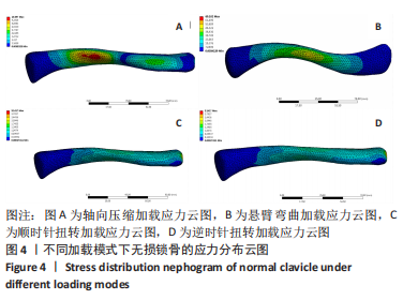
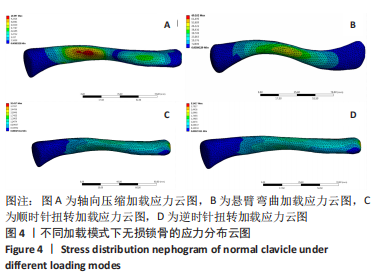
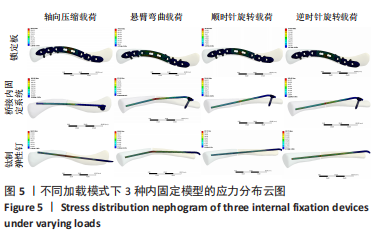
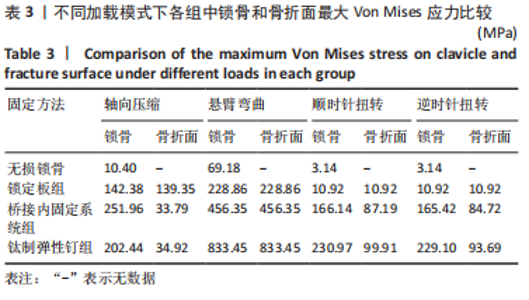
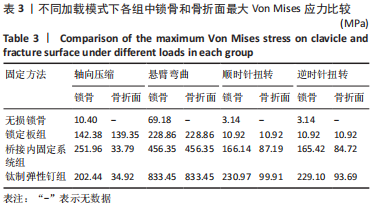
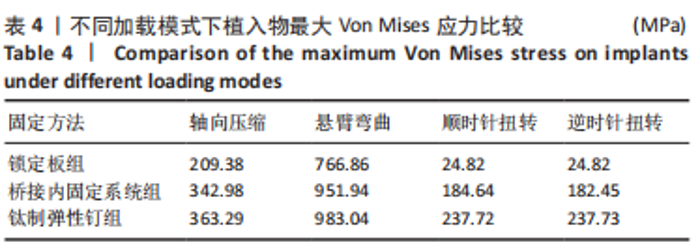
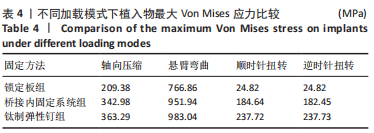
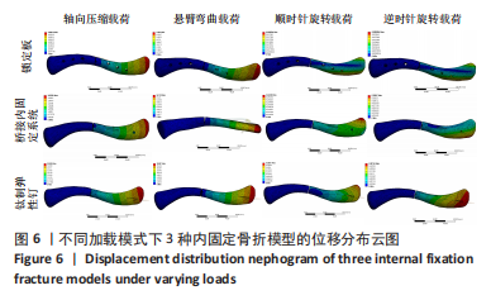
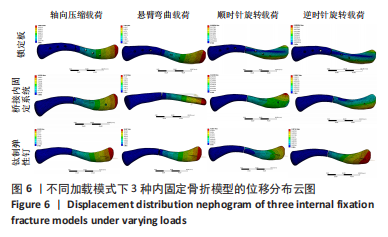
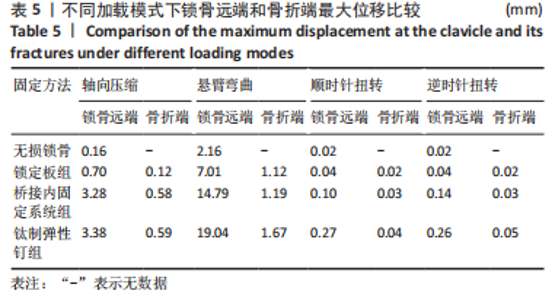
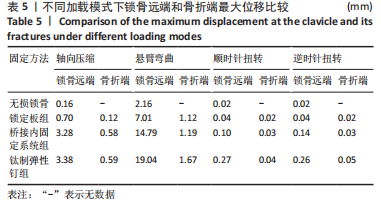
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (29): 4599-4606.doi: 10.12307/2023.645
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of middle clavicle fracture with ortho-bridge system intramedullary fixation
Ma Tianyong, Wang Dewei
- Second Department of Orthopedics, Fifth Affiliated Hospital (Zhuhai) of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519100, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-18Accepted:2022-08-27Online:2023-10-18Published:2022-12-02 -
Contact:Wang Dewei, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Second Department of Orthopedics, Fifth Affiliated Hospital (Zhuhai) of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519100, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Ma Tianyong, Master candidate, Second Department of Orthopedics, Fifth Affiliated Hospital (Zhuhai) of Zunyi Medical University, Zhuhai 519100, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Tianyong, Wang Dewei. Finite element analysis of middle clavicle fracture with ortho-bridge system intramedullary fixation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4599-4606.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] CHEN W, ZHU Y, LIU S, et al. Demographic and socioeconomic factors influencing the incidence of clavicle fractures,a national population-based survey of five hundred and twelve thousand, one hundred and eighty seven individuals. Int Orthop. 2018;42(3):651-658. [2] AMER KM, CONGIUSTA DV, SURI P, et al. Clavicle fractures: Associated trauma and morbidity. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;13:53-56. [3] ROBINSON CM. Fractures of the clavicle in the adult. Epidemiology and classification. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(3):476-484. [4] SHI F, HU H, TIAN M, et al. Comparison of 3 treatment methods for midshaft clavicle fractures: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Injury. 2022;53(6):1765-1776. [5] 谭伟源,王德伟,陈军平,等. 锁骨中段骨折的微创治疗进展[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2021,23(6):476-478. [6] CHARLES SJ, CHEN SR, MITTWEDE P, et al. Risk Factors for Complications and Reoperation Following Operative Management of Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures [published online ahead of print, 2022 Apr 23]. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2022;S1058-2746(22)00404-9. [7] ZHAO E, ZHANG R, WU D, et al. Comparison between minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis and conventional open plating for midshaft clavicle fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:1-9. [8] SONG HS, KIM H. Current concepts in the treatment of midshaft clavicle fractures in adults. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2021;24(3):189-198. [9] KING PR, LAMBERTS RP. Management of clavicle shaft fractures with intramedullary devices: a narrative review. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2020;17(8):807-815. [10] JU W, MOHAMED SO, QI B. Comparison of plate fixation vs. intramedullary fixation for the management of mid-shaft clavicle fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(3):2783-2793. [11] KRISHNA KR, SRIDHAR I, GHISTA DN. Analysis of the helical plate for bone fracture fixation. Injury. 2008;39(12):1421-1436. [12] HAQUE MA, TOVANI-PALONE MR, FRANCHI T, et al. Optimal configuration of a three-rod ortho-bridge system in the treatment of Vancouver type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures: A finite element analysis. J Orthop. 2022;30:120-126. [13] AXELROD DE, EKHTIARI S, BOZZO A, et al. What Is the Best Evidence for Management of Displaced Midshaft Clavicle Fractures? A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of 22 Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2020;478(2):392-402. [14] MARTIN JR, SAUNDERS PE, PHILLIPS M, et al. Comparative effectiveness of treatment options for displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: a systematic review and network meta-analysis[J]. Bone Jt Open. 2021; 2(8):646 -654. [15] NATHE T, TSENG S, YOO B. The anatomy of the supraclavicular nerve during surgical approach to the clavicular shaft. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469:890-894. [16] LEMIEUX V, AFSHARPOUR S, NAM D, et al. Incisional paresthesia following clavicle plate fixation: does it matter to patients? BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):928. [17] LI L, YANG X, XING F, et al. Plate fixation versus intramedullary nail or Knowles pin fixation for displaced midshaft clavicle fractures: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(39):e22284. [18] 陈哲,石清阳,高卓,等.不同干预措施和植入物治疗锁骨中段移位性骨折功能恢复与并发症的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5240-5248. [19] 赵志辉,冯雪峰,王永清,等.弹性带锁髓内钉固定治疗锁骨中段骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2022,42(3):164-171. [20] 李磊,朱建华,徐洲,等.髓内钉固定与钢板固定治疗锁骨中段骨折的Meta分析[J].局解手术学杂志,2020,29(6):494-500. [21] JEON A, SEO CM, LEE JH, et al. The distributed pattern of the neurovascular structures around clavicle to minimize structural injury in clinical field: anatomical study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2018;40(11): 1261-1265. [22] STEINMETZ G, CONANT S, BOWLIN B, et al. The Anatomy of the Clavicle and Its In Vivo Relationship to the Vascular Structures: A 2D and 3D Reconstructive Study Using CT Scans. J Orthop Trauma. 2020; 34(1):e14-e19. [23] FONTANA AD, HOYEN HA, BLAUTH M, et al. The variance of clavicular surface morphology is predictable: an analysis of dependent and independent metadata variables. JSES Int. 2020;4(3):413-421. [24] HOOGERVORST P, VAN DAM T, VERDONSCHOT N, et al. Functional outcomes and complications of intramedullary fixation devices for Midshaft clavicle fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):395. [25] SUN YT, NIE WZ. Biomechanical properties of fixation methods for clavicle fractures. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2021;25(33): 5369-5373. [26] 曾浪清,陈云丰,张长青,等.重建钢板与钛制弹性钉两种内固定方式治疗锁骨中段骨折的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2013, 28(4):441-447. [27] 樊友亮,吴一雄,张文,等.重建钢板和Herbert螺钉内固定治疗锁骨中段骨折的有限元分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(11): 1152-1155. [28] WILSON DJ, SCULLY WF, MIN KS, et al. Biomechanical analysis of intramedullary vs. superior plate fixation of transverse midshaft clavicle fractures. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2016;25:949-953. [29] HOOGERVORST P, KONINGS P, HANNINK G, et al. Functional outcomes, union rate, and complications of the Anser Clavicle Pin at 1 year: a novel intramedullary device in managing midshaft clavicle fractures. JSES Int. 2020;4(2):272-279. [30] 赵志辉,陈居文,王永清,等.弹性带锁髓内钉与锁定钢板治疗锁骨中段骨折的疗效比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(16):1029-1036. [31] SIDHU N, HUNTINGTON LS, RICHARDSON M, et al. Biomechanical performance of an intramedullary Echidna pin for fixation of comminuted mid-shaft clavicle fractures. ANZ J Surg. 2019;89(10): 1308-1313. [32] KING PR, IKRAM A, EKEN MM, et al. The Effectiveness of a Flexible Locked Intramedullary Nail and an Anatomically Contoured Locked Plate to Treat Clavicular Shaft Fractures: A 1-Year Randomized Control Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(7):628-634. [33] FROST HM. A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians. Angle Orthod. 2004;74(1):3-15. [34] NI M, NIU W, WONG DW, et al. Finite element analysis of locking plate and two types of intramedullary nails for treating mid-shaft clavicle fractures. Injury. 2016;47(8):1618-1623. [35] 尹峰,王晓东,梁炜,等. 建立锁骨个性化锁定接骨板模型及有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(35):5244-5249. [36] PENGRUNG N, LAKDEE N, PUNCREOBUTR C, et al. Finite element analysis comparison between superior clavicle locking plate with and without screw holes above fracture zone in midshaft clavicular fracture. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):465. [37] 熊川,李锦,陈李伟. 锁骨中段骨折三种固定的有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(20):1873-1877. [38] KITZEN J, PAULSON K, KORLEY R, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Different Plat Configurations for Midshaft Clavicle Fracture Fixation: Single Plating Compared with Dual Mini-Fragment Plating. JB JS Open Access. 2022;7(1):e21.00123. [39] EICKHOFF A, FISCHER M, GEBHARD F, et al. Complications after intramedullary stabilization of clavicle fractures. [German] Unfallchirurg. 2018;121:810-816. [40] ZHOU X, LI J, YANG H, et al. Comparison of 2 Different Fixation Implants for Operative Treatment of Mid-Shaft Clavicle Fractures: A Retrospective Study. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9728-9736. [41] 王雨辰,俞伟忠.桥接组合式内固定系统的临床应用及生物力学研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(24):2256-2258. [42] ZHUANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHOU L, et al. Management of comminuted mid-shaft clavicular fractures: comparison between dual-plate fixation treatment and single-plate fixation. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020; 28:2309499020915797. |
| [1] | Zhong Yizheng, Huang Peizhen, Cai Qunbin, Zheng Liqin, He Xingpeng, Dong Hang. Microstructural indexes that determine the trabecular bone maximum stress of micro-finite element models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1313-1318. |
| [2] | Wu Taoguang, Nie Shaobo, Chen Hua, Zhu Zhengguo, Qi Lin, Tang Peifu. Biomechanical characteristics of a new multi-dimensional cross locking plate in the treatment of subtrochanteric nonunion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1330-1334. |
| [3] | Peng Zhixin, Yan Wengang, Wang Kun, Zhang Zhenjiang. Finite element analysis and structural optimization design of 3D printed forearm braces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1340-1345. |
| [4] | Wu Tianliang, Tao Xiuxia, Xu Hongguang. Influence of different bone mineral densities on cage subsidence after stand-alone oblique lateral interbody fusion: three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1352-1358. |
| [5] | Liu Jinyu, Zhang Hanshuo, Cui Hongpeng, Pan Lingzhi, Zhao Boran, Li Fei, Ding Yu. Finite element biomechanical analysis of minimally invasive treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and accurate exercise rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [6] | He Yujie, Kang Zhijie, Xue Mingming, Jin Feng, Li Zhijun, Wang Xing, Xu Yangyang, Gao Mingjie, Li Jiawei, Li Xiaohe, Wang Haiyan. Finite element analysis of transarticular screw fixation of adolescent thoracic vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1365-1370. |
| [7] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [8] | Liu Jiaxin, Jia Peng, Men Yutao, Liu Lu, Wang Yeming, Ye Jinduo. Design and optimization of bone trabecular structure with triply periodic minimal surfaces [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 992-997. |
| [9] | Zhu Lin, Gu Weiping, Wang Can, Chen Gang. Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 985-991. |
| [10] | Sun Jiangwei, Wang Junxiang, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Dai Huijuan, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in different smooth collar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1004-1011. |
| [11] | Jiang Yifang, Cai Qimin, Chu Zhengyi, Qin Min, Shen Yurong, Gu Yuanping. Simulation analysis of stress distribution of NRT FILES in curved root canals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1038-1042. |
| [12] | Li Huiqin, Wang Chunjuan, Wang Yu, Wang Weifeng, Chen Dinggen, Li Na. Clear aligner orthodontic therapy of rotated mandibular teeth with different shapes: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1050-1054. |
| [13] | Liu Qinghua, Cai Yongqiang, Jin Feng, Yu Jinghong, Wang Haiyan, Zhang Yunfeng, Wang Lidong, Li Jiawei, Wang Xing, He Yujie, Dai Lina, Wang Jianzhong, Wu Chao, Tong Ling, Kang Zhijie, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe. Finite element model of the 12-year-old child whole cervical spine: establishment and validity verification based on CT data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 500-504. |
| [14] | Li Yaping, Liu Hong, Gao Zhen, Chen Xiaolin, Huang Wujie, Jiang Zheng. Three-dimensional motion analysis of lower limb biomechanical performance in Tai Chi practitioners accompanied by knee joint pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 520-526. |
| [15] | Li Shihao, Li Qi, Li Zhen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Liu Miaomiao, Ouyang Yi, Xu Weiguo. Plantar pressure and gait analysis in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||