Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (22): 3544-3549.doi: 10.12307/2023.354
Previous Articles Next Articles
Surgical versus conservative treatment of volar Die-punch fractures of the medial column of the distal radius: who can get a more stable wrist joint?
Zhao Yuhang, Yang Zhaohui
- Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2022-03-21Accepted:2022-05-25Online:2023-08-08Published:2022-11-02 -
Contact:Yang Zhaohui, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhao Yuhang, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhao Yuhang, Yang Zhaohui. Surgical versus conservative treatment of volar Die-punch fractures of the medial column of the distal radius: who can get a more stable wrist joint?[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3544-3549.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
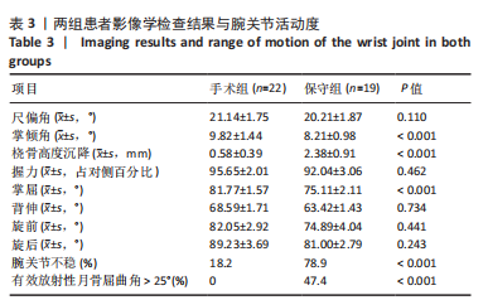
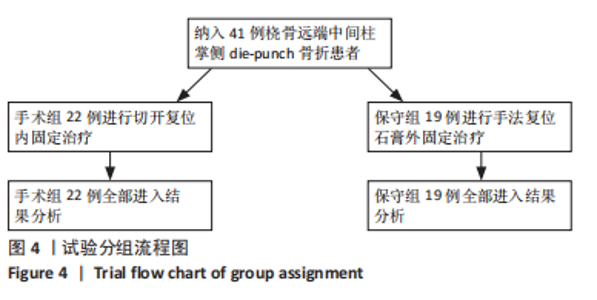
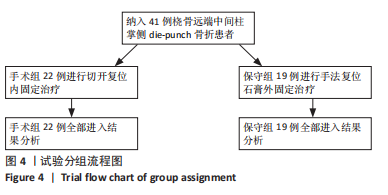
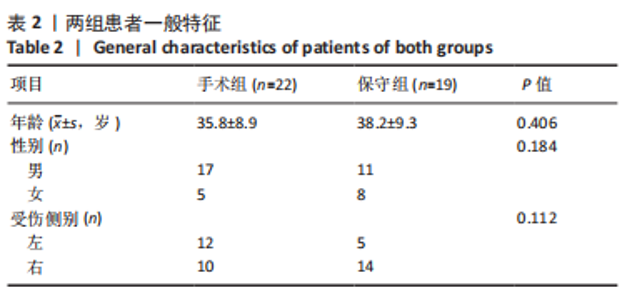
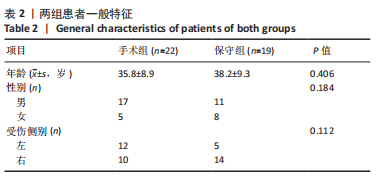
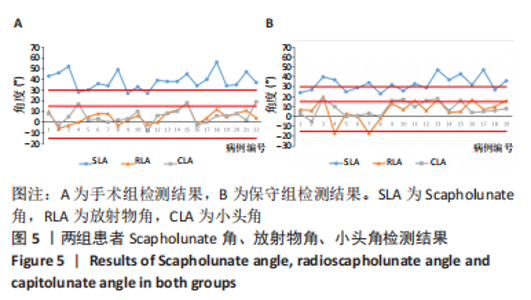
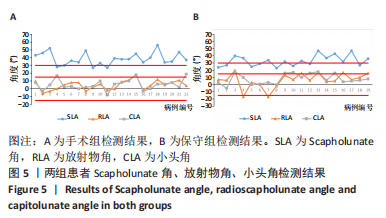
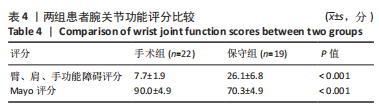
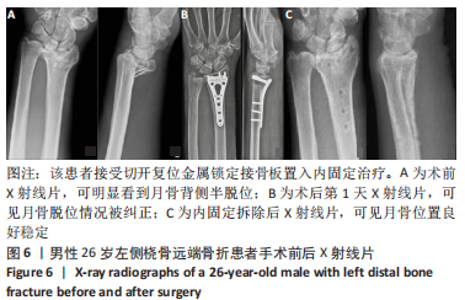
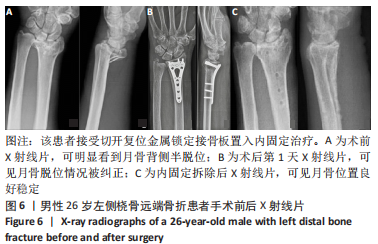
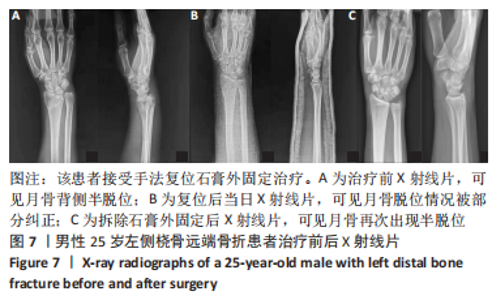
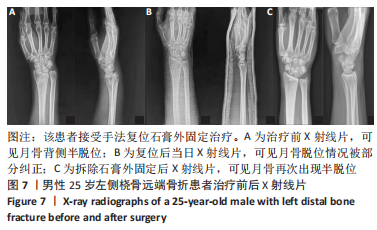
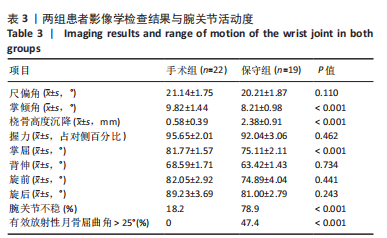
2.4 不良反应 41例患者术后获得平均14.5个月(12-18个月)随访,术后平均8.5周获得骨性愈合,未出现切口感染、骨折不愈合、内固定松动、断裂等并发症。 手术组中有1例患者出现创伤性关节炎,进行关节镜手术治疗,末次随访时诉腕部疼痛症状好转;1例患者在取除内固定后出现手部麻木,末次随访时麻木症状消失。 保守组中有4例患者出现创伤性关节炎,均拒绝手术治疗,其中3例口服非类固醇抗炎药对症治疗,1例未重视,末次随访时3例患者诉服药后腕部不适症状可缓解,未治疗患者诉腕部疼痛对其日常生活有影响;3例患者出现腕管综合征,均接受手术治疗,末次随访时其中1例因病情拖延过久手术效果一般,其余2例术后恢复佳,无其他并发症出现。 2.5 两组患者握力与腕关节活动度比较 两组患者患肢握力比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);手术组患者腕关节掌屈角度大于保守组(P < 0.001),两组间腕关节背伸、旋前、旋后角度比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。"
| [1] DIGEO FF, BRUNO EC, CHRISTIANO AT, et al. What is the best radiographic view for “die punch” distal radius fractures? a cadaver model study. Rev Bras Ortop. 2012;47(1):27-30. [2] JOHANNA R, ALICJA B, CECILIA MN, et al. Epidemiology, classification, treatment and mortality of distal radius fractures in adults: an observational study of 23,394 fractures from the national Swedish fracture register. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord. 2020;21(1):88. [3] EUAN RBS,NICK AJ, JOSEOH JD. Epidemiology of distal radius fractures in a geographically defined adult population. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2018;43(9): 974-982. [4] KEVIN CC. Physiologic vs Chronologic Age for Distal Radius Fracture Treatment. JAMA Surg. 2022. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2022.0810. [5] JEONG HK, SEOK WH. Risk Factors of Frailty in Patients with Distal Radius Fractures. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2022;13:21514593221094736. [6] AZAD A, KANG HP, AM KALLURI RK, et al. Epidemiological and Treatment Trends of Distal Radius Fractures across Multiple Age Groups. J Wrist Surg. 2019;8(4):305-311. [7] SCHECK M. Long-term follow-up of treatment of comminuted fractures of the distal end of the radius by transfixation with Kirschner wires and cast. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1962;44-A:337-351. [8] UNGLAUB F, LANGER MF, HOHENDORFF B, et al. Distal radius fracture of the adult : Diagnostics and therapy. Der Orthopade. 2017;46(1):93-110. [9] LAUREN MS, ROBIN NK. Management of Distal Radius Fractures Work Group, et al. Distal Radius Fracture Clinical Practice Guidelines-Updates and Clinical Implications. J Hand Surg Am. 2021;46(9):807-811. [10] MICHELA S, CAMILLO F, CALOGERO V, et al. Safety and reliability of carbon-peek plate for the treatment of distal radius fractures: a review of the literature. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2021;13(2):28362. [11] DONALD DA, BALACHANDRA RD,THOMAS ED, et al. A three-dimensional finite element model of the radiocarpal joint: distal radius fracture step-off and stress transfer. Iowa Orthop J. 2005;25:108-117. [12] DOMINIK G, STEFAN L, CHRISTOPH A, et al.Anatomical study of all carpal and adjoining bones of the wrist using 3D CT reconstruction -Finding the ultimate biomechanical theory. Ann Anat. 2022;242:151909. [13] GARCIA EM. Carpal Instability// WOLFE SW, HOTCHKISS RN, PEDERSON WC, editors. Green’s operative hand surgery. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone, 2011. [14] FEIPEL V, RINNEN D, ROOZE M. Postero-anterior radiography of the wrist. Normal database of carpal measurements. Surg Radiol Anat. 1998;20(3): 221-226. [15] AJAY G, SUMIT B, PANKAJ J, et al. Carpal alignment in distal radial fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2002;3:14. [16] FREDERICK WW, LEVI GS, MARI AA, et al. Scaphoid and lunate translation in the intact wrist and following ligament resection: a cadaver study. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(2):291-298. [17] BERGER RA. The anatomy of the ligaments of the wrist and distal radioulnar joints. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(383):32-40. [18] TALEISNIK J, WATSON HK. Midcarpal instability caused by malunited fractures of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1984;9(3):350-357. [19] DAVID MKT, JIN XL. Treatment of Carpal Instability and Distal Radioulnar Joint Instability. Clin Plast Surg. 2019;46(3):451-468. [20] MARCO G, VIVIANE N, NORA H, et al. The Painful Wrist. Praxis. 2021;110(12): 661-665. [21] MARK JW, LIRON SD, MADINA A, et al. Perilunate Injury Timing and Treatment Options: A Systematic Review. J Wrist Surg. 2022;11(2):164-176. [22] ZHOU J, TANG W, LI D, et al. Morphological characteristics of different types of distal radius die-punch fractures based on three-column theory. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):390. [23] ZHANG J, JI XR, PENG Y, et al. New classification of lunate fossa fractures of the distal radius. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):124. [24] ZHANG B, HU P, CHENG XD, et al. Volar, Splitting, and Collapsed Type of Die-Punch Fracture Treated by Volar Locking Plate (VLP): A Retrospective Study. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):869-877. [25] YU LL, ZHANG X, ZHANG B, et al. Outcomes of volar locking plate (VLP) fixation for treatment of die-punch fracture of the distal radius: A retrospective single-surgeon study. Medicine. 2019;98(33):e16796. [26] SONG J, YU AX, LI ZH. Comparison of conservative and operative treatment for distal radius fracture: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):17023-17035. [27] 门常胜.桡骨远端骨折手法复位后采用动态小夹板固定的应用效果[J].中国现代药物应用,2021,15(17):89-92. [28] ZHOU Y, ZHU Y, ZHANG X, et al. Comparison of radiographic and functional results of die-punch fracture of distal radius between volar locking plating (VLP) and external fixation (EF). J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):373. [29] SHUN H, HIROSHI Y, MASANORI H, et al. Radiographic Change in Articular Reduction After Volar Locking Plating for Intra-Articular Distal Radius Fractures. J Hand Surg Am. 2020;45(4):335-340. [30] QUADLBAUER S, PEZZEI C, JURKOWITSCH J, et al. Rehabilitation after distal radius fractures: is there a need for immobilization and physiotherapy? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(5):651-663. [31] JU JH, JIN GZ, LI GX, et al. Comparison of treatment outcomes between nonsurgical and surgical treatment of distal radius fracture in elderly: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2015;400(7): 767-779. [32] ZHANG X, ZHAO Y, HU C, et al. Comparative study of type B distal radius fractures with and without lunate facet involvement treated by volar locking plate, an observational study. Int J Surg. 2017;44:317-323. [33] CHEN Y, LIN C, HUANG X, et al. Comparison of treatment results between surgical and conservative treatment of distal radius fractures in adults: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2021;55(2):118-126. [34] GRUNZ JP, GIETZEN CH, GRUNZ K, et al. Imaging of Carpal Instabilities. RoFo. 2021;193(2):139-150. [35] ERHART S, TOTH S, KAISER P, et al. Comparison of volarly and dorsally displaced distal radius fracture treated by volar locking plate fixation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(6):879-885. [36] MENG H, YAN JZ, WANG B, et al. Influence of volar margin of the lunate fossa fragment fixation on distal radius fracture outcomes: A retrospective series. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(24):7022-7031. [37] RAINER S, NINA H, FLORIAN G, et al. Carpal Instability: I. Pathoanatomy. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2021;25(2):191-202. [38] BUCKNER JF, GARNER HW, BURGNER RT, et al. A Case of Short Radiolunate Avulsion Injury: Magnetic Resonance Diagnosis and Surgical Reconstruction. J Hand Surg Am. 2021;46(9):820.e1-820.e5. [39] JORG E, JIANZHANG L, VALENTIN Q, et al. Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Loads of the Wrist Joint. Life (Basel, Switzerland). 2022;12(2):188.. [40] SANDOW MJ, FISHER TJ, HOWARD CQ, et al. Unifying model of carpal mechanics based on computationally derived isometric constraints and rules-based motion - the stable central column theory. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014;39(4):353-363. |
| [1] | Zhou Yulan, Yuan Dechao, Li Ying, Gao Tao, Zeng Jian, Yin Chongfang, Yang Jilan. High-frequency ultrasound-guided manual reduction and small splint external fixation in the treatment of stable fractures of the distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2377-2381. |
| [2] | Li Jia, Fu Tingting, Ma Yuanchen, Liu Xiangqian, Chen Min. Serum inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress in patients with type C distal radius fractures treated with external fixator combined with mid-frequency pulse therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5351-5355. |
| [3] | Cheng Wenjing, Ding Guozheng, Xie Jiabing, Wang Lin. Risk factors for joint stiffness after volar plate fixation for distal radius fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4374-4378. |
| [4] | Wu Shitong, Ning Rende, Fang Run, Bi Chenghao. Therapeutic effects of different fixation methods of fragment of the dorsal ulnar of distal radius fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3343-3348. |
| [5] | Yan Wei, Jiang Tao, Wu Changgui, Kong Bo, Xi Xiaobing. Progress in the study of appearance, material and fixation band of splint for distal radius fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1430-1434. |
| [6] | Xia Changjiang, Yuan Zhifeng, Fang Ning. Biomechanical characteristics of the distal radius fracture based on three-dimensional finite element model of ulna and radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 893-897. |
| [7] | Chen Xiaojun, Luo Tao, Ou Changliang, He Zhiyu, Zhou Xin, Tang Xincheng, Mo Deping, Zou Yonggen. Comparison of external fixator-assisted reduction and locking plate internal fixation and simple locking plate internal fixation in the treatment of type C distal radius fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5315-5320. |
| [8] | Ye Shuming, Xu Chungui, Zhang Jisen, Xu Xinzhong, Xu Youjia, Jing Juehua. Effect of healing of ulnar styloid fracture on joint function after distal radius fracture surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5321-5325. |
| [9] | Li Yongyao, Zhao Yong, Cheng Hao, Xu Huiqing, Wei Xu, Liu Guangwei, Cheng Yongzhong, Cui Xin. Finite element analysis of intervention of splint to ulnar column in the treatment of type Frykman VIII fracture of distal radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4769-4774. |
| [10] | Yang Shun, Chen Keyi, Cheng Yabo, Xiang Wang, Zhang Jing, Gu Hongji, Chi Haotian. Wrist arthroscopy-assisted titanium internal fixator for the treatment of complex distal radius fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 366-371. |
| [11] | Li Yongyao, Zhao Yong, Cheng Hao, Xu Huiqing, Wei Xu, Liu Guangwei, Cheng Yongzhong, Cui Xin. Establishment and mechanical analysis of the finite element model of the type Frykman VIII fracture of the distal radius with steel plate fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(27): 4272-4277. |
| [12] | Wang Haonan, Wen Shuzheng, Wang Jihong, Hao Zengtao, Fan Dongsheng, Jing Shangfei, Han Chaoqian, Wang Yongfei, Wang Xiaolong, Yin Chao, Jiang Dong. Research and development of fluoroscopy for the detection of dorsal screw penetration in the fixation of distal radius fracture with volar locking plate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(12): 1957-1961. |
| [13] | Zhuo Jin, Wang Shasha, Chen Qiqiang, Cao Xianchang, Zhang Zhongwei. Wrist join function and resetting quality of type C distal radius fractures patients: a comparison of Kirschner wire external fixator, external fixator and volar approach plate internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5126-5132. |
| [14] | Qin Hong, Liang Ai-jun, Qian Wen-liang, Huang Xi-bin, Song Ya-wei. Rubber band stretching and stress relaxation tests during the treatment of fractures with traction splint [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(13): 2352-2357. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||