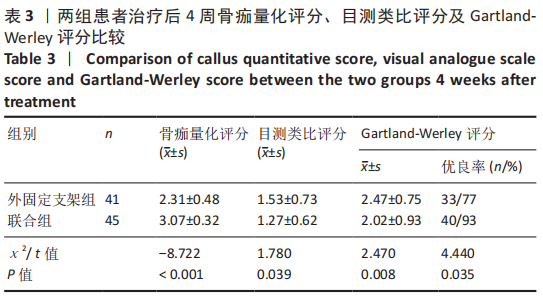
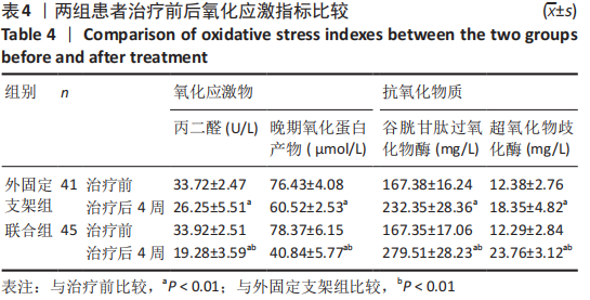
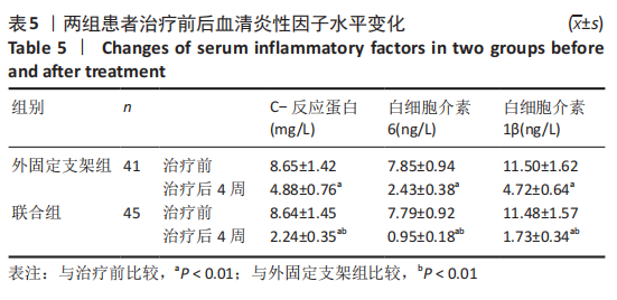
[1] CUI Z, MENG X, FENG H, et al. Estimation and projection about the standardized prevalence of osteoporosis in mainland China. Arch Osteoporos. 2019;6;15(1):2.
[2] 杨速剑,陈婷,余燕儿.万向锁定板联合仙灵骨葆对老年复杂桡骨远端骨折合并骨质疏松患者的疗效及血清碱性磷酸酶胰岛素样生长因子-1的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2019,19(19):3370-3372.
[3] 于鸿,洪云飞.尺骨茎突与乙状切迹骨折对桡骨远端骨折患者腕关节功能的影响[J]. 中国烧伤创疡杂志,2021,33(1):51-54.
[4] HEIDGERD R, MORGAN J, SCHENTRUP D. Evaluation of functional outcomes for adult patients after distal radius fracture treated with volar plate fixation versus nonsurgical care. J Trauma Nurs. 2019;26(1): 59-64.
[5] 郑立程,季滢瑶,赵政.外固定支架结合Kapandji技术治疗老年桡骨远端不稳定性骨折[J]. 中医正骨,2020,32(3):67-69,73.
[6] ROH YH,KOH YD,NOH JH,et al. Effect of health literacy on adherence to osteoporosis treatment among patients with distal radius fracture. Arch Osteoporos. 2017;12(1):42.
[7] QUADLBAUER S, PEZZEI C, JURKOWITSCH J, et al. Rehabilitation after distal radius fractures: is there a need for immobilization and physiotherapy? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2020;140(5):651-663.
[8] 黄菊,祁方遒.中频脉冲电疗法对单纯性胸腰椎压缩性骨折病人腹胀的影响[J].全科护理,2018,16(1):75-77.
[9] WALKER LS,STONE AL,SMITH CA, et al. Interacting influences of gender and chronic pain status on parasympathetically mediated heart ratevariability in adolescents and young adults. Pain. 2017;158(8):1509-1516.
[10] KEITH DS,VRANIC G,NISHIO-LUCAR A. Graft Function and Intermediate-Term Outcomes of Kidney Transplants Improved in the Last Decade: Analysis of the United States Kidney Transplant Database. Transplant Direct. 2017;3(6):e166.
[11] 许新忠,赵耀,张积森,等.难复性胫骨干骨折影像学特点及临床意义[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(8):722-726.
[12] 李红,郑一舟,毛文,等.外固定支架联合掌侧锁定钢板治疗桡骨远端C3型骨折[J].实用手外科杂志,2020,34(3):297-299.
[13] ZHANG J, ZHUANG YQ, ZHOU L, et al. Sparing the pronator quadratus for volar plating of distal radius fractures: a comparative study of two methods. J Int Med Res. 2019;19:300060519893851.
[14] PORRINO JA JR, MALONEY E, SCHERER K, et al. Fracture of the distal radius: epidemiology and premanagement radiographic characterization. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(3):551-559.
[15] 褚庭纲,陈星隆,李志杰,等.扩展桡侧腕屈肌入路辅助骨折灶内原位自体植骨治疗桡骨远端粉碎性骨折[J].中华手外科杂志,2018, 34(2):102-106.
[16] 陈达鑫,陈臻,吴晓鹏. 基于理筋手法的早期功能锻炼对高龄AO-C型桡骨远端骨折患者的影响[J]. 广州医科大学学报,2020,48(3):39-43.
[17] 杨贺杰,张亮,邵荣学,等.球囊扩张复位外固定支架固定与切开复位锁定加压钢板内固定治疗骨质疏松性 桡骨远端C型骨折的对比研究[J].中医正骨,2019,31(9):14-19,29.
[18] 桑梓英,唐建军,王长鑫.掌侧锁定加压钛板与外固定支架治疗不稳定桡骨远端C型骨折的临床疗效分析[J].重庆医学,2018,47(8): 1049-1051.
[19] 曹发奇,周武,夏天,等.跨关节外固定支架治疗老年AO分型C3型桡骨远端骨折术后并发症分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018, 20(11):960-963.
[20] 李家德,钟永翔,陈榆,等.外固定架结合克氏针有限固定与掌侧锁定板治疗桡骨远端粉碎骨折的疗效对比[J].中华手外科杂志, 2018,34(3):185-188.
[21] 桑庆华,张世虎,姜佩瑜,等.外固定架联合克氏针撬拨复位固定在治疗桡骨远端复杂关节内骨折的应用研究[J]. 浙江临床医学, 2018,20(8):1421-1423.
[22] 李育刚,张元松,许泽川,等.斜T型钢板内固定联合植骨在老年桡骨远端C型骨折治疗中的应用[J].创伤外科杂志,2019,21(10): 750-753.
[23] 冯政,陆亚钧,王磊,等.掌侧锁定钢板与外固定支架治疗AO-C2/3型桡骨远端骨折的对比研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2020,9(12): 944-948.
[24] KEITH DS, VRANIC G, NISHIO-LUCAR A. Graft Function and Intermediate-Term Outcomes of Kidney Transplants Improved in the Last Decade: Analysis of the United States Kidney Transplant Database. Transplant Direct. 2017;25:3(6):e166.
[25] GASPERONI F, IEVA F, BARBATI G, et al.Multi-state modelling of heart failure care path: A population-based investigation from Italy. PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0179176.
[26] 谢成龙,安荣泽,齐新文,等.中频脉冲疗法辅助治疗骨质疏松性桡骨远端骨折的临床效果及机制[J].山东医药,2017,57(16):52-54.
[27] 冯文龙,周炳华,黄伟,等.股骨颈骨折患者氧化应激水平与骨折愈合进度和凝血功能的相关性研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2018,20(7): 544-546.
[28] 金鑫,关凯.股骨粗隆间粉碎性骨折患者围手术期凝血功能和氧化应激指标的变化[J].血栓与止血学,2018,24(2):234-236.
[29] 罗宝宁,王国新.中频脉冲疗法联合外固定对骨质疏松性桡骨远端骨折患者骨代谢、炎症反应及氧化应激的影响[J].海南医学院学报, 2017,23(17):2377-2380.
[30] CELER O, AKALIN A, OZTUNALI C. Effect of teriparatide treatment on endothelial function, glucose metabolism and inflammation markers in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2016,85(4):556-560.
[31] HIGGS J, DERBYSHIRE E, STYLES K. Nutrition and osteoporosis prevention for the orthopaedic surgeon: A wholefoods approach. EFORT Open Rev. 2017;2(6):300-308.
(责任编辑:GD,ZN,ZH)
|