Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (13): 2101-2106.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1654
Previous Articles Next Articles
Eph/ephrin signaling pathway and neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation
Liu Zheng1, 2, Shao Ziwei1, Yuan Wenhua1, 2, Shen Wei1, 2, Feng Xiaofei1, 2, Zhou Haiyu1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Bone and Joint Diseases of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China
-
Revised:2018-12-22Online:2019-05-08Published:2019-05-08 -
Contact:Zhou Haiyu, MD, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Liu Zheng, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China; Key Laboratory of Bone and Joint Diseases of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730030, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, No. 17JR5RA189 (to ZHY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Zheng, Shao Ziwei, Yuan Wenhua, Shen Wei, Feng Xiaofei, Zhou Haiyu. Eph/ephrin signaling pathway and neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2101-2106.
share this article
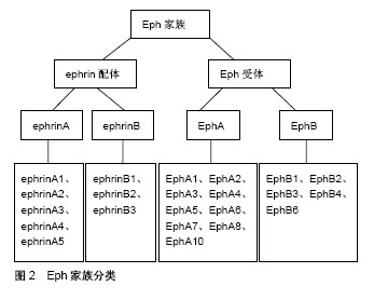
2.1 神经干细胞 Panov[1]在1989年参照造血系统干细胞的性质提出了神经干细胞的概念,它是一类多能干细胞,能够长期自我更新,并具有分化形成神经元、星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞的多潜能特性。在1992年Reynodls等[2]自成年动物脑纹状体内分离出了一种能在体外不断增殖且具有多种分化潜能的细胞群,并正式提出了神经干细胞的概念。从20世纪90年代后,国内外兴起了神经干细胞的研究热潮。现已证明,神经干细胞不仅存在于胚胎神经系统,也存在于成年脑的某些部位[3-4]。许多脑部疾病,包括脑卒中和创伤性脑损伤,可以激活各种旨在修复神经元损伤的防御机制[5]。调节神经干细胞增殖、分化和神经胶质细胞谱系选择的机制对于神经元修复是非常重要的[6]。大量研究表明,神经干细胞在一定条件能增殖和分化为神经元和神经胶质细胞。尽管有大量关于神经干细胞治疗的研究,但是特异性参与神经干细胞行为的靶基因报道较少。因此,迫切需要研究调节神经干细胞增殖和分化的分子机制。 2.2 Eph/ephrin信号通路 2.2.1 Eph受体与ephrin配体 Eph受体及其ephrin配体统称为Eph家族蛋白[7],见图2。Eph受体作为最大的酪氨酸激酶受体家族,与ephrin配体结合产生双向信号在胚胎发育、血管生成、细胞迁移和神经信号传导等多种生理过程中起着关键作用。Eph和ephrin是膜结合蛋白,它们必须是膜结合型或者人为地通过抗体成簇后才具有活性,因此它们之间的信号传导依赖于细胞间接触[8]。Ephrin不仅是Eph的配体,它还具有受体样功能,即在以ephrin为配体向Eph表达细胞胞内转导信号(正向信号)的同时,ephrin也反向对自身细胞胞内信号转导(反向信号)。Eph约由16个基因组成,根据Eph受体家族的序列同源性、结构、表达、分布及与配体亲和力的不同而将其分为EphA受体和EphB受体亚家族,哺乳动物体内含有两大类14种Eph受体:EphA1-A8和A10,以及EphB1-B4和B6[9-10]。Ephrin配体也分为两类:ephrinA和ephrinB,即ephrinA1-A5和ephrinB1-B3。EphrinA配体通常与EphA受体结合,ephrinB配体通常与EphB受体结合;此外,也存在一些特殊情况,例如EphA4能结合所有的ephrinA及ephrinB配体,EphB2能和ephrinA5结合,EphB4只能结合ephrinB2[11]。"


Eph受体属于跨膜蛋白,具有胞外区、跨膜结构域和胞内区。胞外区有配体结合域、1个富含半胱氨酸的结构和2个纤维连接蛋白重复序列;胞内区有2个酪氨酸残基的近膜区、经典蛋白酪氨酸激酶结构域、不育α基序(SAM)结构域以及盘状同源区域(PDZ)结合模序。这些结构域和区域有助于理解蛋白质的3D拓扑结构并促进其与细胞信号传导网络内的其他蛋白质的相互作用。活化的Eph受体中的磷酸化氨基酸残基介导这些相互作用。然而,由于激酶结构域内保守区序列的改变,EphA10和EphB6缺乏激酶活性[12]。 Ephrin配体含有1个保守的胞外受体结合域,结合相应的Eph受体。EphrinA通过糖基-磷脂酰肌醇(glycosyl phosphatidylinositol,GPI)接头锚定在质膜的细胞外侧,而ephrinB具有细胞浆域部分[6],可与细胞浆分子发生作用[13]。9种EphA受体优先结合5种GPI锚定的ephrinA配体(ephrinA1-A5)。此外,5种EphB受体与3种跨膜ephrinB配体(ephrinB1-B3)具有高亲和力结合结构域。Ephrin配体的Eph结合结构域通过可变长度的连接区段附着于质膜。两类配体的特征在于ephrinA配体中存在GPI锚,ephrinB配体中存在跨膜片段[14]。 2.2.2 Eph/ephrin信号通路及其作用 Eph受体细胞外区域中的几个结构域可以与ephrin配体结合,氨基末端“ephrin结合”结构域含有高亲和力结合位点,其介导细胞之间的Eph受体-ephrin配体相互作用[15]。Eph/ephrin信号传导的一个显著特征是它能够触发Eph受体下游的前向信号传导和ephrin配体下游的反向信号传导,即经典的经Eph受体酪氨酸激酶途径和反向的Eph作为配体经ephrin进行信号转导途径[16-17]。通过Eph/ ephrin相互作用控制细胞迁移涉及蛋白质磷酸化级联的复杂网络,以及其他细胞内途径,其调节肌动蛋白细胞骨架的组装和/或细胞黏附的强度。Eph受体和ephrin信号传导可能具有相反的作用,例如促进或限制细胞迁移,与EphB/ephrinB激活相比,EphA/ephrinA可能不同[18]。Eph“前向”信号依赖于ephrin结合,其诱导Eph受体聚集、自身磷酸化和激酶活性。在与Eph受体相互作用后,ephrin“反向”信号传导也被激活。Bruckner等[19]研究发现Eph受体的下游基因和ephrin配体的下游基因均参与双向信号调节。在同一细胞中共表达的Eph受体和ephrin配体之间的侧向“顺式”相互作用可以减弱由“反式”相互作用诱导的细胞接触依赖性信号[20]。Eph受体及其ephrin配体是与发育过程中细胞迁移和轴突导向相关的指导分子[21-22]。在细胞质结合域Eph受体特定的酪氨酸残基被磷酸化后与相应的配体结合。磷酸化后基序的作用就是为细胞质信号蛋白提供相互作用的位点。随着受体与配体相结合,跨膜ephrin配体的酪氨酸残基上发生磷酸化[19]。 Eph受体和ephrin配体的组织结构需要在相同或不同类型的两个相互作用细胞的表面上存在。因此,物理接触对于在不同细胞类型中启动正向和/或反向信号传导是必需的。这些受体-配体对接触介导的生理功能已被广泛记载用于多个方面。Eph/ephrin信号通路具有多种生物学作用。虽然他们在神经系统之外的最佳研究角色是在血管系统发育期间的作用,但相关研究也揭示了Eph受体和ephrin配体在免疫系统、骨骼、干细胞、上皮细胞以及肿瘤发展和转移中的重要性。Eph受体和ephrin配体在发育中的神经系统中高度表达,它们在调节细胞群的空间组织、组织模式、轴突导向和突触连接的形成中具有重要作用[23-24]。神经系统中的轴突长距离延伸到达目标,这个过程由Eph受体和ephrin配体促进。EphrinA与TrkB和p75神经营养因子受体的相互作用通过反向信号传导导致轴突延伸。EphrinB募集细胞骨架调节因子用于轴突导向、树突形态发生和突触后成熟[25]。成熟神经元从生发区迁移,启动导致形态复杂性的细胞程序,特别是细胞突起的延伸,最终形成成熟神经元的轴突和树突。适当的形态学分化是神经元连接的先决条件。这一过程的基础是诱导一系列细胞骨架成分,这些成分支撑复杂的细胞结构和信号机制,介导神经元的反应性和可塑性[26]。相关研究已经证实Eph/ephrin信号在神经发生轴突导向中起核心作用。Eph/ephrin信号通路还与神经病理学相关,包括创伤性损伤和脑卒中后神经修复的抑制等。Eph/ephrin信号通路对于心血管发育也至关重要,例如由Eph受体或ephrin配体敲除引起的心脏和血管缺陷[27-28]。EphB4和ephrinB2因其在背主动脉和主要静脉中的作用而闻名。EphrinB2标记动脉内皮细胞,而EphB4标记静脉内皮细胞。动脉中的ephrinB2与静脉中的Eph受体的相互作用表明它们在定义静脉和动脉边界中的作用[29]。淋巴管系统是由有盲端的毛细淋巴管和集合淋巴管组成[30],初始淋巴管需要经过重塑和成熟变成功能性淋巴管网络系统,其中许多重要的蛋白参与该过程,包括EphB4和ephrinB2。此外,Eph/ephrin也参与炎症过程。受损或发炎的血管愈合通过血小板栓塞形成和外渗血液凝固而发生。该过程涉及信号传导途径,其促进炎性细胞的募集和成纤维细胞、上皮细胞的增殖。Eph/ephrin蛋白作为血管生成的调节因子参与组织愈合和细胞迁移[31]。相关研究也发现,Eph受体和ephrin在肿瘤中异常表达,并且可以通过双向信号传导和与其他信号系统相互作用而显著影响恶性肿瘤[32]。Eph受体/ephrin配体的过表达和各种肿瘤中Eph/ephrin分子的下调表明这些蛋白质具有促进生长和抑制生长的活性。这些不同的信号传导方式对癌细胞的多种影响,也取决于细胞环境。此外,Eph受体和ephrin是肿瘤微环境及其与癌细胞通讯的关键调节因子。某些Eph受体和ephrin在病毒感染中也参与了抗病毒治疗的新途径。最具特色的作用是将ephrinB2和ephrinB3作为henipaviruses的入门受体,henipaviruses是一种新兴的人畜共患致病病毒[33]。Eph/ephrin在多个系统中的作用,见表1。"

| [1] Panov AA. The histology of the cerebral neurosecretory system in several representatives of Cleroidea (Coleoptera, Insecta). J Hirnforsch. 1989;30(1):5-10.[2] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1992;255(5052):1707-1710.[3] Doetsch F, Caillé I, Lim DA, et al. Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell. 1999;97(6):703-716.[4] Tropepe V, Coles BL, Chiasson BJ, et al. Retinal stem cells in the adult mammalian eye. Science. 2000;287(5460): 2032-2036.[5] Reekmans K, Praet J, Daans J, et al. Current challenges for the advancement of neural stem cell biology and transplantation research. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(1):262-278.[6] Cheng W, Yu P, Wang L, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling mediates resveratrol to increase proliferation of neural stem cells after oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation injury in vitro. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;35(5):2019-2032.[7] Luo H, Yu G, Wu Y, et al. EphB6 crosslinking results in costimulation of T cells. J Clin Invest. 2002;110(8):1141-1150.[8] Oricchio E, Nanjangud G, Wolfe AL, et al. The Eph-receptor A7 is a soluble tumor suppressor for follicular lymphoma. Cell. 2011;147(3):554-564.[9] Lai KO, Ip NY. Synapse development and plasticity: roles of ephrin/Eph receptor signaling. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2009; 19(3):275-283.[10] Bolsover S, Fabes J, Anderson PN. Axonal guidance molecules and the failure of axonal regeneration in the adult mammalian spinal cord. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2008; 26(2-3):117-130.[11] Murai KK, Pasquale EB. Eph receptors and ephrins in neuron-astrocyte communication at synapses. Glia. 2011; 59(11):1567-1578.[12] Mendrola JM, Shi F, Park JH, et al. Receptor tyrosine kinases with intracellular pseudokinase domains. Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(4):1029-1036.[13] 余剑,曾进圣. Eph/ephrin与中枢神经可塑性[J]. 中国临床康复, 2002, 6(21):3198-3199.[14] Pasquale EB. Eph receptor signalling casts a wide net on cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(6):462-475.[15] Himanen JP, Saha N, Nikolov DB. Cell-cell signaling via Eph receptors and ephrins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19(5): 534-542.[16] Aoto J, Chen L. Bidirectional ephrin/Eph signaling in synaptic functions. Brain Res. 2007;1184:72-80.[17] Klein R. Bidirectional modulation of synaptic functions by Eph/ephrin signaling. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12(1):15-20.[18] Triplett JW, Feldheim DA. Eph and ephrin signaling in the formation of topographic maps. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012; 23(1):7-15. [19] Brückner K, Pasquale EB, Klein R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of transmembrane ligands for Eph receptors. Science. 1997; 275(5306):1640-1643.[20] Falivelli G, Lisabeth EM, Rubio de la Torre E, et al. Attenuation of eph receptor kinase activation in cancer cells by coexpressed ephrin ligands. PLoS One. 2013;8(11): e81445.[21] Krull CE, Lansford R, Gale NW, et al. Interactions of Eph-related receptors and ligands confer rostrocaudal pattern to trunk neural crest migration. Curr Biol. 1997;7(8):571-580.[22] Eberhart J, Swartz M, Koblar SA, et al. Expression of EphA4, ephrin-A2 and ephrin-A5 during axon outgrowth to the hindlimb indicates potential roles in pathfinding. Dev Neurosci. 2000;22(3):237-250.[23] Pasquale EB. Eph receptor signalling casts a wide net on cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(6):462-475.[24] Pasquale EB. Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell. 2008;133(1):38-52.[25] Xu NJ, Henkemeyer M. Ephrin reverse signaling in axon guidance and synaptogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012; 23(1):58-64.[26] Hotulainen P, Hoogenraad CC. Actin in dendritic spines: connecting dynamics to function. J Cell Biol. 2010;189(4): 619-629.[27] Frieden LA, Townsend TA, Vaught DB, et al. Regulation of heart valve morphogenesis by Eph receptor ligand, ephrin-A1. Dev Dyn. 2010;239(12):3226-3234.[28] Salvucci O, Tosato G. Essential roles of EphB receptors and EphrinB ligands in endothelial cell function and angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res. 2012;114:21-57.[29] Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C, et al. Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 1999;13(3):295-306. [30] Kim KW, Song JH. Emerging Roles of Lymphatic Vasculature in Immunity. Immune Netw. 2017;17(1):68-76.[31] Pitulescu ME, Adams RH. Eph/ephrin molecules--a hub for signaling and endocytosis. Genes Dev. 2010;24(22):2480-2492.[32] Pasquale EB. Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010; 10(3):165-180.[33] Xu K, Broder CC, Nikolov DB. Ephrin-B2 and ephrin-B3 as functional henipavirus receptors. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012; 23(1):116-123.[34] Laussu J, Khuong A, Gautrais J, et al. Beyond boundaries--Eph:ephrin signaling in neurogenesis. Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(4):349-359.[35] Liebl DJ, Morris CJ, Henkemeyer M, et al. mRNA expression of ephrins and Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in the neonatal and adult mouse central nervous system. J Neurosci Res. 2003;71(1):7-22. [36] Laussu J, Khuong A, Gautrais J, et al. Beyond boundaries--Eph:ephrin signaling in neurogenesis. Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(4):349-359.[37] Aoki M, Yamashita T, Tohyama M. EphA receptors direct the differentiation of mammalian neural precursor cells through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(31):32643-32650.[38] Del Valle K, Theus MH, Bethea JR, et al. Neural progenitors proliferation is inhibited by EphB3 in the developing subventricular zone. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2011;29(1):9-14.[39] Jiao JW, Feldheim DA, Chen DF. Ephrins as negative regulators of adult neurogenesis in diverse regions of the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105(25):8778-8783.[40] Theus MH, Ricard J, Bethea JR, et al. EphB3 limits the expansion of neural progenitor cells in the subventricular zone by regulating p53 during homeostasis and following traumatic brain injury. Stem Cells. 2010;28(7):1231-1242.[41] Baumann G, Travieso L, Liebl DJ, et al. Pronounced hypoxia in the subventricular zone following traumatic brain injury and the neural stem/progenitor cell response. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013;238(7):830-841. [42] Khodosevich K, Watanabe Y, Monyer H. EphA4 preserves postnatal and adult neural stem cells in an undifferentiated state in vivo. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 8):1268-1279.[43] Chumley MJ, Catchpole T, Silvany RE, et al. EphB receptors regulate stem/progenitor cell proliferation, migration, and polarity during hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci. 2007;27(49):13481-13490.[44] Khodosevich K, Watanabe Y, Monyer H. EphA4 preserves postnatal and adult neural stem cells in an undifferentiated state in vivo. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 8):1268-1279.[45] Holmberg J, Armulik A, Senti KA, et al. Ephrin-A2 reverse signaling negatively regulates neural progenitor proliferation and neurogenesis. Genes Dev. 2005;19(4):462-471.[46] Chumley MJ, Catchpole T, Silvany RE, et al. EphB receptors regulate stem/progenitor cell proliferation, migration, and polarity during hippocampal neurogenesis. J Neurosci. 2007; 27(49):13481-13490.[47] Ashton RS, Conway A, Pangarkar C, et al. Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-B signaling. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15(10):1399-1406. [48] Triplett JW, Feldheim DA. Eph and ephrin signaling in the formation of topographic maps. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012; 23(1):7-15.[49] Jiao JW, Feldheim DA, Chen DF. Ephrins as negative regulators of adult neurogenesis in diverse regions of the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105(25):8778-8783.[50] Bowman AN, van Amerongen R, Palmer TD, et al. Lineage tracing with Axin2 reveals distinct developmental and adult populations of Wnt/β-catenin-responsive neural stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(18):7324-7329.[51] Sakaki-Yumoto M, Katsuno Y, Derynck R. TGF-β family signaling in stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830(2): 2280-2296. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||