Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (19): 3110-3116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3524
Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis
Xia Wenshen1, 2, He Renjiao2, Ai Jinwei2, 3, Wang Jun4, Li Desheng2, Pei Bin1, 3
- 1Postgraduate Training Basement of Jinzhou Medical University, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China; 2Third Department of Orthopedics, 3Evidence-Based Medicine Center, 4Department of Cardiology, Xiangyang No.1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2020-03-23Revised:2020-03-27Accepted:2020-05-30Online:2021-07-09Published:2021-01-14 -
Contact:Pei Bin, Master, Chief physician, Professor, Postgraduate Training Basement of Jinzhou Medical University, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China; Evidence-Based Medicine Center, Xiangyang No.1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Xia Wenshen, Master candidate, Physician, Postgraduate Training Basement of Jinzhou Medical University, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China; Third Department of Orthopedics, Xiangyang No.1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China He Renjiao, Senior nurse, Third Department of Orthopedics, Xiangyang No.1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China Xia Wenshen and He Renjiao contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:the General Items of Health and Family Planning Western Medicine in Hubei Province from 2015 to 2016, No. WJ2015MB187 (to PB); the Key Teaching and Research Project of Hubei Medical University, No. 2015025 (to PB); the Science and Technology Project in Xiangyang, No. 2010GG3A21 (to PB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xia Wenshen, He Renjiao, Ai Jinwei, Wang Jun, Li Desheng, Pei Bin. Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3110-3116.
share this article
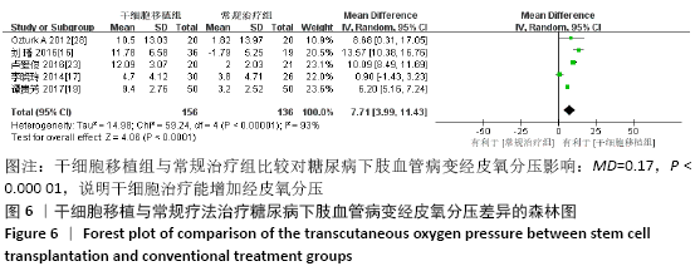
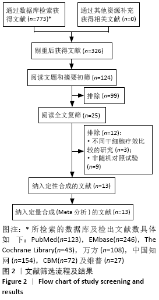
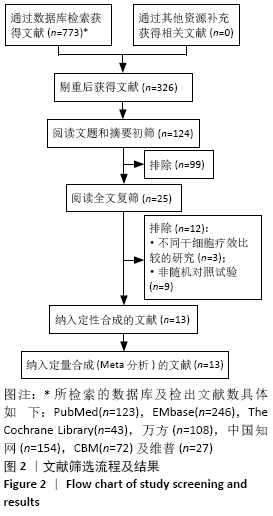
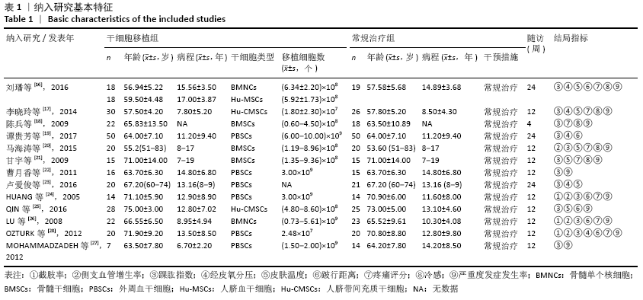
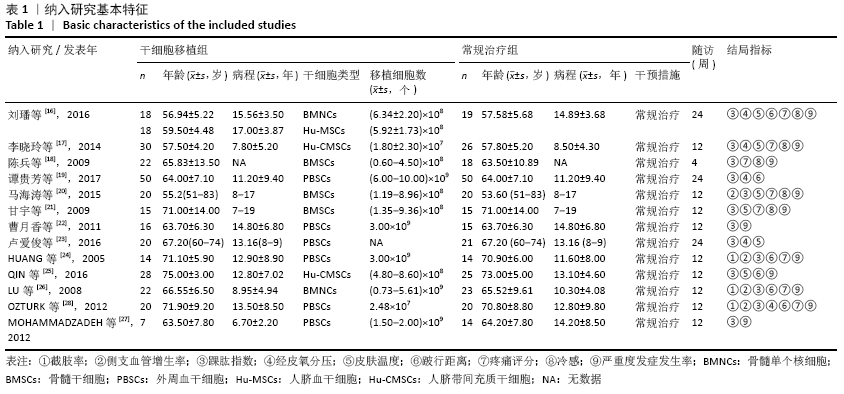
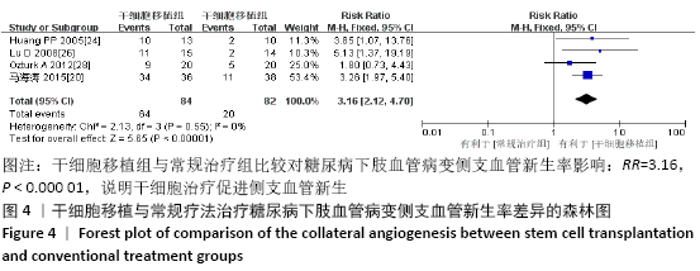
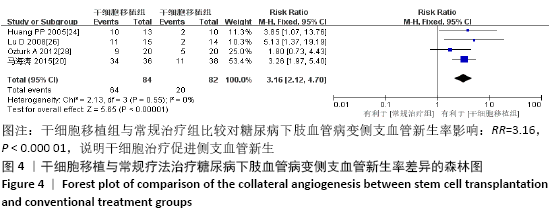
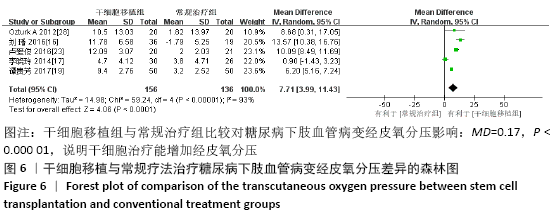
2.3.4 各组经皮氧分压差异 共纳入5个研究[16-17,19,23,28],共292例患者,干细胞移植组156例,常规治疗组136例。随机效应模型结果显示与常规治疗比较,干细胞移植能增加经皮氧分压(MD=7.71,95%CI:3.99-11.43,P < 0.000 01),见图6。根据随访时间进行亚组分析,结果显示与常规治疗比较,治疗4,12周时干细胞移植能增加经皮氧分压,但差异无显著性意义(4周:MD=0.09,95%CI:-4.69-6.48,P=0.75;12周:MD=1.39,95%CI: -1.29-4.06,P=0.31)。而治疗24周时干细胞移植能增加经皮氧分压,且差异有显著性意义(MD=9.71,95%CI:5.89-13.54,P < 0.000 01)。 "
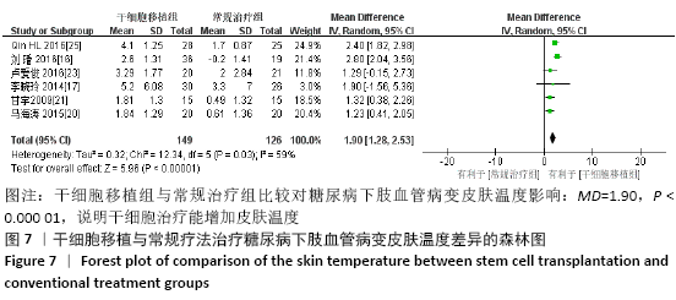
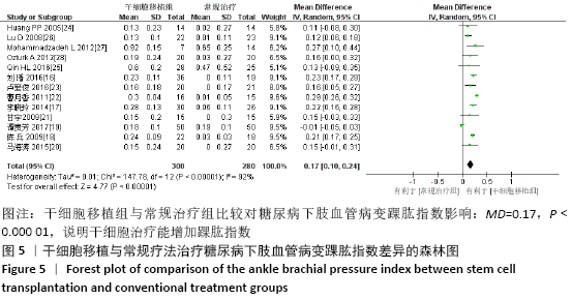
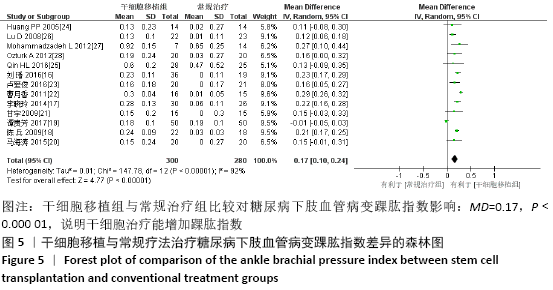
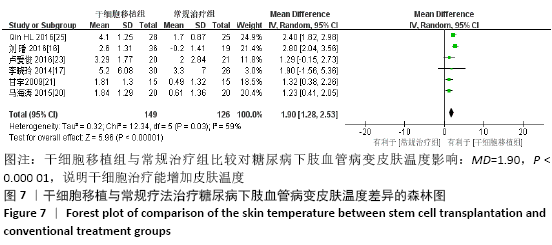
2.3.5 各组皮肤温度差异 共纳入6个研究[16-17,20-21,23,25],共275例患者,干细胞移植组149例,常规治疗组126例。随机效应模型结果显示,与常规治疗比较,干细胞移植能增加下肢皮肤温度(MD=1.90,95%CI:1.28-2.53,P < 0.000 01),见图7。根据随访时间进行亚组分析,结果显示与常规治疗比较,治疗4周干细胞移植能增加皮肤温度,但差异无显著性意义(MD= -0.39,95%CI:-0.11-0.34,P=0.30),治疗12,24周时差异有显著性意义(12周:MD=1.58,95%CI:0.86-2.30,P < 0.000 01;24周:MD=2.17,95%CI:0.72-3.63,P=0.003)。 "
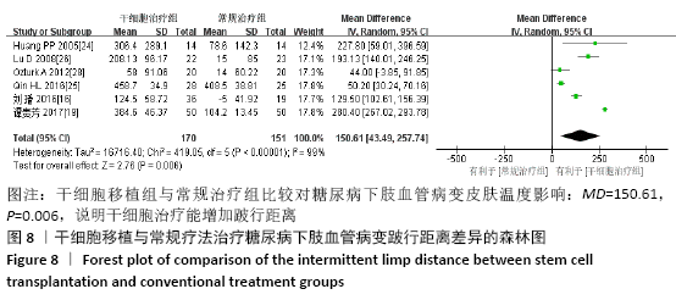
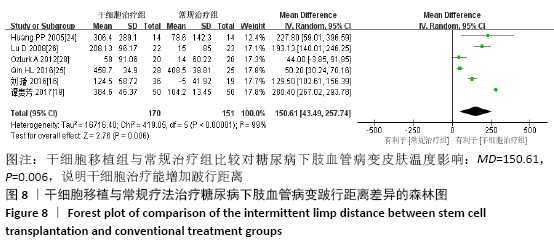
2.3.6 各组跛行距离差异 共纳入6个研究[16,19,24-26,28],共321例患者,干细胞移植组170例,常规治疗组151例。随机效应模型结果显示与常规治疗比较,干细胞移植能增加跛行距离(MD=150.61,95%CI:43.49-257.74,P=0.006),见图8。根据随访时间进行亚组分析,结果显示与常规治疗比较,治疗4周干细胞移植能增加跛行距离,但差异无显著性意义(MD=9.22,95%CI:-10.16-28.60,P=0.35),治疗 12周及24周时差异有显著性意义(12周:MD=110.67,95%CI:32.85-188.48,P=0.005;24周:MD=205.42,95%CI:57.54-353.03,P=0.006)。 "

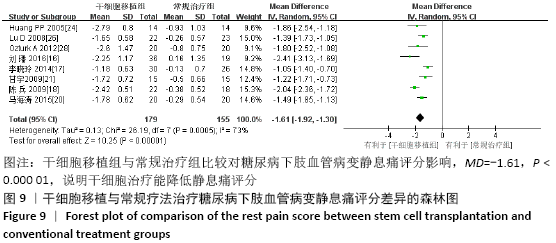
2.3.7 各组静息痛评分差异 共纳入8个研究[16-18,20-21,24,26,28],共334例患者,干细胞移植组179例,常规治疗组155例。随机效应模型结果显示与常规治疗比较,干细胞移植能降低静息痛评分(MD=-1.61,95%CI:-1.92至-1.30, P < 0.000 01),见图9。根据随访时间进行亚组分析,结果显示与常规治疗比较,治疗4,12,24周,干细胞移植均能降低静息痛评分(4周:MD=-2.04,95%CI:-2.04至-1.72,P < 0.000 01; 12周:MD=-1.36,95%CI:-1.56至 -1.16,P < 0.000 01;24周:MD= -2.41,95%CI:-3.13至-1.69,P < 0.000 01)。 "
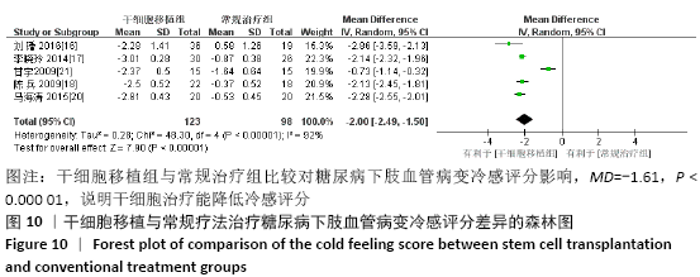
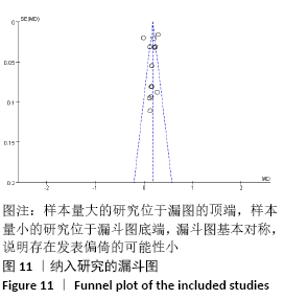
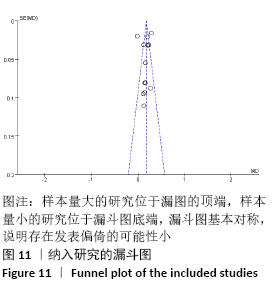
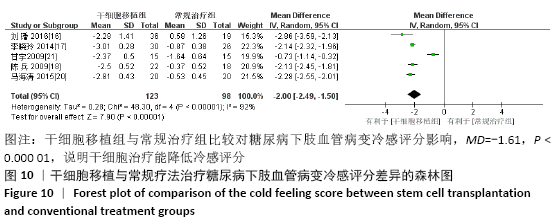
2.3.8 各组冷感评分差异 共纳入5个研究[16-18,20-21],共221例患者,干细胞移植组123例,常规治疗组98例。随机效应模型结果显示与常规治疗比较,干细胞移植能降低冷感评分(MD= -2.00,95%CI:-2.49至-1.50,P < 0.000 01),见图10。根据随访时间进行亚组分析,结果显示与常规治疗比较,治疗4,12,24周,干细胞移植均能降低冷感评分(4周:MD=-1.44,95%CI:-2.81至-0.06,P < 0.000 01;12周:MD=-2.09,95%CI:-2.39至-1.79,P < 0.000 01;24周:MD=-2.86,95%CI: -3.59至-2.13,P < 0.000 01)。 "
| [1] SHEARMAN CP, WINDHABER R. Foot complications in patients with diabetes. Surgery. 2010;28(6):288-292. [2] 李翠芳,姚远.脐血干细胞移植2型糖尿病下肢血管病变患者内皮依赖性血管舒张的变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(50):8098-8102. [3] 余宏建,阮继银,赵正平,等.血管腔内成形术联合自体外周血干细胞移植对老年糖尿病足患者血管内皮生长因子水平及治疗效果的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015,35(23):6772-6774. [4] 浦晓琪,陆颖理.糖尿病下肢血管病变的防治进展[J].医学综述,2015,21(5):851-853. [5] 李玲,臧莎莎,宋光耀.糖尿病足溃疡的危险因素与治疗进展[J].中国全科医学, 2013,16(9C):3159-3163. [6] 张明珠,俞光荣.干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足的基础研究与临床应用进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(3):358-361. [7] 谷涌泉,张建,汪忠镐.糖尿病足诊断与治疗的进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2011,6(4):503-508. [8] 王爱红,许樟荣.干细胞移植-治疗糖尿病缺血性下肢血管病变的新手段[J].国外医学(内分泌学分册),2005,25(6):430-432. [9] 刘彦君.糖尿病下肢动脉病变的干细胞治疗[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2011, 3(3):50-52. [10] LOPES L, SETIA O, AURSHINA A, et al. Stem cell therapy for diabetic foot ulcers: a review of preclinical and clinical research. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):188. [11] TATEISHI-YUYAMA E, MATSUBARA H, MUROHARA T, et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis for patients with limb ischaemia by autologous transplantation of bone-marrow cells: a pilot study and a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 360(9331):427-435. [12] 曾宪涛,包翠萍,曹世义,等.Meta分析系列之三:随机对照试验的质量评价工具[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012, 4(3):183-185. [13] 曾宪涛,Joey S,田国祥,等.Meta分析系列之二:Meta分析的软件[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2012,4(2):89-91. [14] 文进,李幼平.Meta分析中效应尺度指标的选择[J].中国循证医学杂志,2007,7(8): 606-613. [15] 王丹,翟俊霞,牟振云,等.Meta分析中的异质性及其处理方法[J].中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(10):1115-1118. [16] 刘璠,周慧敏,杨爱格,等.不同来源单个核细胞移植对2型糖尿病下肢血管病变的疗效比较[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2016,6(6):351-355. [17] 李晓玲,朱旅云,宋光耀,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(23):3670-3675. [18] 陈兵,陆德宾,梁自文,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞体外扩增后移植治疗糖尿病足[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(32):6227-6230. [19] 谭贵芳.自体外周血干细胞联合介入治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变的临床分析[J].医学理论与实践,2017,30(5):668-670. [20] 马海涛,周涛,邱文淼,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植联合当归活血汤治疗糖尿病足[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(50): 8139-8143. [21] 甘宇,李铁男,于黎丽,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植与通脉化瘀汤合用治疗糖尿病足溃疡的研究[J].中国中西医结合皮肤性病学杂志,2009,8(1):5-7. [22] 曹月香,高怀林,张华.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变16例疗效观察[J].山东医药,2011,51(32):46-47. [23] 卢爱俊,赵杰,张书评,等.自体外周血干细胞移植治疗20例糖尿病缺血性下肢血管病变的临床观察[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2016,48(4):402-404. [24] HUANG P, LI S, HAN M, et al. Autologous transplantation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood mononuclear cells improves critical limb ischemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(9):2155-2160. [25] QIN HL, ZHU XH, ZHANG B, et al. Clinical evaluation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation after angioplasty for diabetic foot. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2016;124(8):497-503. [26] LU DB, JIANG YZ, LIANG ZW, et al. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on diabetic patients with lower limb ischemia. Journal of Medical Colleges of PLA. 2008;23(2):106-115. [27] MOHAMMADZADEH L, SAMEDANIFARD SH, KESHAVARZI A, et al. Therapeutic outcomes of transplanting autologous granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilised peripheral mononuclear cells in diabetic patients with critical limb ischaemia. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013;12(1):48-53. [28] OZTURK A, KUCUKARDALI Y, TANGI F, et al. Therapeutical potential of autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cell transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetic critical limb ischemia. J Diabetes Complications. 2012;26(1):29-33. [29] 张会峰,赵志刚,袁慧娟,等.自体骨髓单个核细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢周围神经病变[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(6):1137-1140. [30] 韦喜,韦华.间充质干细胞治疗糖尿病足的研究进展[J].右江民族医学院学报, 2016,38(5):524-526. [31] 刘国强,魏蕊,洪天配.干细胞移植治疗糖尿病的研究进展[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2014,6(1):9-13. [32] BURA A, PLANAT-BENARD V, BOURIN P, et al. Phase I trial: the use of autologous cultured adipose-derived stroma/stem cells to treat patients with non-revascularizable critical limb ischemia. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(2):245-257. [33] 陈明卫,李燕萍,唐益忠,等.不同来源和移植途径的自体干细胞治疗糖尿病缺血性下肢血管病变的随机对照研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2013,7(14): 6418-6423. [34] 刘永进,杜博,黄博威,等.干细胞移植干预糖尿病缺血性下肢血管病变康复疗效的Meta分析[J].康复学报,2017,27(1): 49-54. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [4] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [5] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [6] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [7] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [8] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [9] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [10] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [11] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [12] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [13] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [14] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [15] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||