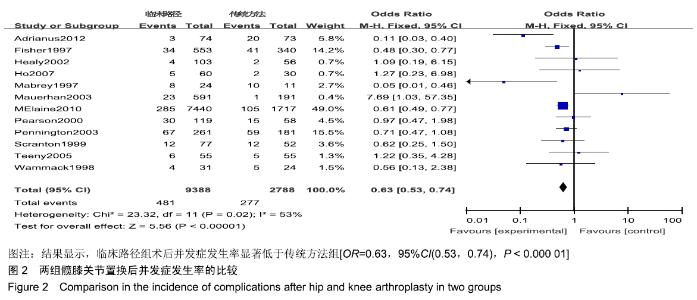
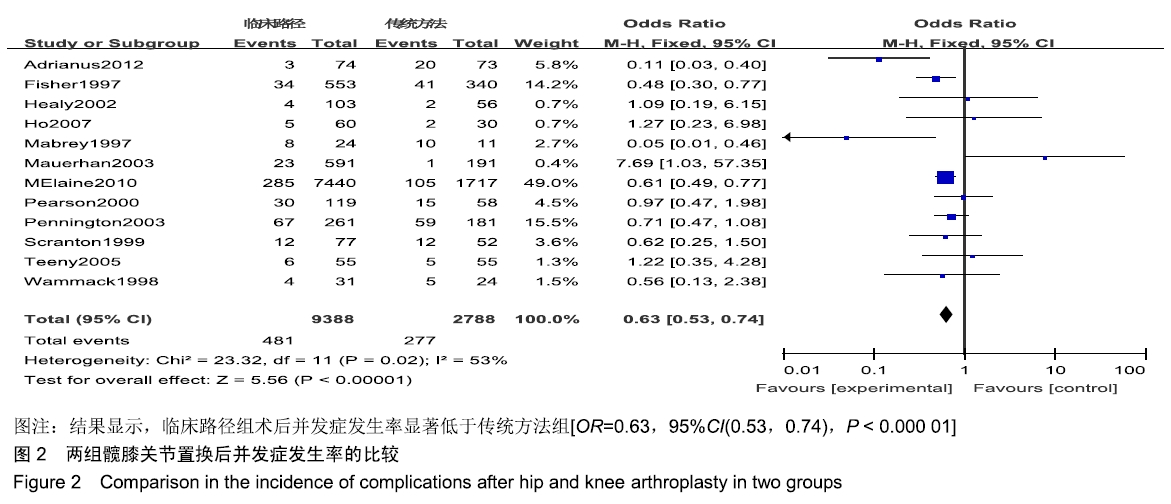
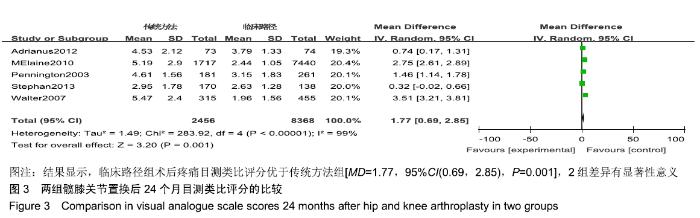
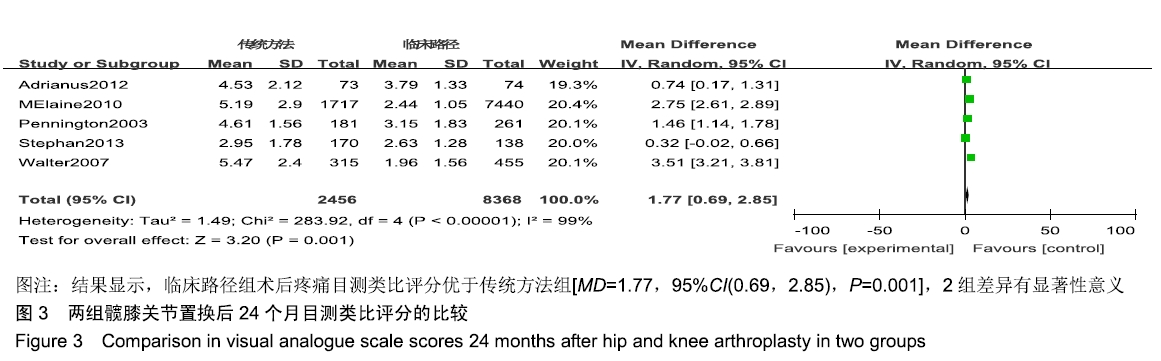
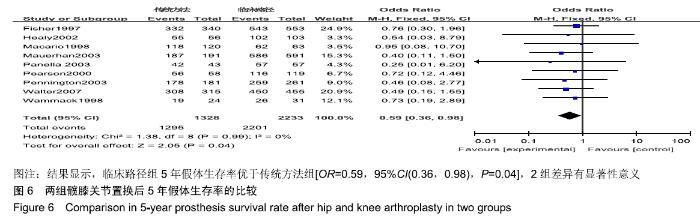
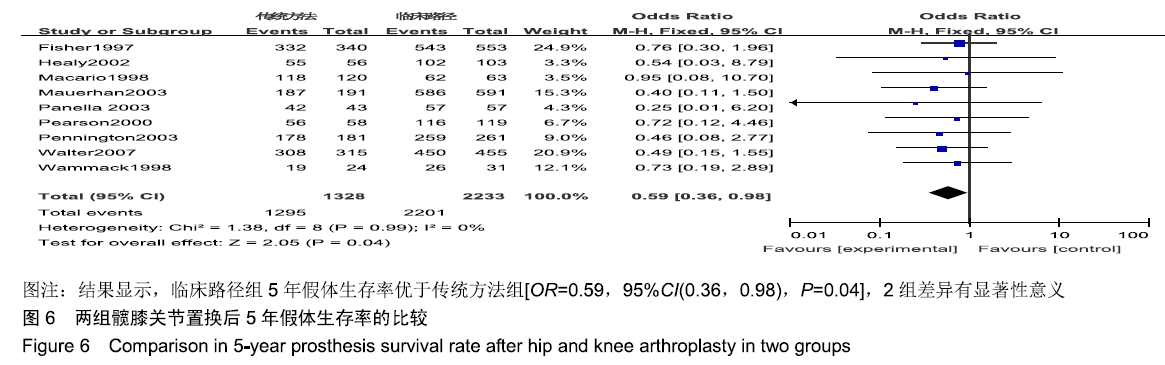
[1] FISHER DA, TRIMBLE S, CLAPP B. Effect of a patient management system on outcomes of total hip and knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;345:155-160.
[2] MABREY JD, TOOHEY JS, ARMSTRONG DA. Clinical pathway management of total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; 345:125-133.
[3] WAMMACK L, MABREY JD. Outcomes assessment of total hip and total knee arthroplasty: critical pathways, variance analysis, and continuous quality improvement. Clin Nurse Spec. 1998;12:122-129.
[4] SCRANTON PE. The cost effectiveness of streamlined care pathways and product standardization in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1999;14:182-186.
[5] PEARSON S, MORAW I, MADDERN GJ. Clinical pathway management of total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective comparative study. Aust N Z J Surg. 2000;70:351-354.
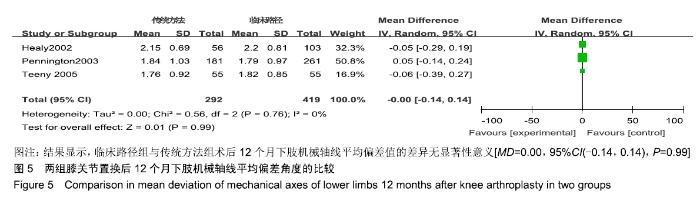
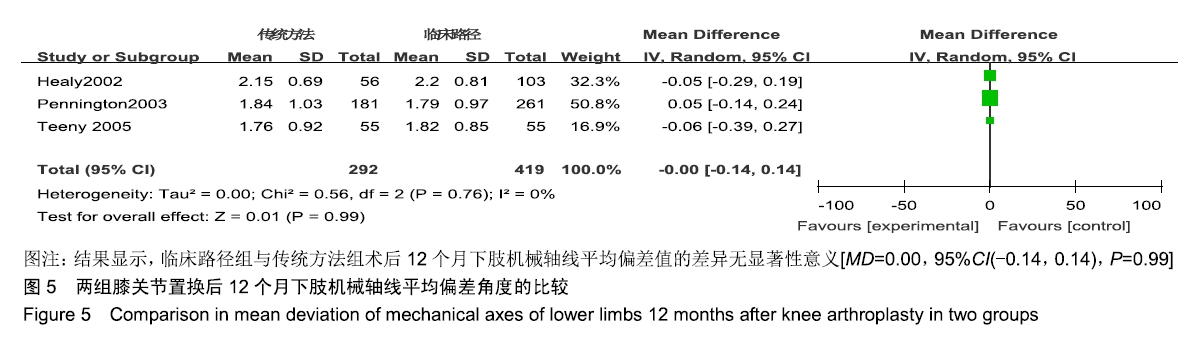
[6] HEALY WL, IORIO R, KO J, et al. Impact of cost reduction programs on short-term patient outcome and hospital cost of total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84:348-353.
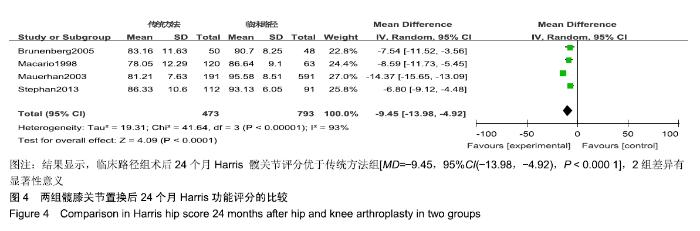
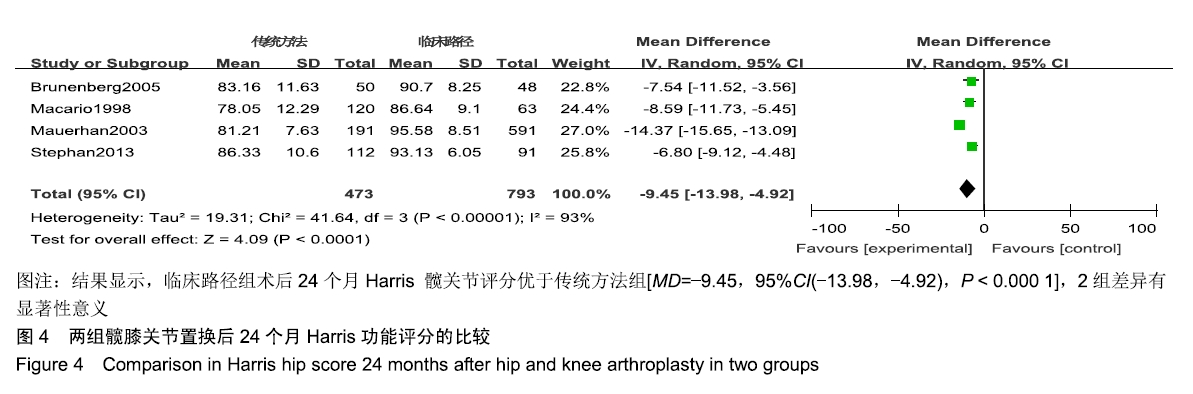
[7] MAUERHAN DR, LONERGAN RP, MOKRIS JG. Relationship between length of stay and dislocation rate after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18:963-967.
[8] PENNINGTON JM, JONES DP, MCINTYRE S. Clinical pathways in total knee arthroplasty: a New Zealand experience. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2003;11:166-173.
[9] TEENY SM, YORK SC, BENSON C, et al. Does shortened length of hospital stay affect total knee arthroplasty rehabilitation outcomes. J Arthroplasty.2005;20:39-45.
[10] HO DM, HUO MH. Are critical pathways and implant standardization programs effective in reducing costs in total knee replacement operations? J Am Coll Surg. 2007;205:97-100.
[11] HUSNI ME, LOSINA E, FOSSEL AH, et al. Decreasing medical complications for total knee arthroplasty: Effect of Critical Pathways on Outcomes. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2010;11:160.
[12] DEN HERTOG A, GLIESCHE K, TIMM J, et al. Pathway-controlled fast-track rehabilitation after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized prospective clinical study evaluating the recovery pattern, drug consumption, and length of stay. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012; 132(8):1153-1163.
[13] MACARIO A, HORNE M, GOODMAN S. The effect of a perioperative clinical pathway for knee replacement surgery on hospital costs. Anesth Analg. 1998;86:978-984.
[14] PANELLA M, MARCHISIO S, DI STANISLAO F. Reducing clinical variations with clinical pathways: do pathways work? Int J Qual Health Care. 2003;15:509-521.
[15] BRUNENBERG DE, VAN STEYN MJ, SLUIMER JC. Joint recovery programme versus usual care: an economic evaluation of a clinical pathway for joint replacement surgery. Med Care. 2005;43:1018-1026.
[16] WALTER FL, BASS N, BOCK G. Success of clinical pathways for total joint arthroplasty in a community hospital. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 457:133-137.
[17] MERTES SC, RAUT S, KHANDUJA V. Integrated care pathways in lower-limb arthroplasty: are they effective in reducing length of hospital stay? Int Orthop.2013;37(6):1157-1163.
[18] HIPP R, ABEL E, WEBER RJ. A primer on clinical pathways. Hosp Pharm. 2016;51(5):416-421.
[19] MOLLOY IB, MARTIN BI, MOSCHETTI WE, et al. Effects of the Length of Stay on the Cost of Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty from 2002 to 2013. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2017;99(5):402-407.
[20] BURGERS PT, VAN LIESHOUT EM, VERHELST J, et al. Implementing a clinical pathway for hip fractures; effects on hospital length of stay and complication rates in five hundred and twenty six patients. Int Orthop. 2014;38(5):1045-1050.
|