Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (34): 5486-5491.doi: 10.12307/2022.460
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of alkali-and-heat treatment combined with ultraviolet photofunctionalization pure titanium on osteoblast activity
Zheng Rui1, 2, Sun Yong2
- 1Department of Implantology, Mianyang Stomatological Hospital, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-29Accepted:2021-03-31Online:2022-12-08Published:2022-04-15 -
Contact:Sun Yong, Chief physician, School of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zheng Rui, Master, Attending physician, Department of Implantology, Mianyang Stomatological Hospital, Mianyang 621000, Sichuan Province, China; School of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Rui, Sun Yong. Effects of alkali-and-heat treatment combined with ultraviolet photofunctionalization pure titanium on osteoblast activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(34): 5486-5491.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
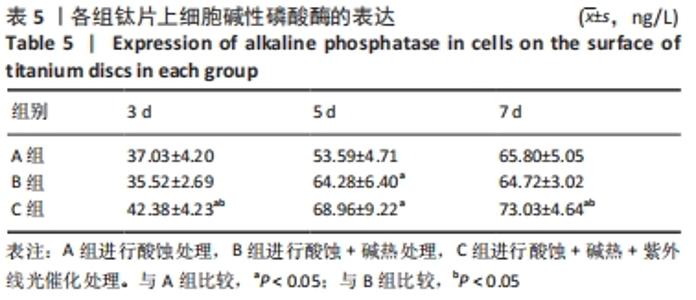
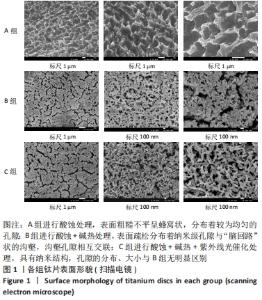
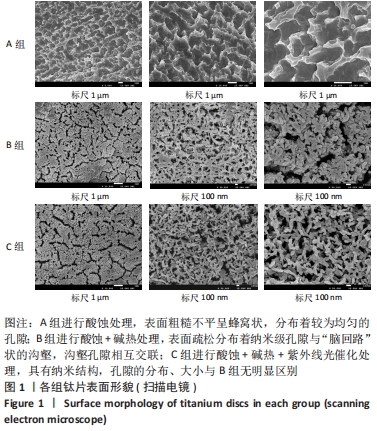
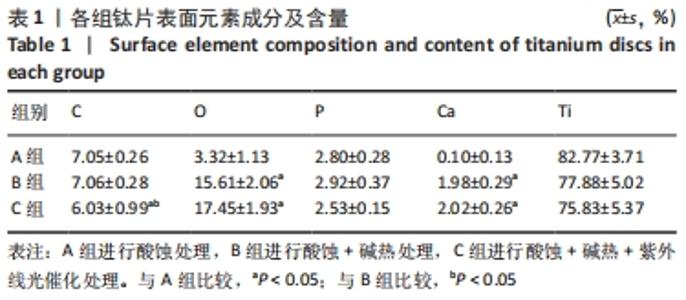
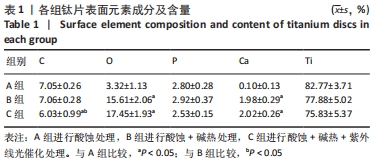
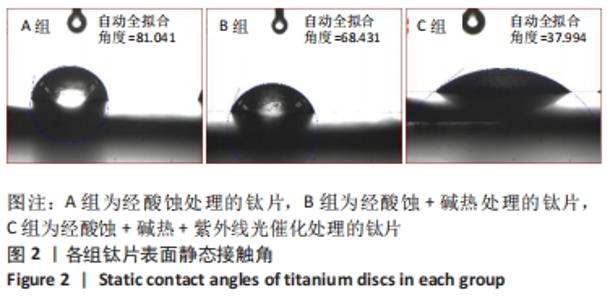
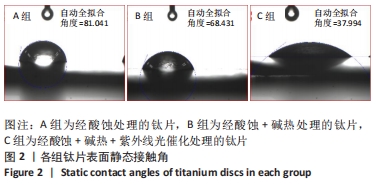
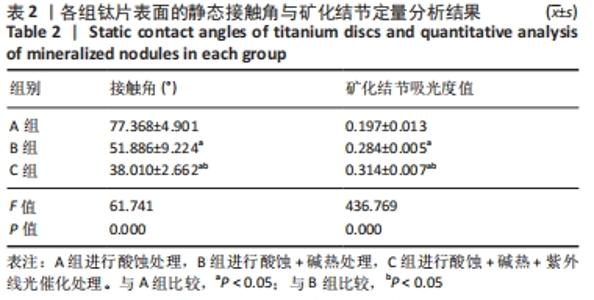
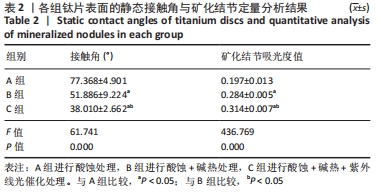
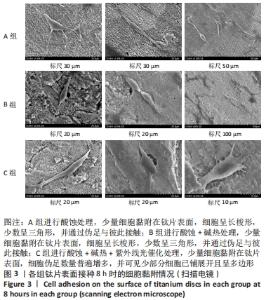
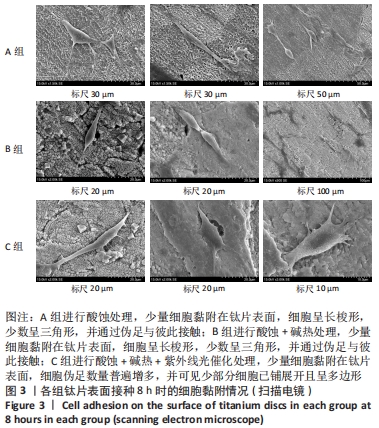
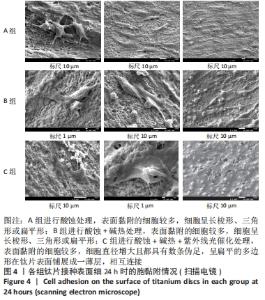
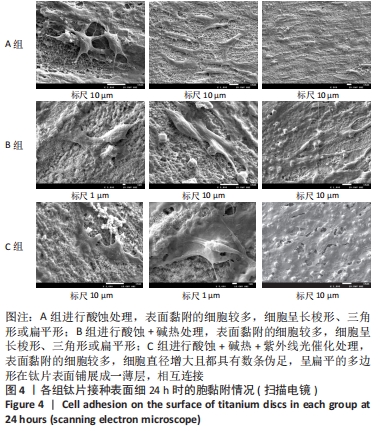
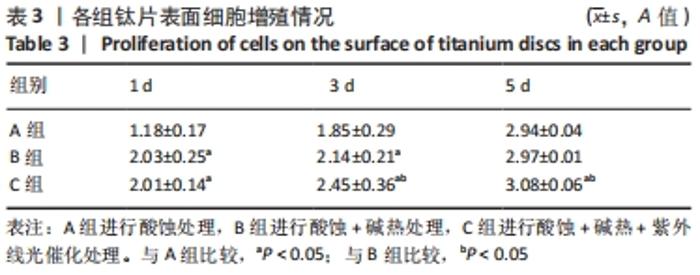
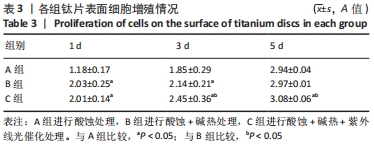
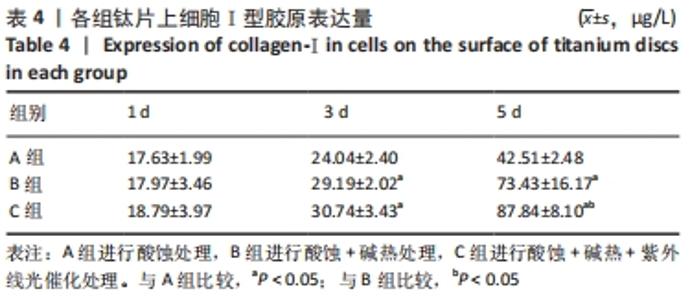
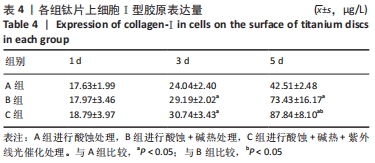
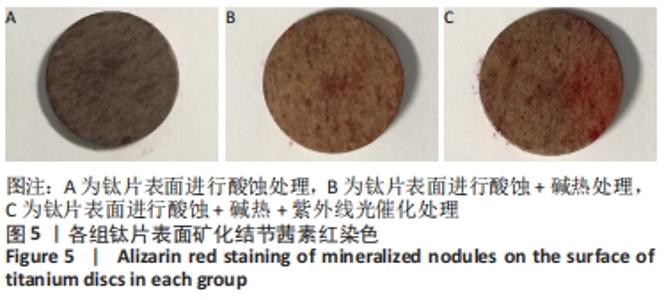
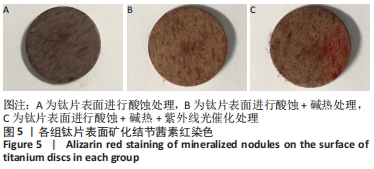
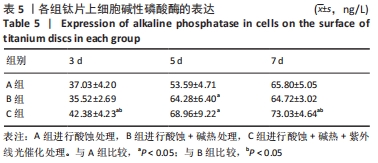
培养1 d时,3组间Ⅰ型胶原表达量比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养3 d时,3组Ⅰ型胶原表达量较1 d时有明显增加(P < 0.01),A组表达量最少,明显低于B组和C组(P < 0.01),B组与C比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养5 d时,3组Ⅰ型胶原表达量进一步增加(P < 0.01),3组之间两两比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),Ⅰ型胶原表达量为A组<B组<C组。 各组钛片表面细胞碱性磷酸酶表达结果,见表5。培养3 d时,A、B组细胞碱性磷酸酶表达比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),C组高于A、B组(P < 0.01);培养5 d时,各组细胞碱性磷酸酶表达较3 d时增加(P < 0.01),A组低于B、C组(P < 0.01),B、C组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);培养7 d时,3组胞碱性磷酸酶表达较5 d时不同程度地增加,C组明显高于A、B组(P < 0.01),A、B组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] 高岩.不同波长紫外线激发微弧氧化纯钛表面光催化作用的体外生物活性研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2012. [2] KOKUBO T, YAMAGUCHI S. Bioactive titanate layers formed on titanium and itsalloys by simple chemical and heat treatments. Open Biomed Eng J. 2015;9:29-41. [3] XING H, KOMASA S, TAGUCHI Y, et al. Osteogenic activity of titanium surfaces with nanonetwork structures. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9: 1741-1755. [4] SO K, KANEUJI A, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Is the bone-bonding ability of a cementless total hip prosthesis enhanced by alkaline and heat treatments? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(12):3847-3855. [5] 栗兴超.表面粗化处理不均衡螺纹钛人工牙种植体的生物学性能研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2017. [6] KOKUBO T, KIM HM, KAWASHITA M, et al. Bioactive metals: preparation and properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2004;15(2):99-107. [7] 韩石磊,赵颖,李大鹏,等.碱热处理联合紫外光照后钛体外活性的研究[J].口腔医学,2017,37(5):408-412. [8] ZHANG H, KOMASA S, MASHIMO C, et al. Effect of ultraviolet treatment on bacterial attachment and osteogenic activity to alkali-treated titanium with nanonetwork structures. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:4633-4646. [9] AITA H, HORI N, TAKEUCHI M, et al. The effect of ultraviolet functionalization of titanium on integration with bone.Biomaterials. 2009;30(6):1015-1025. [10] BUDDY D, ALLAN S, FREDERICK J, et al. Biomaterials Science: An Introduction to Materials in Medicine. Elsevier Academic Press,1985. [11] TEXTOR M, SITTIG C, FRAUCHIGER V, et al. Properties and Biological Significance of Natural Oxide Films on Titanium and Its Alloys. In: Titanium in Medicine. Engineering Materials. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. 2001. [12] CHO SA, PARK KT. The removal torque of titanium screw inserted in rabbit tibia treated by dual acid etching. Biomaterials. 2003;24(20): 3611-3617. [13] PARK JY, DAVIES JE. Red blood cell and platelet interactions with titanium implant surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2000;11(6):530-539. [14] COCHRAN DL, BUSER D, TEN BRUGGENKATE CM, et al. The use of reduced healing times on ITI implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched (SLA) surface: early results from clinical trials on ITI SLA implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13(2):144-153. [16] MAROM R, SHUR I, SOLOMON R, et al. Characterization of adhesion and differentiation markers of osteogenic marrow stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 2005;202(1):41-48. [17] EHARA A, OGATA K, IMAZATO S, et al. Effects of alpha-TCP and TetCP on MC3T3-E1 proliferation, differentiation and mineralization.Biomaterials. 2003;24(5):831-836. [18] WONG M, EULENBERGER J, SCHENK R, et al. Effect of surface topology on the osseointegration of implant materials in trabecular bone. J Biomed Mater Res. 1995;29(12):1567-1575. [19] WEBSTER TJ, ERGUN C, DOREMUS RH, et al. Specific proteins mediate enhanced osteoblast adhesion on nanophase ceramics. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(3):475-483. [20] KARLSSON M, PÅLSGÅRD E, WILSHAW PR, et al. Initial in vitro interaction of osteoblasts with nano-porous alumina. Biomaterials. 2003;24(18):3039-3046. [21] 冯智敏.糖尿病对大鼠正畸牙齿移动的影响[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2006. [22] GOUGH JE, JONES JR, HENCH LL. Nodule formation and mineralisation of human primary osteoblasts cultured on a porous bioactive glass scaffold. Biomaterials. 2004;25(11):2039-2046. [23] ZHOU J, LI B, LU S, et al. Regulation of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by interrod spacing of Sr-HA nanorods on microporous titania coatings. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(11):5358-5365. [24] CAI YL, ZHANG JJ, ZHANG S, et al. Osteoblastic cell response on fluoridated hydroxyapatite coatings: the effect of magnesium incorporation. Biomed Mater. 2010;5(5):054114. [25] LANDI E, TAMPIERI A, MATTIOLI-BELMONTE M, et al. Biomimetic Mg- and Mg,CO3-substituted hydroxyapatites: synthesis characterization and in vitro behaviour. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2006;26(13):2593-2601. [26] WANG J, ZHAO Y, CHENG X, et al. Effects of different Ca2+ level on fluoride-induced apoptosis pathway of endoplasmic reticulum in the rabbit osteoblast in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018;116(Pt B):189-195. [27] DE COLLI M, RADUNOVIC M, ZIZZARI VL, et al. Osteoblastic differentiating potential of dental pulp stem cells in vitro cultured on a chemically modified microrough titanium surface. Dent Mater J. 2018;37(2):197-205. [28] LEE MN, HWANG HS, OH SH, et al. Elevated extracellular calcium ions promote proliferation and migration of mesenchymal stem cells via increasing osteopontin expression. Exp Mol Med. 2018;50(11):1-16. [29] KOPF BS, RUCH S, BERNER S, et al. The role of nanostructures and hydrophilicity in osseointegration: In-vitro protein-adsorption and blood-interaction studies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(8):2661-2672. [30] ALBORZI A, MAC K, GLACKIN CA, et al. Endochondral and intramembranous fetal bone development: osteoblastic cell proliferation, and expression of alkaline phosphatase, m-twist, and histone H4. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1996;16(2):94-106. [31] LOTZ EM, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, BERNER S, et al. Osteogenic response of human MSCs and osteoblasts to hydrophilic and hydrophobic nanostructured titanium implant surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(12):3137-3148. [32] LOTZ EM, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, et al. Comparable responses of osteoblast lineage cells to microstructured hydrophilic titanium-zirconium and microstructured hydrophilic titanium. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(7):e51-e59. [33] Hotchkiss KM, Reddy GB, Hyzy SL, et al.Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434. [34] ALFARSI MA, HAMLET SM, IVANOVSKI S. Titanium surface hydrophilicity enhances platelet activation. Dent Mater J. 2014;33(6):749-756. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Li Jian, Bao Zhengqi, Zhou Pinghui, Zhu Ruizhi, Li Zhixiang, Wang Jinzi. Effects of posterior single open-door laminoplasty and anterior cervical corpectomy fusion on cervical sagittal balance parameters in the treatment of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 949-953. |
| [4] | Peng Kun. Improvement of the treatment effect of osteoporotic fractures: research status and strategy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 980-984. |
| [5] | Wang Hailong, Li Long, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yilihamu·Tuoheti. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of acetabular prosthesis in the Lewinnek safety zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 843-847. |
| [6] | Gao Wenbo, Ma Zongmin, Li Shuxian, Nie Xiuji. Finite element analysis on the effect of implant length and diameter on initial stability under different bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 875-880. |
| [7] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [8] | Yang Sidi, Wang Qian, Xu Nuo, Wang Ronghan, Jin Chuanqi, Lu Ying, Dong Ming. Biodentine enhances the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts through upregulating bone morphogenetic protein-2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 516-520. |
| [9] | Qiu Peng, Fu Qilin, Liu Min, Lan Yuyan, Wang Pin. Comparison of oral micro-adhesion on polyetheretherketone, zirconium dioxide, and pure titanium abutment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 540-545. |
| [10] | Chen Shuo, Xiao Dongqin, Li Xingping, Ran Bin, Shi Feng, Zhang Chengdong, Deng Li, Huang Nanxiang, Liu Kang, Feng Gang, Duan Ke. Preparation and characterization of tantalum functional coating on titanium implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 546-552. |
| [11] | Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 567-572. |
| [12] | Wang Can, Gu Weiping, Jiang Yubin, Zhu Lin, Chen Gang. Finite element analysis of the influence of different implant designs on the stress of mandibular edentulous jaw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 573-578. |
| [13] | Zhang Jianguo, Chen Chen, Hu Fengling, Huang Daoyu, Song Liang. Design and biomechanical properties of dental implant pore structure based on three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 585-590. |
| [14] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Lu Yingzi. Intra-articular tranexamic acid at different volumes and doses affects blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5303-5310. |
| [15] | Huang Gao, Xu Jun, Chen Wenge. Implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-loaded platelet-rich plasma combined with extracorporeal shock wave in the repair of bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4812-4818. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||