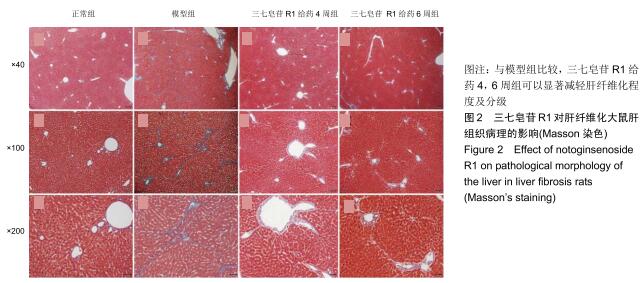
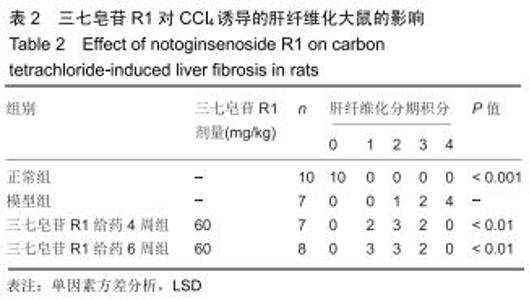
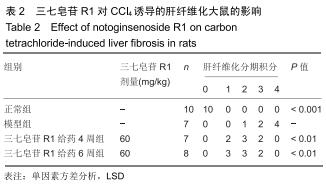
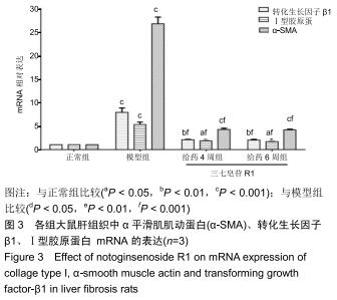
|
[1] PAN Q, WANG YQ, LI GM, et al. Fuzheng Huayu Recipe Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis by Restoring Balance between Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Mesenchymal-to- Epithelial Transition in Hepatic Stellate Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:935903.
[2] 陈维武,王海荣,霍璇,等.仁青芒觉胶囊对二甲基亚硝胺诱导的大鼠肝纤维化的治疗作用[J].药物评价研究,2019,42(6):64-69.
[3] LIU X, LIU R, HOU F, et al. Fibronectin expression is critical for liver fibrogenesis in vivo and in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2016; 14(4):3669-3675.
[4] 于俊民,鞠礼,王慧冬,等.三七皂苷R1对大鼠缺血心肌VEGF、bFGF的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(30):5845-5848.
[5] 何红艳,杨建华,杨秀娟,等.维药护肝布祖热对四氯化碳诱导肝纤维化大鼠的保护作用[J].中药药理与临床,2018,34(6):21-24.
[6] HAFEZ MM, HAMED SS, EL-KHADRAGY MF, et al. Effect of ginseng extract on the TGF-β1 signaling pathway in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17(1):45.
[7] HE J, BAI K, HONG B, et al. Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Int Immunopharmacol.2017;53:56-62.
[8] 王莹,禇扬,李伟,等.三七中皂苷成分及其药理作用的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2015,46(9):1381-1392.
[9] 杨晶晶,刘英,王承潇,等.三七皂苷R_1的现代研究进展[J].中国医院药学杂志,2015,35(5):463-467
[10] 谭亮.三七皂苷R1药理作用的研究进展[J].中国药理学通报, 2018,34(5):604-607.
[11] 姜辉,汪永忠,刘晓闯,等.三七总皂苷对肝纤维化大鼠细胞因子的影响[J].中药材,2013,36(7):1123-1127.
[12] 王淑君,刘立宾,黎关龙,等.三七皂苷单体R_1抑制低氧高二氧化碳诱导的肺动脉平滑肌细胞p38 MAPK信号通路的活化[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(1):111-114.
[13] 魏晓光,郭辉,陈永珍,等.腹腔注射四氯化碳建立大鼠肝纤维化模型[J].实验室研究与探索,2015,34(11):34-37.
[14] 王琦,李海荣,李佩阳,等.三七皂苷R1对创伤性休克大鼠心脏功能、肺组织损伤及免疫失衡的实验研究[J].西部医学,2019, 31(12):1826-1836.
[15] 宋献美,石科,葛文静,等.不同引经药配伍大黄-丹参药对抗大鼠肝纤维化的比较[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(20): 132-137.
[16] 王宪东,石安华,陈文玲.肝纤维化大鼠模型的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2016,16(94):256-269
[17] 黄小梅,郭莉娜,李灿,等.锁阳通过抑制炎症因子的表达对抗CCL4导致的小鼠肝纤维化[J].成都医学院学报,2018,13(3): 249-252,261.
[18] 毛忠懿,吴雄健,胡志燕.贝那普利对肝纤维化大鼠TGF-β_1和α-SMA影响的研究[J].中国当代医药,2013,20(36):30-33.
[19] 刘伟,符小红,黄思远,等.藏药波棱瓜子总木脂素对四氯化碳致大鼠肝纤维化的保护作用及机制探讨[J].2017,42(3):567-571.
[20] 李洁,邱建利,许华.加味茵陈四逆汤对肝纤维化小鼠Smad7及Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原蛋白表达的影响[J].中药
材,2016,39(6): 1384-1388.
|