定向分化的调控作用[J].成都中医药大学学报,2010,33(1):48-52.
[4] 马笃军,彭力平,王立新,等.牛膝醇提物诱导兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨定向分化的实验研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(2):6-11.
[5] 马笃军,彭力平,王立新,等.实验兔骨髓间充质干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定[J].基因组学与应用生物学,2017,36(1):99-104.
[6] AKGUN I, UNLU MC, ERDAL OA, et al. Matrix-induced autologous mesenchymal stem cell implantation versus matrix-induced autologous chondrocyte implantation in the treatment of chondral defects of the knee: a 2-year randomized study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(2):251-263.
[7] 李强强,谢亚东,杨国清,等.骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].医学综述,2022,28(3):434-438.
[8] 高松,孙珍珍.近20年中医药治疗骨关节炎临床用药规律分析[J].西南医科大学学报,2021,44(1):73-77.
[9] 黄艳峰,谢新宇,林晴,等.基于计算机模拟探讨牛膝治疗骨关节炎软骨退变机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(15):148-155.
[10] 张巍,张慧,张振凌.牛膝、酒牛膝饮片色度测定方法的建立及检测[J].中医药导报,2022,28(1):59-62.
[11] LI Z, MA D, PENG L, et al. Compatibility of Achyranthes bidentata components in reducing inflammatory response through Arachidonic acid pathway for treatment of Osteoarthritis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):1746-1757.
[12] 肖伟,马笃军,彭力平,等.牛膝醇提物对兔骨关节炎软骨细胞体外增殖及糖胺聚糖的干预作用[J].中国医药导报,2017,14(5):20-24.
[13] 马笃军,彭力平,蒋顺琬,等.牛膝醇提物干预BMSC-Exos对 OA模型兔局部骨组织超微结构及炎症小体的影响[J].中医药导报,2022,28(1):12-18.
[14] 刘璐,刘传慧,段智霞.膝关节炎患者血清RANKL、IL-17水平与疾病严重程度的关系[J].中国实用医刊,2021,48(19):16-19.
[15] 孙桂芳,张雪锋,茅瑜,等.温针灸治疗轻中度膝骨关节炎疗效观察及其对TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2021,40(12):1452-1457.
[16] 刘晶,林巧璇,卢莉铭,等.基于Wnt3a/β-catenin信号通路探讨针刀对膝骨关节炎兔股直肌纤维化的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(1):136-140.
[17] 邓欢,吕艺蓁,刘宣,等.PI3K/AKT信号通路调控骨关节疾病软骨细胞自噬及损伤的机制[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(2):309-314.
[18] 曹舒兴,周楠,王进,等.姜黄素通过Akt-mTOR信号通路调控细胞自噬对骨关节炎大鼠的保护作用研究[J].河北医药,2021,43(24):3685-3689.
[19] 徐斌,周明旺,李盛华,等.JAK/STAT信号通路在骨关节炎致病机制及治疗靶点的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2022,28(2):125-129.
[20] 郑晓慧,董博,袁普卫,等.NF-κB信号通路在骨性关节炎软骨破坏中的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2021,27(7):540-544.
[21] 冯帅华,吴官保,文哲,等.超微肿痛贴对兔膝骨关节炎模型的软骨中JNK/p38 MAPK信号通路的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2022,42(1):31-36.
[22] 马笃军,华树良,彭力平,等.牛膝醇提物对实验兔膝骨关节炎模型AMPK/Wnt/MAPK信号通路串话的影响[J].中医药导报,2021,27(7):16-21,26.
[23] 徐高丽,张建兴,周健,等.静压力下缺氧诱导因子-1α信号通路对髁突软骨细胞增殖与凋亡的调控作用[J].中华老年病研究电子杂志,2021,8(3):24-29. |