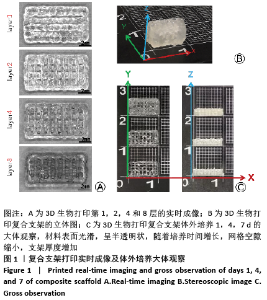
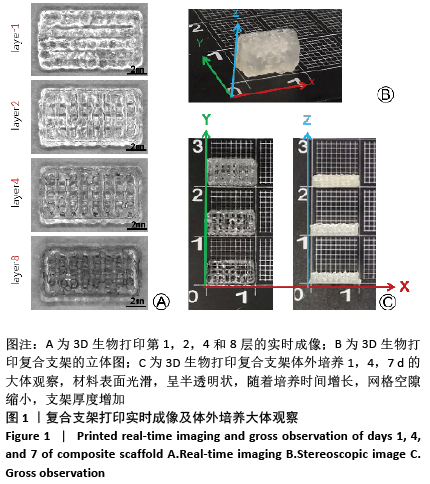
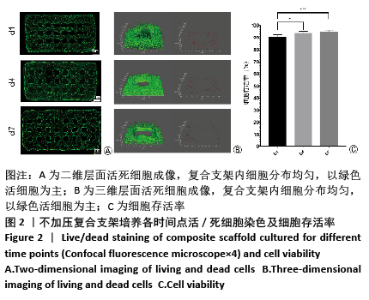
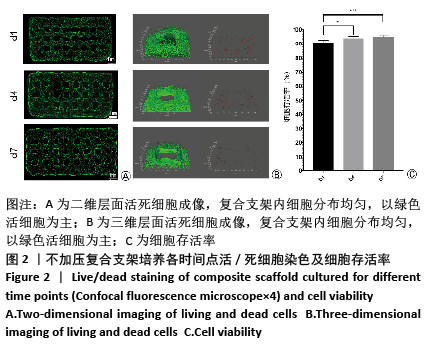
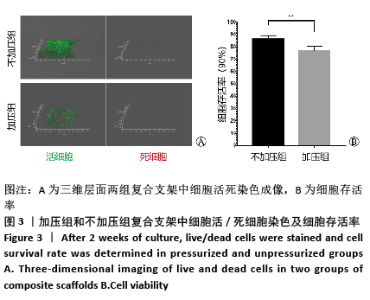
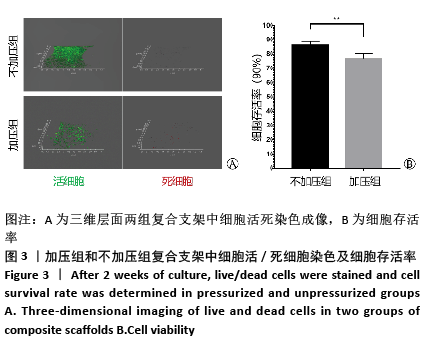
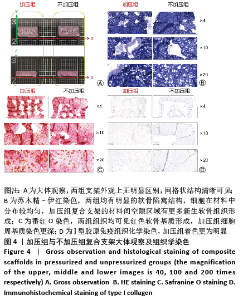
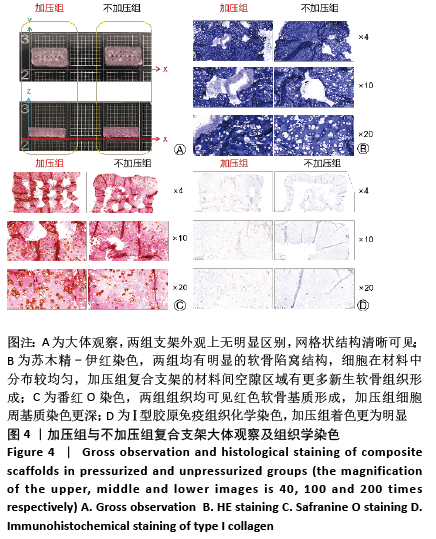
[1] ZHOU G, JIANG H, YIN Z, et al. In Vitro Regeneration of Patient-specific Ear-shaped Cartilage and Its First Clinical Application for Auricular Reconstruction. EBioMedicine. 2018;28: 287-302.
[2] NABZDYK C, PRADHAN L, MOLINA J, et al. Review: auricular chondrocytes - from benchwork to clinical applications. In Vivo. 2009;23(3): 369-380.
[3] 董可欣.弹性纤维相关组分在工程化软骨组织中的表达及作用研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院, 2020.
[4] MOHAGHEGH S, HOSSEINI SF, RAD MR, et al. 3D Printed Composite Scaffolds in Bone Tissue Engineering: A systematic review. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021.doi: 10.2174/1574888X16666210810111754.
[5] MANDRYCKY C, WANG Z, KIM K, et al. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol Adv. 2016;34(4): 422-434.
[6] YANG J, ZHANG YS, YUE K, et al. Cell-laden hydrogels for osteochondral and cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2017;57:1-25.
[7] GUNGOR-OZKERIM PS, INCI I, ZHANG YS, et al. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: an overview. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(5): 915-946.
[8] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73: 254-271.
[9] BYAMBAA B, ANNABI N, YUE K, et al. Bioprinted Osteogenic and Vasculogenic Patterns for Engineering 3D Bone Tissue. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017; 6(16).doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700015.
[10] HU H, DONG L, BU Z, et al. miR-23a-3p-abundant small extracellular vesicles released from Gelma/nanoclay hydrogel for cartilage regeneration. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020; 9(1): 1778883.
[11] KAUPP JA, WEBER JF, WALDMAN SD. Mechanical stimulation of chondrocyte-agarose hydrogels. J Vis Exp. 2012;(68): e4229.
[12] BOOS MA, LAMANDé SR, STOK KS. Multiscale Strain Transfer in Cartilage. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 795522.
[13] APPELMAN TP, MIZRAHI J, ELISSEEFF JH, et al. The differential effect of scaffold composition and architecture on chondrocyte response to mechanical stimulation. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4): 518-525.
[14] 周丽斌,徐冰心,丁瑞英,等.应用微纤维胶原支架构建组织工程软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(22):3483-3487.
[15] YU K, ZHANG X, SUN Y, et al. Printability during projection-based 3D bioprinting. Bioact Mater. 2022;11: 254-267.
[16] TANG P, SONG P, PENG Z, et al. Chondrocyte-laden GelMA hydrogel combined with 3D printed PLA scaffolds for auricle regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;130: 112423.
[17] CHOE R, DEVOY E, KUZEMCHAK B, et al. Computational investigation of interface printing patterns within 3D printed multilayered scaffolds for osteochondral tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2022;14(2).10.1088/1758-5090/ac5220. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac5220.
[18] WANG Y, CAO X, MA M, et al. A GelMA-PEGDA-nHA Composite Hydrogel for Bone Tissue Engineering [J]. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(17):3735.
[19] KILIC BEKTAS C, HASIRCI V. Cell Loaded GelMA:HEMA IPN hydrogels for corneal stroma engineering. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;31(1): 2.
[20] KOSIK-KOZIOŁ A, COSTANTINI M, MRóZ A, et al. 3D bioprinted hydrogel model incorporating β-tricalcium phosphate for calcified cartilage tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2019;11(3): 035016.
[21] PATTAPPA G, ZELLNER J, JOHNSTONE B, et al. Cells under pressure - the relationship between hydrostatic pressure and mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis. Eur Cell Mater. 2019;37: 360-381.
[22] YOUNG IC, CHUANG ST, GEFEN A, et al. A novel compressive stress-based osteoarthritis-like chondrocyte system. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(10): 1062-1071.
[23] ANDERSON DE, JOHNSTONE B. Dynamic Mechanical Compression of Chondrocytes for Tissue Engineering: A Critical Review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5: 76.
[24] RICHARDSON BM, WALKER CJ, MAPLES MM, et al. Mechanobiological Interactions between Dynamic Compressive Loading and Viscoelasticity on Chondrocytes in Hydrazone Covalent Adaptable Networks for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(9): e2002030.
[25] SHIN SJ, YANAGISAWA H. Recent updates on the molecular network of elastic fiber formation. Essays Biochem. 2019;63(3): 365-376.
[26] KOZEL BA, MECHAM RP. Elastic fiber ultrastructure and assembly. Matrix Biol. 2019;84: 31-40. |