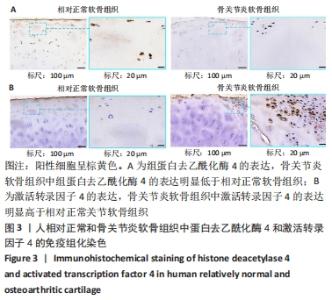
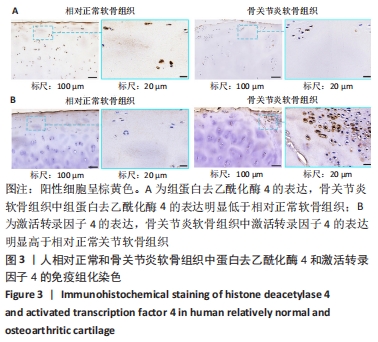
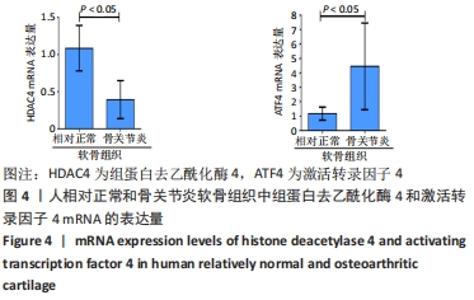
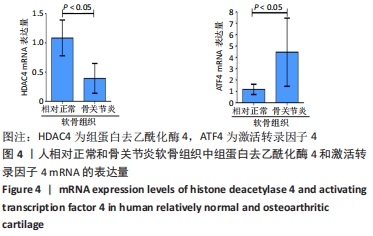
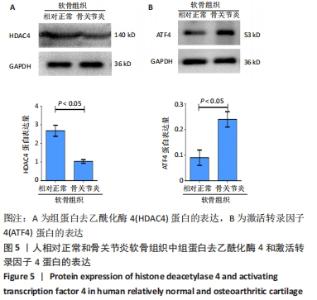
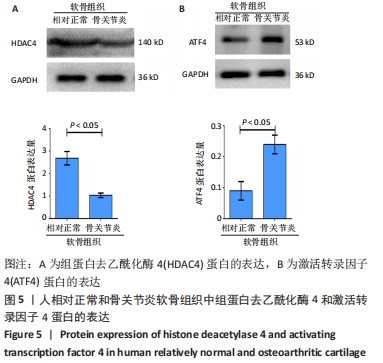
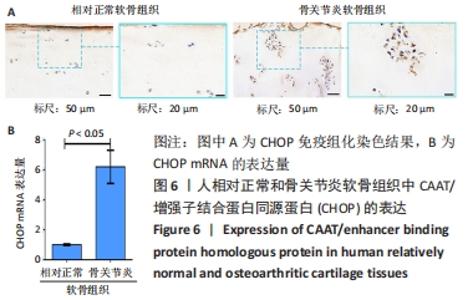
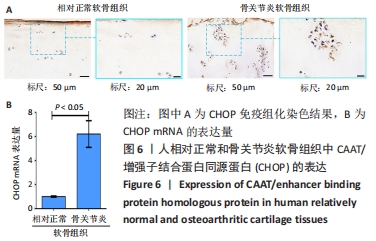
[1] SACITHARAN PK. Ageing and Osteoarthritis. Subcell Biochem. 2019;91:123-159.
[2] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65.
[3] XU M, FENG M, PENG H, et al. Epigenetic regulation of chondrocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis through Sirt1/P53/P21 pathway in surgery-induced osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;528(1):179-185.
[4] OYADOMARI S, MORI M. Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11(4):381-389.
[5] CHEN Z, ZHANG Z, GUO L, et al. The role of histone deacetylase 4 during chondrocyte hypertrophy and endochondral bone development. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(2):82-89.
[6] CAO K, WEI L, ZHANG Z, et al. Decreased histone deacetylase 4 is associated with human osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration by releasing histone deacetylase 4 inhibition of runt-related transcription factor-2 and increasing osteoarthritis-related genes: a novel mechanism of human osteoarthritis cartilage degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(6):491.
[7] ZHANG P, SUN Q, ZHAO C, et al. HDAC4 protects cells from ER stress induced apoptosis through interaction with ATF4. Cell Signal. 2014;26(3):556-563.
[8] KIKUCHI S, SUZUKI R, OHGUCHI H, et al. Class IIa HDAC inhibition enhances ER stress-mediated cell death in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 2015;29(9): 1918-1927.
[9] SLATTERY C, KWEON CY. Classifications in Brief: Outerbridge Classification of Chondral Lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(10):2101-2104.
[10] DU G, ZHAN H, DING D, et al. Abnormal Mechanical Loading Induces Cartilage Degeneration by Accelerating Meniscus Hypertrophy and Mineralization After ACL Injuries In Vivo. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(3):652-653.
[11] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311.
[12] JAHANBAN-ESFAHLAN R, MEHRZADI S, REITER RJ, et al. Melatonin in regulation of inflammatory pathways in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: involvement of circadian clock genes. Br J Pharmacol. 2018; 175(16):3230-3238.
[13] WU L, LIU H, LI L, et al. 5,7,3’,4’-Tetramethoxyflavone protects chondrocytes from ER stress-induced apoptosis through regulation of the IRE1α pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):157-166.
[14] ALMONTE-BECERRIL M, NAVARRO-GARCIA F, GONZALEZ-ROBLES A, et al. Cell death of chondrocytes is a combination between apoptosis and autophagy during the pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis within an experimental model. Apoptosis. 2010;15(5):631-638.
[15] BAO J, CHEN Z, XU L, et al. Rapamycin protects chondrocytes against IL-18-induced apoptosis and ameliorates rat osteoarthritis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(6):5152-5167.
[16] RONG K, XIA QQ, WU XH, et al. Articular Cartilage Stem Cells Influence the Postoperative Repair of Hip Replacement by Regulating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Chondrocytes via PERK Pathway. Orthop Surg. 2020; 12(2):609-616.
[17] TABAS I, RON D. Integrating the mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(3):184-190.
[18] ZHANG S, CAO M, FANG F. The Role of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate in Autophagy and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress (ERS)-Induced Apoptosis of Human Diseases. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e924558.
[19] MORIGUCHI M, WATANABE T, FUJIMURO M. Capsaicin Induces ATF4 Translation with Upregulation of CHOP, GADD34 and PUMA. Biol Pharm Bull. 2019;42(8):1428-1432.
[20] FU HY, OKADA K, LIAO Y, et al. Ablation of C/EBP Homologous Protein Attenuates Endoplasmic Reticulum–Mediated Apoptosis and Cardiac Dysfunction Induced by Pressure Overload. Circulation. 2010;122(4): 361-369.
[21] VEGA RB, MATSUDA K, OH J, et al. Histone Deacetylase 4 Controls Chondrocyte Hypertrophy during Skeletogenesis. Cell. 2004;119(4):555-566.
|