Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (7): 1122-1128.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1076
Previous Articles Next Articles
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in tissue and organ regeneration: research status and prospects
Dang Haixia1, Wang Fu2
- (1Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Stomatology College, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China)
-
Received:2018-10-07Online:2019-03-08Published:2019-03-08 -
Contact:Wang Fu, MD, Associate professor, Stomatology College, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Dang Haixia, Master, Physician, Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dang Haixia1, Wang Fu2. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in tissue and organ regeneration: research status and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(7): 1122-1128.
share this article
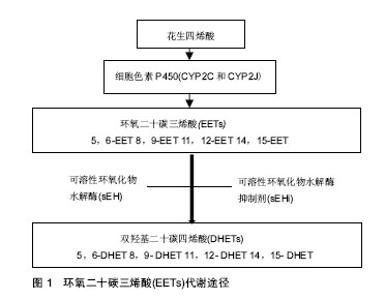
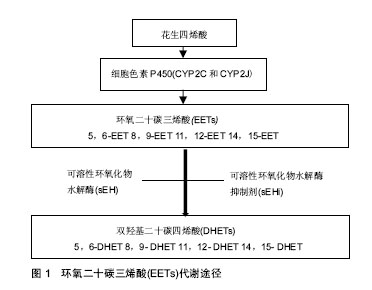
2.1 EETs的来源及代谢 EETs是花生四烯酸的代谢产物。花生四烯酸在生物体内主要是以磷脂的形式存在于细胞膜上,当细胞膜受到各种刺激时,其通过甘油二酯脂肪酶和磷脂酶A2等多种酶代谢而产生游离的花生四烯酸,而后迅速被一系列酶代谢而生成脂质介质,这一代谢过程被称为信号级联反应[8-10]。该信号级联的脂质信号在调节许多基本生物过程中发挥着很重要的作用,成为人类多种疾病重要的治疗靶点[8-10]。花生四烯酸主要有3条代谢通路:环氧合酶(Cyclooxygenase,COX),脂氧合酶(Lipoxygenase,LOX)和细胞色素P450(Cytochrome P450,CYP)代谢途径[8]。花生四烯酸通过环氧合酶和脂氧合酶途径主要合成前列腺素和白三烯,这两类类花生酸在组织再生方面已有广泛研究[11-12],而关于CYP衍生的类花生酸研究主要集中于炎症和心血管功能[8,13]。 花生四烯酸的CYP代谢途径又分为两个分支:CYP的ω-1羟化酶(主要为CYP4A和CYP4F)催化花生四烯酸羟基化生成19-羟二十酸(19-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid,19-HETE)和20羟二十烷四烯酸(20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid,20-HETE)。其中,20-HETE被研究证实可诱发高血压、内皮功能障碍、炎症、心血管疾病、血管生成和肿瘤成长[14-17]。CYP途径的另一个分支,即CYP表氧化酶(主要是CYP2C和CYP2J)催化花生四烯酸环氧化生成EETs,其包括4种异构体,即5,6-EET,8,9-EET,11,12-EET和14,15-EET[5]。EETs的生物活性较高,但其在体内高度不稳定,在体内合成后即迅速被可溶性环氧化物水解酶(soluble epoxide hydrolase,sEH,由EPHX2编码) 水解生成相对应的生理活性较低的双羟基二十碳四烯酸(dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acids,DHETs),相应的4种异构体为:5,6-DHET、8,9-DHET、11,12-DHET和14,15-DHET(见图1)。当前,通过靶向阻断sEH而提高内源性EETs成为主要研究手段。在过去的10多年,人们对于sEH的抑制剂(soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor,sEHi)进行了大量的研发,从早期的环氧类sEHi已开发到第3代脲类sEHi,sEHi在体内应用和临床试验中得到了快速的发展[18-21]。"
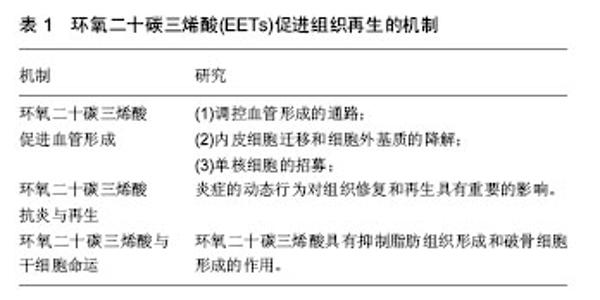
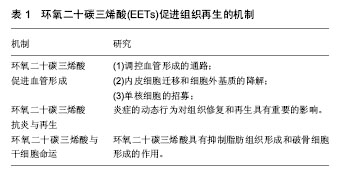
2.2 EETs促进组织和器官的生长及再生 2.2.1 EETs促进组织生长 研究显示,EETs具有促进胰岛增大和轴突生长的功能。Luria等[22]发现EETs可增加胰岛的大小并可改进胰岛素的信号和灵敏度。该研究组通过基因敲除编码sEH的基因EPHX2以及外源性给予sEHi研究发现,与野生型小鼠相比,实验组小鼠胰岛明显增大,胰腺组织学切片发现新生血管明显增多。此外,有研究者通过体外研究发现,EETs还具有促进轴突生长的功能[3]。该研究组运用大脑皮质、交感神经、感觉神经原代神经元细胞培养物,通过免疫反应证实sEH位于神经元的轴突,通过添加外源性EETs以及sEHi发现,与对照组相比,实验组神经元细胞轴突长度明显增长。 2.2.2 EETs促进组织和器官再生 近些年研究表明,EETs具有促进伤口愈合、颅骨缺损区骨组织再生、角膜新生血管、新生视网膜血管形成及器官再生等功能[2,4-5]。有研究者通过体外实验在小鼠耳背部创建标准化的全层皮肤缺损创面,发现EETs可明显促进伤口处上皮和血管新生,并研究得出该作用可能是通过SDF1α和血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelia growth factor,VEGF)协同上调实现的[4]。在骨组织再生方面,利用C57BL/6小鼠颅骨缺损模型,发现14,15-EET处理侧新生骨量、血管内皮生长因子表达和新生血管数较对照侧明显增多,提示14,15-EET促进颅骨缺损区骨组织再生可能与其改善局部微循环有关[2]。这些研究结果可能为牙周病、创伤、炎症和肿瘤等造成的骨缺损疾病提供一种新的治疗思路。此外,2013年Panigrahya等[5],发现EETs可明显促进伤口愈合、角膜新生血管和视网膜血管的形成。通过基因学和药理学手段控制内源性EETs水平发现EETs在促进器官再生中也发挥了关键的作用,能够促进肝再生,肾和肺代偿性生长。这些研究结果为评估EETs或sEHi对人类多种疾病作为新的治疗靶点提供了线索,可望用于肝损伤或手术切除后的肝功能不全的组织再生。此外,鉴于EETs具有促进肺代偿性生长的作用,EETs或其代谢酶抑制剂sEHi可能对肺发育不良具有一定的治疗效果,如支气管肺发育不良[5]。 2.3 EETs促进组织再生的机制研究 见表1。"
| [1] Morisseau C, Hammock BD. Impact of soluble epoxide hydrolase and epoxyeicosanoids on human health. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2013;53(2):37-58. [2] 党海霞,霍欣茹,王福,等.14,15-环氧二十碳三烯酸促进颅骨缺损骨再生[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(7):692-695.[3] Abdu E, Bruun DA, Yang D, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids enhance axonal growth in primary sensory and cortical neuronal cell cultures. J Neurochem. 2011;117(4): 632-642. [4] Sander AL, Jakob H, Sommer K, et al. Cytochrome P450-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids accelerate wound epithelialization and neovascularization in the hairless mouse ear wound model. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2011;396(8): 1245-1253. [5] Panigrahy D, Kalish BT, Huang S, et al. Epoxyeicosanoids promote organ and tissue regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(33):13528-13533. [6] Vanella L, Kim DH, Sodhi K, et al. Crosstalk between EET and HO-1 downregulates Bach1 and adipogenic marker expression in mesenchymal stem cell derived adipocytes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011;96(1):54-62. [7] Guan H, Zhao L, Cao H, et al. Epoxyeicosanoids suppress steoclastogenesis and prevent ovariectomy-induced bone loss. FASEB J. 2015;29(3):1092-1101. [8] Shahabi P, SiestG, Visvikis-siest S. cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Drug Metab Rev. 2014;46(1):33-56. [9] Buczynski MW, Dumlao DS, Dennis EA. Thematic review series: proteomics. An integrated omics analysis of eicosanoid biology. J Lipid Res. 2009;50(11):1015-1038. [10] Funk CD. Prostaglandins and leukotrienes: advances in eicosanoid biology. Science. 2001;294(5548):1871-1875. [11] Buch PR, Desai I, Balakrishnan S. COX-2 activity and expression pattern during regenerative wound healing of tail in lizard Hemidactylus flaviviridis. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2018;135:11-15. [12] Chiang N, Riley IR, Dalli J, et al. New maresin conjugates in tissue regeneration pathway counters leukotriene D4-stimulated vascular responses. FASEB J. 2018;32(7): 4043-4052. [13] He J, Wang C, Zhu Y, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase: A potential target for metabolic diseases. J Diabetes. 2015; 8(3):305-313. [14] Elshenawy OH, Anwar-Mohamed A, El-Kadi AO. 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid is a potential therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases. Curr Drug Metab. 2013; 14(6):706-719. [15] Hoopes SL, Garcia V, Edin ML, et al. Vascular actions of 20-HETE.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015;120:9-16. [16] Imig JD. Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids and 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic Acid on Endothelial and Vascular Function. Adv Pharmacol. 2016;77:105-141. [17] Garcia V, Schwartzman ML. Recent developments on the vascular effects of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2017;26(2):74-82. [18] Swardfager W, Hennebelle M, Yu D, et al. Metabolic/ inflammatory/vascular comorbidity in psychiatric disorders; soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) as a possible new target. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 201887:56-66. [19] Lee KS, Liu JY, Wagner KM, et al. Optimized inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase improve in vitro target residence time and in vivo efficacy. J Med Chem. 2014;57(16):7016-7030. [20] Yu Z, Xu F, Huse LM, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase regulates hydrolysis of vasoactive epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Circ Res. 2000;87(11):992-998. [21] Imig JD, Zhao X, Zaharis CZ, et al. An orally active epoxide hydrolase inhibitor lowers blood pressure and provides renal protection in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2005; 46(4):975-981. [22] Luria A, Bettaieb A, Xi Y, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase deficiency alters pancreatic islet size and improves glucose homeostasis in a model of insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(22):9038-9043. [23] Fleming I. Vascular cytochrome p450 enzymes: physiology and pathophysiology. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2008;18(1): 20-25. [24] Street J, Bao M, Bunting S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates bone repair by promoting angiogenesis and bone turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(15): 9656-9661. [25] Folkman J. Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? . Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6(4):273-286. [26] 鲍小刚,许国华.组织工程骨的快速血管化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(7):1063-1069.[27] Zhang C, Harder DR. Cerebral capillary endothelial cell mitogenesis and morphogenesis induced by astrocytic epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. Stroke. 2002;33(12):2957-2964. [28] Capozzi ME, McCollum GW, Penn JS. The role of cytochrome P450 epoxygenases in retinal angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(7):4253-4260. [29] Pulin Li, Jamie L, Lahvic, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids Enhance Embryonic Haematopoiesis and Adult Marrow Engraftment. Nature. 2015;523(7561):468-471. [30] Tassi E, McDonnell K, Gibby KA, et al. Impact of fibroblast growth factor-binding protein–1 expression on angiogenesis and wound healing. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(5):2220-2232. [31] Cheranov SY, Karpurapu M, Wang D, et al. An essential role for SRC-activated STAT-3 in 14, 15-EET–induced VEGF expression and angiogenesis. Blood. 2008;111(12):5581-5591. [32] Michaelis UR, Fisslthaler B, Barbosa-Sicard E, et al. Cytochrome P450 epoxygenases t2C8 and 2C9 are implicated in hypoxia-induced endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(23):5489-5498. [33] Chen JK, Capdevila J, Harris RC. Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor mediates the biological effects of P450 arachidonate epoxygenase metabolites in epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(9):6029-6034. [34] Xu DY, Davis BB, Wang ZH. A potent soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor, t-AUCB, acts through PPARγ to modulate the function of endothelial progenitor cells from patients with acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(4):1298-1304. [35] Revermann M, Schloss M, Barbosa-Sicard E. Soluble epoxide hydrolase deficiency attenuates neointima formation in the femoral cuff model of hyperlipidemic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(5):909-914. [36] Davis BB, Thompson DA, Howard LL. Inhibitors of soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuate vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(4):2222-2227. [37] Ng VY, Morisseau C, Falck JR, et al. Inhibition of smooth muscle proliferation by urea-based alkanoic acids via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha-dependent repression of cyclin D1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006; 26(11):2462-2468. [38] Kim HS, Kim SK, Kang KW. Differential Effects of sEH Inhibitors on the Proliferation and Migration of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12):2683. [39] Carmeliet P. Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 2000;6(4):389-395. [40] Fleming I, Michaelis UR, Bredenkötter D, et al. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor synthase (Cytochrome P450 2C9) is a functionally significant source of reactive oxygen species in coronary arteries. Circ Res. 2001; 88(1):44-51[41] Eming SA, Wynn TA, Martin P. Inflammation and metabolism in tissue repair and regeneration. Science. 2017;356(6342): 1026-1030. [42] Liu H, Li D, Zhang Y, et al. Inflammation, mesenchymal stem cells and bone regeneration. Histochem Cell Biol. 2018;149 (4): 393-404. [43] Runyan CM, Gabrick KS. Biology of Bone Formation, Fracture Healing, and Distraction Osteogenesis. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(5):1380-1389. [44] Chen FM, Lu H, Wu LA, et al. Surface-engineering of glycidyl methacrylated dextran/gelatin microcapsules with thermo-responsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gates for controlled delivery of stromal cell-derived factor-1α. Biomaterials. 2013;34(27):6515-6527. [45] Godot V, Arock M, Garcia G, et al. H4 histamine receptor mediates optimal migration of mast cell precursors to CXCL12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120(4):827-834. [46] Melief SM, Zwaginga JJ, Fibbe WE, et al. Adipose tissue-derived multipotent stromal cells have a higher immunomodulatory capacity than their bone marrow-derived counterparts. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(6):455-463. [47] Kim KS, Kim HS, Park JM, et al. Long-term immunomodulatory effect of amniotic stem cells in an Alzheimer's disease model. Neurobiol Aging. 2013;34(10): 2408-20. [48] Liu D, Xu J, Liu O, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from inflamed periodontal ligaments exhibit impaired immunomodulation. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39:1174-1182. [49] Liu Y, Wang L, Kikuiri T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue regeneration is governed by recipient T lymphocytes via IFN-γ and TNF-α. Nat Med. 2011;17:1594-1601. [50] Vanella L, Kim D H, Sodhi K, Barbagallo I, Burgess AP, Falck JR, Schwartzman ML, Abraham NG. Crosstalk between EET and HO-1 downregulates Bach1 and adipogenic marker expression in mesenchymal stem cell derived adipocytes. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2011;96(1):54-62. [51] Harada S, Rodan GA. Control of osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature. 2003;15; 423(6937): 349-355. [52] Zhu XB, Lin WJ, Lv C, et al. MicroRNA-539 promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation and osteoclast apoptosis through the AXNA-dependent Wnt signaling pathway in osteoporotic rats. J Cell Biochem. 2018 Jun 12. [53] Bao Y, Gao Y, Du M, et al. opical Treatment with Xiaozheng Zhitong Paste (XZP) Alleviates Bone Destruction and Bone Cancer Pain in a Rat Model of Prostate Cancer-Induced Bone Pain by Modulating the RANKL/RANK/OPG Signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:215892. [54] Rangaswami H, Schwappacher R, Tran T, et al. Protein kinase G and focal adhesion kinase converge on Src/Akt/ β-catenin signaling module in osteoblast mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(25): 21509-21519. [55] Liang D, Yang M, Guo B, et al. Zinc inhibits H(2)O(2)-induced MC3T3-E1 cells apoptosis via MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2012;148(3):420-429. [56] Oni-Orisan A, Deng Y, Schuck RN, et al. Dual modulation of cyclooxygenase and CYP epoxygenase metabolism and acute vascular inflammation in mice. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2013;104-105:67-73. [57] Wang H, Lin L, Jiang J, et al. Up-regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase by endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor involves mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase C signaling pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003; 307(2):753–764. [58] Abraham NG, Sodhi K, Silvis AM, et al. CYP2J2 targeting to endothelial cells attenuates adiposity and Vascular Dysfunction in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet by Reprogramming Adipocyte Phenotype. Hypertension. 2014;64(6):1352–1361. [59] Duflot T, Roche C, Lamoureux F, et al. Design and discovery of soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014;9(3): 229-243. [60] Lazaar AL, Yang L, Boardley RL, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and adverse event profile of GSK2256294, a novel soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;81(5):971-979. [61] Chen D, Whitcomb R, MacIntyre E, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of AR9281, an inhibitor of soluble epoxide hydrolase, in single- and multiple-dose studies in healthy human subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;52(3): 319-328. [62] Bellien J, Iacob M, Remy-Jouet I, et al. Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids contribute with altered nitric oxide and endothelin-1 pathways to conduit artery endothelial dysfunction in essential hypertension. Circulation. 2012;125(10):1266-1275. [63] Noonan JE, Dusting GJ, Nguyen TT, et al. Flicker light-induced retinal vasodilation is unaffected by inhibition of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids and prostaglandins in humans. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(10):7007-7013. [64] Liu JY, Park SH, Morisseau C, et al. Sorafenib has soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity, which contributes to its effect profile in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8(8):2193-2203. [65] Kim JH, Cho CW, Tai BH, et al. Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitory Activity of Selaginellin Derivatives from Selaginella tamariscina. Molecules. 2015;20(12):21405-21414. [66] Kitamura S, Morisseau C, Inceoglu B, et al. Potent natural soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors from Pentadiplandra brazzeana baillon: synthesis, quantification, and measurement of biological activities in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2015;6:10(2):e0117438. [67] Bai MM, Shi W, Tian JM, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory components from the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver (duzhong). J Agric Food Chem. 2015;63(8):2198-2205. [68] Sun YN, Li W, Song SB, et al. A new phenolic derivative with soluble epoxide hydrolase and nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitory activity from the aqueous extract of Acacia catechu. Nat Prod Res. 2016;30(18):2085-2092. [69] Sun YN,Kim JH,Li W,et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity of anthraquinone components from Aloe. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015;23(20):6659-6665. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||