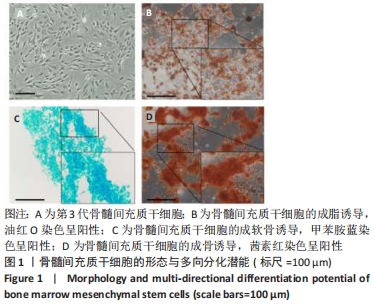
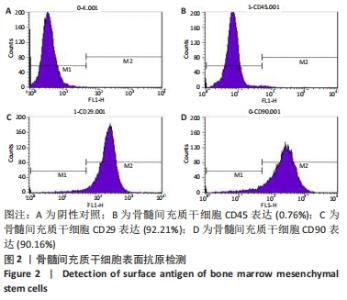
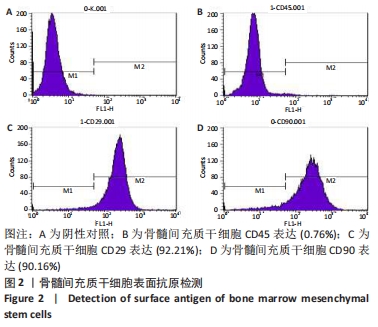
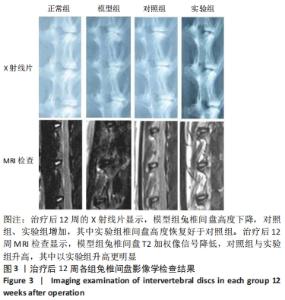
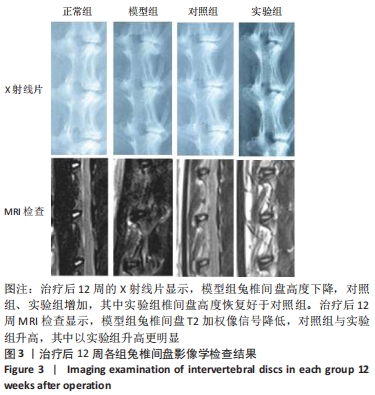
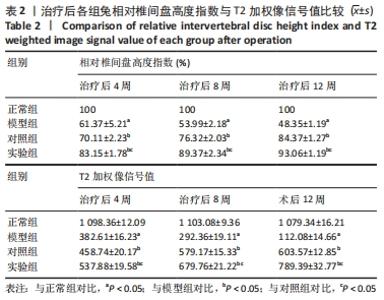
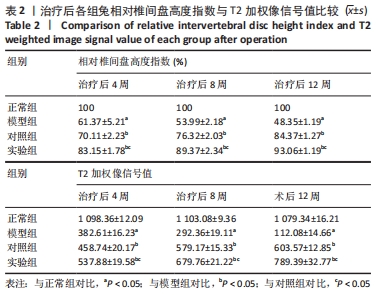
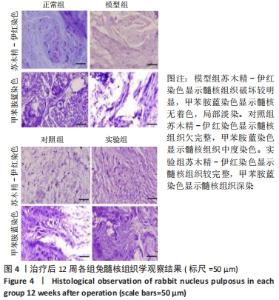
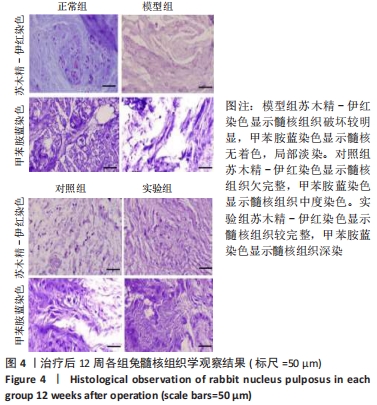
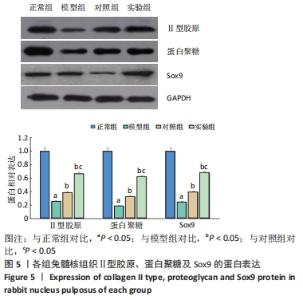
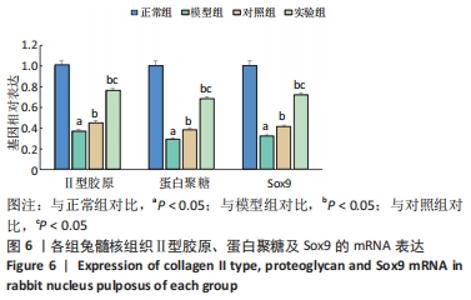
[1] Sampara P, Banala RR, Vemuri SK, et al. Understanding the molecular biology of intervertebral disc degeneration and potential gene therapy strategies for regeneration: a review. Gene Ther. 2018; 25(2):67-82.
[2] ANITUA E, PADILLA S. Biologic therapies to enhance intervertebral disc repair. Regen Med. 2018;13(1):55-72.
[3] LI Z, CHEN X, XU D, et al. Circular RNAs in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6):e12704.
[4] LI Z, LI X, CHEN C, et al. Long non-coding RNAs in nucleus pulposus cell function and intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Prolif. 2018;51(5): e12483.
[5] XIA K, GONG Z, ZHU J, et al. Differentiation of Pluripotent Stem Cells into Nucleus Pulposus Progenitor Cells for Intervertebral Disc Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;14(1):57-64.
[6] HOLGUIN N, SILVA MJ. In-Vivo Nucleus Pulposus-Specific Regulation of Adult Murine Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):11191.
[7] KOS N, GRADISNIK L, VELNAR T. A Brief Review of the Degenerative Intervertebral Disc Disease. Med Arch. 2019;73(6):421-424.
[8] SURI P, PEARSON AM, ZHAO W, et al. Pain Recurrence After Discectomy for Symptomatic Lumbar Disc Herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(10):755-763.
[9] KANNO H, AIZAWA T, HAHIMOTO K, et al. Minimally invasive discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: current concepts, surgical techniques, and outcomes. Int Orthop. 2019;43(4):917-922.
[10] LOUIE PK, VARTHI AG, NARAIN AS, et al. Stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of symptomatic adjacent segment degeneration following previous lumbar fusion. Spine J. 2018;18(11): 2025-2032.
[11] TABA HA, WILLIAMS SK. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion.Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2020;31(1):33-42.
[12] MELKE J, MIDHA S, GHOSH S, et al. Hofmann S.Silk fibroin as biomaterial for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:1-16.
[13] LI DW, HE J, HE FL, et al. Silk fibroin/chitosan thin film promotes osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(9):1164-1173.
[14] PATIL S, SINGH N. Silk fibroin-alginate based beads for human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation in 3D. Biomater Sci. 2019; 7(11):4687-4697.
[15] GAIHRE B, USWATTA S, JAYASURIYA AC. Nano-scale characterization of nano-hydroxyapatite incorporated chitosan particles for bone repair. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;165:158-164.
[16] 张亚楠,严霞,孟增东. Zn、Mg增强羟基磷灰石骨修复材料临床应用与机制:生物活性及成骨诱导的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(4):606-611.
[17] 岳聚安,郭晓忠,王冉东,等.纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66支撑棒结合同种异体骨治疗ARCOⅢ期股骨头坏死[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(28):4485-4491.
[18] 王志平,赵蒙蒙,董志恒,等.纳米羟基磷灰石复合树脂与牙釉质之间粘接界面电镜观察[J].口腔医学研究,2019,35(5):457-460
[19] 黄术,吴江怡,杨君君,等.天冬氨酸修饰纳米羟基磷灰石/聚乳酸复合物制备软骨组织工程支架及其生物性能研究[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2018,35(5):616-620.
[20] 臧晓龙,孙健,李亚莉,等.3D生物打印构建聚乳酸羟基乙酸/纳米羟基磷灰石支架骨形态发生蛋白2缓释复合体的实验研究[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(16):2405-2411.
[21] 徐瑞,黄鹏,张祎冰,等.miR-205-5p/PRKCA/p38信号通路在淫羊藿苷抑制动脉粥样硬化中的介导作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2020, 40(10):2169-2176.
[22] 杨全中,张煜,王亚娟,等.淫羊藿苷激活CaMKⅡ-JNK通路抑制人非小细胞肺癌A549细胞存活和转移特性[J].中国公共卫生, 2020,36(7):1014-1019.
[23] 鞠静,谭人千,钟勇,等.淫羊藿苷对气管切开模型大鼠早期β-防御素-2和T细胞亚群的影响[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2020, 45(1):1-7.
[24] 肖军,马德彰,杨钟华,等.淫羊藿苷促进入骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(7):1357-1359
[25] 闫建国,周亚莉,邢雪琨,等.辛硫磷对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞DNA损伤、细胞凋亡及P53蛋白表达的影响[J].卫生研究,2013, 42(4):664-669,681.
[26] WATANABE A, MAINIL-VARLET P, DECAMBRON A, et al. Efficacy of HYADD®4-G single intra-discal injections in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Mater Eng. 2019; 30(4):403-417.
[27] WANG F, NAN LP, ZHOU SF, et al. Injectable Hydrogel Combined with Nucleus Pulposus-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Degenerative Intervertebral Disc in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019: 8496025.
[28] LIGORIO C, ZHOU M, WYCHOWANIEC JK, et al. Graphene oxide containing self-assembling peptide hybrid hydrogels as a potential 3D injectable cell delivery platform for intervertebral disc repair applications. Acta Biomater. 2019;92:92-103.
[29] ALINEJAD Y, ADOUNGOTCHODO A, GRANT MP, et al. Injectable Chitosan Hydrogels with Enhanced Mechanical Properties for Nucleus Pulposus Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(5-6):303-313.
[30] GHORBANI M, AI J, NOURANI MR, et al. Injectable natural polymer compound for tissue engineering of intervertebral disc: In vitro study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;80:502-508.
[31] NEO PY, SHI P, GOH JC, et al. Characterization and mechanical performance study of silk/PVA cryogels: towards nucleus pulposus tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2014;9(6):065002.
[32] 唐俊杰,李文杰,李根,等.骨组织工程诱导性支架材料修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3):340-346.
[33] 蓝蔚仁,潘赛,孙超,等.大鼠髓核细胞来源外泌体对骨髓间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化的作用研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2019,29(1):74-81.
[34] 张宁峰,袁俊虎,苏帆,等.骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基对退变髓核细胞生物学活性及细胞外基质表达的调节作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(11):1945-1948.
[35] 白亦光,陈巧玲,刘康,等.髓核细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞对早期椎间盘退行性变干预作用对比[J].广西医科大学学报,2019, 36(12):1902-1908. |