Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (10): 1581-1587.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1604
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of flow rate and blade outlet width on hemolytic performance of centrifugal blood pump
Hu Wanqian1, Li Xuemin2, Xu Lin3, Liu Jiwei2, Sun Hao2
- 1China Yangtze Power Co., Ltd., Yichang 443000, Hubei Province, China; 2School of Energy and Power Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China; 3Central Southern China Electric Power Design Institute, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2018-11-06 -
Contact:Li Xuemin, Associate professor, School of Energy and Power Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Hu Wanqian, Master, China Yangtze Power Co., Ltd., Yichang 443000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research & Development Program of China, No. 2018YFB0606101
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hu Wanqian, Li Xuemin, Xu Lin, Liu Jiwei, Sun Hao. Effects of flow rate and blade outlet width on hemolytic performance of centrifugal blood pump[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(10): 1581-1587.
share this article

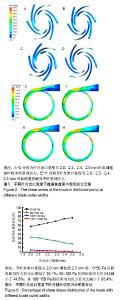
泵的扬程、功率、效率等性能参数与泵流量存在着一定的关系。当人工心脏泵的流量发生变化,心脏泵入口流速随之变化,这将影响到血液在泵内的流速、血液流经血泵的运动时间及血液在泵内所受到的切应力,最终影响到泵内血细胞的溶血值。 将在设计流量Q=6 L/min的基础上,增加Q=2,3,4,5,7 L/min 5组算例;在设计出口宽度b2=2.2 mm的基础上,增加b2=2.0,2.1,2.3,2.4,2.5 mm 5组算例,以研究流量、叶片出口宽度与血泵内溶血值的关系。 2.1 流量对离心血泵溶血性能的影响 2.1.1 流量对切应力的影响 图2A-D表明,当流量为 3 L/min时,血液在叶轮中所受到的最大切应力最小(680.668 Pa);当流量为5 L/min时,最大切应力出现最大值(710.393 Pa);当流量为3-7 L/min时,最大切应力在5%的范围内波动。图2E-H表明,在不同的流量下,蜗壳中血液所受到的最大切应力均位于隔舌处和蜗壳外壁面,血液在蜗壳中所受最大切应力明显小于叶片部分;当流量Q= 2 L/min时,蜗壳中血液所受到的最大切应力最大 (401.462 Pa);当流量Q=5 L/min时,血液于蜗壳处所受到的最大切应力急剧减小。 2.1.2 切应力分布 图3表明,随着流量的增大,0-50 Pa范围内的切应力所占比例逐渐减小,同时50-100 Pa、100-150 Pa及150-1 000 Pa范围内的切应力所占比例逐渐增加。当Q=7 L/min时,血液在叶片部分所受切应力在150-1 000 Pa范围内所占百分比最高,达到3.02%;当Q= 3 L/min时,血液在叶片部分所受切应力在150-1 000 Pa范围内所占百分比最低(1.95%)。"

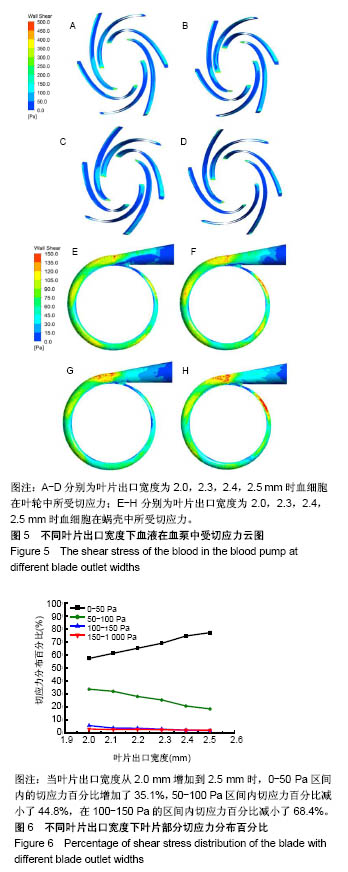
2.2 叶片出口宽度对血泵溶血性能的影响 2.2.1 叶片出口宽度对切应力的影响 图5A-D表明,随着叶片出口宽度b2的改变,高切应力(大于150 Pa)区域所占面积较小且均位于叶片入口与叶片出口工作面处,当叶片出口宽度b2=2.2 mm时,血液在叶片部分的切应力最大(709.71 Pa),当叶片出口宽度减小或增大时,血液在叶片部分的最大切应力均急剧下降,当b2=2.1 mm时,最大切应力最小(525.81 Pa)。图5E-H表明,在不同的叶片出口宽度下,蜗壳中血液所受到的最大切应力均位于蜗壳外壁面,0-150 Pa范围内的切应力所占比例均大于99%;仅当叶片出口宽度b2=2.5 mm,血液于蜗壳处所受到的最大切应力(277.901 Pa)超过150 Pa,且所占比例仅为0.88%。 2.2.2 切应力分布 图6显示,随着出口宽度的增大,0- 50 Pa、50-100 Pa与100-150 Pa区间内的切应力分布百分比基本呈线性变化,当出口宽度b2从2.0 mm增加到 2.5 mm时,0-50 Pa区间内的切应力百分比增加了35.1%,50-100 Pa区间内切应力百分比减小了44.8%,在100- 150 Pa的区间内切应力百分比减小了68.4%。"
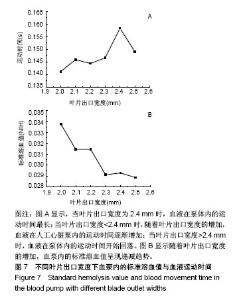
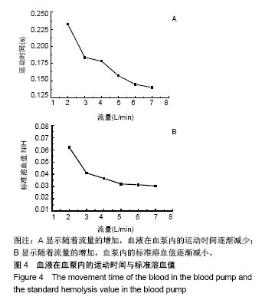
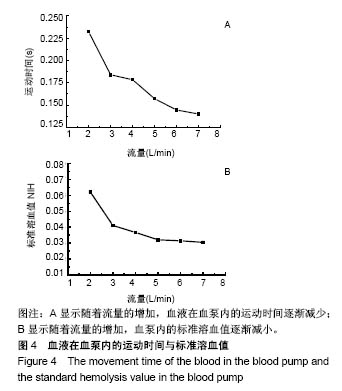
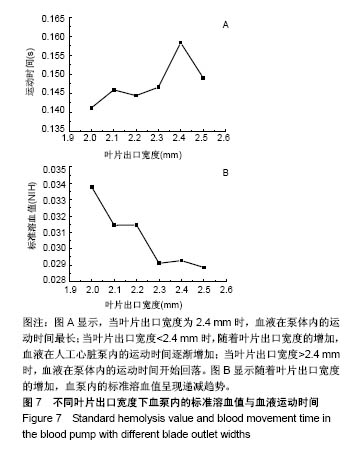
2.2.3 标准溶血值分析 图7A所示,当叶片出口宽度b2=2.4 mm时,血液在泵体内的运动时间最长(0.158 3 s);当叶片出口宽度<2.4 mm时,随着叶片出口宽度的增加,血液在人工心脏泵内的运动时间逐渐增加,其中叶片出口宽度b2=2.0 mm运动时间最短(0.141 2 s);当叶片出口宽度>2.4 mm时,血液在泵体内的运动时间开始回落。图7B为叶片出口宽度b2=2.0 mm到2.5 mm时离心式人工心脏泵内的标准溶血值,可看到随着叶片出口宽度的增加,血泵内的标准溶血值呈现递减趋势;当出口宽度b2=2.0 mm时,泵内标准溶血值最高为0.034,当叶片出口宽度增加时,标准溶血值迅速减小;当b2从2.0 mm增加到2.1 mm时,标准溶血值降低了6.9%;增加至2.3 mm时,标准溶血值降低了13.8%;增加到2.5 mm时,标准溶血值降低了14.5%。"
| [1] 陈伟伟,高润霖,刘力生,等.中国心血管病报告2017概要[J].中国循环杂志,2018,33(1):1-8.[2] 宋云虎,胡盛寿,董念国,等.中国心脏移植现状[J].中国循环杂志, 2016,31(z1):77-77.[3] Isomura T, Fukada Y, Miyazaki T,et al. Posterior ventricular restoration treatment for heart failure: a review, past, present and future aspects.Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;65(3): 1-7.[4] 张岩,孙寒松,胡盛寿.左心室辅助血泵及其临床应用研究进展[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2017,24(2):152-155.[5] Muslem R,Caliskan K,Leebeek FWG. Acquired coagulopathy in patients with Left Ventricular Assist Devices. J Thromb Haemost.2018;16(3):429-440.[6] 寿宸,郭勇君,苏磊,等.基于快速溶血预估模型的离心血泵叶轮特性数值分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2014,31(6):1260-1264.[7] 王芳群.应用 CFD 技术探明叶轮设计对人工心脏血泵内流场及切应力分布的影响[D].镇江:江苏大学,2003.[8] 陈松松.基于溶血估算的离心血泵设计[D].杭州:浙江大学, 2011.[9] 李卫东,姚奇,杜建军,等.基于 CFD 的液悬浮人工心脏泵叶轮入口优化分析[J].北京生物医学工程,2017, 36(1):21-28.[10] Takami Y,Nakazawa T,Makinouchi K,et al. Hemolytic effect of surface roughness of an impeller in a centrifugal blood pump. Artif Organs.1997;21(7):686-690.[11] Umezu M,Yamada T,Fujimasu H,et al.Effects of surface roughness on mechanical hemolysis. Artif Organs. 1996; 20(5):575-578.[12] Heck ML,Yen A,Snyder TA,et al.Flow-Field Simulations and Hemolysis Estimates for the Food and Drug Administration Critical Path Initiative Centrifugal Blood Pump.Artif Organs. 2017; 41(10): 129-140.[13] da Silva C,da Silva BU,Leme J,et al.In Vivo Evaluation of Centrifugal Blood Pump for Cardiopulmonary Bypass—Spiral Pump.Artif Organs.2013;37(11):954-957.[14] Chiu WC,Slepian MJ,Bluestein D.Thrombus Formation Patterns in the HeartMate II VAD-Clinical Observations Can Be Predicted by Numerical Simulations. ASAIO J. 2014;60(2): 237-240. [15] Wernicke JT,Meier D,Mizuguchi K,et al.A fluid dynamic analysis using flow visualization of the Baylor/NASA implantable axial flow blood pump for design improvement. Artif Organs. 1995; 19(2):161-177.[16] Reich HJ,Morgan J,Arabia F,et al.Comparative analysis of von Willebrand Factor profiles after implantation of left ventricular assist device and total artificial heart.J Thromb Haemost. 2017; 15(8):1620-1624.[17] Akamatsu T, Nakazeki T, Itoh H. Centrifugal blood pump with a magnetically suspended impeller. Artif Organs. 1992;16(3): 305-308.[18] Wu J, Paden BE, Borovetz HS, et al. Computational fluid dynamics analysis of blade tip clearances on hemodynamic performance and blood damage in a centrifugal ventricular assist device. Artif Organs.2010;34(5):402-411.[19] Daisuke S, Tomotaka M, Ryo K, et al. Real-Time Observation of Thrombus Growth Process in an Impeller of a Hydrodynamically Levitated Centrifugal Blood Pump by Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging. Artif Organs. 2015; 39(8): 714-719. [20] Carpentier A,Latrémouille C,Cholley B,et al.First clinical use of a bioprosthetic total artificial heart: report of two cases. Lancet. 2015;386(10003):1556-1563.[21] Song G, Chua LP, Lim TM.Numerical Study of a Bio‐Centrifugal Blood Pump With Straight Impeller Blade Profiles. Artif Organs.2010;34(2):98-104.[22] Leme J,Silva C,Fonseca J,et al. Centrifugal blood pump for temporary ventricular assist devices with low priming and ceramic bearings.Artif Organs.2013;37(11):942-945.[23] Özalp F,Bhagra S,Bhagra C,et al.Four-year outcomes with third-generation centrifugal left ventricular assist devices in an era of restricted transplantation.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014; 46(3):35-40.[24] Miller JR, Lawrance CP, Silvestry SC. Current Options and Practices in Long-Term Ventricular Assist Devices.Curr Surg Rep.2014;2(5):1-9.[25] Velicki L, Frazier OH. Long-term ventricular assist devices in current clinical practice. Vojnosanit Pregl.2013;70(7):679.[26] Sun P, Leng W, Zhang CS, et al.ALE Method for a Rotating Structure Immersed in the Fluid and Its Application to the Artificial Heart Pump in Hemodynamics[C]//International Conference on Computational Science.Springer,Cham, 2018: 9-23.[27] Bente T, Bastian B, Jens S, et al. Numerical Analysis of Blood Damage Potential of the eart Mate II and Heart Ware HVAD Rotary Blood Pumps.Artif Organs.2015;39(8):651-659. [28] Apel J, Paul R, Klaus S, et al. Assessment of hemolysis related quantities in a microaxial blood pump by computational fluid dynamics.Artif Organs. 2001;25(5):341-347.[29] Garon A, Farinas MI. Fast Three‐dimensional Numerical Hemolysis Approximation. Artif Organs.2004; 28(11): 1016-1025.[30] 谢雄,谭建平,刘云龙.轴流式血泵流体特性CFD研究[J].工程设计学报,2014,21(2):154-160. [31] 牛彦文.人工心脏泵叶轮结构参数优化及有限元分析[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2016.[32] Sakota R, Lodi CA, Sconziano SA, et al. In Vitro Comparative Assessment of Mechanical Blood Damage Induced by Different Hemodialysis Treatments. Artif Organs. 2015;39(12): 1015-1023.[33] 王立群.我国开展心衰终末期治疗新技术(127)[J].临床心电学杂志, 2018,27(1):73.[34] McIlvennan CK,Magid KH,Ambardekar AV,et al.Clinical outcomes after continuous-flow left ventricular assist device: a systematic review. Heart Fail.2014;7(6):1003-1013.[35] Schmitto JD, Hanke JS, Rojas SV, et al. First implantation in man of a new magnetically levitated left ventricular assist device (HeartMate III). J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015;34(6): 858-860. [36] 胡盛寿.心力衰竭外科治疗现状与进展[J].中国循环杂志, 2016, 31(3):209-213.[37] 李卫东.离心式人工心脏泵血流动力学特性分析与优化研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2016.[38] Szwast M, Moskal A, Piatkiewicz W. A new method for assessing haemolysis in a rotary blood pump using large eddy simulations(LES).Chem Proc Eng.2017;38(2):231-239.[39] Telyshev D,Denisov M,Pugovkin A,et al. The Progress in the Novel Pediatric Rotary Blood Pump Sputnik Development. Artif Organs.2018;42(4):432-443.[40] Murashige T,Kosaka R,Sakota D,et al.Evaluation of a spiral groove geometry for improvement of hemolysis level in a hydrodynamically levitated centrifugal blood pump. Artif Organs. 2015;39(8):710-714. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Xu Jianxia, Wang Zhaoxu, Wang Chunren. Blood compatibility of disposable blood perfusion device in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 588-592. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||