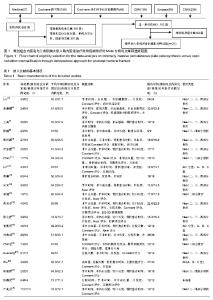
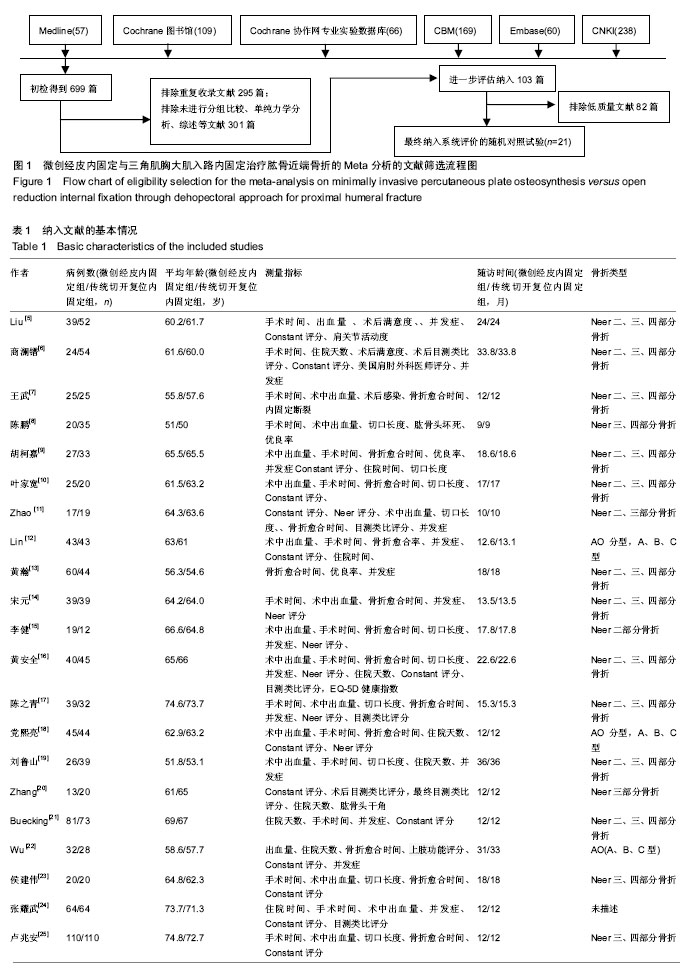
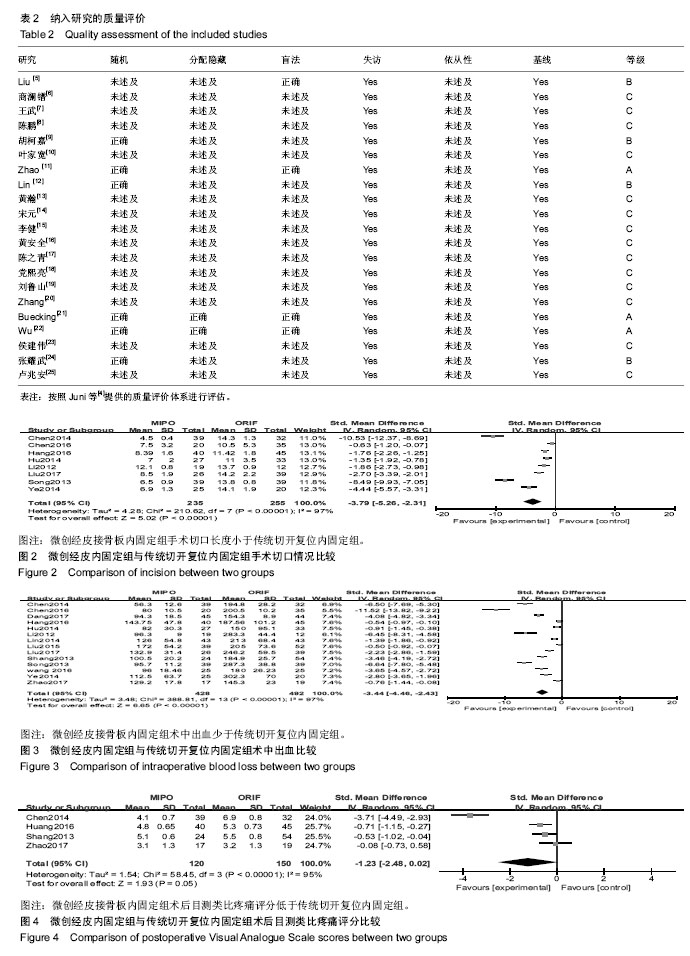
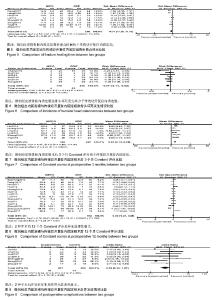
| [1] 吴望晟,刘剑,朱显科,等. 肱骨近端骨折的治疗现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(12):117-1120.[2] 黄沛彦,董有海,顾军,等. 经皮微创钢板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折的解剖学研究及初步临床报告[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(8):710-714. [3] Jaberg H,Warner JJ,Jakob RP. Percutaneous stabilization of unstable fractures of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg. 1992;74(4): 508-515. [4] Juni P, Altman DG, Egger M. Assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. BMJ. 2001;323(7303):42-46. [5] Liu K, Liu PC,Liu R,et al. Advantage of minimally invasive lateral approach relative to conventional deltopectoral approach for treatment of proximal humerus fractures. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21: 496-504.[6] 商澜镨,周方,姬洪全,等. 微创锁定接骨板与传统切开复位内固定术治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2013,45(5):711-716. [7] 王武,齐保军,崔泳. 经皮微创锁定钢板与切开复位锁定加压钢板治疗肱骨外科颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志,2016,32(11):991-994. [8] 陈鹏,田晓滨. 切开复位内固定与微创经皮钢板接骨术治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(7):592-596. [9] 胡柯嘉,孙振中,芮永军,等. 三角肌劈开入路微创治疗肱骨近端骨折的临床研究[J].中华手外科杂志, 2014,30(6):434-438. [10] 叶家宽,叶福生,钟亮,等. 胸大肌三角肌入路和肩关节前外侧劈开三角肌入路治疗肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014,16(10): 862-866. [11] Zhao L,Yang P,Zhu L,et al. Minimal invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) through deltoid-pectoralis approach for the treatment of elderly proximal humeral fractures. Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2017;18:187. [12] Lin T, Xiao BJ, Ma XC, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis with a locking compression plate is superior to open reduction and internal fixation in the management of the proximal humerus fractures. Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2014; 15:206. [13] 黄瀚,廖前德,王成功. 经皮改良三角肌联合肱肌分离入路锁定钢板治疗肱骨近端骨折60例临床分析[J]. 医学综述, 2014,20(22):4212-4213. [14] 宋元. 两种手术方法治疗老年人肱骨近端骨折的比较研究[J]. 中国医药导刊,2013,15(4):597-598. [15] 李健,王瑞,孔小川,等. 三种手术方法治疗老年人肱骨近端二部分骨折的比较研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012,14(4):283-287. [16] 黄安全,沈军,缪烨,等. 微创技术与传统入路锁定钢板内固定治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(11): 1147-1150. [17] 陈之青,谢金兔,李坚. 微创切口与传统大切口结合锁定钢板内固定治疗老年人肱骨近端骨折疗效比较[J].中国医师杂志,2014,16(3):386-388. [18] 党熙亮,李浩鹏,张建,等. 微创锁定接骨板与传统切开复位内固定术治疗肱骨近端骨折的临床疗效比较[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2017,17(27):5369-5371. [19] 刘鲁山,于国平,方俊英,等.微创锁定接骨板与传统切开复位内固定术治疗肱骨近端骨折的临床疗效研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2017,46(27):3804-3807. [20] Zhang Z, Zhang GZ, Peng Y, et al. Modified minimally invasive approach and intra-osseous portal for three-part proximal humeral fractures: a comparative study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018; 13:1-8. [21] Buecking B, Mohr J, Bockmann B, et al. Deltoid-split or deltopectoral approaches for the treatment of displaced proximal humeral fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1576-1585. [22] Wu CH, Ma CH, Yeh JJ, et al. Locked plating for proximal humeral fractures: differences between the deltopectoral and deltoid-splitting approaches. J Trauma. 2011;71(5):1364-1370. [23] 侯建伟,谢仁国,王晓东,等.改良肩关节外侧入路和三角肌胸大肌入路治疗老年肱骨近端骨折的疗效分析[J].中华手外科杂志,2017,33(5):330-333. [24] 张耀武,洪汉刚,陈平波,等. 经三角肌与经三角肌胸大肌间隙入路结合钢板治疗老年移位肱骨近端骨折的疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(1): 160-162. [25] 卢兆安,周建国,韩枫,等. 不同手术方式治疗老年 Neer Ⅲ、Ⅳ型骨折的临床效果分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(10):951-954. [26] 黄强,王满宜,荣国威.复杂肱骨近端骨折的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志, 2005,25(3):159-164.[27] Robinson CM , Khan L , Akhtar A , et al . The extended deltoid-splitting approach to the proximal humerus. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(9): 657-662.[28] Gardner MJ,Griffith MH,Dines JS,et al. The extended anterolateral acromial approach allows minimally invasive access to the proximal humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;(434):123-129.[29] 孙万驹,王予彬,蔡俊丰,等. 肩外侧小切口内固定治疗近端肱骨骨折的解剖学研究[J]. 同济大学学报(医学版),2012, 33(1):19-23. [30] 黄沛彦,董有海,顾军,等. 经皮微创钢板内固定治疗肱骨近端骨折的解剖学研究及初步临床报告[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(8):710-714. [31] 许文胜,周君琳,刘清和,等.经肩峰外侧小切口治疗肱骨近端骨折的相关解剖学研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2011,33(6):648-650. [32] 杨雷,李彬,潘孝云,等. 经皮闭合复位微创固定治疗高龄患者肱骨近端骨质疏松性骨折[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(12):830-832. [33] Gardner MJ,Voos JE,Wanich T,et al. Vascular implications of minimally invasive plating of proximal humerus fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006; 20(9):602-607. [34] 曾浪清,唐三元. 肱骨近端骨折的流行病解剖分型及影像学研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(18):1670-1674. [35] 朱乃锋,张睿,陈云丰,等.肱骨近端骨折手术安全区的解剖学研究和临床意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2011,29(2):168-170. [36] Lungershausen W,Bach O,Lorenz CO. Locking plate osteosynthesis for fractures of the proximal humerus. Zentralblatt Fur Chirurgie. 2003;128(1):28-33. |