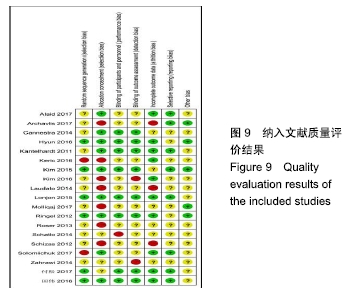
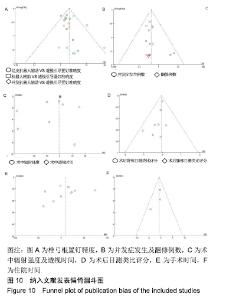
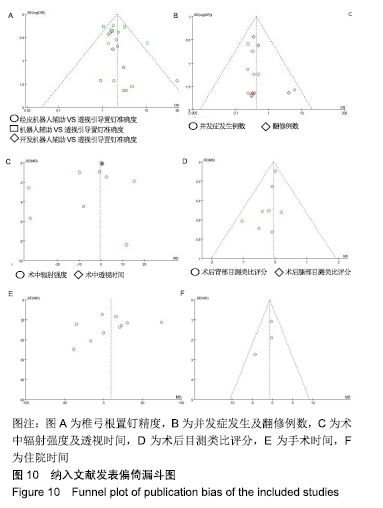
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (18): 2932-2938.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2670
Previous Articles Next Articles
Robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw placement: a meta-analysis
Xu Zhaojian1, Han Pengfei2, Wu Zhuangzhuang1, Zhao Bin1, Wang Yongfeng1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Heping Hospital Affiliated to Changzhi Medical College, Changzhi 046000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2019-08-21Revised:2019-08-31Accepted:2019-10-19Online:2020-06-28Published:2020-04-07 -
Contact:Wang Yongfeng, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Xu Zhaojian, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Clinical Medical College of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, No. 2018011046-8
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Zhaojian, Han Pengfei, Wu Zhuangzhuang, Zhao Bin, Wang Yongfeng. Robot-assisted and fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw placement: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2932-2938.
share this article
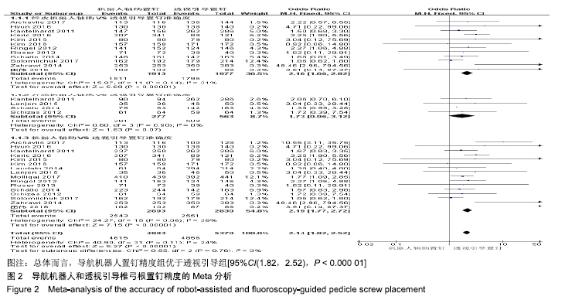
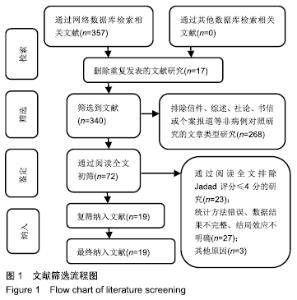
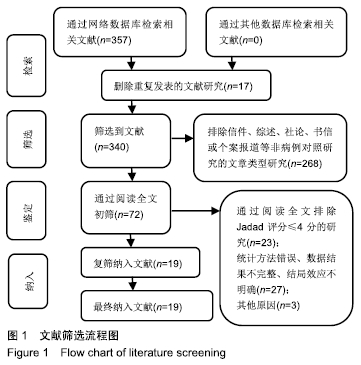
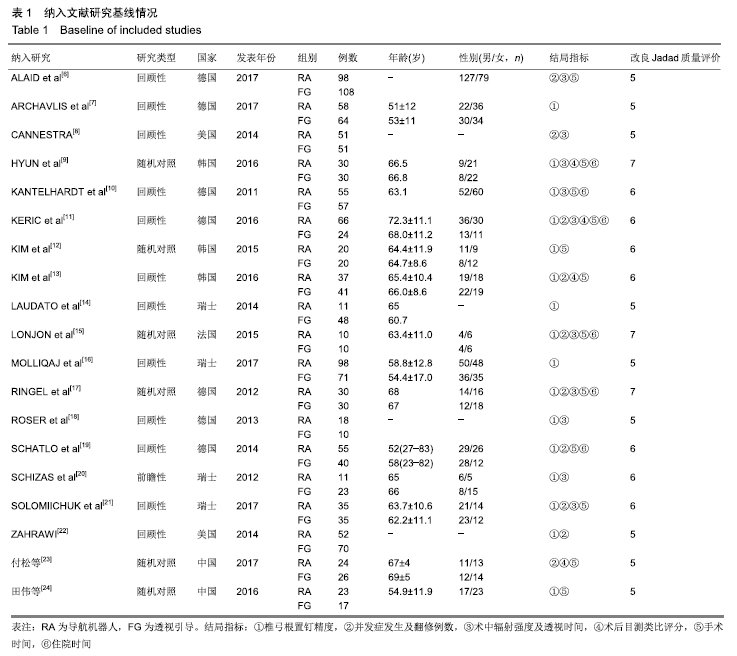
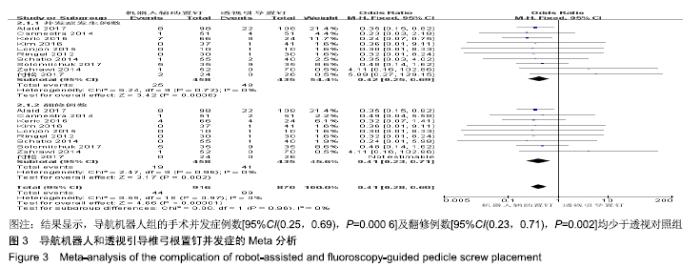
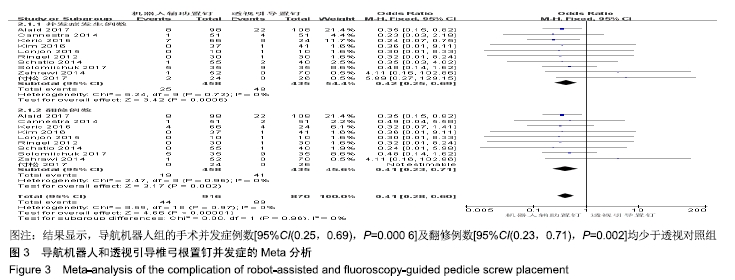
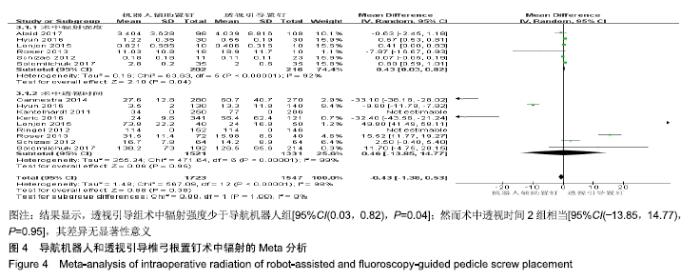
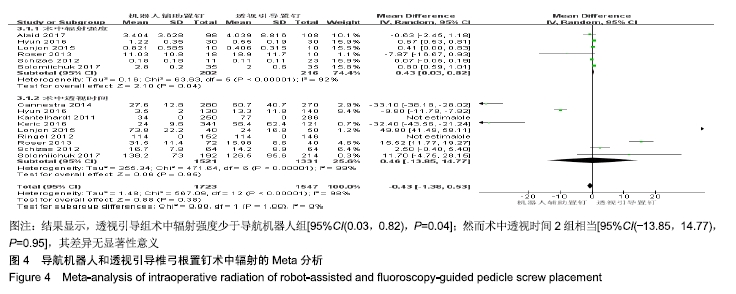
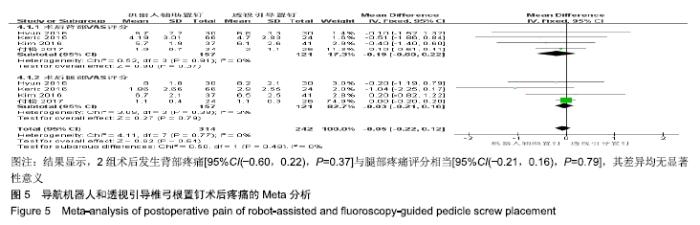
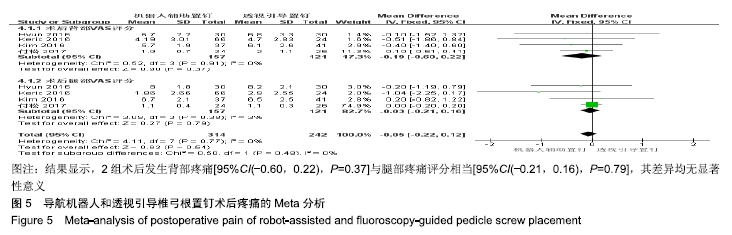
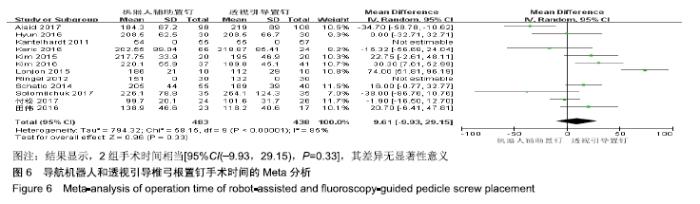
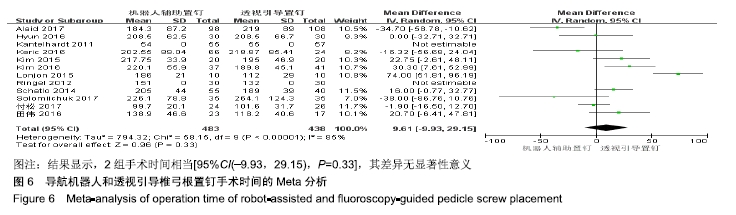
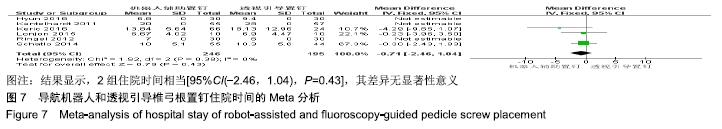
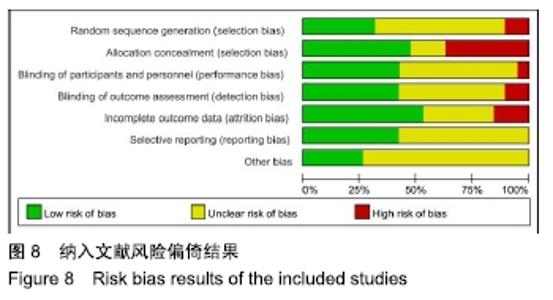
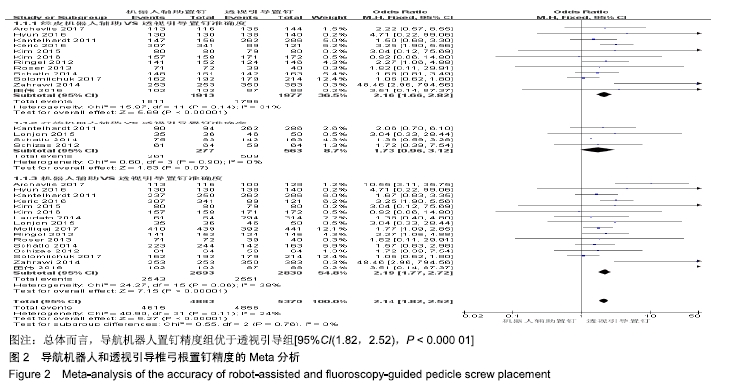
2.2 Meta分析结果 2.2.1 椎弓根置钉精度 根据经皮或开放入路不同,将纳入的16篇文献分为2个亚组[7,9-22,24]。对于导航机器人和透视引导椎弓根置钉精度做比较,因为各研究结果及亚组间异质性不大(I2 < 50%),故进行Meta分析时采用固定效应模型。结果显示,经皮入路下导航机器人置钉精度优于透视引导组[95%CI(1.66,2.82),P < 0.001],而开放入路下2组置钉精度相当[95%CI(0.96,3.12),P=0.070]。若不计入路区别时,总体而言,导航机器人置钉精度组优于透视引导组[95%CI(1.82,2.52),P < 0.000 01],其差异有显著性意义,见图2。 "
| [1] 汤旭日,马安军,傅弛,等. 单侧与双侧椎弓根螺钉固定对行TLIF治疗的腰椎退行性病变患者的效果比较[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(6): 965-967. [2] ELDER BD, LO SF, HOLMES C, et al. The biomechanics of pedicle screw augmentation with cement. Spine J. 2015; 15(6):1432-1445. [3] GALBUSERA F, VOLKHEIMER D, REITMAIER S, et al. Pedicle screw loosening: a clinically relevant complication? Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(5): 1005-1016. [4] VADALÀ G, ACCOTO D, RUSSO F, et al. A new surgical positioning system for robotic assisted minimally invasive spine surgery and transpedicular approach to the disc. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017; 31(4 suppl 1):159-165. [5] MALHAM GM, PARKER RM. Early experience of placing image-guided minimally invasive pedicle screws without K-wires or bone-anchored trackers. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018; 28(4):357-363. [6] ALAID A, VON ECKARDSTEIN K, SMOLL NR, et al. Robot guidance for percutaneous minimally invasive placement of pedicle screws for pyogenic spondylodiscitis is associated with lower rates of wound breakdown compared to conventional fluoroscopy-guided instrumentation. Neurosurg Rev. 2018; 41(2):489-496. [7] ARCHAVLIS E, AMR N, KANTELHARDT SR, et al. Rates of upper facet joint violation in minimally invasive percutaneous and open instrumentation: a comparative cohort study of different insertion techniques. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2018; 79(1):1-8. [8] CANNESTRA AF. Significant decreased radiation exposure in percutaneous adult degenerative spinal instrumentation with robotic guidance. Spine J. 2014; 14(11):S171. [9] HYUN SJ, KIM KJ, JAHNG TA, et al. Minimally invasive robotic versus open fluoroscopic-guided spinal instrumented fusions: a randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(6):353-358. [10] KANTELHARDT SR, MARTINEZ R, BAERWINKEL S, et al. Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement. Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(6):860-868. [11] KERIC N, EUM DJ, AFGHANYAR F, et al. Evaluation of surgical strategy of conventional vs. percutaneous robot-assisted spinal trans-pedicular instrumentation in spondylodiscitis. J Robot Surg. 2017; 11(1):17-25. [12] KIM HJ, LEE SH, CHANG BS, et al. Monitoring the quality of robot-assisted pedicle screw fixation in the lumbar spine by using a cumulative summation test. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015; 40(2):87-94. [13] KIM HJ, JUNG WI, CHANG BS, et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of robot-assisted vs freehand pedicle screw fixation in spine surgery. Int J Med Robot. 2017; 13(3): 1-7. [14] LAUDATO PA, PIERZCHALA K, SCHIZAS C. Pedicle screw insertion accuracy using o-arm, robotic guidance, or freehand technique: a comparative study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018; 43(6):E373-E378. [15] LONJON N, CHAN-SENG E, COSTALAT V, et al. Robot-assisted spine surgery: feasibility study through a prospective case-matched analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(3):947-955. [16] MOLLIQAJ G, SCHATLO B, ALAID A, et al. Accuracy of robot-guided versus freehand fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2017; 42(5):E14. [17] RINGEL F, STÜER C, REINKE A, et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws: a prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012; 37(8):E496-501. [18] ROSER F, TATAGIBA M, MAIER G. Spinal robotics: current applications and future perspectives. Neurosurgery. 2013; 72 Suppl 1:12-18. [19] SCHATLO B, MOLLIQAJ G, CUVINCIUC V, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw insertion for degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine: a matched cohort comparison. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014; 20(6):636-643. [20] SCHIZAS C, THEIN E, KWIATKOWSKI B, et al. Pedicle screw insertion: robotic assistance versus conventional C-arm fluoroscopy. Acta Orthop Belg. 2012; 78(2):240-245. [21] SOLOMIICHUK V, FLEISCHHAMMER J, MOLLIQAJ G, et al. Robotic versus fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw insertion for metastatic spinal disease: a matched-cohort comparison. Neurosurg Focus. 2017; 42(5): E13. [22] ZAHRAWI F. Comparative analysis of robotic-guided pedicle screw placement accuracy and freehand controls in percutaneous adult degenerative spinal instrumentation. Spine J. 2014; 14(11):S63. [23] 付松,邵诗泽,王龙强,等. Quadrant系统下椎间融合辅助机器人治疗老年单节段腰椎退变的临床研究[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2017,3(2):70-76. [24] 田伟,范明星,韩晓光,等. 机器人辅助与传统透视辅助脊柱椎弓根螺钉内固定的临床对比研究[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志, 2016,1(1): 4-10. [25] XU YF, LE XF, TIAN W, et al. Computer-assisted, minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: One surgeon's learning curve A STROBE-compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(27): e11423. [26] OVERLEY SC, CHO SK, MEHTA AI, et al. Navigation and Robotics in Spinal Surgery: Where Are We Now? Neurosurgery. 2017; 80(3S): S86-S99. [27] ONEN MR, NADERI S. Robotic systems in spine surgery. Turk Neurosurg. 2014; 24(3):305-311. [28] RINGEL F, VILLARD J, RYANG YM, et al. Navigation, robotics, and intraoperative imaging in spinal surgery. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2014; 41:3-22. [29] 陈龙,海涌,关立,等.机器人辅助置入与徒手置入椎弓根螺钉的对比研究[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2017, 6(10): 730-736. [30] 王洪伟. 微创椎弓根螺钉置入中脊柱手术机器人的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(53): 8647. |
| [1] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [2] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [3] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [4] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [5] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [6] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [7] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [8] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [9] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [10] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [11] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [12] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [13] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [14] | Xiang Feifan, Ye Junwu, Zhang Xihai, Ge Jianhua, Tang Lian, Yang Yunkang. Comparison of three different internal fixation methods in treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 403-408. |
| [15] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||