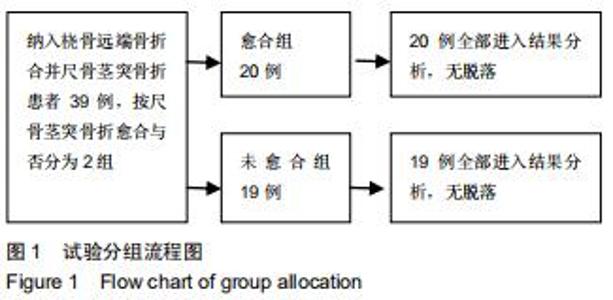
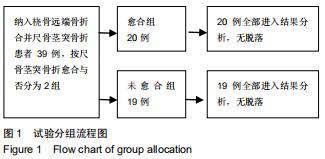
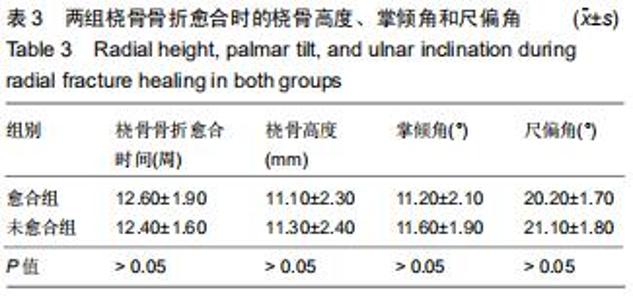
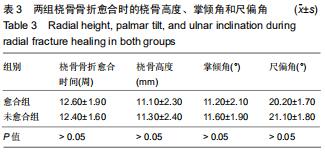
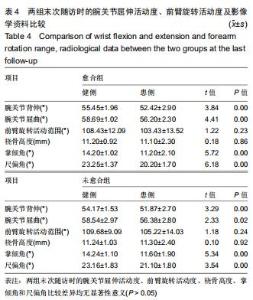
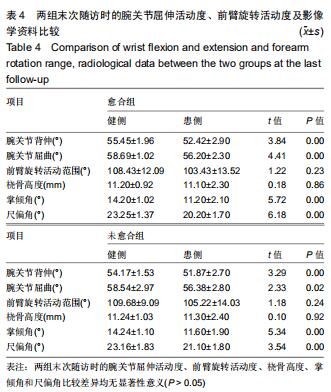
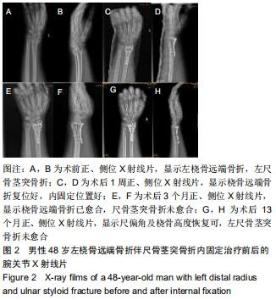
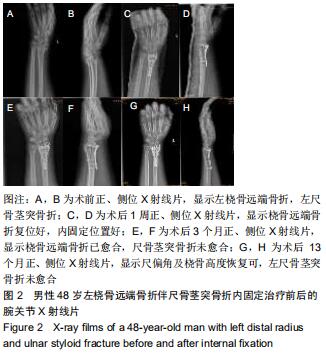
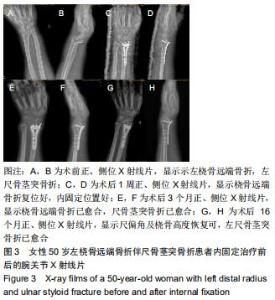
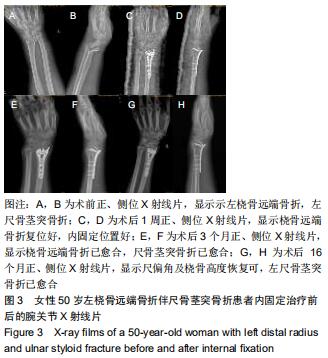
|
[1] WIJFFELS MM, KEIZER J, BUIJZE GA, et al. Ulnar styloid process nonunion and outcome in patients with a distal radius fracture: a meta-analysis of comparative clinical trials.Injury.2 014;45(12):1889-1895.
[2] 姜保国,张殿英,付中国,等.桡骨远端粉碎性骨折及关节内骨折的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(2):19-22.
[3] YUAN C, ZHANG H, LIU H. Does concomitant ulnar styloid fracture and distal radius fracture portend poorer outcomes? A meta-analysis of comparative studies.Injury.2017;48(11):2575-2581.
[4] ALMEDGHIO S, ARSHAD MS, ALMARI F. Effects of Ulnar Styloid Fractures on Unstable Distal Radius Fracture Outcomes: A Systematic Review of Comparative Studies.J Wrist Surg.2018;7(2):172-181.
[5] 王强,周龙云,梁斌,等.掌侧正中微创入路与Henry入路锁定钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端骨折的疗效比价[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017,32(7): 710-714.
[6] VAN EGMOND JC, SELLES CA, CLEFFKEN BI, et al. Plate Fixation for Unstable Displaced Distal Radius Fractures in Children.J Wrist Surg.2019;8(5):384-387.
[7] CHEN AC, CHIU CH, WENG CJ, et al. Early and late fixation of ulnar styloid base fractures yields different outcomes.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):193-197.
[8] RIKLI DA, REGAZZONI P. Fractures of the distal end of the radius treated by internal fixation and early function.A preliminary report of 20 cases.J Bone J Surg Br.1996;78(4):588-592.
[9] ZOETSCH S, KRAUS T, WEINBERG AM, et al. Fracture of the ulnar styloid process negatively influences the outcome of paediatric fractures of the distal radius.Acta Orthop Belg.2013;79(1):48-53.
[10] PIDGEON TS, CRISCO JJ, WARYASZ GR, et al. Ulnar Styloid Base Fractures Cause Distal Radioulnar Joint Instability in a Cadaveric Model. Hand (New York, N.Y.).2018;13(1):65-73.
[11] TURAN S, ÇANKAYA D, YıLMAZ S, et al. Effect of ulnar styloid fracture on outcomes after conservative treatment of distal radius fracture.Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi.2016;27(2):87-93.
[12] DAUMILLARE A, BOSCH C, JULIA M, et al.Volar locking plate fixation of distal radius fractures: Isokinetic assessment of the influence of an ulnar styloid process fracture on pronation-supination strength.Hand Surg Rehabil.2020;39(1):23-29.
[13] MULDERS MAM, FUHRI SNETHLAGE LJ, DE MUINCK KEIZER RO,et al. Functional outcomes of distal radius fractures with and without ulnar styloid fractures: a meta-analysis.J Hand Surg-Eur Vol. 2018;43(2):150-157.
[14] KIM JK, YUN YH, KIN DJ, et al. Comparison of United and Nonunited Fractures of the Ulnar Styloid Following Volar-Plate Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures.Injury.2011;42(4):371-375.
[15] BUIJZE GA. Clinical impact of United versus nonunited fractures of the proximal half of the ulnar styloid following volar plate fixation of the distal radius.J Hand Surg-AM.2010;35(2):223-227.
[16] 颜勇卿,张培训,王天兵,等.钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端骨折是否合并尺骨茎突骨折对预后影响的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤, 2015,28(3):226-229.
[17] 曾卡斌,潘俊晖,吴天旺.尺骨茎突骨折类型对桡骨远端骨折治疗效果的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(1):88-89.
[18] 岳肖华,李晏乐,程灏,等.尺骨茎突骨折有限元分析模型的建立与力学分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(10):6-9.
[19] MAY MM, LAWTON JN, BLAZAR PE. Ulnar styloid fracture associated with distal radital radius fracture:incidence and implicatins for distal radioulnar joint instability.J Hand Surg Am.2002;27(6):965-971.
[20] 牛学刚,许良.尺骨茎突骨折愈合与否对桡骨远端骨折术后关节功能影响[J].中华关节外科杂志,2019,13(1):114-117.
[21] 吴佳俊,王子平,易存国,等.桡骨远端骨折内固定治疗预后与尺骨茎突骨折的相关临床分析[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2018,15(6):52-54.
[22] 张俊,厉国定,尹伟忠,等.尺骨茎突骨折与否及不同分型对桡骨远端骨折术后疗效的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2019,34(3):321-323.
[23] GOGNA P, SELHI HS, MOHINDRA M, et al. Ulnar styloid fracture in distal radius fractures managed with volar locking plates: to fix or not? J Hand Microsurg.2014;6(2):53-58.
[24] 徐春归,张积森,许新忠,等.合并尺骨茎突骨折对桡骨远端骨折钢板内固定术后功能恢复的影响[J].临床骨科杂志, 2019,22(4):466-470.
[25] 张超,谢雪涛,胡顺东,等.尺骨茎突骨折对桡骨远端骨折内固定术后腕关节功能影响[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,4(37):264-266.
|