Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (19): 3092-3096.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1256
Previous Articles Next Articles
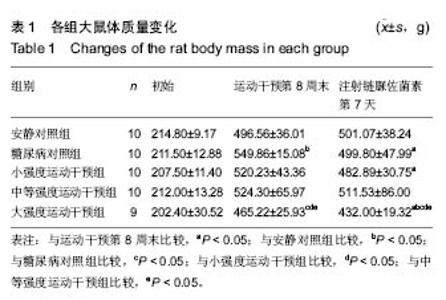
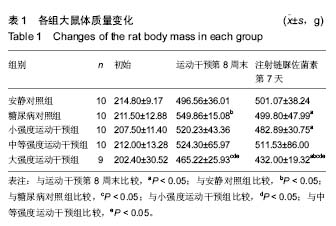
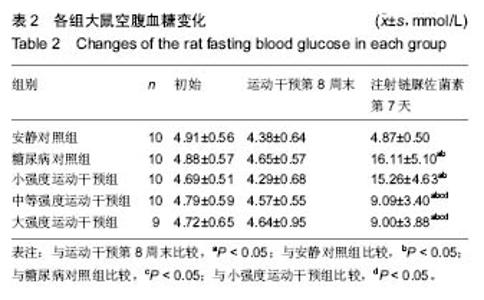
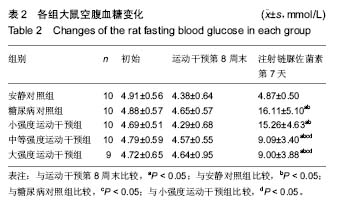
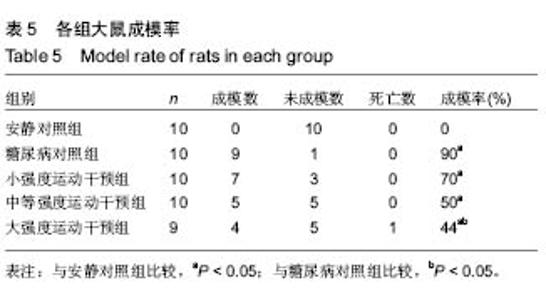
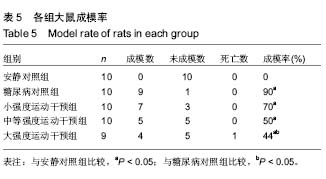
Effect of early different intensities of exercise on the modelling rate and blood glucose level of rats with late-stage type 2 diabetes
Jin Shanhu, Hu Yazhe
- (School of Physical Education, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, Hubei Province, China)