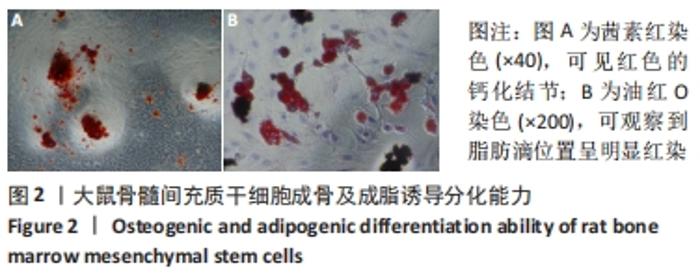
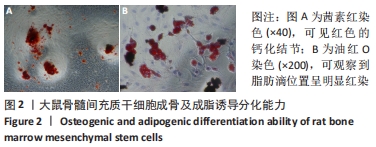
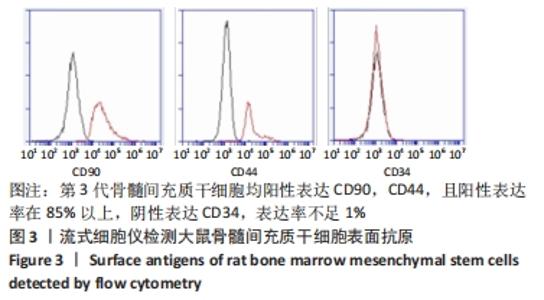
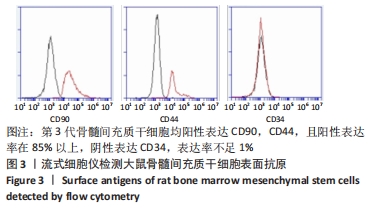
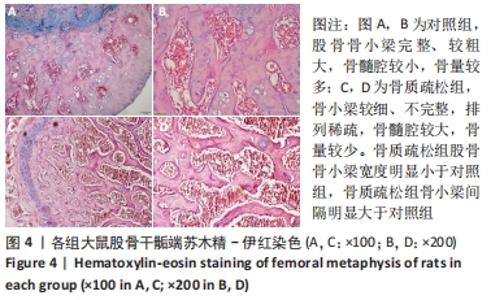
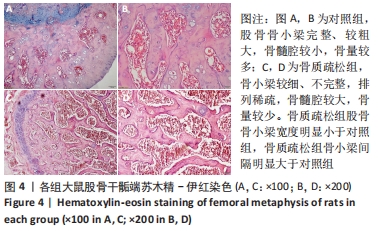
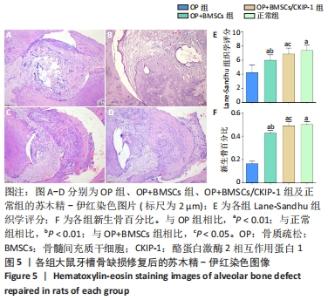
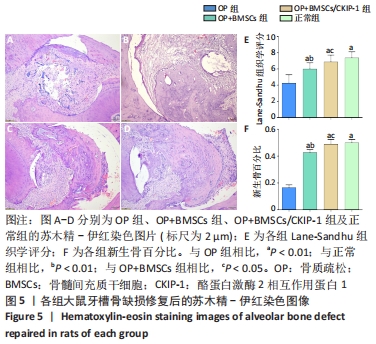
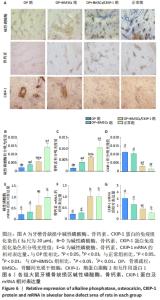
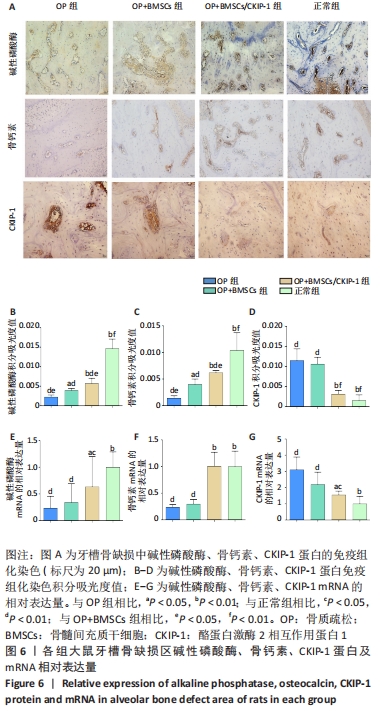
[1] SIDIROPOULOU-CHATZIGIANNIS S, KOURTIDOU M, TSALIKIS L. The effect of osteoporosis on periodontal status, alveolar bone and orthodontic tooth movement. A literature review. J Int Acad Periodontol. 2007;9(3):77-84.
[2] BOLLEN AM, TAGUCHI A, HUJOEL PP, et al. Case-control study on self-reported osteoporotic fractures and mandibular cortical bone. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000;90(4):518-524.
[3] 曾勇,李庆,何睿,等.单一钙制剂与钙制剂联合维生素D干预治疗老年男性骨质疏松症疗效的随机对照临床研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2014,13(8):625-629.
[4] ZHANG XZ, WANG B, YANG J, et al. A randomized, multicenter controlled trial to compare the efficacy of recombinant human parathyroid hormone (1-34) with elcatonin in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis in China. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(24):2933-2938.
[5] ARTHUR A, GRONTHOS S. Clinical Application of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells to Repair Skeletal Tissue. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9759.
[6] BOSC DG, GRAHAM KC, SAULNIER RB, et al. Identification and characterization of CKIP-1, a novel pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein that interacts with protein kinase CK2. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(19):14295-14306.
[7] LU K, YIN X, WENG T, et al. Targeting WW domains linker of HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 for activation by CKIP-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10(8):994-1002.
[8] PENG X, WU X, ZHANG J, et al. The role of CKIP-1 in osteoporosis development and treatment. Bone Joint Res. 2018;7(2):173-178.
[9] YING SX, HUSSAIN ZJ, ZHANG YE. Smurf1 facilitates myogenic differentiation and antagonizes the bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced osteoblast conversion by targeting Smad5 for degradation. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(40):39029-39036.
[10] SANGADALA S, RAO METPALLY RP, B REDDY BV. Molecular Interaction Between Smurfl WW2 Domain and PPXY Motifs of Smadl, Smad5, and Smad6-Modeling and Analysis. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2007;25(1): 11-23.
[11] CHAN MC, NGUYEN PH, DAVIS BN, et al. A novel regulatory mechanism of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway involving the carboxyl-terminal tail domain of BMP type II receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(16):5776-5789.
[12] 田晓光,沈舒宁,段银钟,等.CKIP-1对骨髓间充质干细胞体外增殖和分化能力的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(1):10-14.
[13] 梁建飞.下调CKIP-1通过骨形成相关信号通路促进MSCs增殖及成骨分化的作用研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2017.
[14] LIU J, LU C, WU X, et al. Targeting osteoblastic casein kinase-2 interacting protein-1 to enhance Smad-dependent BMP signaling and reverse bone formation reduction in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41295.
[15] NIE J, LIU L, HE F, et al. CKIP-1: a scaffold protein and potential therapeutic target integrating multiple signaling pathways and physiological functions. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12(1):276-281.
[16] ZHANG G, GUO B, WU H, et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic therapy. Nat Med. 2012;18(2):307-314.
[17] ZHANG L, WU K, SONG W, et al. Chitosan/siCkip-1 biofunctionalized titanium implant for improved osseointegration in the osteoporotic condition. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10860.
[18] CHEN S, YANG L, JIE Q, et al. MicroRNA‑125b suppresses the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow‑derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(5): 1820-1826.
[19] 蒋月桂,孙斌,苟建重,等.rhBMP-2HACo复合材料异位诱导成骨中碱性磷酸酶活性的检测[J].中国美容医学,2010,19(4):521-523.
[20] ZHENG L, ZHANG G, TANG T, et al. Identifying a cross-species siRNA targeting a newly discovered inhibitor of bone formation CKIP-I for promoting osteoblast differentiation and mineralization in vitro. Bone. 2010;47: S371-S372.
[21] GUNDBERG CM. Biochemical markers of bone formation. Clin Lab Med. 2000;20(3):489-501.
[22] LIU Q, ZHANG X, JIAO Y, et al. In vitro cell behaviors of bone mesenchymal stem cells derived from normal and postmenopausal osteoporotic rats. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):669-678.
[23] 张月峰,韩景献.骨质疏松动物模型研究进展[J].动物医学进展, 2005,26(3):8-11.
[24] 郭鱼波,马如风,王丽丽.骨质疏松动物模型及其评价方法的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(9):1149-1154.
[25] 谢林.中医药防治骨质疏松症研究中动物模型的选择和思考[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,1997,5(4):50-51.
[26] GIANGREGORIO L, BLIMKIE CJ. Skeletal adaptations to alterations in weight-bearing activity: a comparison of models of disuse osteoporosis. Sports Med. 2002;32(7):459-476.
[27] KANZAKI S, ITO M, TAKADA Y, et al. Resorption of auditory ossicles and hearing loss in mice lacking osteoprotegerin. Bone. 2006;39(2):414-419.
[28] 许鹏,郭雄,张银刚,等.维甲酸诱导骨质疏松模型大鼠的效果及机理[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2005,36(2):229-232.
[29] 许鹏,郭雄,姚建锋,等.维甲酸诱导雌性大鼠骨质疏松的效果及机理分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(10):995-998.
[30] 朱虎虎,孙炜.维甲酸诱导雌性大鼠骨质疏松模型建立的效果观察[J].当代医学,2013,19(14):24-26.
|