Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (13): 2002-2008.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1685
Previous Articles Next Articles
Regulatory effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on macrophage polarization
Song Yuxian1, Zhang Dongya2, Xu Yujun2, Hou Yayi2, Ni Yanhong1
- 1Nanjing Stomatological Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Immunology Laboratory and Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2018-12-24Online:2019-05-08Published:2019-05-08 -
Contact:Song Yuxian, Nanjing Stomatological Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Song Yuxian, PhD, Assistant researcher, Nanjing Stomatological Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81702680 (to SYX); Nanjing Medical Science and Technology Development Foundation, No. YKK17138 (to SYX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Yuxian, Zhang Dongya, Xu Yujun, Hou Yayi, Ni Yanhong. Regulatory effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on macrophage polarization[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 2002-2008.
share this article
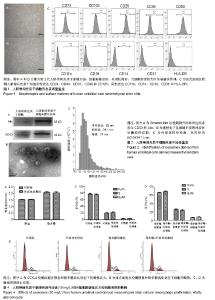
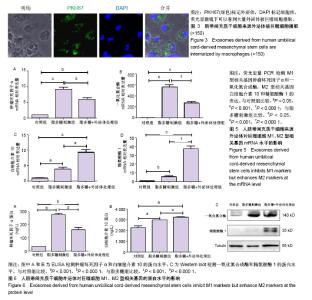
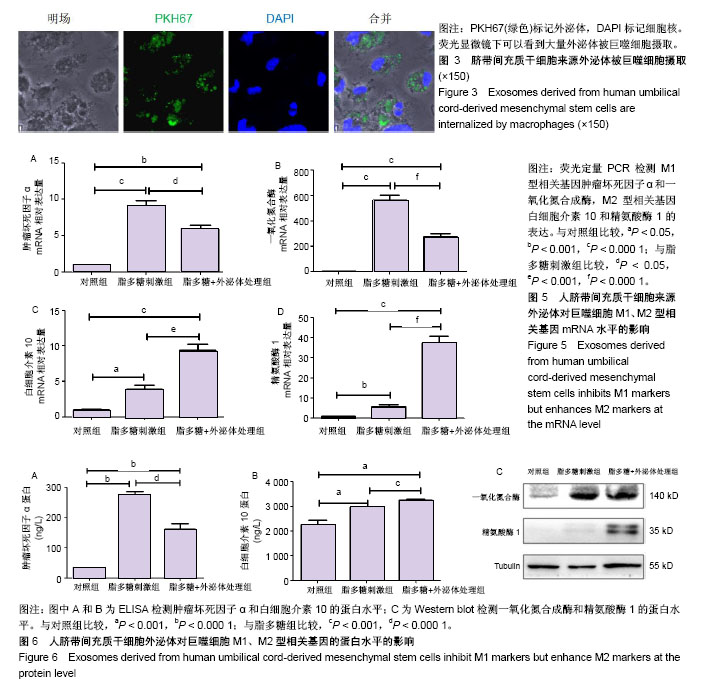
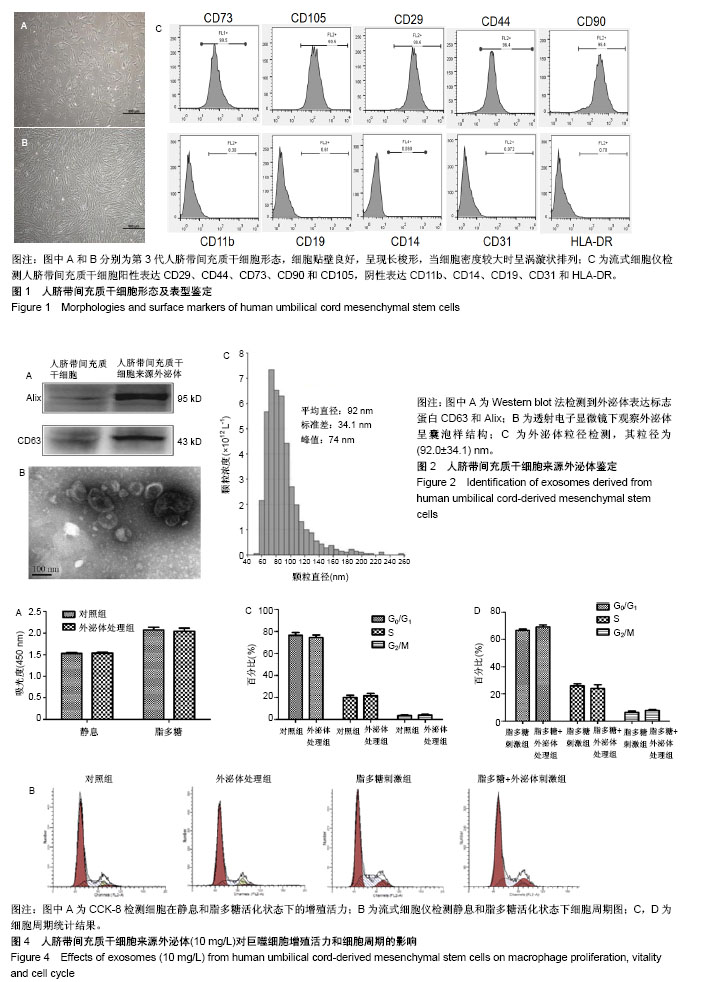
2.1 人脐带间充质干细胞的形态及表型鉴定 用酶消化法获取人脐带间充质干细胞,在显微镜下观察细胞形态,可见细胞贴壁良好,呈现长梭形,见图1A;当细胞密度较大时呈涡漩状排列,见图1B。用流式细胞术检测细胞表面标志物,结果显示细胞阳性表达CD29、CD44、CD73、CD90和CD105,阴性表达CD11b、CD14、CD19、CD31和HLA-DR,见图1C,与文献报道的的间充质干细胞标准相符[20]。 2.2 外泌体的提取与鉴定 收集人脐带间充质干细胞培养上清,采用经典的差速-超速离心方法提取外泌体[18]。采用Western blot检测外泌体常见标志物CD63和Alix的表达,其中CD63是一种四次跨膜蛋白,Alix是一种参与多泡体发生的蛋白,这两种蛋白在不同来源的外泌体中都有富集。结果显示CD63和Alix在人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体中有表达,而在人脐带间充质干细胞中则几乎检测不到,见图2A;透射电子显微镜观察外泌体形态,可见囊泡样结构,见图2B;粒径分析检测得知人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体的粒径为(92.0±34.1) nm,符合外泌体的基本特征[21-22]。 2.3 外泌体被巨噬细胞摄取 用荧光标记物(PKH67-绿色)对外泌体进行标记后加入培养的巨噬细胞中,外泌体终质量浓度为10 mg/L,同时用脂多糖刺激,4 h后在荧光显微镜下可以看到大量外泌体被巨噬细胞摄取,见图3。 2.4 外泌体不影响巨噬细胞增殖活力和周期 采用CCK-8实验检测细胞增殖活力,结果显示,10 mg/L外泌体对静息状态巨噬细胞、脂多糖活化状态巨噬细胞的增殖活力都没有影响,见图4A。细胞周期实验结果表明,该浓度的外泌体也不会影响细胞周期,见图4B,分别比较静息和活化状态下细胞周期G0/G1、S和G2/M期的百分比,发现外泌体处理组与不处理组差异均无显著性意义,见图4C。 2.5 外泌体促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化 脂多糖刺激后巨噬细胞M1型活化标志肿瘤坏死因子α和一氧化氮合成酶的mRNA水平显著升高,而脂多糖+外泌体处理组与单独脂多糖组相比M1活化水平显著降低,见图5A,B;另外,M2型活化标志白细胞介素10和精氨酸酶1在脂多糖的作用下略有升高,而外泌体能显著上调M2的活化水平,见图5C,D。外泌体对M1和M2型活化标志蛋白水平的影响趋势与mRNA水平基本一致,即抑制M1而增强M2,见图6。"
| [1] Da Silva Meirelles L, Chagastelles PC, Nardi NB.Mesenchymal stem cells reside in virtually all post-natal organs and tissues. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 11):2204-2213.[2] Le Blanc K, Tammik C, Rosendahl K, et al. HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2003;31(10):890-896.[3] Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol. 2003;57(1):11-20.[4] Rosario CM, Yandava BD, Kosaras B, et al. Differentiation of engrafted multipotent neural progenitors towards replacement of missing granule neurons in meander tail cerebellum may help determine the locus of mutant gene action. Development. 1997; 124(21):4213-4224.[5] Li TS, Takahashi M, Ohshima M, et al. Myocardial repair achieved by the intramyocardial implantation of adult cardiomyocytes in combination with bone marrow cells. Cell Transplant. 2008;17(6): 695-703.[6] Lai RC, Chen TS, Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosome: a novel stem cell-based therapy for cardiovascular disease. Regen Med. 2011;6(4):481-492.[7] Shi H, Xu X, Zhang B, et al. 3,3'-Diindolylmethane stimulates exosomal Wnt11 autocrine signaling in human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to enhance wound healing. Theranostics. 2017;7(6):1674-1688.[8] Vizoso FJ, Eiro N, Cid S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9): E1852.[9] Vlassov AV, Magdaleno S, Setterquist R, et al. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820(7): 940-948.[10] Barile L, Vassalli G. Exosomes: Therapy delivery tools and biomarkers of diseases. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:63-78.[11] Huang L, Ma W, Ma Y, et al. Exosomes in mesenchymal stem cells, a new therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2015;11(2):238-245.[12] Zhang B, Wang M, Gong A, et al. HucMSC-Exosome Mediated- Wnt4 Signaling Is Required for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Stem Cells. 2015;33(7):2158-2168.[13] Zhang S, Chuah SJ, Lai RC, et al. MSC exosomes mediate cartilage repair by enhancing proliferation, attenuating apoptosis and modulating immune reactivity. Biomaterials. 2018;156:16-27.[14] Keshtkar S, Azarpira N, Ghahremani MH. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: novel frontiers in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):63.[15] Gordon S, Taylor PR. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5(12):953-964.[16] Sica A, Mantovani A. Macrophage plasticity and polarization: in vivo veritas. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(3):787-795.[17] Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(12):677-686.[18] Martinez FO. Regulators of macrophage activation. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41(6):1531-1534.[19] Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22.[20] Lv FJ, Tuan RS, Cheung KM, et al. Concise review: the surface markers and identity of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(6):1408-1419.[21] Zaborowski MP, Balaj L, Breakefield XO, et al. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience. 2015;65(8):783-797.[22] Théry C, Ostrowski M, Segura E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9(8):581-593.[23] Tolar J, Le Blanc K, Keating A, et al. Concise review: hitting the right spot with mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells. 2010;28(8): 1446-1455.[24] Kidd S, Spaeth E, Watson K, et al. Origins of the tumor microenvironment: quantitative assessment of adipose-derived and bone marrow-derived stroma. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30563.[25] Li J, Liu K, Liu Y, et al. Exosomes mediate the cell-to-cell transmission of IFN-α-induced antiviral activity. Nat Immunol. 2013;14(8):793-803.[26] Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.[27] Ratajczak J, Miekus K, Kucia M, et al. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia. 2006; 20(5): 847-856.[28] Tkach M, Théry C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell. 2016;164(6):1226-1232.[29] Lai RC, Yeo RW, Lim SK. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015;40:82-88.[30] 张恩国,陈尚雅,杨叶,等. 干细胞源外泌体应用于再生医学的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(5):801-806.[31] Zhang B, Yeo RW, Tan KH, et al. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(2):174.[32] Németh K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 2009;15(1):42-49.[33] Kim J, Hematti P. Mesenchymal stem cell-educated macrophages: a novel type of alternatively activated macrophages. Exp Hematol. 2009; 37(12):1445-1453.[34] Maggini J, Mirkin G, Bognanni I, et al. Mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells turn activated macrophages into a regulatory-like profile. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9252.[35] Zhang QZ, Su WR, Shi SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells elicit polarization of m2 macrophages and enhance cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells. 2010;28(10): 1856-1868.[36] Dayan V, Yannarelli G, Billia F, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells mediate a switch to alternatively activated monocytes/macrophages after acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res Cardiol. 2011;106(6): 1299-1310.[37] Guilloton F, Caron G, Ménard C, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells orchestrate follicular lymphoma cell niche through the CCL2-dependent recruitment and polarization of monocytes. Blood. 2012;119(11): 2556-2567.[38] Yin Y, Hao H, Cheng Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells direct macrophage polarization to alleviate pancreatic islets dysfunction in type 2 diabetic mice. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):760.[39] Lankford KL, Arroyo EJ, Nazimek K, et al. Intravenously delivered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target M2-type macrophages in the injured spinal cord. PLoS One. 2018;13(1): e0190358.[40] Willis GR, Fernandez-Gonzalez A, Anastas J, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes Ameliorate Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Restore Lung Function through Macrophage Immunomodulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197(1):104-116. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||