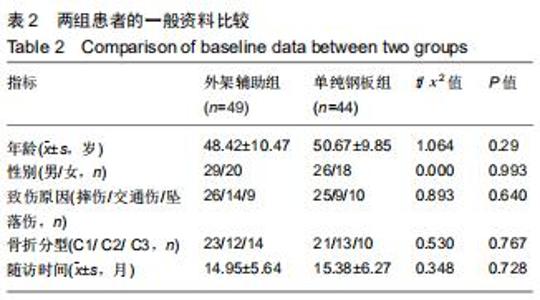
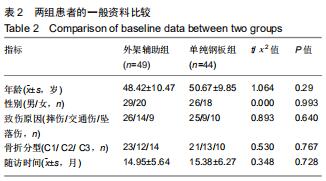
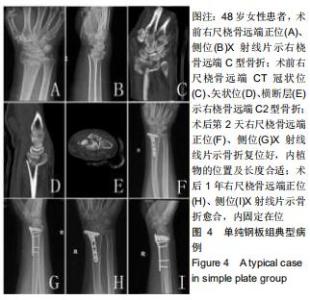
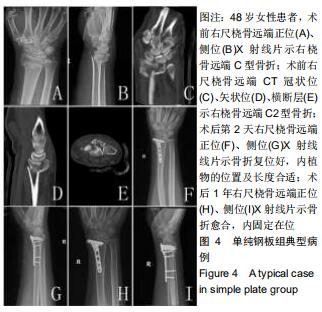
|
[1] 高志强,安贵生,李绍良.应用扩展的桡侧腕屈肌入路治疗复杂的桡骨远端关节内骨折[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2017,49(2):349-353.
[2] SAVING J, SEVERIN WS, OLSSON K, et al. Nonoperative Treatment Compared with Volar Locking Plate Fixation for Dorsally Displaced Distal Radial Fractures in the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2019;101(11):961-969.
[3] 唐芳根,钟俊桥,刘建庭.2.4mm锁定加压接骨板治疗桡骨远端C型骨折的临床效果及腕关节功能评价[J].广东医学,2019,40(8):1160-1163.
[4] 杨召,苑珍珍,马剑雄,等.切开复位内固定与外固定治疗不稳定桡骨远端骨折远期疗效的荟萃分析[J].中华医学杂志,2017,97(41):3269-3272.
[5] 白求恩公益基金会创伤骨科专业委员会,中国医疗保健国际交流促进会加速康复外科学分会创伤骨科学组.加速康复外科理念下桡骨远端骨折诊疗方案优化的专家共识[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(2):93-101.
[6] OGUNLEYE AA, MULLNER DF, SKOCHDOPOLE A, et al. Remote Injuries and Outcomes After Distal Radius Fracture Management. Hand (N Y).2019;14(1):102-106.
[7] ZENGIN EC, OZCAN C, ASLAN C, et al. Cast immobilization versus volar locking plate fixation of AO type C distal radial fractures in patients aged 60 years and older. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2019; 53(1):15-18.
[8] 张东伟.闭合复位外固定支架与掌侧锁定钢板内固定治疗桡骨远端C型骨折的疗效[J].实用临床医学,2019,20(4):51-52.
[9] 夏丽平,杨德福,郁辉,等.掌侧锁定钢板联合背侧植骨治疗C3型桡骨远端骨折的疗效观察[J].骨科,2019,10(4):356-358.
[10] HUETTEMAN HE, SHAUVER MJ, MALAY S, et al. Variation in the Treatment of Distal Radius Fractures in the United States: 2010 to 2015. Plast Reconstr Surg.2019;143(1):159-167.
[11] TOON DH, PREMCHAND RAX, SIM J, et al. Outcomes and financial implications of intra-articular distal radius fractures: a comparative study of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) with volar locking plates versus nonoperative management. J Orthop Traumatol.2017; 18(3):229-234.
[12] 刘磊,蒋建农,王勇,等.2.7mm掌侧双柱锁定加压钢板内固定治疗C型桡骨远端骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(7):721-723.
[13] RONGIÈRES M. Is external or internal distraction useful for treating distal radial fractures?. Hand Surg Rehabil.2016;35S:S86-S88.
[14] 卓金,王莎莎,陈其强,等.C型桡骨远端骨折患者腕关节功能及骨折复位质量:克氏针辅助外固定架、外固定架及掌侧入路钢板内固定的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5126-5132.
[15] 曹发奇,周武,夏天,等.跨关节外固定支架治疗老年AO分型C3型桡骨远端骨折术后并发症分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(11):960-963.
[16] 张亮,邹宁,周健伟,等.桡骨远端骨折掌、背侧钢板固定的生物力学研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(2):131-134.
[17] LEE DY, PARK YJ, PARK JS. A Meta-analysis of Studies of Volar Locking Plate Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures: Conventional versus Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis.Clin Orthop Surg.2019;11(2): 208-219.
[18] YANG Z, LIM PPH, TEO SH, et al. Association of wrist and forearm range of motion measures with self-reported functional scores amongst patients with distal radius fractures: a longitudinal study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2018;19:142.
[19] 王东昕,韩鑫,李志德,等.影响桡骨远端骨折有限切开复位外固定架联合克氏针固定术后功能恢复的相关因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017, 25(2):97-101.
[20] LAMEIJER CM, DUIS HJT, DUSSELDORP IV, et al. Prevalence of posttraumatic arthritis and the association with outcome measures following distal radius fractures in non-osteoporotic patients: a systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2017;137(11):1499-1513.
[21] BOBOS P, LALONE EA, GREWAL R, et al. Do Impairments Predict Hand Dexterity After Distal Radius Fractures? A 6-Month Prospective Cohort Study. Hand (N Y). 2018;13(4):441–447.
[22] 张勇,阿良,张乐,等.固定方式对C型桡骨远端骨折术后长度维持的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2016,45(03):246-248+254.
[23] 刘海涛.DVR解剖型掌侧锁定接骨板治疗C型桡骨远端骨折的临床疗效[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2016,9(3):237-240.
[24] 张英泽.骨折顺势复位固定理论在创伤骨科中的应用[J].中华创伤杂志, 2017,33(7):577-580.
[25] 柯巍,李珂,王思博,等.切开复位钢板内固定与闭合复位外固定支架固定治疗桡骨远端骨折:评分及线性回归分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(8): 1196-1202.
[26] 李家德,钟永翔,陈榆,等.外固定架结合克氏针有限固定与掌侧锁定板治疗桡骨远端粉碎骨折的疗效对比[J].中华手外科杂志, 2018,34(3):185-188.
[27] 黎俊豪,郑伟坤,蔡维山.锁定加压钢板联合外固定架与单纯锁定加压钢板治疗C型桡骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].临床骨科杂志, 2018,21(1):82-85.
[28] 刘俊,危蕾,廖苏平,等.掌侧锁定钢板联合外固定支架治疗桡骨远端C2、C3型骨折[J].中华手外科杂志,2018,34(1):67-68.
[29] 郑伟坤,汤俊芬,黎俊豪,等.单纯锁定钢板与钢板联合外固定架治疗桡骨远端复杂关节内骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(3): 277-280.
[30] RONGIÈRES M. Is the external fixator yet useful for treating fractures of the distal radius?. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2018;28(8): 1495-1497.
[31] VAKHSHORI V, ROUNDS AD, HECKMANN N, et al. The Declining Use of Wrist-Spanning External Fixators. Hand (N Y).2018;7: 1558944718791185.
[32] TAYLOR KF, GENDELBERG D, LUSTIK MB, et al. Restoring Volar Tilt in AO Type C2 Fractures of the Distal Radius With Unilateral External Fixation. J Hand Surg Am.2017;42(7):511-516.
[33] 王洪平,王川,兰玉平,等.陈旧性桡骨远端骨折内固定术中临时辅助应用单边跨腕关节外固定架的意义[J].中国伤残医学,2019,27(6):39-40.
[34] 韦新宁,韦仁智,黄小美,等.腕关节外固定支架联合断端植骨治疗桡骨远端C型骨折的疗效分析[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(2):122-125.
|