Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (14): 2207-2213.doi: 10.12307/2023.153
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role of growth differentiation factor 5 in osteoarthritis
Li Feifei, Zhang Yong, Wang Buyu, Yang Zhihang, Deng Jiang
- Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, First People’s Hospital of Zunyi, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-04-19Accepted:2022-05-30Online:2023-05-18Published:2022-09-30 -
Contact:Deng Jiang, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, First People’s Hospital of Zunyi, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Li Feifei, Physician, Third Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, First People’s Hospital of Zunyi, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81660367 (to DJ); Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Fund, No. (2016)1420 (to DJ); Guizhou Provincial Health Commission Science and Technology Fund, No. gzwkj 2021-236 (to DJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Feifei, Zhang Yong, Wang Buyu, Yang Zhihang, Deng Jiang. The role of growth differentiation factor 5 in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2207-2213.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
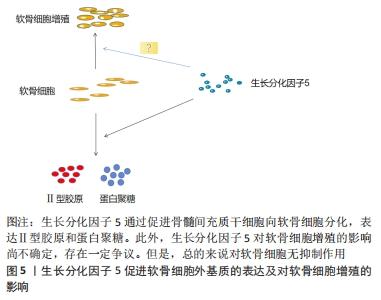
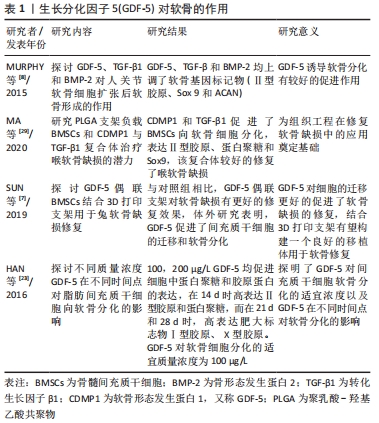
2.1.1 GDF-5促进软骨细胞生成 GDF-5对关节软骨的发育和内环境稳定是必要的,其与骨关节炎易感性之间存在相关性,GDF-5的缺乏可导致骨关节炎的发生。GDF-5的表达谱表明其在软骨形成,特别是软骨前凝结中具有重要作用。GDF-5可显著促进间充质干细胞的成软骨分化。MURPHY等[8]研究表明用GDF-5诱导人间充质干细胞,可显著上调软骨形成基因Ⅱ型胶原、SOX 9和蛋白聚糖(ACAN)的表达以及软骨特异性基质(糖胺聚糖、Ⅱ/Ⅰ型胶原比值)的合成。GDF-5不仅促进骨髓间充质干细胞的软骨形成,还促进了其他干细胞的软骨形成,如人胚胎干细胞[9]、兔脂肪间充质细胞[10]。GDF-5作为软骨诱导因子,通过与两种类型的丝氨酸-苏氨酸激酶跨膜受体(bone morphogenic protein receptor,BMPR)结合发挥作用。MANG等[11]证明GDF-5通过与BMPR1A受体结合促进了软骨形成和骨形成,GDF-5与BMPR1B受体结合可防止软骨细胞肥大分化,这有利于关节软骨的修复。吴磊等[12]探讨了质粒携带GDF-5转染鼠脂肪干细胞向成软骨细胞分化方向的影响,结果表明,GDF-5转染脂肪干细胞促进了脂肪干细胞向成软骨细胞分化,显著增加了Ⅱ型胶原、蛋白聚糖的表达,表明GDF-5促进间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化有较好的作用。 2.1.2 GDF-5对细胞增殖的影响 间充质干细胞大量存在于骨髓、滑膜、脂肪组织中,具有多向分化能力,在诱导因子的作用下可向成软骨、成骨和成脂等方向分化。以细胞为基础的软骨组织工程对于骨关节炎的治疗展现出有希望的治疗。骨关节炎的特点之一是关节软骨的进行性退变,由于软骨细胞的促分解大于促合成,从而导致软骨的退变。间充质干细胞分化为软骨组织需要经历一系列变化,首先是间充质干细胞的凝结,凝结后分化为软骨细胞,最后变成软骨组织。软骨细胞继续增殖和成熟进入肥大分化阶段,最终这些终末分化的软骨细胞发生凋亡,并被初级骨化中心的骨所替代,即发生软骨内成骨[13]。研究发现,GDF-5可促进间充质干细胞增殖,这对于间充质干细胞的凝结有重要作用,从而进一步促进软骨细胞分化。GDF-5表达在软骨前凝结过程中。在间充质细胞凝结过程中,GDF-5的存在增加了细胞与细胞的黏附,从而促进了细胞的凝结。杨治等[14]采用GDF5基因转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,发现可促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的同时诱导其向软骨细胞分化。ZHAO等[15]采用不同浓度的GDF-5诱导表皮干细胞,通过CCK-8试剂检测GDF-5对鼠表皮干细胞增殖的影响,表明在一定浓度范围内GDF-5促进细胞增殖,GDF-5最适质量浓度为100 μg/L,超过此质量浓度时细胞的增殖下降。提示GDF-5对表皮干细胞的增殖可能促进伤口的愈合。也有研究发现,GDF5对血管内皮细胞的增殖起抑制作用但促进了血管内皮细胞的迁移[16],而这对于血管的形成起着重要作用,GDF-5也可促进血管内皮生长因子的表达,因此,GDF-5可能在血液循环中血管的再通扮演潜在作用。在许多研究认为,GDF-5诱导间充质干细胞增殖及向成软骨细胞分化成剂量依赖性,在100 μg/L GDF-5组的细胞增殖率显著高于其他浓度组,并且显著促进Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖的表达。然而,相关研究也证明,GDF-5转染骨髓间充质干细胞可促进其向软骨表型分化,对细胞增殖无明显影响[17]。卢康荣等[18]探讨将人GDF-5基因转染人骨髓间充质干细胞对细胞生长和分化的影响,发现转染组和未转染组细胞增殖能力无显著差异,说明GDF-5对细胞增殖无显著促进作用。因此,这与之前的说法相矛盾,究竟对细胞的增殖有无促进作用还需进一步验证,可能GDF-5对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖无影响,而对其它细胞(如表皮干细胞、血管内皮细胞)增殖有促进作用。但是,可以肯定的是GDF-5对细胞增殖无抑制作用,不影响间充质干细胞向软骨表型分化,见图5。"

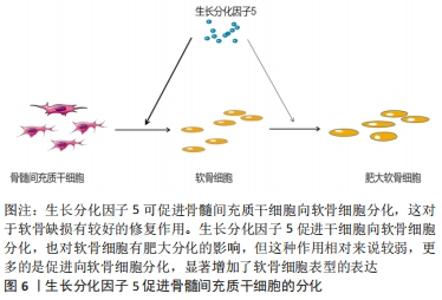
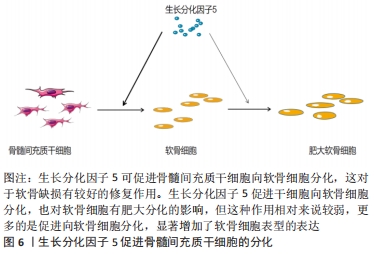
2.1.3 GDF-5促进细胞迁移 有研究表明,骨髓间充质干细胞在体内募集和迁移到缺损部位有利于软骨缺损的修复,进而促进病灶的愈合[19]。而有研究报道GDF-5可促进细胞迁移,SUN等[7]用外源性GDF-5和GDF-5过表达处理体外培养的骨髓间充质干细胞,与对照组比较,显著促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移;在水凝胶负载的骨髓间充质干细胞支架偶联GDF-5,通过划痕检测发现,GDF-5显著增加了水凝胶包埋的骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移。在兔软骨缺损模型中,植入GDF-5修饰的水凝胶负载骨髓间充质干细胞支架也更好地促进软骨的修复,这种对软骨损伤的修复可能与GDF-5促进缺损处以外干细胞向病灶部位迁移,进而促进干细胞向软骨细胞分化所致[7]。 表皮干细胞迁移对伤口的愈合起着重要作用,而GDF-5在促进表皮干细胞的迁移中有着明显作用。LI等[20]研究表明GDF-5可以促进小鼠表皮干细胞在体内外的迁移,认为可能是通过RhoA-MMP9信号触发表皮干细胞的迁移。也有研究者报道,在全层的皮肤缺损中,GDF-5加速皮肤缺损的修复和伤口的闭合[21],这在未来应用于伤口愈合显现出良好的前景。 2.1.4 GDF-5对软骨细胞肥大分化的影响 软骨细胞肥大分化被认为是骨关节炎的基本特征。然而,如何抑制软骨细胞肥大分化是治疗骨关节炎较为棘手的问题,目前许多研究也集中在抑制软骨细胞肥大分化治疗骨关节炎,但是还没有能够有效逆转软骨细胞肥大分化的药物。COLEMAN等[22]证实GDF-5增强了体外间充质细胞的软骨形成和肥大,增加Ⅱ型胶原和糖胺聚糖的形成的同时也增加了Ⅰ型胶原和X型胶原的形成。HAN等[23]研究也证明,GDF-5促进体外培养的脂肪间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化,认为GDF-5的质量浓度在100 μg/L时对软骨分化是合适的;在14 d时高表达软骨特异性基因(Ⅱ型胶原和Aggrecan),然而在第21,28天时高表达肥大标志物(Ⅰ型胶原和X型胶原):这表明GDF-5在后期促进了软骨细胞肥大分化。研究表明,骨关节炎的发生可能是关节软骨细胞肥大分化引起的[24]。软骨细胞的肥大分化被认为是软骨修复的主要障碍,软骨细胞肥大最终可能导致细胞凋亡和骨化。在相关的研究报道中,人间充质干细胞用于软骨修复中观察到其向肥大分化,因此,防止软骨细胞向肥大细胞分化对于治疗骨关节炎具有重要意义[25]。对于GDF-5促进软骨细胞肥大成熟更多的集中在体外研究,张山锋等[26]也证明体外GDF-5诱导成人骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化的同时,促进其肥大成熟。然而,也有体外研究证实,将人GDF-5转染至骨髓间充质干细胞,促进了其向软骨细胞分化,高表达Ⅱ型胶原和蛋白聚糖;但是,免疫组化和免疫荧光显示不表达软骨细胞肥大标记物Ⅰ型胶原[27],这与其他人的研究结果相矛盾。许多研究应用GDF-5修复软骨缺损的体内研究中,均发现较好的促进了软骨损伤的修复,未见说明有软骨肥大分化的报道[28]。 GDF-5可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨、成软骨方向分化,软骨细胞肥大分化后继而成骨。KATAYAMA等[30]研究表明,GDF-5转染骨髓间充质干细胞,促进了软骨细胞外基质(Ⅱ型胶原和Aggrecan)的表达,同时也有软骨细胞肥大标记物(Ⅰ型胶原)的表达,但是相对于未转染组,转染后Ⅰ型胶原的表达是降低的,这表明GDF-5促进软骨细胞分化大于软骨细胞肥大分化。此外,有研究表明,GDF-5显著增加了软骨细胞特异性基因(Aggrecan和Sox 9)的表达[31],因此,GDF-5可能更倾向于修复软骨缺损,而不是阻碍其修复;对于促进软骨细胞肥大分化可能更多的是向成骨分化,在这篇研究中免疫组织化学染色显示,在软骨下骨区域填充了大量的Ⅰ型胶原,在缺损表面表达大量的Ⅱ型胶原,较好地修复了关节软骨及软骨下骨。但是,目前存在的一个问题是基于组织工程修复骨软骨缺损,如何使间充质干细胞上层向软骨细胞分化,分化为永久性软骨,下层向成骨方向分化,这是仍待解决的问题。因为骨关节炎不仅累及关节软骨,还常累及到软骨下骨。有研究者认为,当间充质干细胞直接放置在关节软骨缺损中,它们自发分化导致Ⅱ型胶原的表达,而没有X型胶原,这表明出现了一种关节样表型[32]。这可能结合相关受体或者激活某个信号分子,但是相关的作用机制仍然不清楚,还需要进一步深入研究。见图6。 "
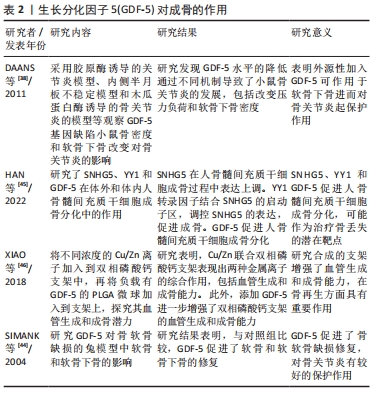
2.2 GDF-5对软骨下骨的作用 软骨下骨是指透明软骨和骨水泥线以下的骨层,解剖学上可分为软骨下骨板和软骨下骨小梁两部分。软骨下骨在骨关节炎的发生发展中具有重要作用,表现为骨关节炎的微观结构和组织病理改变(如骨髓病变、软骨下骨硬化及微损伤),进而导致软骨下骨及上覆软骨的微结构改变[33]。在骨关节炎的早期阶段,出现了骨的丢失、骨小梁的厚度增加,晚期出现松质骨塌陷[34-35]。随着对骨关节炎的认识进展,关节软骨和软骨下骨的同时进行性改变是骨关节炎发病的关键因素,表明骨-软骨相互作用在骨关节炎的发展中发挥重要作用[36-37]。在骨关节炎患者中,存在不同程度的软骨下骨质硬化,但由于骨矿化不足,增加了软骨下骨对软骨的应力,进而导致关节软骨破坏,逐渐导致关节间隙变狭窄,加重骨关节炎的发生发展。 有研究表明,GDF-5可导致软骨下骨的改变。DAANS等[38]研究表明GDF-5基因缺乏的小鼠软骨下骨密度减低,小鼠体内GDF-5水平降低促进了骨关节炎的发展;相反,可能说明外源性加入GDF-5可增加软骨下骨矿化密度,从而起到促进软骨修复的作用。在骨关节炎中,早期软骨下骨改变主要以骨吸收为主,晚期骨形成增加,导致软骨下骨发生硬化,但是由于其矿化不足,在异常的负荷作用下,软骨下骨易发生微骨折,继而引起关节软骨的退行性改变[39-40]。GDF-5可促进间充质干细胞向成骨分化,用于骨再生修复。促进骨折愈合的一个至关重要的因素是良好的血液供应。研究发现,GDF-5不仅可促进间充质干细胞向成骨分化,而且还可刺激血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)的表达,从而刺激骨再生[41-42]。GDF-5是骨形态发生蛋白家族成员,骨形态发生蛋白对骨形成有较强的作用。GDF-5的突变将导致骨骼的畸形(如短趾、短肢等)。GDF-5能够诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化,促进Ⅰ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶和骨钙素的表达。有相关研究认为GDF-5诱导成骨分化成剂量依赖性。KAKUDO等[43]将不同剂量的GDF-5与Ⅰ型胶原混合植入大鼠腿部肌肉,3周后组织学检查发现,500 μg GDF-5组只有骨组织而没有软骨,300 μg GDF-5组表达有软骨组织和部分骨组织,说明GDF-5诱导成骨呈剂量依赖性。但是对于GDF-5诱导成骨分化的剂量界限值并没有明确指出,在这方面还需要进一步探讨。SIMANK等[44]运用Ⅰ型胶原和GDF-5复合物应用于全层软骨缺损,研究GDF-5对兔骨软骨缺损模型软骨和软骨下骨的影响,发现与单纯Ⅰ型胶原对照组比较,在术后4和8周,实验组的软骨的修复效果显著优于对照组,并且软骨下骨部分再生,随着时间延长,软骨下骨已经完全被修复,表明GDF-5对软骨下骨缺损有较好的作用。但是对于GDF-5促进软骨分化的同时也促进成骨分化的作用机制仍然不清楚,尚需要进一步的研究。 综上,GDF-5对软骨下骨也具有一定的修复作用。促进间充质干细胞成骨分化,同时也刺激血管内皮生长因子的表达,对骨再生发挥重要作用。 GDF-5对成骨作用的汇总,见表2。 "
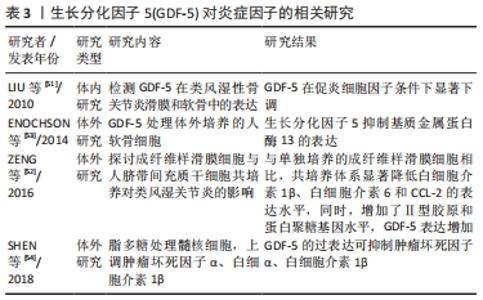
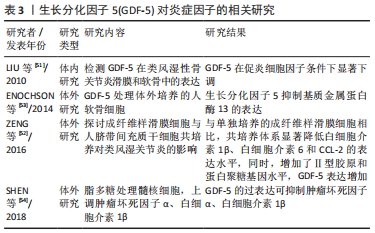
2.3 GDF-5对炎症因子的作用 骨关节炎是中老年人群中最常见的关节疾病,其主要临床表现是疼痛和关节的功能障碍,严重影响着患者的身心健康。骨关节炎的是多样且复杂的,有学者认为滑膜炎症在疾病发展中具有重要作用。研究表明,骨关节炎的一个早期表现为滑膜的炎症,滑膜炎的发生发展加重了骨关节炎的严重程度[47]。而且滑膜炎症与疼痛、关节结构损害密切相关[48]。炎症因子是骨关节炎患者关节中的软骨细胞和滑膜细胞产生的,在骨关节炎条件下,滑膜成纤维细胞是促炎细胞因子和基质降解酶的来源。促炎细胞因子,如白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α是早期骨关节炎分泌的介质之一[49-50],而这些炎症因子导致了软骨细胞外基质的降解。总之,炎症在促进骨关节炎发生发展中发挥至关重要的。 LIU等[51]研究表明,类风湿性关节炎和骨关节炎患者滑膜和关节软骨中均有GDF-5的表达,其表达被促炎细胞因子白细胞介素1β所抑制,表明外源性加入GDF-5可能对炎症有抑制作用,从而起一个保护作用,延缓骨关节炎的进展。ZENG等[52]将成纤维样滑膜细胞与人间充质干细胞共培养探讨对类风湿关节炎的影响,研究发现,与成纤维样滑膜细胞单独培养相比,共培养系统显著降低了炎症因子(白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和CCL-2)的表达,增加了GDF-5和软骨形成,高表达软骨特异性基因(蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原)。在这里猜测可能是GDF-5抑制了炎症因子的表达,促进软骨形成。然而,目前大多数对GDF-5的研究主要集中在促进软骨损伤修复方面,在关节内注射GDF-5是否能够抑制骨关节炎中炎症因子的表达还少有报道。在体外实验相关研究发现,GDF-5可抑制炎症因子的表达。ENOCHSON等[53]发现GDF-5刺激人软骨细胞合成代谢基因的表达,抑制软骨细胞外基质降解酶(基质金属蛋白酶13和ADAMTS4)。SHEN等[54]证明体外分离培养的髓核细胞用脂多糖处理,使培养液中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、前列腺素E2蛋白表达水平和NO浓度上调,而过表达GDF-5可降低脂多糖诱导的髓核细胞肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、前列腺素E2的表达水平。这实验说明在体外GDF-5可抑制炎症因子的释放,许多体内实验研究修复软骨缺损均未检测是否能降低关节内炎症因子的表达,而抑制炎症因子的表达也可延缓骨关节炎的进展。在骨关节炎中,GDF-5对炎症因子的作用在未来还需要进一步的研究来说明是否具有抗炎作用。 GDF-5对炎症因子作用的汇总,见表3。 "
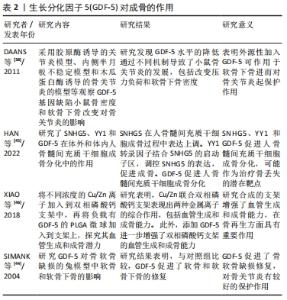
| [1] GARCIADIEGO-CáZARES D, AGUIRRE-SáNCHEZ HI, ABARCA-BUIS RF, et al. Regulation of α5 and αV Integrin Expression by GDF-5 and BMP-7 in Chondrocyte Differentiation and Osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0127166. [2] KANIA K, COLELLA F, RIEMEN A, et al. Regulation of Gdf5 expression in joint remodelling, repair and osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):157. [3] BUNGARTZ M, KUNISCH E, MAENZ S, et al. GDF5 significantly augments the bone formation induced by an injectable, PLGA fiber-reinforced, brushite-forming cement in a sheep defect model of lumbar osteopenia. Spine J. 2017;17(11):1685-1698. [4] FITZGERALD M J, MUSTAPICH T, LIANG H, et al. Tendon Transection Healing Can Be Improved With Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Cultured With Growth Differentiation Factor 5 and Platelet-Derived Growth Factor. Hand (N Y). 2021:15589447211028929. [5] XU H, SUN M, WANG C, et al. GDF5-GelMA injectable microspheres laden with adipose-derived stem cells for disc degeneration repair. Biofabrication. 2020. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/abc4d3. [6] XIA B, CHEN G, ZOU Y, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combination with induced pluripotent stem cells-derived neural crest stem cells and growth differentiation factor 5 promotes sciatic nerve regeneration and functional recovery. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(4):625-636. [7] SUN Y, YOU Y, JIANG W, et al. 3D-bioprinting a genetically inspired cartilage scaffold with GDF5-conjugated BMSC-laden hydrogel and polymer for cartilage repair. Theranostics. 2019;9(23):6949-6961. [8] MURPHY MK, HUEY DJ, HU JC, et al. TGF-β1, GDF-5, and BMP-2 stimulation induces chondrogenesis in expanded human articular chondrocytes and marrow-derived stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2015; 33(3):762-773. [9] WANG T, NIMKINGRATANA P, SMITH CA, et al. Enhanced chondrogenesis from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2019;39:101497. [10] 刘振宁,贾长青,韩长旭,等.生长分化因子5诱导兔脂肪干细胞成软骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009, 23(4):483-489. [11] MANG T, KLEINSCHMIDT-DOERR K, PLOEGER F, et al. BMPR1A is necessary for chondrogenesis and osteogenesis, whereas BMPR1B prevents hypertrophic differentiation. J Cell Sci. 2020;133(16): jcs246934. [12] 吴磊,刘洋,谭俊峰,等.生长分化因子5诱导脂肪干细胞向成软骨细胞方向分化的实验研究[J].生物医学工程与临床,2017,21(4): 429-434. [13] MELROSE J, SHU C, WHITELOCK JM, et al. The cartilage extracellular matrix as a transient developmental scaffold for growth plate maturation. Matrix Biol. 2016;52-54:363-383. [14] 杨治,张铭,许鹏.生长分化因子5转染对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报,2016,41(10):1197-1203, 1207. [15] ZHAO X, BIAN R, WANG F, et al. GDF-5 promotes epidermal stem cells proliferation via Foxg1-cyclin D1 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):42. [16] 李博,吴慧颖,朴虎林,等.生长分化因子5对血管内皮细胞增殖和运动的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2011,37(6):1062-1064. [17] 任晓勇,张银刚,陈文弦.hGDF5基因转染对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和分化的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2006,27(1):15-19. [18] 卢康荣,朴仲贤,刘真喜,等.生长分化因子5基因转染诱导骨髓基质干细胞分化的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(8):750-754. [19] FREYMANN U, METZLAFF S, KRüGER JP, et al. Effect of Human Serum and 2 Different Types of Platelet Concentrates on Human Meniscus Cell Migration, Proliferation, and Matrix Formation. Arthroscopy. 2016; 32(6):1106-1116. [20] LI X, WANG F, LAN Y, et al. GDF-5 induces epidermal stem cell migration via RhoA-MMP9 signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):1939-1948. [21] SCHIEFER JL, HELD M, FUCHS PC, et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 5 Accelerates Wound Closure and Improves Skin Quality During Repair of Full-Thickness Skin Defects. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2017;30(5):223-229. [22] COLEMAN CM, VAUGHAN EE, BROWE DC, et al. Growth differentiation factor-5 enhances in vitro mesenchymal stromal cell chondrogenesis and hypertrophy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(13):1968-1976. [23] HAN C, REN Y, JIA Y, et al. The effective mode of growth and differentiation factor-5 in promoting the chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(1):105-115. [24] PEREIRA D, RAMOS E, BRANCO J. Osteoarthritis. Acta Med Port. 2015; 28(1):99-106. [25] STUDER D, MILLAN C, ÖZTüRK E, et al. Molecular and biophysical mechanisms regulating hypertrophic differentiation in chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;24:118-135; discussion 135. [26] 张山锋,勘武生,刘军,等.生长分化因子5促进软骨细胞肥大成熟的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(17):1611-1614. [27] 许鹏,许珂,张银刚,等.人生长分化因子5重组质粒转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外成软骨观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016, 31(9):952-954. [28] PARRISH WR, BYERS BA, SU D, et al. Intra-articular therapy with recombinant human GDF5 arrests disease progression and stimulates cartilage repair in the rat medial meniscus transection (MMT) model of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(4):554-560. [29] MA L, ZHANG Y, WANG C. Coaction of TGF-β1 and CDMP1 in BMSCs-induced laryngeal cartilage repair in rabbits. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(12):130. [30] KATAYAMA R, WAKITANI S, TSUMAKI N, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defects in rabbits using CDMP1 gene-transfected autologous mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2004;43(8):980-985. [31] AYERST BI, SMITH RA, NURCOMBE V, et al. Growth Differentiation Factor 5-Mediated Enhancement of Chondrocyte Phenotype Is Inhibited by Heparin: Implications for the Use of Heparin in the Clinic and in Tissue Engineering Applications. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(7-8): 275-292. [32] STECK E, FISCHER J, LORENZ H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell differentiation in an experimental cartilage defect: restriction of hypertrophy to bone-close neocartilage. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(7): 969-978. [33] LI G, YIN J, GAO J, et al. Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: insight into risk factors and microstructural changes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15(6):223. [34] MADRY H, ORTH P, CUCCHIARINI M. Role of the Subchondral Bone in Articular Cartilage Degeneration and Repair. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(4):e45-46. [35] BARR AJ, CAMPBELL TM, HOPKINSON D, et al. A systematic review of the relationship between subchondral bone features, pain and structural pathology in peripheral joint osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):228. [36] GOLDRING MB, GOLDRING SR. Articular cartilage and subchondral bone in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1192: 230-237. [37] GOLDRING SR. Alterations in periarticular bone and cross talk between subchondral bone and articular cartilage in osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2012;4(4):249-258. [38] DAANS M, LUYTEN FP, LORIES RJ. GDF5 deficiency in mice is associated with instability-driven joint damage, gait and subchondral bone changes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(1):208-213. [39] HU Y, CHEN X, WANG S, et al. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone Res. 2021;9(1):20. [40] LI B, ASPDEN RM. Material properties of bone from the femoral neck and calcar femorale of patients with osteoporosis or osteoarthritis. Osteoporos Int. 1997;7(5):450-456. [41] ZENG Q, LI X, BECK G, et al. Growth and differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) stimulates osteogenic differentiation and increases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in fat-derived stromal cells in vitro. Bone. 2007;40(2):374-381. [42] SENA K, SUMNER DR, VIRDI AS. Modulation of VEGF expression in rat bone marrow stromal cells by GDF-5. Connect Tissue Res. 2007; 48(6):324-331. [43] KAKUDO N, WANG YB, MIYAKE S, et al. Analysis of osteochondro-induction using growth and differentiation factor-5 in rat muscle. Life Sci. 2007;81(2):137-143. [44] SIMANK HG, SERGI C, JUNG M, et al. Effects of local application of growth and differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) in a full-thickness cartilage defect model. Growth Factors. 2004;22(1):35-43. [45] HAN Y, YANG Q, HUANG Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the miR-212-3p/GDF5/SMAD pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13(1):130. [46] XIAO D, YANG F, ZHAO Q, et al. Fabrication of a Cu/Zn co-incorporated calcium phosphate scaffold-derived GDF-5 sustained release system with enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis properties. RSC Adv. 2018;8(52):29526-29534. [47] 丁呈彪,周云.膝骨性关节炎患者滑膜炎的发病机制及研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8327-8332. [48] STOPPIELLO LA, MAPP PI, WILSON D, et al. Structural associations of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(11): 3018-3027. [49] MIN S, WANG C, LU W, et al. Serum levels of the bone turnover markers dickkopf-1, osteoprotegerin, and TNF-α in knee osteoarthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36(10):2351-2358. [50] CHANG X, SHEN J, YANG H, et al. Upregulated expression of CCR3 in osteoarthritis and CCR3 mediated activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cytokine. 2016;77:211-219. [51] LIU FL, LIN LH, SYTWU HK, et al. GDF-5 is suppressed by IL-1beta and enhances TGF-beta3-mediated chondrogenic differentiation in human rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Exp Mol Pathol. 2010;88(1):163-170. [52] ZENG J, WANG F, MAO M. Co‑culture of fibroblast‑like synoviocytes with umbilical cord‑mesenchymal stem cells inhibits expression of pro‑inflammatory proteins, induces apoptosis and promotes chondrogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(4):3887-3893. [53] ENOCHSON L, STENBERG J, BRITTBERG M, et al. GDF5 reduces MMP13 expression in human chondrocytes via DKK1 mediated canonical Wnt signaling inhibition. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(4):566-577. [54] SHEN L, WU Y, HAN L, et al. Overexpression of growth and differentiation factor-5 inhibits inflammatory factors released by intervertebral disc cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(4):3603-3608. [55] LIU Y, PENG L, LI L, et al. 3D-bioprinted BMSC-laden biomimetic multiphasic scaffolds for efficient repair of osteochondral defects in an osteoarthritic rat model. Biomaterials. 2021;279:121216. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [4] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [5] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [6] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [7] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [8] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [9] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [10] | Li Zhichao, Tan Guoqing, Su Hui, Xu Zhanwang, Xue Haipeng. Regulatory role of non-coding RNAs as potential therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 758-764. |
| [11] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [12] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [13] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [14] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [15] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||