Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (27): 4374-4378.doi: 10.12307/2021.199
Previous Articles Next Articles
Risk factors for joint stiffness after volar plate fixation for distal radius fractures
Cheng Wenjing, Ding Guozheng, Xie Jiabing, Wang Lin
- The First Affiliated Hospital of Wannan Medical College, Wuhu 241000, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2020-10-24Revised:2020-10-29Accepted:2020-12-07Online:2021-09-28Published:2021-04-10 -
Contact:Ding Guozheng, Chief physician, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wannan Medical College, Wuhu 241000, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Cheng Wenjing, Master candidate, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wannan Medical College, Wuhu 241000, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province, No. 1708085QH209 (to WL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Wenjing, Ding Guozheng, Xie Jiabing, Wang Lin. Risk factors for joint stiffness after volar plate fixation for distal radius fractures[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4374-4378.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
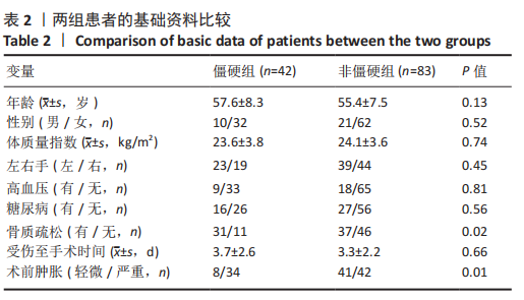
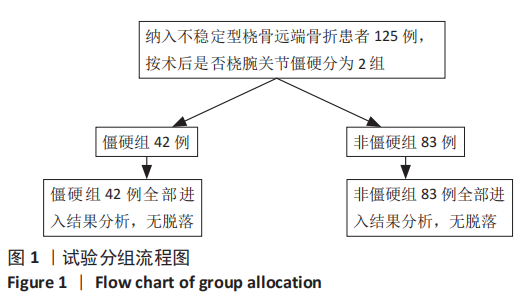
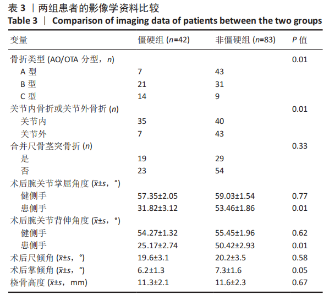
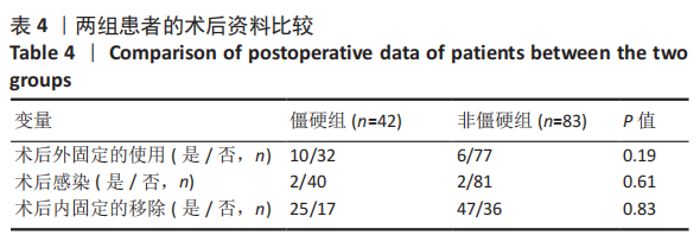
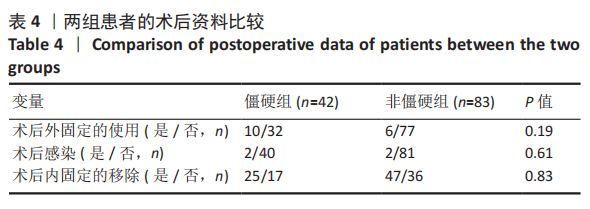
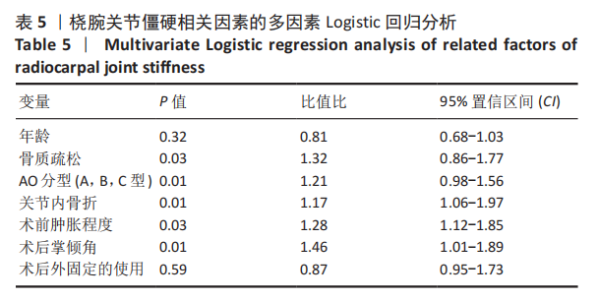
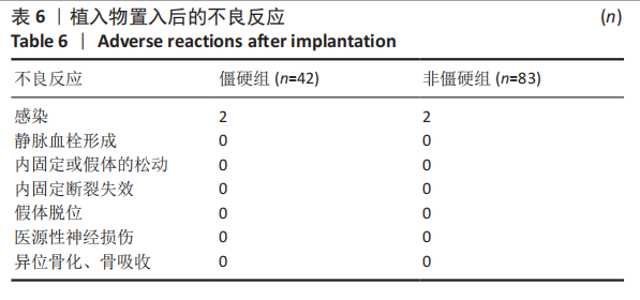
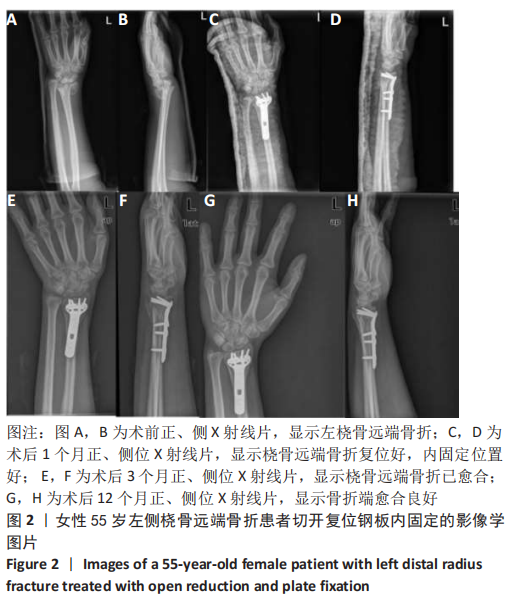
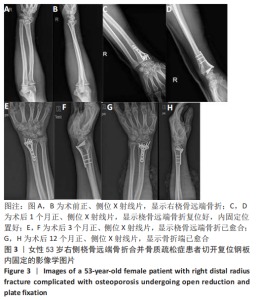
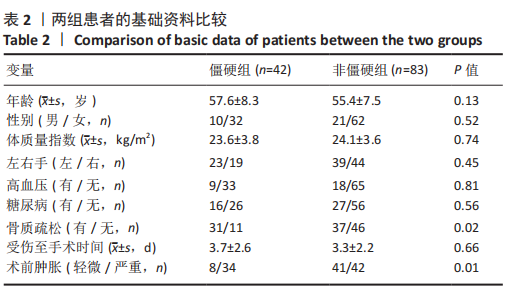
2.3 单因素分析 此次研究共纳入125例接受桡骨掌远端锁定钢板内固定的患者,其中男31例(24.8%),女94例(76.2%);手术时平均年龄(55.4±9.6)岁;术前肿胀轻微40例(32.0%),严重肿胀85例(68.0%);按AO/OTA分型,A型50例,B型52例,C型23例;关节外骨折26例(20.8%),关节内骨折99例(79.2%);40例(32.0%)患者术后辅助石膏,85例(68.0%)患者术后辅助石膏;42例(33.6%)为RJS,83例(66.4%)为非RJS。 单因素分析发现,年龄(P=0.13)、术前肿胀(P=0.01)、骨质疏松症(P=0.02)、骨折类型(AO分型)(P=0.01)、关节内骨折(P=0.01)、术后掌倾角(P=0.01)、术后外固定的使用(P=0.19)都是潜在的风险因素,而性别、体质量指数、吸烟或酗酒史、糖尿病、受伤至手术时间、尺侧茎突骨折、术后辅以石膏外固定、术后感染、内固定取出等与术后RJS无关 (P > 0.20),见表2-4。"
| [1] FILER J, SMITH A, GIDDINS G. Assessing distal radius malrotation following fracture using computed tomography. J Orthop Surg. 2019;27(3):2309499019862872. [2] YAO H, ZHANG W, XU W, et al. A new method to predict the outcome of the volar locked plate treatment for distal radius fracture. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):538. [3] LANDGREN M, TEURNEAU V, ABRAMO A, et al. Intermediate-Term Outcome After Distal Radius Fracture in Patients With Poor Outcome at 1 Year: A Register Study With a 2- to 12-Year Follow-Up. J Hand Surg Am. 2019;44(1):39-45. [4] 姜保国,张殿英,付中国,等. 桡骨远端骨折的治疗建议[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(11):1053-1056. [5] TEUNIS T, JUPITER J, SCHASER K, et al. Evaluation of radiographic fracture position 1 year after variable angle locking volar distal radius plating: a prospective multicentre case series. J Hand Surg Eur. 2017;42(5):493-500. [6] SEKI Y, AOKI T, MAEHARA H, et al. Distal locking screw length for volar locking plate fixation of distal radius fractures: Postoperative stability of full-length unicortical versus shorter screws. Hand Surg Rehabil. 2019;38(1):28-33. [7] BERGSMA M, DOORNBERG J, DUIT R, et al. Volar plating in distal radius fractures: A prospective clinical study on efficacy of dorsal tangential views to avoid screw penetration. Injury. 2018;49(10):1810-1815. [8] TANAKA Y, GOTANI H, YANO K, et al. Evaluation of flexor pollicis longus tendon attrition using color Doppler imaging after volar plate fixation for distal radius fracture. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(3):447-452. [9] KONG L, ZHAI Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Radiocarpal joint stiffness following surgical treatment for distal radius fractures: the incidence and associated factors. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):313. [10] THOMAS D, ZANIN D. Hand rehabilitation after distal radius fracture. Hand Surg Rehabil. 2016;35S:S156-S61. [11] YUAN C, ZHANG H, LIU H, et al. Does concomitant ulnar styloid fracture and distal radius fracture portend poorer outcomes? A meta-analysis of comparative studies. Injury. 2017;48(11):2575-2581. [12] MCQUEEN M, CASPERS J. Colles’ fractures: does anatomical result affect the final function? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70:649-651. [13] 姜保国, 张殿英, 傅忠国, 等. 桡骨远端粉碎性骨折及关节内骨折的手术治疗[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2002,22(2):80-83. [14] GABL M, ARORA R, KLAUSER AS, et al. Characteristics of secondary arthrofibrosis after intra-articular distal radius fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(8): 1181-1188. [15] KREDER HJ, HANEL DP, AGEL J, et al. Indirect reduction and percutaneous fixation versus open reduction and internal fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the distal radius. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87-B:829-836. [16] FORWARD DP, DAVIS TRC, SITHOLE JS. Do young patients with malunited fractures of the distal radius inevitably develop symptomatic post-traumatic osteoarthritis? J Bone Joint Surg. 2008;90-B:629-637. [17] 李哲, 孙天祥, 钟易林, 等. 手法复位石膏外固定与切开复位锁定钢板内固定 治疗 AO-B、C 型桡骨远端骨折的比较[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019, 34(5):534-536. [18] KHAN M, NOORDIN S, HASHMI P. Intra-articular distal radius fractures: Postoperative roentgenographic and functional outcomes. J Pak Med Assoc. 2016; 66(3):275-279. [19] LOISEL F, BOURGEOIS M, RONDOT T, et al. Treatment goals for distal radius fractures in 2018: recommendations and practical advice. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(8):1465-1468. [20] 张兴平. 桡骨远端骨折治疗方法的选择与思考[J]. 中国骨伤,2011,24(11): 887-889. [21] THELEN S, GRASSMANN JP, JUNGBLUTH P, et al. Distal radius fractures : Current treatment concepts and controversies. Chirurg. 2018;89(10):798-812. [22] 廉志明, 晶杨, 张太良, 等. 桥接外固定架联合克氏针与掌侧锁定板修复桡骨远端不稳定型骨折的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(44):6590-6598. [23] MANSURIPUR P, GIL J, CASSIDY D, et al. Fixation Strength in Full and Limited Fixation of Osteoporotic Distal Radius Fractures. Hand (N Y). 2018;13(4):461-465. [24] WILSON J, HOLZGREFE R, STALEY C, et al. Use of a 5-Item Modified Frailty Index for Risk Stratification in Patients Undergoing Surgical Management of Distal Radius Fractures. J Hand Surg. 2018;43(8):701-709. [25] ROSENAUER R, PEZZEI C, QUADLBAUER S, et al. Complications after operatively treated distal radius fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(5):665-673. [26] JOHNSON N, DIAS J, WILDIN C, et al. Comparison of distal radius fracture intra-articular step reduction with volar locking plates and K wires: a retrospective review of quality and maintenance of fracture reduction. J Hand Surg. 2017; 42(2):144-150. |
| [1] | Yuan Jiabin, Zhu Zongdong, Tang Xiaoming, Wei Dan, Tan Bo, Xiao Chengwei, Zhao Ganlinwei, Liao Feng. Classification and reduction strategies for irreducible intertrochanteric femoral fracture based on anatomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1341-1345. |
| [2] | Pan Baoshun, Fang Zhen, Gao Mingjie, Fang Guiming, Chen Jinshui. Design for posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation system with fusion cage based on imaging data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1372-1376. |
| [3] | Li Kun, Gao Erke, Xiong Feng, Wang Xing, Wu Danqi, Li Zhijun, Zhang Shaojie, Liu Yanan, Duo Lan, Li Ziyu. Feasibility of axial transpedicle screw internal fixation in children aged 1 to 6 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1383-1387. |
| [4] | Yang Jun, Yang Qun, Zhang Rui, Jiang Chang. A novel slidable pedicle screw-rod system for lumbar tuberculosis: promoting bone graft fusion by producing stress stimulation to fused segment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 914-918. |
| [5] | Zhang Xinlong, Ci Wentao, Luo Kaiwen, Yan shi. Internal fixation failure after proximal femoral nail antirotation: causes and reoperation strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 973-979. |
| [6] | Chen Weijian, Chen Zehua, Wu Jiatao, Xu Xuemeng, Du Jianping. Imbalance of mechanical properties about bilateral shoulder and neck muscle in patients with cervical spondylotic radiculopathy using MyotonPRO [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 430-434. |
| [7] | Liang Haoran, Zhou Xin, Yang Yanfei, Niu Wenjie, Song Wenjie, Ren Zhiyuan, Wang Xueding, Liu Yang, Duan Wangping. Pathogenesis of femoral head necrosis after internal fixation of femoral neck fractures in young adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 456-460. |
| [8] | Yang Ruijia, Jiang Lingkai, Dong Zhengquan, Wang Yunfei, Ma Zhou, Cong Linlin, Guo Yanjing, Gao Yangyang, Li Pengcui. Open reduction and internal fixation versus circular external fixation for tibial plateau fractures: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 480-486. |
| [9] | Cai Feng, Yu Bo, Zeng Duo, Chen Qincan, Liao Qi. Cortical bone trajectory in elderly patients with osteoporosis of lumbar disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 403-407. |
| [10] | Tian Chong, Gao Bo, Yu Hongwei, Wang Pei. Theoretical research and technical application of bone repair materials in the treatment of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3586-3591. |
| [11] | Zhan Yi, Kang Xin, Wang Yuhang, Zhang Haiping, He Simin, Sun Honghui, Hao Dingjun, Wang Biao. Biomechanical properties of a novel bone cement screw and traditional methods for Kummell’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(21): 3381-3388. |
| [12] | Zhan Yi, Wang Biao, Ma Yuli, He Simin, Sun Honghui, Hao Dingjun. Biomechanical evaluation of Kummell’s disease model fixed with novel bone cement screw system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2795-2800. |
| [13] | Yan Kun, Mou Limin, Yang Xiaohui, Wang Jian, Ran Jian. Finite element analysis of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture fixed with three configurations of cannulated screws [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2807-2811. |
| [14] | Wang Sizhe, Gao Kunfan, Xu Zhenzhen, Gao Haiyan, Huang Haoran, Dai Shiyou, Ma Jianlin, Wang Feng. 3D printing technology assisted traditional plate fixation for the treatment of complex tibial plateau fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2823-2827. |
| [15] | Wang Lei, Li Jia, Li Tao, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Femoral neck system for internal fixation of femoral neck fracture in high altitude areas [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(18): 2844-2848. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||