Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (14): 2248-2253.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1652
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and research of iron oxide nanoparticles in bone tissue repair
Shen Mengjie, Yang Kun, Liu Qi
- Department of Periodontology, Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2018-12-17 -
Contact:Liu Qi, MD, Professor, Department of Periodontology, Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Shen Mengjie, Master candidate, Department of Periodontology, Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2017, No. 81760199 (to YK); the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2018, No. 81860196 (to LQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shen Mengjie, Yang Kun, Liu Qi . Application and research of iron oxide nanoparticles in bone tissue repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2248-2253.
share this article
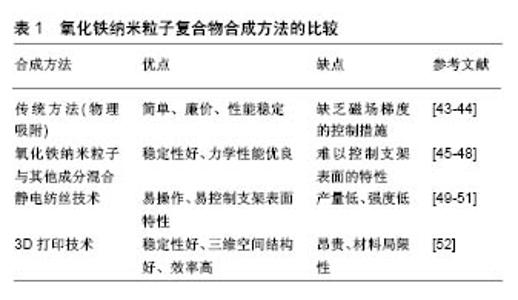
2.1 氧化铁纳米粒子的基本特性 氧化铁纳米粒子具有优良的生物相容性、良好的化学稳定性,而且无内在毒性[3]。通常,纳米材料的毒性取决于其物理化学性质,如粒径、表面性质和化学成分[4],因此在评价纳米颗粒的体内外毒性之前,必须准确地确定其理化特性。到目前为止,许多研究报告低剂量的氧化铁纳米颗粒子对生物体是无毒的[5]。Paik等[6]也证明了氧化铁纳米粒子在体内外具有生物安全性。另外,氧化铁本身是人体内自然存在的一种金属,并且对于外源性氧化铁,机体也能够通过代谢途径处理降解铁离子。然而有研究发现,裸露的氧化铁纳米粒子可能因其表面聚集发生化学反应,具有毒性,所以氧化铁纳米粒子表面常需要涂布有机或无机涂层,这样可减少氧化铁氧化、防止纳米粒子的聚集和团聚、提高生物相容性[7]。目前有机涂层包括柠檬酸盐、葡聚糖、壳聚糖等[8],无机涂层包括二氧化硅、磷酸钙等[9]。氧化铁纳米粒子的性质可随涂层的改变而改变,这些涂层可通过与靶向分子(即配体、抗体)结合进而与特异性受体结合,达到某些治疗目的[10]。另外氧化铁纳米粒子会对外加磁场作出响应,即使没有外加磁场,氧化铁纳米粒子本身也可被认为是一个磁畴,在纳米尺度上提供磁场[11]。氧化铁纳米粒子与外加磁场的相互作用,以及纳米粒子之间的相互作用,会在系统中产生能量变化,这种能量变化将为氧化铁纳米粒子在生物医学中的应用奠定坚实基础[12-13]。氧化铁纳米粒子的磁性质,与纳米颗粒的大小、形貌及结构相关,有学者发现这些因素能够影响氧化铁纳米粒子在生物体内的分布和血液循环时间[14-15]。因此,在构建氧化铁纳米粒子的过程中,应考虑细胞或组织靶向性、细胞摄取速率、功能分子或药物等影响因素。 2.2 氧化铁纳米粒子与干细胞 近年来,干细胞治疗为骨缺损修复提供了一种策略,尤其是在修复大面积骨缺损方面[16-17]。目前,虽然干细胞移植在治疗动物骨缺损模型中取得了成功,但这些传统的干细胞移植并没有达到理想效果。如何保持持久有效的干细胞特性是治疗成功的关键,因此对于体外扩增的细胞,保持稳定的细胞表型,体内移植后减少缺损部位细胞的坏死和丢失,是骨缺损修复所必须的。随着材料学和化工生物学的发展,多年来人们一直尝试应用氧化铁纳米粒子作为研究和控制干细胞的工具[18]。氧化铁纳米粒子通过与外加磁场结合在一起,它将对细胞黏附、增殖、运动和分布及干细胞成骨分化等都产生影响,另外也可用氧化铁纳米粒子标记细胞进行体内追踪和监测[19]。 2.2.1 氧化铁纳米粒子与细胞跟踪 细胞的迁移、分布、存活、分化对干细胞治疗疗效起着至关重要的作 用[20]。了解这些参数可优化细胞选择、给药途径及治疗剂量,为特定的临床应用提供细胞基础治疗。为解决这一问题,研究人员一直在寻找工具,允许实时、定量和长期监测细胞在体内的行为,这种现象称为细胞跟踪。氧化铁纳米粒子作为一种核磁共振对比剂,可用于细胞跟踪[21]。有学者发现,将氧化铁纳米粒子标记的骨髓间充质干细胞植入SD大鼠颅骨缺损中,通过MRI对标记的细胞进行了体内跟踪,结果表明,氧化铁纳米粒子标记不会影响骨髓间充质干细胞的存活和分化能力。同样在绵羊肌腱炎模型中,使用氧化铁纳米粒子标记的间充质干细胞进行治疗,术后7 d,MRI检测发现标记的细胞仍然可被检测到[22]。这些结果与纳米颗粒介导的磁效应有关,这将有利于干细胞技术的深入研究和广泛应用。 2.2.2 氧化铁纳米粒子与干细胞归巢 氧化铁纳米粒子在干细胞治疗中的应用之一,是将干细胞磁性靶向到合适的部位。有学者采用体外磁靶向系统来吸引兔骨髓间充质干细胞,结果发现这项技术显著促进了氧化铁纳米粒子标记的细胞渗透到移植于兔尺骨缺损的多孔羟基磷灰石陶瓷中,并促进骨形成[23]。同样Ito等[24]也报道了一种以Fe3O4纳米粒子为核心的磁铁矿阳离子脂质体(MCLS)和柱状钕磁体进行间充质干细胞扩增,结果发现磁铁矿阳离子脂质体标记的骨髓间充质干细胞经过培养后,密度和数量明显高于常规培养的细胞,这些就表明氧化铁纳米粒子能够吸引干细胞归巢,而且发现氧化铁纳米粒子还能够促进间充质干细胞的体内外成骨分化。Mahmoud等[25]利用磁标记的间充质干细胞,借助外部磁性装置,研究了一种用于修复严重慢性骨缺损的磁性靶向系统,结果发现以2×105个细胞移植就能够完全修复严重的慢性骨缺损。除了通过控制干细胞促进骨再生的策略外,氧化铁纳米粒子本身,特别是在外加磁场的刺激下会诱导干细胞的成骨分化。Wang等[26]制备了聚葡萄糖山梨醇羧甲基醚包覆的氧化铁纳米粒子,并探讨了其对骨髓间充质干细胞的影响,结果表明氧化铁纳米粒子在骨髓间充质干细胞中结构稳定,并促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。基因微阵列分析和生物信息学分析表明,氧化铁纳米粒子可激活经典的丝裂原活化脯氨酸激酶(MAPK)信号通路,其下游基因被调控,以促进成骨分化。此外,氧化铁纳米粒子可上调长链非编码RNA INZEB2,可调控ZB2表达和BMP/Smads途 径[27]。在静态磁场下,Fe3O4/BSA颗粒能显著促进间充质干细胞中碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原及骨钙蛋白在mRNA和蛋白水平的表达[28]。通过纳米粒子与间充质干细胞结合后的磁效应及促进成骨分化的特性,初步说明了氧化铁纳米粒子在骨再生修复中具有很大的潜力。 2.3 磁性给药促进骨生长 抗生素、生长因子及与成骨相关的microRNA和siRNA等药物,可提高骨缺损修复效果[29-30]。然而,这些药物往往不能针对特定部位,不能产生直接的修复作用。近年来,人们一直致力于寻找最佳给药系统,以减少药物的不良反应和毒性,减少药效的丧失,提高治疗效果。研究发现,氧化铁纳米粒子可作为一种运载工具,在外部磁场的作用下可有效携带药物分子,靶向体内的特定部位。将药物分子悬浮在磁性载体上或分散在磁性纳米颗粒上,是一种简单而直接的磁性靶向给药途径。例如有研究采用溶剂蒸发和冻干法制备了可降解的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物辣椒素包被的磁性纳米粒子,此磁性纳米粒子提供了辣椒素的持续释放,在外部磁场作用下,该磁性纳米粒子能够到达特定的位置,提高对特定部位的治疗效果。除了磁靶向外,磁加热也被用于控制热反应药物载体释放治疗药物。Karazisis等[31]使用双膦酸盐与葡聚糖包被氧化铁纳米粒子,得到了双膦酸盐/葡聚糖/Fe3O4纳米粒子,然后使用射频系统对其进行热分解,结果发现其对破骨细胞吞噬有很强的破坏作用。另有学者将磁性多壁碳纳米管、羟基磷灰石和氯膦酸盐制备成纳米复合体,同样发现氯膦酸盐可从系统中不断释放,并抑制破骨细胞的形成[32]。利用氧化铁纳米粒子嵌入到脂质体膜中获得磁脂质体,当外部施加交变磁场时,产生的热量会破坏细胞膜,进而释放脂质体中包裹的药物,达到治疗目的[33]。氧化铁纳米粒子除了促进成骨分化外,还具有良好的骨传导能力[34]。目前在骨再生医学领域,氧化铁纳米粒子复合物常被用作药物控释的载体。有研究在多功能磁性介孔生物活性玻璃中装入庆大霉素,多功能磁性介孔生物活性玻璃中的Fe3O4纳米颗粒改善了庆大霉素的持续释放,有利于减少细菌的黏附,防止生物膜的形成。复合材料中的Fe3O4纳米颗粒除了能治疗感染外,还能促进骨髓间充干细胞的黏附、增殖和成骨分化。纳米材料作为载体在细胞内传递治疗药物,包括蛋白质、生长因子、小分子化学物质和DNA/RNA等,这种磁性药物传递系统,将为骨缺损修复提供一个有用的支撑平台。 2.4 氧化铁纳米粒子复合支架修复骨缺损 组织工程是一种在受损部位重建功能性组织的方法,通常包括种子细胞、生长因子和三维(3D)生物降解支架。组织工程复合体的构建,对促进组织再生或愈合具有重要意义。目前面临的问题是细胞通常停留在材料表面,不能进入支架内。近年来的研究发现,利用磁-机械驱动可将细胞驱动到三维支架的中心。Shimizu等[35]报道了一种利用磁力进行细胞播种的技术,使用一种猪脱细胞颈总动脉支架,然后将猪脱细胞颈总动脉支架浸没在磁性标记细胞的悬浮液中,结果发现几乎所有的细胞都附着在猪脱细胞颈总动脉支架上,并且发现随着对氧化铁纳米粒子的吸收,细胞黏附逐渐增强。另外,也有学者发现涂有壳聚糖的氧化铁纳米粒子可增强人成骨细胞进入3D支架的深度,并且可利用磁力增加细胞间相互作用,缩短细胞增殖周期[36]。这种磁性技术的应用,在促进骨组织修复再生方面具有重要价值,也为研究人员及临床医生提供了重要的理论依据。近年来,基于磁力组织工程的应用,其可构建多层细胞膜片,这将对骨组织修复有很大的推动作用[37]。Shimizu等[38]将磁性标记的人骨髓间充质干细胞接种到低附着培养皿表面,在其背面放置柱状钕磁体,培养24 h后,骨髓间充质干细胞可形成多层片状结构。另外,将骨髓间充质干细胞膜片移植到裸鼠颅骨5 mm缺损中,组织学观察显示,移植14 d后缺损区周围有新骨形成,对照组未发现骨细胞的形成。另外也有学者发现,磁力组织工程不仅能诱导多功能干细胞膜片形成,而且还可促进修复性血管的生成[39]。磁力组织工程的应用,可为骨组织工程提供新的方法。 磁性支架能够通过磁性驱动吸引体内的生长因子、干细胞迁移,或者通过磁性氧化铁纳米粒子结合其他生物制剂,进而促进骨修复和再生。目前,磁性支架促进细胞增殖和新生骨组织生长的作用已被证实[40]。该支架具有广泛的组成成分,主要包括生物大分子、合成聚合物、聚乙二醇、无机材料等[41]。Russo等[42]将超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子加入到羟基磷灰石中,制备成了磁性羟基磷灰石支架,结果发现其能显著改善骨细胞的黏附和增殖,促进骨组织再生。关于氧化铁纳米粒子复合支架的合成有很多种方法,现对于不同技术合成的氧化铁纳米粒子复合支架总结于表1。另外有学者发现在静磁场作用下,磁性复合支架材料对MC3T3-E1细胞的增殖、分化及细胞外基质分泌具有明显的促进作用[44],此外在体内也有很好的修复作用[48]。同样Singh等[50]制备了氧化铁纳米粒子与聚己内酯磁性纳米复合支架,结果发现与单纯聚己内酯支架相比,磁性纳米复合支架的细胞黏附、穿透纳米纤维的能力、碱性磷酸酶活性及成骨相关基因(Ⅰ型胶原、骨桥蛋白和骨唾液蛋白)表达明显提高。此外,氧化铁纳米粒子纳米纤维支架能促进桡骨节段缺损的骨再生。"

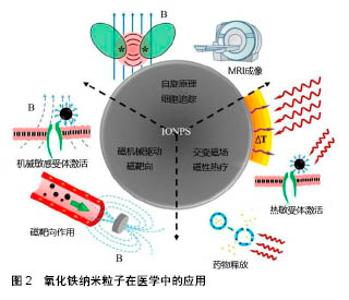
关于氧化铁纳米粒子在体内外增强成骨作用的潜在机制还在探索中。Zhu等[53]在体内实验中发现与单纯的羟基磷灰石支架相比,磁性羟基磷灰石支架上的钙离子、G蛋白偶联受体和MAPK/ERK级联蛋白相关蛋白浓度升高,并且发现磁性羟基磷灰石支架上富集的功能蛋白可有效激活MAPK/ERK信号通路,导致MC3T3-E1细胞增殖增加,加快成骨分化。Yun等[54]也研究了磁性聚己内酯/Fe3O4纳米粒子复合支架对成骨功能和骨形成的联合作用,发现静态磁场与磁性支架可促进小鼠颅骨成骨细胞的成骨分化,增强骨相关基因(Runx2和Osterix)表达和碱性磷酸酶活性。虽然越来越多的实验数据证实,氧化铁纳米粒子对骨细胞的存活和分化作用明显,特别是在外部磁场作用下,但氧化铁纳米粒子与复合支架、磁性支架,磁场及磁性支架和磁场与骨细胞之间的相互作用,还需要进一步的研究。氧化铁纳米粒子在医学中的应用,见图2[55]。"
| [1] Ferreira RV,Silva-Caldeira PP,Pereira-Maia EC,et al. Bio-inactivation of human malignant cells through highly responsive diluted colloidal suspension of functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res. 2016; 18(4):92.[2] Özbey A,Karimzadehkhouei M,Yalç?n SE,et al.Modeling of ferrofluid magnetic actuation with dynamic magnetic fields in small channels.Microfluid Nanofluid.2015;18(3):447-460.[3] Salehiabar M,Nosrati H,Davaran S,et al.Facile Synthesis and Characterization of L-Aspartic Acid Coated Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles (IONPs) For Biomedical Applications. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2018;68(5):280-285.[4] Huang YW,Cambre M,Lee HJ.The Toxicity of Nanoparticles Depends on Multiple Molecular and Physicochemical Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci.2017;18(12):2702.[5] Pariti A,Desai P,Maddirala SKY,et al.Superparamagnetic Au-Fe3O4 nanoparticles: one-pot synthesis, biofunctionalization and toxicity evaluation.Mater Res Exp. 2014;1(3):035023.[6] Paik SYR,Kim JS,Shin SJ,et al.Characterization, Quantification, and Determination of the Toxicity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles to the Bone Marrow Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2015; 16(9): 22243-22257.[7] Setyawan H,Fajaroh F,Pusfitasari MD,et al.A facile method to prepare high‐purity magnetite nanoparticles by electrooxidation of iron in water using a pulsed direct current. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng.2015;9(5):768-774.[8] Iyer SR,Xu S,Stains JP,et al.Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Musculoskeletal Biology.Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2017;23(4):4578-4578.[9] Manchón A,Alkhraisat MH,Rueda-Rodriguez C,et al.A new iron calcium phosphate material to improve the osteoconductive properties of a biodegradable ceramic: a study in rabbit calvaria.Biomed Maters.2015;10(5):055012.[10] Polo E,Collado M,Pelaz B,et al.Advances toward More Efficient Targeted Delivery of Nanoparticles in Vivo: Understanding Interactions between Nanoparticles and Cells. Acs Nano.2017; 11(3):2397-2402.[11] Guo X,Li W,Luo L,et al.External Magnetic Field Enhanced Chemo-Photothermal Combination Tumor Therapy via Iron Oxide Nanoparticles.Acs Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(19): 16581-16593.[12] Soika AK,Sologub IO,Shepelevich VG,et al.Magnetoplastic effect in metals in strong pulsed magnetic fields.Phys Solid State.2015;57(10):1997-1999.[13] Milyaev VA,Binhi VN.On the physical nature of magnetobiological effects.Quantum Electron. 2006;36(8): 691-701.[14] Veiseh O,Gunn J,Zhang M.Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2010;62(3):284-304.[15] Corot C,Robert P,Idée JM,et al.Recent advances in iron oxide nanocrystal technology for medical imaging.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2007;58(14):1471-1504.[16] Sniadecki NJ.A tiny touch: activation of cell signaling pathways with magnetic nanoparticles. Endocrinology. 2010; 151(2):451.[17] Watanabe Y,Harada N,Sato K,et al.Stem cell therapy: is there a future for reconstruction of large bone defects? Injury. 2016; 47:S47-S51.[18] Michael B,Arthur T,Patricia M,et al.Design considerations for the synthesis of polymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles for stem cell labelling and tracking using MRI.Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(19):6733-6748.[19] Meng J,Zhang Y,Qi X,et al.Paramagnetic nanofibrous composite films enhance the osteogenic responses of pre-osteoblast cells.Nanoscale.2010;2(12):2565-2569.[20] Silva AH, Lima E Jr,Mansilla MV,et al.Superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles mPEG350– and mPEG2000-coated: cell uptake and biocompatibility evaluation. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(4):909-919.[21] Hua P,Wang Y,Liu L,et al.In vivo magnetic resonance imaging tracking of transplanted superparamagnetic iron oxide-labeled bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction.Mol Med Rep.2015;11(1):113-120.[22] Scharf A,Holmes S,Thoresen M,et al.Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as a means to track mesenchymal stem cells in a large animal model of tendon injury. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2015;10(5):388-397.[23] Chen Y,Bose A,Bothun GD.Controlled release from bilayer-decorated magnetoliposomes via electromagnetic heating.Acs Nano.2010;4(6):3215-3221.[24] Ito A,Hibino E,Honda H,et al.A new methodology of mesenchymal stem cell expansion using magnetic nanoparticles.Biochem Eng J.2004;19(2):119-125.[25] Mahmoud EE,Kamei G,Harada Y,et al.Cell magnetic targeting system for repair of severe chronic osteochondral defect in a rabbit model. Cell Transplant.2016;25(6):1073-1083.[26] Wang Q,Chen B,Cao M,et al.Response of MAPK pathway to iron oxide nanoparticles in vitro treatment promotes osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs. Biomaterials. 2016;86:11-20.[27] Wang L,Wu S.The National Center for Nanoscience and Technology,China(NCNST):an international innovation engine for nano research.Nati Sci Rev.2017;(3):500-509.[28] Jiang P,Zhang Y,Zhu C,et al.Fe3O4/BSA particles induce osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells under static magnetic field.Acta Biomaterialia.2016;46:141-150.[29] Canadian Paediatric Society,Infectious Diseases and Immunization Committee.The use of antibiotic therapy as an adjunct in treatment of bone and joint infections. Can J Infect Dis.1994;5(1):10.[30] Shi CH,Wang WS,Chang-Jun LI,et al.Construction of uPA-siRNA lentiviral vector and its promotion on proliferation of rabbit chondrocytes.Basic Clin Med.2014;7(8):678-698.[31] Karazisis D,Ballo AM,Petronis S,et al.The90 role of well-defined nanotopography of titanium implants on osseointegration: cellular and molecular events in vivo.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:1367-1382.[32] Afroze JD,Abden MJ,Islam MA.An efficient method to prepare magnetic hydroxyapatite–functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite for bone defects.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2018;86:95-102.[33] Liu Y,Yin JJ,Nie ZH.Harnessing the collective properties of nanoparticle ensembles for cancer theranostics.Nano Res. 2014;7(12):1719-1730.[34] Prodan AM,Iconaru SL,Ciobanu CS,et al.Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles: Characterization and Toxicity Evaluation by In Vitro and In Vivo Assays.J Nanomater.2013;2013(47):5.[35] Shimizu K,Ito A,Arinobe M,et al.Effective cell-seeding technique using magnetite nanoparticles and magnetic force onto decellularized blood vessels for vascular tissue engineering. J Biosci Bioeng. 2007;103(5):472-478.[36] Sasaki T,Iwasaki N,Kohno K,et al.Magnetic nanoparticles for improving cell invasion in tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;86(4):969-978.[37] Gonçalves AI,Rodrigues MT,Gomes ME.Tissue-Engineered Magnetic Cell Sheet Patches For Advanced Strategies in Tendon Regeneration.Acta Biomater.2017;63(8):456-467.[38] Shimizu K,Ito A,Yoshida T,et al.Bone tissue engineering with human mesenchymal stem cell sheets constructed using magnetite nanoparticles and magnetic force.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010,82B(2):471-480.[39] Kito T,Shibata R,Ishii M,et al.iPS cell sheets created by a novel magnetite tissue engineering method for reparative angiogenesis.Sci Rep.2013;3(3):1418.[40] Xia Y,Chen H,Zhang F,et al.Injectable calcium phosphate scaffold with iron oxide nanoparticles to enhance osteogenesis via dental pulp stem cells. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.2018:1-11.[41] Bramhill J,Ross S,Ross G.Bioactive Nanocomposites for Tissue Repair and Regeneration: A Review. Int J Environ Res Public Health.2017;14(1):66.[42] Russo A,Bianchi M,Sartori M,et al.Bone regeneration in a rabbit critical femoral defect by means of magnetic hydroxyapatite macroporous scaffolds.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2018;106(2):546-554.[43] Bock N,Riminucci A,Dionigi C,et al.A novel route in bone tissue engineering: Magnetic biomimetic scaffolds.Acta Biomater.2010;6(3):786-796.[44] Usov NA, GudoshnikovO SA,Serebryakova N,et al.Properties of Dense Assemblies of Magnetic Nanoparticles Promising for Application in Biomedicine.J Supercond Nov Magn. 2013; 26(4):1079-1083.[45] Akaraonye E,Filip J,Safarikova M,et al.Composite scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering based on natural polymers of bacterial origin, thermoplastic poly(3‐hydroxybutyrate) and micro‐fibrillated bacterial cellulose.Polym Int. 2016;65(7): 780-791.[46] Bhowmick A,Jana P,Pramanik N,et al.Multifunctional zirconium oxide doped chitosan based hybrid nanocomposites as bone tissue engineering materials. Carbohydr Polym.2016;151:879-588.[47] Aliramaji S,Zamanian A,Mozafari M.Super-paramagnetic responsive silk fibroin/chitosan/magnetite scaffolds with tunable pore structures for bone tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;70(Pt 1):736-744.[48] Huang JH,Xiong JY,Wang DP,et al.Performance of magnetic nanocomposite artificial bone scaffolds prepared by low-temperature rapid prototyping 3D printing.Hainan Med J. 2017;6(7):678-687.[49] Meng J,Xiao B,Zhang Y,et al.Super-paramagnetic responsive nanofibrous scaffolds under static magnetic field enhance osteogenesis for bone repair in vivo.Sci Rep. 2013; 3(6151): 2655.[50] Singh RK,Patel KD,Lee JH,et al.Potential of magnetic nanofiber scaffolds with mechanical and biological properties applicable for bone regeneration.Plos One.2014;9(4):e91584.[51] Li Y,Chen H,Wu J,et al.Preparation and characterization of APTES modified magnetic MMT capable of using as anisotropic nanoparticles.Appl Surf Sci.2018.9(7):112-117.[52] Zhao S,Zhu M,Zhang J,et al.Three dimensionally printed mesoporous bioactive glass and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) composite scaffolds for bone regeneration.J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(36): 6106-6118.[53] Zhu Y,Yang Q,Yang M,et al.Protein Corona of Magnetic Hydroxyapatite Scaffold Improves Cell Proliferation via Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway.Acs Nano.2017;11(4):3690.[54] Yun HM,Ahn SJ,Park KR,et al.Magnetic nanocomposite scaffolds combined with static magnetic field in the stimulation of osteoblastic differentiation and bone formation. Biomaterials. 2016;85:88-98.[55] Li Y,Ye D,Li M,et al.Adaptive Materials Based on Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Bone Regeneration. Chemphyschem. 2018; 19(16):1965-1979. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [5] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [6] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [7] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [8] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [9] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [11] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [12] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [13] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [14] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [15] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||