Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (26): 4101-4108.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1346
Cobalt-chromium particles inducing preosteoblasts may aggravate periprosthetic inflammation
- 1Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, the University of Kansas School of Medicine-Wichita, Wichita, KS, USA; 3Department of Biological Sciences, Wichita State University, Wichita, KS, USA
-
Contact:Yang Shuye, MD, Attending physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Binzhou Medical University Hopital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Jiang Jianhao, MD, Attending physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81241061 (to ZK); the Medical and Health Technology Development Project of Shandong Province, No. 2016WS0023 (to YSY); the Science Research Startup Foundation of Binzhou Medical University, No. BY2016KYQD19 (to YSY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jiang Jianhao, Li Peng, Du Gangqiang, Liu Hongzhi, Wang Hui, Zhang Kai, Yang Shangyou, Yang Shuye. Cobalt-chromium particles inducing preosteoblasts may aggravate periprosthetic inflammation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4101-4108.
share this article
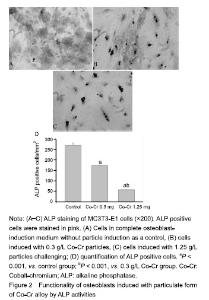
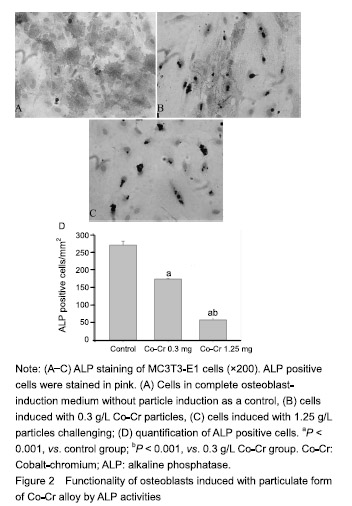
Functionality of osteoblasts induced with Co-Cr particles by ALP activity MC3T3-E1 cells induced with Co-Cr particles exhibited significant negative influence on ALP activity in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.001). Immunohistochemical staining revealed that only sporadic ALP+ cells were identified in particle-challenged pre-osteoblastic cells, significantly fewer than those in the controls (P < 0.001), which complemented the results of ALP activity assay (Figure 2)."
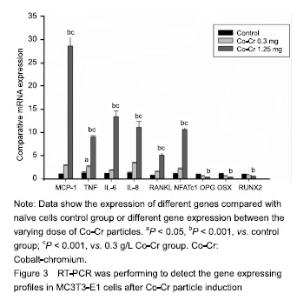
Gene expression profile changes in MC3T3-E1 cells after Co-Cr particle induction Real-time PCR examination suggested that the MC3T3-E1 cells with Co-Cr particle (1.25 g/L), resulted in significant elevation of chemokine MCP-1 expression (P < 0.001), simultaneously, groups with low concentrations of particles also show significant difference compared with naive cell group. Proinflammatory cytokine genes such as tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-6 and IL-8 were significantly up-regulated by Co-Cr particles. Among groups, Co-Cr particles at 1.25 g/L resulted in highest provocation on IL-6 gene expression (Figure 3)."
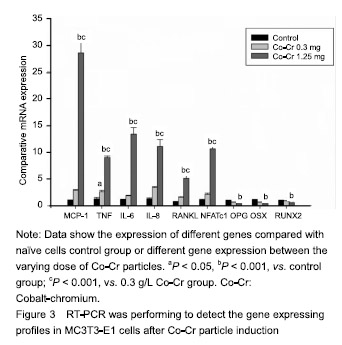
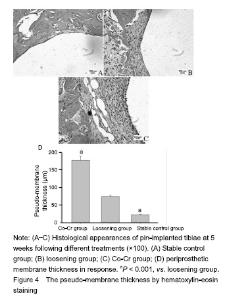
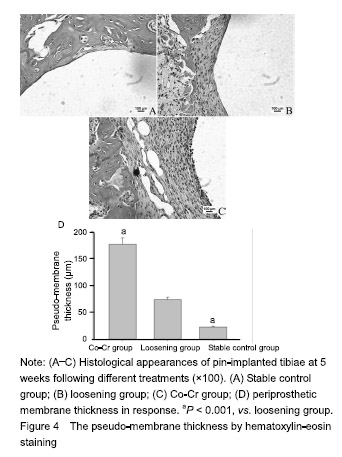
Treatment with higher concentrations of the alloy particles (1.25 g/L) p-regulated RANKL gene expression (Figure 3) and down-regulated OPG gene expression (Figure 3), which resulted in much higher RANKL/OPG ratio than controls. NFATc1 gene expression was stimulated by particles in dose-dependent pattern (P < 0.001). Among groups, the Co-Cr particle 1.25 g/L) provoked the most NFATc1 gene expression (P < 0.001) (Figure 3). Trend of OSX and Runx2 gene expression profiles following particles changes were similar, exhibited low concentration (0.3 g/L) did not show influence on gene expressions of OSX and Runx2, although high dose of particles (1.25 g/L) significantly inhibited OSX and Runx2 gene expression (Figure 3; P < 0.001). Effect of Co-Cr particles on inflammatory membrane thickness in the mouse joint prosthesis Little pseudo-membrance formation was noticed only in the hematoxylin-eosin staining peri-implant sections from the stable controls (Figure 4A). Compared to the loosening group, other two groups have significant difference (P < 0.001). It appeared that there was a significantly thicker soft tissue in the particle induction group than in the loosening group (P < 0.001; Figure 4B-D)."
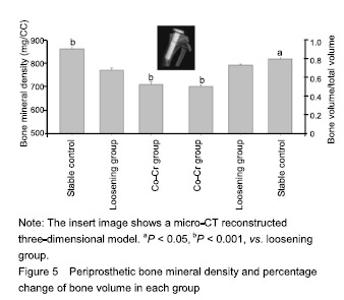
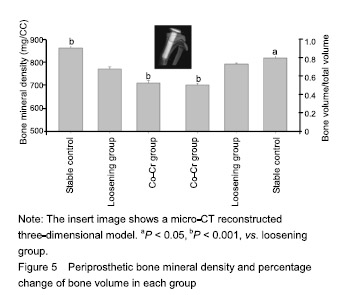
Effect of Co-Cr particles on the BMD in the mouse joint prosthesis The initial micro-CT scan showed that all the metal implants were well placed in position. However, the scans at sacrifice suggested that there were many focal bone resorptions or pit erosions on specimens from Co-Cr particles inducing MC3T3-E1 cell groups compared to the control group. As to the quantification of BMD and BV/TV, the Co-Cr group was significantly different from the other two groups including control group (P < 0.05, P < 0.001). In detail BMD at the peri-implant bone areas among groups indicated a much more severe BMP loss in the challenged-cell transfusion groups, compared to the loosening group (P < 0.001). Meanwhile, the result of BV/TV was similar to the data of BMD (Figure 5)."
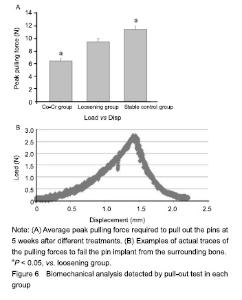
Effect of Co-Cr particles on the implant stability in the mouse joint prosthesis When (9.40 ± 0.49) N was the pick force required on the loosening groups, significantly more force was generally needed to pull out pins in stable control group (11.38± 0.65) N, Cr-Co particle-induced MC3T3-E1 cell transfusion group (6.39±0.52) N (P < 0.05) (Figure 6)."
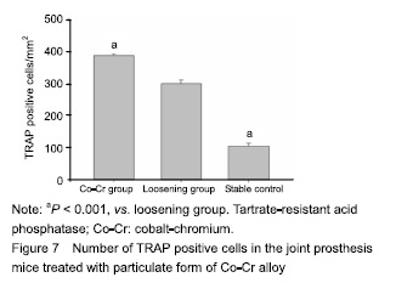
Number of osteoclasts in the mouse joint prosthesis treated with Co-Cr particles TRAP staining was performed to reveal the osteoclasts presence surrounding the pin implantation. The quantity of TRAP+ cells were significant difference in the groups compared to the loosening group (Figure 7; P < 0.01), furthermore Co-Cr groups demonstrated a higher numbers of TRAP+ cells than the loosening group."
| [1]Pajarinen J, Lin TH, Nabeshima A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in the aseptic loosening of total joint replacements. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(4): 1195-1207. [2]Goodman SB, Gibon E, Pajarinen J, et al. Novel biological strategies for treatment of wear particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis of orthopaedic implants for joint replacement. J R Soc Interface. 2014;11(93):20130962. [3]Lombardi AV Jr, Barrack RL, Berend KR, et al. The Hip Society: algorithmic approach to diagnosis and management of metal-on-metal arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(11 Suppl A):14-18. [4]Marti A. Cobalt-base alloys used in bone surgery. Injury. 2000;31 Suppl 4:18-21.[5]Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, et al. Effects of Ti, PMMA, UHMWPE, and Co-Cr wear particles on differentiation and functions of bone marrow stromal cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013;101(10):2817-2825. [6]Kadoya Y, Revell PA, Kobayashi A, et al. Wear particulate species and bone loss in failed total joint arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(340):118-129.[7]Yang SY, Zhang K, Bai L, et al. Polymethylmethacrylate and titanium alloy particles activate peripheral monocytes during periprosthetic inflammation and osteolysis. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(5):781-786.[8]Zhao YP, Wei JL, Tian QY, et al. Progranulin suppresses titanium particle induced inflammatory osteolysis by targeting TNFα signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:20909.[9]An S, Han F, Hu Y, et al. Curcumin Inhibits Polyethylene- Induced Osteolysis via Repressing NF-κB Signaling Pathway Activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(3): 1100-1112. [10]Man K, Jiang LH, Foster R, et al. Immunological Responses to Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Funct Biomater. 2017;8(3):E33. [11]Dyskova T, Gallo J, Kriegova E. The Role of the Chemokine System in Tissue Response to Prosthetic By-products Leading to Periprosthetic Osteolysis and Aseptic Loosening. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1026. [12]Wang Z, Liu N, Liu K, et al. Autophagy mediated CoCrMo particle-induced peri-implant osteolysis by promoting osteoblast apoptosis. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2358-2369. [13]Pajarinen J, Nabeshima A, Lin TH, et al. Murine Model of Progressive Orthopedic Wear Particle-Induced Chronic Inflammation and Osteolysis. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2017;23(12):1003-1011. [14]Terkawi MA, Hamasaki M, Takahashi D, et al. Transcriptional profile of human macrophages stimulated by ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene particulate debris of orthopedic implants uncovers a common gene expression signature of rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:417-425. [15]Ollivere B, Wimhurst JA, Clark IM, et al. Current concepts in osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(1):10-15.[16]Wooley PH, Morren R, Andary J, et al. Inflammatory responses to orthopaedic biomaterials in the murine air pouch. Biomaterials. 2002;23(2):517-526.[17]Zhang K, Jia TH, McQueen D, et al. Circulating blood monocytes traffic to and participate in the periprosthetic tissue inflammation. Inflamm Res. 2009;58(12):837-844. [18]Yang SY, Nasser S, Markel DC, et al. Human periprosthetic tissues implanted in severe combined immunodeficient mice respond to gene transfer of a cytokine inhibitor. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(5):1088-1097.[19]Thomas P, Thomsen M. Allergy diagnostics in implant intolerance. Orthopade. 2008;37(2):131-135. [20]Nakamura-Ota M, Hamanaka R, Yano H, et al. A new murine osteoblastic cell line immortalized with the SV40 large T antigen. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014;15(3):373-380.[21]Bauer TW. Particles and periimplant bone resorption. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(405):138-143.[22]Au A, Ha J, Hernandez M, et al. Nickel and vanadium metal ions induce apoptosis of T-lymphocyte Jurkat cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;79(3):512-521.[23]Cadosch D, Sutanto M, Chan E, et al. Titanium uptake, induction of RANK-L expression, and enhanced proliferation of human T-lymphocytes. J Orthop Res. 2010; 28(3):341-347. [24]Jiang Y, Jia T, Gong W, et al. Titanium particle-challenged osteoblasts promote osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis in a murine model of periprosthestic osteolysis. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(7):7564-7572.[25]Jacobs JJ, Gilbert JL, Urban RM. Corrosion of metal orthopaedic implants. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(2): 268-282.[26]Sunderman FW Jr, Hopfer SM, Swift T, et al. Cobalt, chromium, and nickel concentrations in body fluids of patients with porous-coated knee or hip prostheses. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(3):307-315.[27]Purdue PE, Koulouvaris P, Potter HG, et al. The cellular and molecular biology of periprosthetic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;454:251-261.[28]Hirakawa K, Jacobs JJ, Urban R, et al. Mechanisms of failure of total hip replacements: lessons learned from retrieval studies. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(420):10-17.[29]Tucci M, Tsao A, Hughes J Jr. Analysis of capsular tissue from patients undergoing primary and revision total hip arthroplasty. Biomed Sci Instrum. 1996;32:119-125.[30]Chang YS, Kobayashi M, Li ZL, et al. Significance of peak value and duration of the interfacial shear load in evaluation of the bone-implant interface. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(8):773-779.[31]Goodman S, Ma T, Trindade M, et al. COX-2 selective NSAID decreases bone ingrowth in vivo. J Orthop Res. 2002;20(6):1164-1169.[32]El-Warrak AO, Olmstead M, Schneider R, et al. An experimental animal model of aseptic loosening of hip prostheses in sheep to study early biochemical changes at the interface membrane. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2004;5:7.[33]Warme BA, Epstein NJ, Trindade MC, et al. Proinflammatory mediator expression in a novel murine model of titanium-particle-induced intramedullary inflammation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;71(2):360-366. |
| [1] | Tang Hui, Yao Zhihao, Luo Daowen, Peng Shuanglin, Yang Shuanglin, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. High fat and high sugar diet combined with streptozotocin to establish a rat model of type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1207-1211. |
| [2] | Wang Qiufei, Gu Ye, Peng Yuqin, Xue Feng, Ju Rong, Zhu Feng, Wang Yijun, Geng Dechun, Xu Yaozeng. Effect of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblasts under the action of wear particles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3894-3901. |
| [3] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [4] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [5] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [6] | Liu Zige, Liu Xinrui, Li Yan, Song Guorui, Zhang Chen, Chen Desheng. In vitro experiment of tetrandrine on the model of osteolysis induced by wear particles around the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2358-2363. |
| [7] | Wu Yukun, Han Jie, Wen Shuaibo. Mechanism of Runx2 gene in fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2274-2279. |
| [8] | Jia Wei, Zhang Mandong, Chen Weiyi, Wang Chenyan, Guo Yuan. Effects of femoral prosthetic materials on artificial knee arthroplasty performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1477-1481. |
| [9] | Xu Nuo, Cao Zhen, Li Xiaojie, Shi Chun. MicroRNA-21 regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts in periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1225-1230. |
| [10] | Ge Juncheng, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Sun Wei, Wang Weiguo, Guo Wanshou, Li Zirong. Application of bisphosphonates in avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 753-759. |
| [11] | Zhang Yanan, Yan Xia, Meng Zengdong. Zn and Mg increase the bioactivity and osteogenic induction of hydroxyapatite biomaterial in bone repair: clinical application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 606-611. |
| [12] | Cao Houran, Deng Peng, Ye Pengcheng, Jie Ke, Zeng Jianchun, Feng Wenjun, Chen Jinlun, Qi Xinyu, Li Jie, Tan Xueqiu, Zhang Haitao, Zeng Yirong. Platelet count as a novel potential predictor of periprosthetic joint infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4795-4801. |
| [13] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Mechanism of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulating osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 408-415. |
| [14] | Fan Zhirong, Huang Yongquan, Peng Jiajie, Hong Weiwu, Zhong Degui, Su Haitao, Liu Zitao, Jiang Tao. Outcomes and metal ion levels of Birmingham hip resurfacing versus total hip arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 428-437. |
| [15] | Wu Dalei, Zhou Shouheng, Yan Jianwei, Li Bo, Xu Nuo, Shi Chun, Gao Yang. Alcohol extract of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. promotes bone healing in rats with periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3685-3689. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||