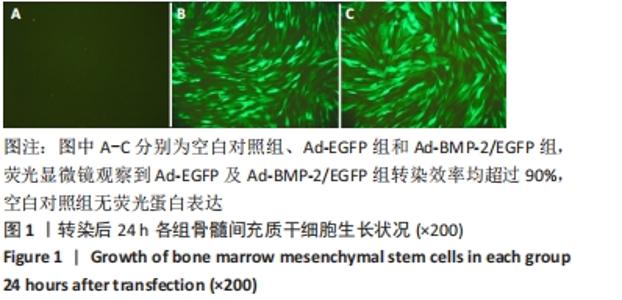
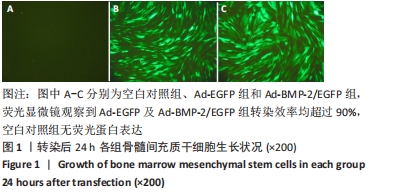
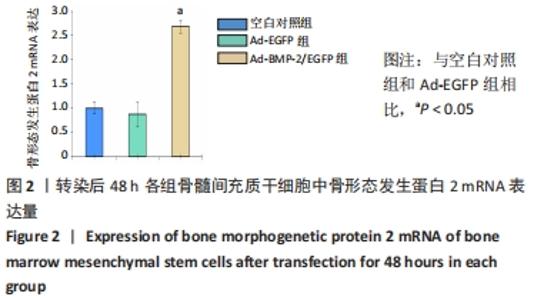
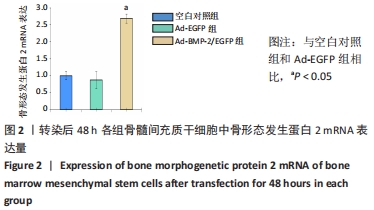
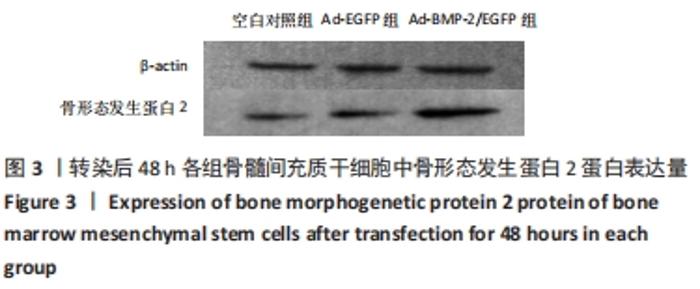
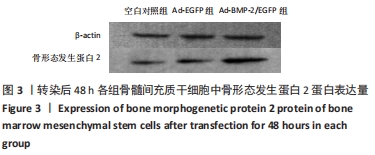
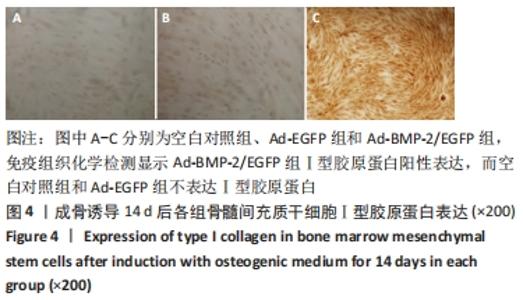
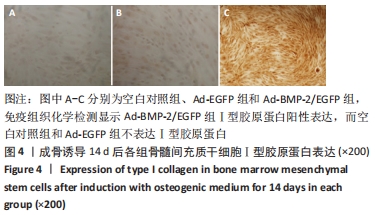
[1] 许锋,詹玉林,宋兴华.骨形态发生蛋白2基因治疗骨缺损研究进展[J].医学综述,2012,18(11):1612-1614.
[2] NGUYEN V, MEYERS CA, YAN N, et al. BMP-2-induced bone formation and neural inflammation. J Orthop. 2017;14(2):252-256.
[3] NARAYANAN KB, HAN SS. Icosahedral plant viral nanoparticles - bioinspired synthesis of nanomaterials/nanostructures. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;248:1-19.
[4] LA WG, KANG SW, YANG HS, et al. The efficacy of bone morphogenetic protein-2 depends on its mode of delivery. Artif Organs. 2010;34(12): 1150-1153.
[5] 俞莉敏,马俊轩,李继云,等.稳定表达人骨形态发生蛋白2基因骨组织工程种子细胞的构建[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(17): 2722-2728.
[6] 武成聪,荣树,任静,等.腺病毒介导增强型绿色荧光蛋白基因转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞的效率及毒性[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(17):2650-2655.
[7] ABDALLAH BM, JAFARI A, ZAHER W, et al. Skeletal (stromal) stem cells: an update on intracellular signaling pathways controlling osteoblast differentiation. Bone. 2015;70:28-36.
[8] LIN H, TANG Y, LOZITO TP, et al. Projection Stereolithographic Fabrication of BMP-2 Gene-activated Matrix for Bone Tissue Engineering. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):11327.
[9] MURRAY SS, BROCHMANN MURRAY EJ, WANG JC, et al. The history and histology of bone morphogenetic protein. Histol Histopathol. 2016; 31(7):721-732.
[10] WANG C, ZANG H, ZHOU D. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 exhibits therapeutic benefits for osteonecrosis of the femoral head through induction of cartilage and bone cells. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(5):4298-4308.
[11] 王世林.骨形态发生蛋白缓释载体的研制与评价[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2020.
[12] 孟会强,郭来威,许田恩,等.促骨再生BMP-2缓释材料的研究进展[J].世界科技研究与发展,2017,39(4):349-354.
[13] 向盈盈,宋飞,杨向红.骨形态发生蛋白-2复合纤维蛋白缓释胶修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].昆明医科大学学报,2016,37(3):27-30.
[14] ROOSTAEIAN J, CARLSEN B, SIMHAEE D, et al. Characterization of growth and osteogenic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow stromal cells. J Surg Res. 2006;133(2):76-83.
[15] 张斌斌.BMP2基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞促进缝牵引区新骨形成的实验研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2018.
[16] XU XL, TANG T, DAI K, et al. Immune response and effect of adenovirus-mediated human BMP-2 gene transfer on the repair of segmental tibial bone defects in goats. Acta Orthop. 2005;76(5):637-646.
[17] 徐丽丽,孙晓娟,郝秀仙,等.在复合成分培养基中骨髓间充质干细胞的诱导成骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(10):1501-1505.
[18] 曾辉,唐成芳,周芳,等.骨碎补总黄酮对去卵巢大鼠牙槽骨结构及骨代谢生化指标的影响[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2018,16(4): 193-196.
[19] CHEN J, SHI ZD, JI X, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by periodic heat shock in self-assembling peptide hydrogel. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(5-6):716-728.
[20] 刘光源,田发明,张柳,等.BMP2信号通路与经典Wnt信号通路及相互交联对成骨分化的调控[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(5): 551-556,561.
[21] LI X, PENG J, WU M, et al. BMP2 promotes chondrocyte proliferation via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2011;4(4):621-626.
[22] CHEN Y, WHETSTONE HC, YOUN A, et al. Beta-catenin signaling pathway is crucial for bone morphogenetic protein 2 to induce new bone formation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(1):526-533.
[23] XU J, LI Z, HOU Y, et al. Potential mechanisms underlying the Runx2 induced osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2015;7(12):2527-2535.
[24] WANG B, HUANG S, PAN L, et al. Enhancement of bone formation by genetically engineered human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells expressing osterix. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;116(4):e221-229.
[25] GUO X, WANG XF. Signaling cross-talk between TGF-beta/BMP and other pathways. Cell Res. 2009;19(1):71-88.
[26] ZHANG M, YAN Y, LIM YB, et al. BMP-2 modulates beta-catenin signaling through stimulation of Lrp5 expression and inhibition of beta-TrCP expression in osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(4):896-905.
[27] ITASAKI N, HOPPLER S. Crosstalk between Wnt and bone morphogenic protein signaling: a turbulent relationship. Dev Dyn. 2010;239(1):16-33.
|