Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (15): 2377-2381.doi: 10.12307/2022.594
Previous Articles Next Articles
High-frequency ultrasound-guided manual reduction and small splint external fixation in the treatment of stable fractures of the distal radius
Zhou Yulan1, Yuan Dechao2, Li Ying1, Gao Tao2, Zeng Jian1, Yin Chongfang1, Yang Jilan1
- 1Department of Ultrasound, 2Department of Orthopedics, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong 643000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-07-27Revised:2021-09-13Accepted:2021-10-28Online:2022-05-28Published:2022-01-06 -
Contact:Yuan Dechao, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong 643000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhou Yulan, Attending physician, Department of Ultrasound, Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital, Zigong 643000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Scientific Research Project of Sichuan Provincial Health Commission, No. 20PJ275 (to YDC); Youth Innovation Research Project of Sichuan Medical Association, No. Q19026 (to YDC); Innovation Seedling Project of Key Science and Technology Plan of Zigong City, No. 2018CXMZ05 (to YDC); Cultivation Project of Zigong Fourth People’s Hospital (to ZYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Yulan, Yuan Dechao, Li Ying, Gao Tao, Zeng Jian, Yin Chongfang, Yang Jilan. High-frequency ultrasound-guided manual reduction and small splint external fixation in the treatment of stable fractures of the distal radius[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(15): 2377-2381.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
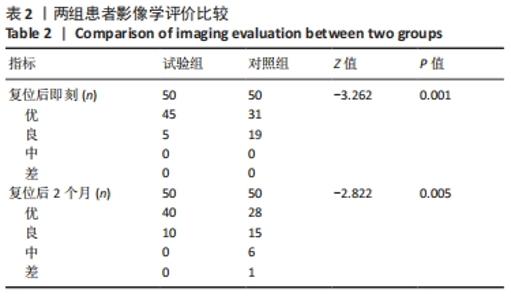
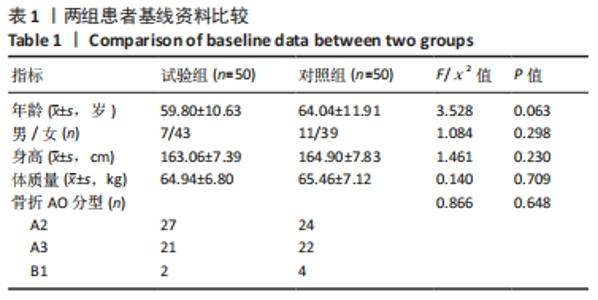
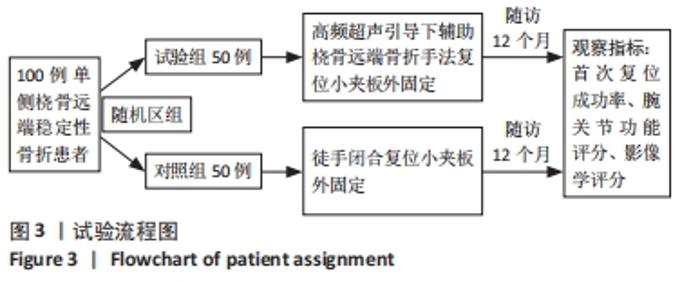
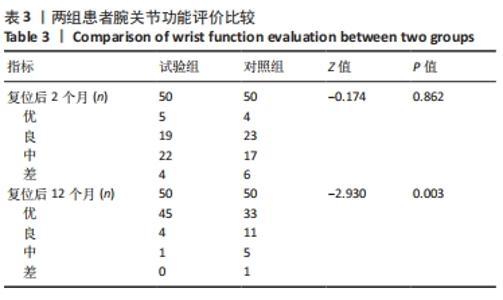
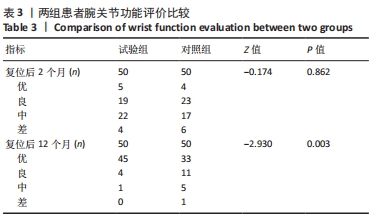
2.4 首次复位成功率 试验组首次复位均达到复位标准,首次复位成功率100.0%,对照组有6例患者首次复位后复查X射线片未达到复位标准,首次复位成功率88.0%,予以再次手法复位后达到复位标准,两组首次复位成功率差异有显著性意义(χ2=6.383,P=0.027)。 2.5 影像学评价 在复位后即刻,试验组和对照组影像学评价优率分别为90.0%,62.0%,两组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);在复位后2个月,试验组和对照组影像学评价优率分别为80.0%,56.0%,两组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。对照组有1例患者在复位后1周复查见骨折端移位明显,影像学评价为差,改为手术治疗,视为复位后2个月影像学评估为差。"

| [1] OCHEN Y, PEEK J, VAN DER VELDE D, et al. Operative vs Nonoperative Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(4):e203497. [2] FLOREK J, KOTELA I, GEORGIEW F, et al. Comparison of Radiographic Outcomes of Surgical Treatment in Patients with Distal Radial Fractures. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2018;20(6):483-492. [3] ÇALBIYIK M, IPEK D. Use of Volar Locking Plate Versus Intramedullary Nailing for Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures: A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:602-613. [4] 姜保国,张殿英,付中国,等.桡骨远端骨折的治疗建议[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(11):1053-1056. [5] YAZDANSHENAS H, WASHINGTON ER 3RD, MADADI F, et al. Introducing and Prospective Efficacy Comparison of an Innovative and Affordable Technique for the Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures. J Orthop. 2019;16(6):596-602. [6] WU YS, YANG J, XIE LZ, et al. Factors associated with the decision for operative versus conservative treatment of displaced distal radius fractures in the elderly. ANZ J Surg. 2019;89(10):E428-E432. [7] CHACHAN S, TUDU B, SAHU B. Ultrasound monitoring of fracture healing: is this the end of radiography in fracture follow-ups? J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(3):e133-138. [8] NERI E, BARBI E, RABACH I, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography for hand bony fractures in paediatric patients. Arch Dis Child. 2014;99(12):1087-1090. [9] 向斌,朱文斌,董遵伟,等.闭合性长骨骨折及指导手法复位的超声诊断的价值[J].中国实验诊断学,2011,15(12):2145-2146. [10] HERREN C, SOBOTTKE R, RINGE MJ, et al. Ultrasound-guided diagnosis of fractures of the distal forearm in children. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101(4):501-505. [11] 陆建华,施晓健,黄莉,等.高频超声引导Colles骨折手法复位的价值[J].南通大学学报(医学版),2010,30(3):164-166. [12] SOCRANSKY S, SKINNER A, BROMLEY M, et al. Ultrasound-Assisted Distal Radius Fracture Reduction. Cureus. 2016;8(7):e674. [13] SABZGHABAEI A, SHOJAEE M, ARHAMI DOLATABADI A, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Reduction of Distal Radius Fractures. Emerg (Tehran). 2016;4(3):132-135. [14] SYNN AJ, MAKHNI EC, MAKHNI MC, et al. Distal radius fractures in older patients: is anatomic reduction necessary? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(6):1612-1620. [15] 蒋协远,王大伟,韩士章,等.骨科临床疗效评价标准[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:45-46. [16] STEWART HD, INNES AR, BURKE FD. Functional cast-bracing for Colles’ fractures. A comparison between cast-bracing and conventional plaster casts. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984;66(5):749-753. [17] FU Q, ZHU L, YANG P, et al. Volar Locking Plate versus External Fixation for Distal Radius Fractures: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Indian J Orthop. 2018;52(6):602-610. [18] SAVING J, PONZER S, ENOCSON A, et al. Distal radius fractures-Regional variation in treatment regimens. PLoS One. 2018;13(11):e0207702. [19] RAUDASOJA L, VASTAMÄKI H, ASPINEN S. Deterioration of initially accepted radiological alignment of conservatively treated AO type-C distal radius fractures: mid-term outcome. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(6):1009-1015. [20] RUNDGREN J, BOJAN A, MELLSTRAND NAVARRO C, et al. Epidemiology, classification, treatment and mortality of distal radius fractures in adults: an observational study of 23,394 fractures from the national Swedish fracture register. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):88. [21] HJELLE AM, GJERTSEN JE, APALSET EM, et al. No association between osteoporosis and AO classification of distal radius fractures: an observational study of 289 patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):811. [22] MELLSTRAND NAVARRO C, BROLUND A, EKHOLM C, et al. Treatment of radius or ulna fractures in the elderly: A systematic review covering effectiveness, safety, economic aspects and current practice. PLoS One. 2019;14(3):e0214362. [23] 程国杰,吕发明,艾克巴尔,等.手法复位小夹板外固定治疗C型老年桡骨远端骨折的前瞻性随机对照临床试验[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,17(8):636-640. [24] BALOCH N, HASAN OH, JESSAR MM, et al. “Sports Ultrasound”, advantages, indications and limitations in upper and lower limbs musculoskeletal disorders. Review article. Int J Surg. 2018;54(Pt B):333-340. [25] JÄSCHKE M, WEBER MA, FISCHER C. CEUS-application possibilities in the musculoskeletal system. Radiologe. 2018;58(6):579-589. [26] WANG JC, TSAI PY, HSU PC, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodilatation With Triamcinolone Acetonide for Adhesive Capsulitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Posterior Glenohumeral Recess and the Rotator Cuff Interval Approaches. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:686139. [27] YOON JP, CHUNG SW, KIM JE, et al. Intra-articular injection, subacromial injection, and hydrodilatation for primary frozen shoulder: a randomized clinical trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(3):376-383. [28] GALLETEBEITIA LAKA I, SAMSON F, GOROSTIZA I, et al. The utility of clinical ultrasonography in identifying distal forearm fractures in the pediatric emergency department. Eur J Emerg Med. 2019;26(2):118-122. [29] ZHANG L, LÜ Y, LU C, et al. Treatment of the fifth metacarpal neck fracture with elastic intramedullary nail under the guidance of high frequency ultrasound. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021;35(2):154-159. [30] 黄克成,江红艳,朱宝林,等.超声引导下弹性髓内钉固定治疗儿童股骨骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(5):599-600. [31] ACKERMANN O, WOJCIECHOWSKI P, DZIERZEGA M, et al. Sokrat II - An International, Prospective, Multicenter, Phase IV Diagnostic Trial to Evaluate the Efficacy of the Wrist SAFE Algorithm in Fracture Sonography of Distal Forearm Fractures in Children. Ultraschall Med. 2019;40(3):349-358. [32] ŞIK N, ÖZTÜRK A, KOŞAY MC, et al. Accuracy of point-of-care ultrasound for determining the adequacy of pediatric forearm fracture reductions. Am J Emerg Med. 2021;48:243-248. [33] AUTEN JD, NAHEEDY JH, HURST ND, et al. Comparison of pediatric post-reduction fluoroscopic- and ultrasound forearm fracture images. Am J Emerg Med. 2019; 37(5):832-838. [34] SIMARD R. Ultrasound Imaging of Orthopedic Injuries. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 2020;38(1):243-265. [35] SHAH AB, BHATNAGAR N. Ultrasound imaging in musculoskeletal injuries-What the Orthopaedic surgeon needs to know. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(4):659-665. |
| [1] | Gao Yi, Ma Yue, Zhao Zeyu. Foot bone self-regulation under weight-bearing standing analyzed by medical imaging measurement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 959-962. |
| [2] | Zhang Xinlong, Ci Wentao, Luo Kaiwen, Yan shi. Internal fixation failure after proximal femoral nail antirotation: causes and reoperation strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 973-979. |
| [3] | Liu Yafei, Wang Yalin, Zuo Yanping, Sun Qi, Wei Jing, Zhao Lixia. Structural changes of the temporomandibular joint in adolescents with skeletal Class III malocclusions after maxillary protraction: an X-ray measurement analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1154-1159. |
| [4] | Pan Qile, Zhang Hong, Zhou Huikang, Cai Guang. Comparison of the Greulich-Pyle method, the CHN method and the China 05 method for assessing bone age in children and adolescents [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 662-667. |
| [5] | Li Jia, Fu Tingting, Ma Yuanchen, Liu Xiangqian, Chen Min. Serum inflammatory mediators and oxidative stress in patients with type C distal radius fractures treated with external fixator combined with mid-frequency pulse therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(33): 5351-5355. |
| [6] | Cheng Wenjing, Ding Guozheng, Xie Jiabing, Wang Lin. Risk factors for joint stiffness after volar plate fixation for distal radius fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4374-4378. |
| [7] | Zhou Yuanbo, Wang Jindong. Etiology and treatment of femoral trochlear dysplasia: congenital genetic determination or stress stimulation of patella [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3908-3913. |
| [8] | Jie Ke, Deng Peng, Zeng Yirong. Application and comparison of four commonly used methods for patellar height measurement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3875-3881. |
| [9] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [10] | Zheng Weipeng, Wei Hewei, Liu Zhijun, Wan Lei, Chen Sheng, Liao Zhihao, Hu Weijian. Application of three-dimensional reconstructive CT versus X-ray in postoperative evaluation of bone tunnel and graft status after single bundle anterior cruciate ligament near-isometric reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2881-2886. |
| [11] | Du Xueting, Yang Yang, Huang Wenhua, Chen Wubiao. Clinical application and breakthrough of three-dimensional printing based on medical imaging technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2887-2894. |
| [12] | Wang Qian, Li Lu, Shu Jingyuan, Dong Zhiheng, Jin Youshi, Wang Qingshan. Micro-morphology and phase of zirconia-based nano-hydroxyapatite functional gradient biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1517-1521. |
| [13] | Zhao Weibiao, He Ziwei, Li Ji, Li Yi. Application value of 3D printing guide plate in SuperPATH technology for elderly hip arthroplasty: retrospective study and evidence analysis of literature retrieval [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1324-1330. |
| [14] | Yan Wei, Jiang Tao, Wu Changgui, Kong Bo, Xi Xiaobing. Progress in the study of appearance, material and fixation band of splint for distal radius fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1430-1434. |
| [15] | Xia Changjiang, Yuan Zhifeng, Fang Ning. Biomechanical characteristics of the distal radius fracture based on three-dimensional finite element model of ulna and radius [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 893-897. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||