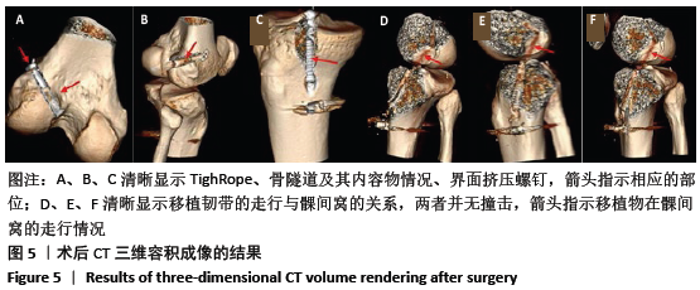
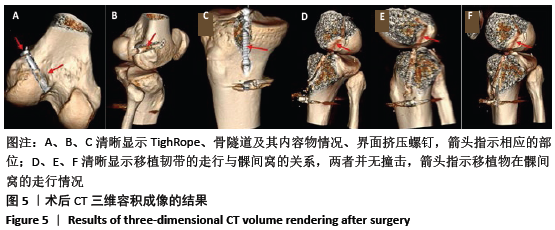
[1] 杨勇,张斌,贺占坤,等.前交叉韧带损伤后不同时间、年龄、性别对半月板和软骨损伤的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013, 28(10):967-968.
[2] 马勇,张家豪,蒋艳芳,等.股骨骨道位置对前交叉韧带术后半年腘绳肌腱移植物信噪比的影响 [J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(6): 469-473.
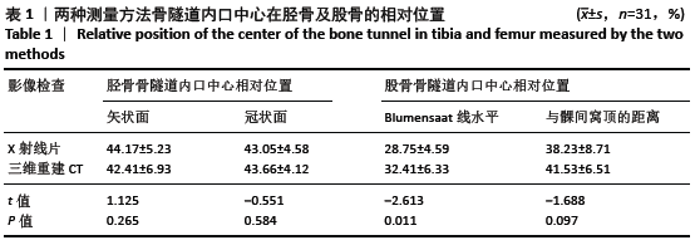
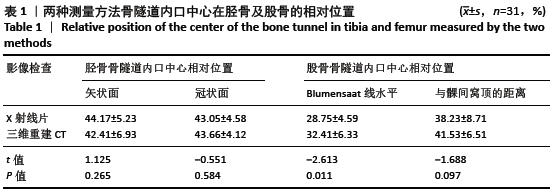
[3] 周波,白希壮,郜玉忠,等.三维重建CT与X线测量前交叉韧带重建后骨道位置对比研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2008(3):290-293.
[4] 高冠奇,张克远.CT图像后处理重建膝关节三维模型:3D-CT评估前交叉韧带重建后的骨道差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(40): 6397-6401.
[5] KLOS TV, HABETS RJ, BANKS AZ, et al. Computer Assistance in Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;354(354):65-69.
[6] 贾国庆,余志平,胡鹏宇,等.前交叉韧带重建中电磁导航系统辅助骨隧道定位的准确性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(15): 2374-2380.
[7] FORSYTHE B, KOPF S, WONG AK, et al. The location of femoral and tibial tunnels in anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction analyzed by three-dimensional computed tomography models. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(6):1418-1426.
[8] BROWN CH JR, SPALDING T, ROBB C. Medial portal technique for single-bundle anatomical anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction. Int Orthop. 2013;37(2):253-269.
[9] LANZETTI RM, LUPARIELLO D, DE CARLI A, et al. Can the outside-in half-tunnel technique reduce femoral tunnel widening in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction? A CT study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27(5):659-664.
[10] 马天骏,曾春,蔡道章.动态CT评价前交叉韧带解剖单束重建术后韧带的等长情况[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(5):393-398.
[11] LAMORIA R, SHARMA A, GOYAL D, et al. Influence of three different fixation methods on femoral tunnel widening in ACL reconstructed patients evaluated using computed tomography (CT) scan. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2020;30(3):411-417.
[12] YASUMA S, NOZAKI M, MURASE A, et al. Anterolateral ligament reconstruction as an augmented procedure for double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction restores rotational stability: Quantitative evaluation of the pivot shift test using an inertial sensor. Knee. 2020;27(2):397-405.
[13] IRRGANG JJ, TASHMAN S, MOORE C, et al. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes Following Anatomic Single vs. Double-Bundle ACL Reconstruction: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Orthop J Sports Med. 2017;5(7_suppl6):2325967117S0024. doi:10.1177/2325967117s00248.
[14] HAKOZAKI A, NIKI Y, ENOMOTO H, et al. Clinical significance of T2*-weighted gradient-echo MRI to monitor graft maturation over one year after anatomic double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A comparative study with proton density-weighted MRI. Knee. 2015;22(1):4-10.
[15] VAN ECK CF, SCHKROHOWSKY JG, WORKING ZM, et al. Prospective Analysis of Failure Rate and Predictors of Failure After Anatomic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction With Allograft. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(4):800-807.
[16] Forsythe B, Lansdown D, Zuke WA, et al. Dynamic 3-Dimension—al Mapping of Isometric Anterior Crueiate Ligament Attachment Sites on the Tibia and Femur.”Is Anatomic Also Isometric? Atthroscopy. 2018;34(8):2466-2475.
[17] 陈铁柱,陈宏文,王靖,等.前交叉韧带前内入路解剖单束重建与过顶位单束重建的疗效比较[J].中国内镜杂志,2019,25(1):41-47.
[18] 韩晓珺,戚文潇,赵金忠.前交叉韧带损伤及重建术后运动学及生物力学研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(5):287-290.
[19] DE PAULA LEITE CURY R, SIMABUKURO AM, DE MARQUES OLIVEIRA V, et al. Anteromedial positioning of the femoral tunnel in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction is the best option to avoid revision: a single surgeon registry. J Exp Orthop. 2020;7(1):11.
[20] ZAVRAS TD, RACE A, BULL AM, et al. A comparative study of isometric points for anterior cruciate ligament graft attachment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2001;9(1):28-33.
[21] 姜方宜,张健,陈世益.前十字韧带类等长重建术中骨隧道位点研究的系统综述[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(11):707-716.
[22] STOLARZ M, BINKOWSKI M, FICEK K, et al. Methodology for X-ray Microtomography Assessment of Regeneration and Growth of Bone Tissue Within the Area of Integration of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Graft in Sheep. J Med Imaging Health Inform. 2016;6(1):14-21.
[23] DABIRRAHMANI D, CHRISTOPHER HOGG M, WALKER P, et al. Comparison of isometric and anatomical graft placement in synthetic ACL reconstruction: a pilot study. Comput Bid Med. 2013;43(12): 2287-2296.
[24] KERNKAMP WA, VARADY NH, LI JS, et al. An In Vivo Prediction of Anisometry and Strain in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction—A Combined Magnetic Resonance and Dual FluoroscopicImaging Analysis. Arthroscopy. 2018;34(4):1094-1103.
[25] VILLARDI JG, VIHARDI A, SOUZA LABD, et al. Topograohic study of the isometry testing in anatomic reconstructions of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee. Cogent Medicine. 2018;5(1):1470067.
[26] 程相允,张升校,曹万全,等.Blumensaat线对于膝关节疾病的辅助参考意义[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(44):6682-6688.
[27] 崔荣涛.三维CT重建技术评估AM和TT两种手术方式行前交叉韧带重建术后膝关节的运动水平[D].大连:大连医科大学,2013.
[28] WEBSTER KE, FELLER JA, ELLIOTT J, et al. A comparison of bone tunnel measurements made using computed tomography and digitalplain radiography after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Arthroscopy. 2004;20(9):946-950.
[29] Sadoghi P, Kr pfl A, Jansson V, et al. Impact of tibial and femoral tunnel position on clinical resul tsafte ranterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(3):355-364.
[30] KOSY JD, WALMSLEY K, ANASPURE R, et al. Flexible reamers create comparable anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction femoral tunnels without the hyperflexion required with rigid reamers: 3D-CT analysis of tunnel morphology in a randomised clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(6):1971-1978.
[31] 戚喜勋,关丽明,郭磊,等.3D-CT在前交叉韧带重建术后评估中的临床价值[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012,29(4):673-676,681.
[32] 李光政,韩先伟,张春礼,等.双源CT三维重建前交叉韧带单束重建术后移植物及其走形与骨隧道定位的关系研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(2):127-131.
[33] KOSY JD, WALMSLEY K, ANASPURE R, et al. Flexible reamers create comparable anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction femoral tunnels without the hyperflexion required with rigid reamers: 3D-CT analysis of tunnel morphology in a randomised clinical trial. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2020;32(1):17.
[34] 杨献峰,王冬梅,陈东阳,等.前交叉韧带重建术后评价的CT和磁共振成像比较研究[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2014,34(11): 1631-1635.
[35] 李丹,赵其纯,尚希福,等.三维CT对前交叉韧带重建术后骨道的早期评估[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(2):130-133.
[36] TIE K, WANG H, WANG X, et al. Measurement of bone mineral density in the tunnel regions for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry,computed tomography scan,and the immersion technique based on Archimedes’ principle. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(10):1464-1471.
[37] MUSAHL V, BEDI A, CITAK M, et al. Effect of single-bundle and double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstructions on pivot-shift kinematics in anterior cruciate ligament and meniscus deficient knees. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(2):289-295.
[38] IRIUCHISHIMA T, HORAGUCHI T, KUBOMURA T, et al. Evaluation of the intercondylar roof impingement after anatomical double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using 3D-CT. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):674-679.
[39] TAKETOMI S, NAKAGAWA T, TAKEDA H, et al. Anatomical placement of double femoral tunnels in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Anteromedial tunnel first or posterolateral tunnel first. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;1(3):424-431.
[40] 张腾,胡晓青,马勇,等.椭圆形骨道重建前交叉韧带股骨隧道的影像学研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(2):106-110.
[41] 孙学斌,曹力.3D打印辅助关节镜下前交叉韧带等长重建股骨隧道定位的研究[J].中国内镜杂志,2019,25(12):54-59.
|