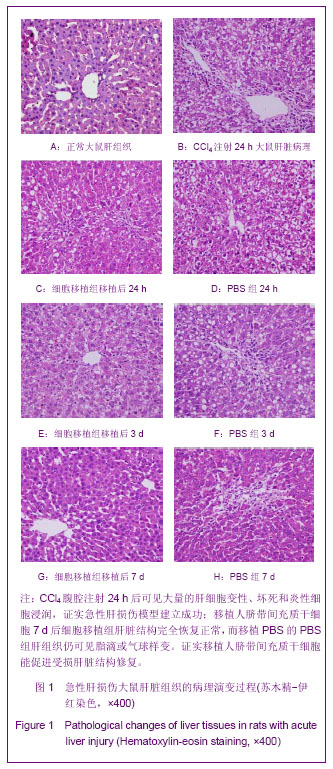
| [1] 闫俊卿,韩涛,朱争艳.人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性及向类肝细胞的分化[J].世界华人消化杂志,2008,16(15):1639-1644. [2] 陈军,刘玉侠,姜文华,等.体外诱导人脐带间充质干细胞向肝样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(49): 9257-9260. [3] Majumdar MK,Thiede MA,Mosca JD,et al.Phenotypic and functional comparison of cultures of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and stromal cells. Cell physicol. 1998;176(1):57-66. [4] Petersen BE,Goff JP,Greenberger JS,et al.Hepatic oval cells express the hematopoietic stem cell marker Thy-1 in the rat. Hepatology 1998;27(2):433-445. [5] Durate RF,Frank DA.SCF and G-CSF lead to the synergistic induction of proliferation and gene expression through complementary signaling pathways. Blood. 2000;96(10): 3422-3430. [6] Delgado MB,Clark-Lewis I,Loetscher P, et al.Rapid inactivation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 by cathepsin G associated with lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 2001;31(3): 699-707. [7] Honczarenko M, Le Y, Swierkowski M,et al.Human bone marrow stromal cells express a distinct set of biologically functional chemokine receptors.Stem Cells. 2006;24(4): 1030-1041. [8] Gaia S, Smedile A, Omedè P, et al.Feasibility and safety of G-CSF administration to induce bone marrow-derived cells mobilization in patients with end stage liver disease.J Hepatol. 2006;45(1):13-19. [9] 陈政,劳学军,高明.人脐带间充质干细胞在肝部分切除模型大鼠体内向肝样细胞的分化[J].暨南大学学报:自然科学与医学版, 2011,32(6):615-619. [10] 石翠翠.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗肝衰竭的临床前研究[D].苏州大学.2012. [11] 冯曜宇.脐带间充质干细胞转染HGF基因对肝损伤再生的研究[D].昆明医学院.2008. |