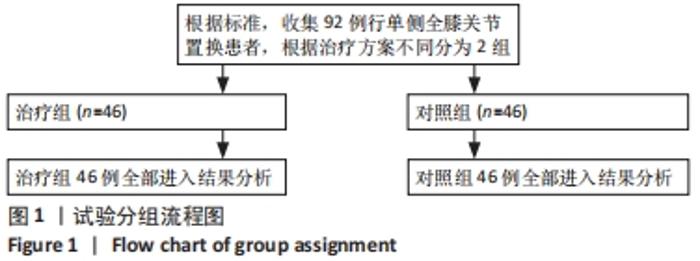
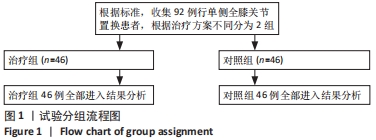
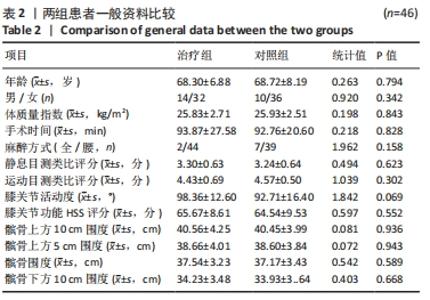
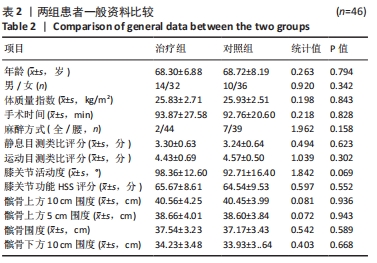
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (33): 5317-5322.doi: 10.12307/2022.744
Previous Articles Next Articles
Adjective application of dexamethasone combined with furosemide for early pain and swelling after total knee arthroplasty
Song Wei, Zhang Yaxin, Jia Dazhou, Sun Yu
- Department of Orthopedics, Clinical Medical College of Yangzhou University, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-09-23Accepted:2021-11-20Online:2022-11-28Published:2022-03-30 -
Contact:Sun Yu, Associate chief physician, MD, Department of Orthopedics, Clinical Medical College of Yangzhou University, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Song Wei, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Clinical Medical College of Yangzhou University, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, Yangzhou 225000, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Wei, Zhang Yaxin, Jia Dazhou, Sun Yu. Adjective application of dexamethasone combined with furosemide for early pain and swelling after total knee arthroplasty[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5317-5322.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
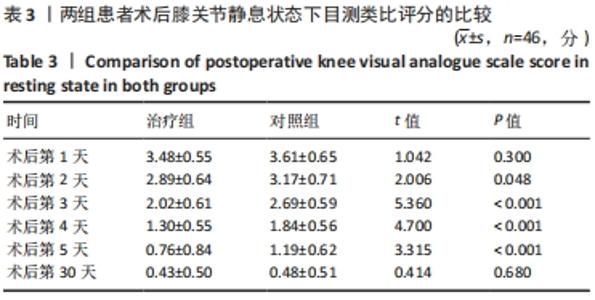
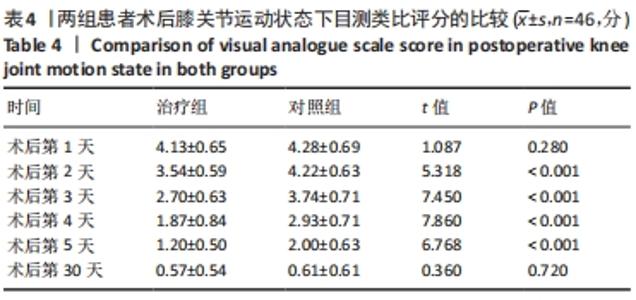
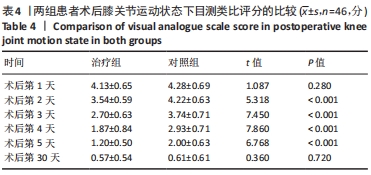
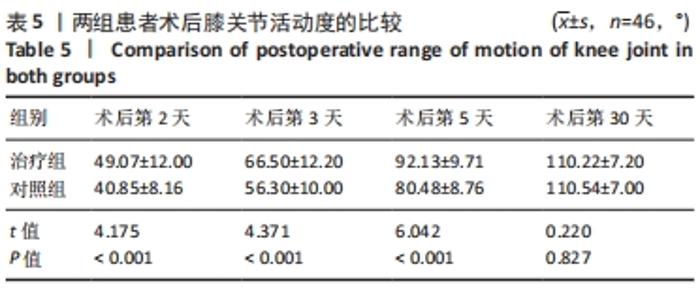
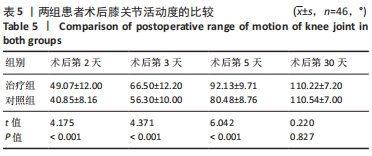
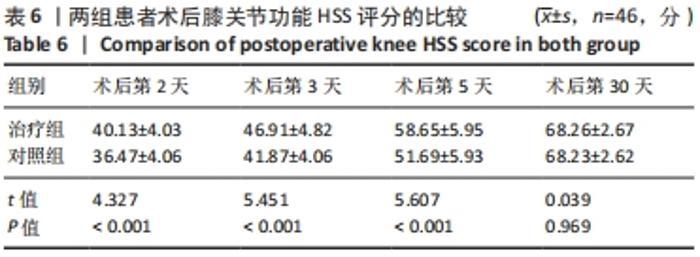
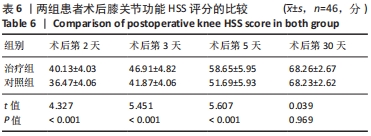
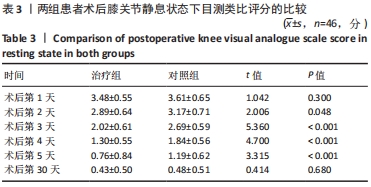
2.4 两组患者术后使用假体材料分析 治疗组46例中使用北京市春立正达医疗器械股份有限公司生产的全膝关节假体22例(48%),使用微创骨科股份有限公司生产的全膝关节假体24例(52%);对照组46例中使用北京市春立正达医疗器械股份有限公司生产的全膝关节假体25例(54%),使用微创骨科股份有限公司生产的全膝关节假体21例(46%)。两组全膝关节假体使用情况比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.5 两组患者膝关节疼痛情况比较 2.5.1 静息状态下的目测类比评分 两独立样本t检验显示,治疗组患者术后第2-5天静息状态下的目测类比评分均低于对照组(P < 0.05),两组患者术后第1,30天静息状态下的目测类比评分比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。"
| [1] MISRA D, BOOTH SL, TOLSTYKH I, et al. Vitamin K defificiency is associated with incident knee osteoarthritis. Am J Med. 2013;126:243-248. [2] SUN YQ, YANG B, TONG SL, et al.Patelloplasty versus traditional total knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis. Orthopedics. 2012;35(3):e343-348. [3] SEO SS, KIM OG, SEO JH, et al. Comparison of the effect of continuous femoral nerve block and adductor canal block after primary total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9:303-309. [4] ASO K, IZUMI M, SUGIMURA N, et al. Additional benefifit of local infifiltration of analgesia to femoral nerve block in total knee arthroplasty: double-blind randomized control study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27:2368-2374. [5] LI X, XU G, XIE W, et al. The efficacy and safety of dexamethasone for pain management after total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;53:65-71. [6] BIAN YY, WANG LC, QIAN WW, et al. Role of parecoxib sodium in the multimodal analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized double-blinded controlled trial. Orthop Surg. 2018;10:321-327. [7] HAWKER GA. Osteoarthritis is a serious disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019;37 Suppl 120(5):3-6. [8] HAFER JF, KENT JA, BOYER KA. Physical activity and age-related biomechanical risk factors for knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture. 2019; 70:24-29. [9] HERMANN W, LAMBOVA S, MULLER-LADNER U. Current Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2018;14(2):108-116. [10] LI JW, MA YS, XIAO LK. Postoperative Pain Management in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(5):755-761. [11] GROSU I, LAVAND’HOMME P, THIENPONT E. Pain after knee arthroplasty: an unresolved issue. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(8):1744-1758. [12] 徐建国.成人术后疼痛治疗进展[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2011,27(3): 299-301. [13] GRAZIOLI L, OLIVETTI L, FUGAZZOLA C, et al. The pseudocapsule in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation between dynamic MR imaging and pathology. Eur Radiol. 1999;9(1):62-67. [14] JIANG M, DENG H, CHEN X, et al. The efficacy and safety of selective COX-2 inhibitors for postoperative pain management in patients after total knee/hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):39. [15] LIN J, ZHANG L, YANG H. Perioperative administration of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors for postoperative pain management in patients after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(2):207-213.e2. [16] DIMACULANGAN D, CHEN JF, BORZIO RB, et al. Periarticular injection and continuous femoral nerve block versus continuous femoral nerve block alone on postoperative opioid consumption and pain control following total knee arthroplasty: randomized controlled trial. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10:81-86. [17] KIM HC, KIM TK, SUNG KB, et al. Preoperative evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma: combined use of CT with arterial portography and hepatic arteriography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003; 180(6):1593-1599. [18] EL-BOGHDADLY K, SHORT AJ, GANDHI R, et al. Addition of dexamethasone to local infiltration analgesia in elective total knee arthroplasty: double-blind, randomized control trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2021;46(2):130-136. [19] KASSIM DY, ESMAT IM, ELGENDY MA. Impact of duloxetine and dexamethasone for improving postoperative pain after laparoscopic gynecological surgeries: A randomized clinical trial. Saudi J Anaesth. 2018;12(1):95-102. [20] FAN Z, MA J, KUANG M, et al. The efficacy of dexamethasone reducing postoperative pain and emesis after total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;52:149-155. [21] TAMMACHOTE N, KANITNATE S. Intravenous Dexamethasone Injection Reduces Pain From 12 to 21 Hours After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(2):394-400. [22] 陆蒂青,张冬云,闪海霞.甘露醇联合地塞米松对感染性脑水肿患者相关指标的影响[J].中国药房,2017,28(24):3362-3364. [23] GASBJERG KS, HÄGI-PEDERSEN D, LUNN TH, et al. DEX-2-TKA - DEXamethasone twice for pain treatment after Total Knee Arthroplasty: Detailed statistical analysis plan for a randomized, blinded, three-group multicentre clinical trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2020;64(6):839-846. [24] GODSHAW BM, MEHL AE, SHAFFER JG, et al. The Effects of Peri-Operative Dexamethasone on Patients Undergoing Total Hip or Knee Arthroplasty: Is It Safe for Diabetics? J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(4):645-649. [25] GATEWOOD CT, TRAN AA, DRAGOO JL. The efficacy of post-operative devices following knee arthroscopic surgery: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(2):501-516. [26] HOLM B, KRISTENSEN MT, BENCKE J, et al. Loss of knee-extension strength is related to knee swelling after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91:1770-1776. [27] 钟洁珠.呋塞米联合甘露醇治疗急性肢体肿胀患者的效果分析[J].临床合理用药杂志,2013,6(8):70-71. [28] GRADALSKI T. Diuretics Combined With Compression in Resistant Limb Edema of Advanced Disease-A Case Series Report. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2018;55(4):1179-1183. [29] GRADALSKI T. Multicomponent Compression Bandaging Combined with Diuretic Therapy of Anasarca Secondary to Palliative Chemotherapy: A Case Report. J Palliat Med. 2021;24(1):144-147. [30] 陈洁,田义华,唐永利,等.全膝关节置换术后患肢不同体位对肢体肿胀与关节活动度的影响[J].重庆医科大学学报,2020,45(10): 1506-1508. |
| [1] | Kan Houming, Fan Lijun, Chen Xuetai, Shen Wen. Application of platelet-rich plasma in neuropathic pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1286-1292. |
| [2] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [3] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [4] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [5] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [6] | Lin Xuchen, Zhu Hainian, Wang Zengshun, Qi Tengmin, Liu Limin, Suonan Angxiu. Effect of xanthohumol on inflammatory factors and articular cartilage in a mouse mode of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 676-681. |
| [7] | Lu Qinxue, Xu Ning, Yang Yinglan, Han Qianqian, Duanmu Xianyu, Guo Yuwei, Han Qing. Femoroacetabular impingement: strength trainings for nerve-muscle, peripheral muscle and core muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 786-791. |
| [8] | Wang Zhenheng, Wang Zhidong, Liu Naicheng, Chen Guangdong, Gao Maofeng, Shi Weidong, Zhu Ruofu. Effect of intravenous dexamethasone preoperatively on pain and complications after unicondylar arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5297-5302. |
| [9] | Liu Jinlei, Yin Li, Zhang Yi, Wang Haitao, Lu Yingzi. Intra-articular tranexamic acid at different volumes and doses affects blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5303-5310. |
| [10] | Quan Honglei, Zheng Jiejiao, Feng Youyan, Zhang Jie, Zhu Yinghui. Early hip abductor training to improve balance and walking ability after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5311-5316. |
| [11] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Evaluation value of cervical sagittal plane sequence parameters on pain, cervical function and clinical efficacy in patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 419-424. |
| [12] | Pan Hao, Zhao Huihui, Wang Jiangjing, Wang Feng, Wang Peng, Shi Qiuling, Guo Jin, Li Lin, Liu Guoqiang. Comparison of kinematic alignment and mechanical alignment to guide gait after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 365-370. |
| [13] | Qu Pengfei, Wang Huisheng, Li Xi. Correlation between blood loss during primary total knee arthroplasty and hypoalbuminemia and hypocalcemia after arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 376-382. |
| [14] | Song Jianzhi, Xu Lisen, Zhang Chen, Tu Feng, Niu Fei. Mechanism by which SC79, an Akt activator, inhibits dexamethasone-induced apoptosis and programmed necrosis of osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4699-4703. |
| [15] | Lu Qigui, Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Li Feilong, Chen Qunqun, Chai Shengting. MicroRNA-20b-5p effects on cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in early-stage osteoarthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4658-4665. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||