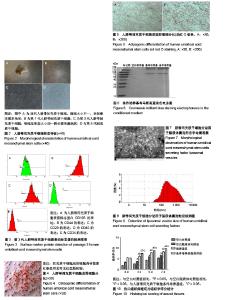
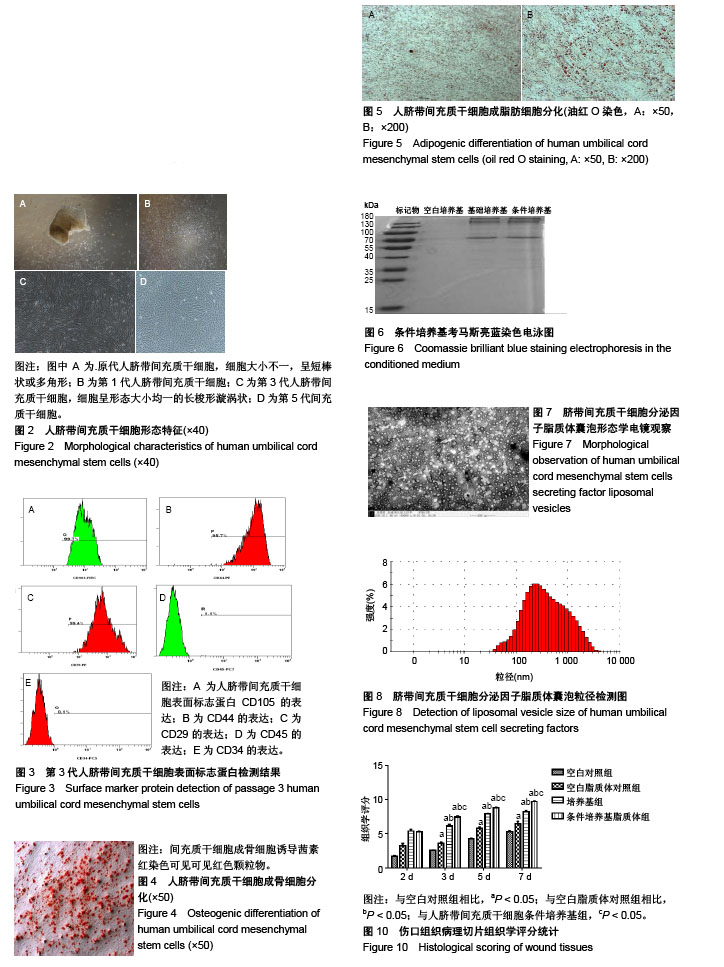
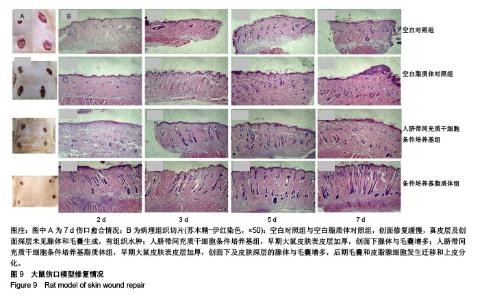
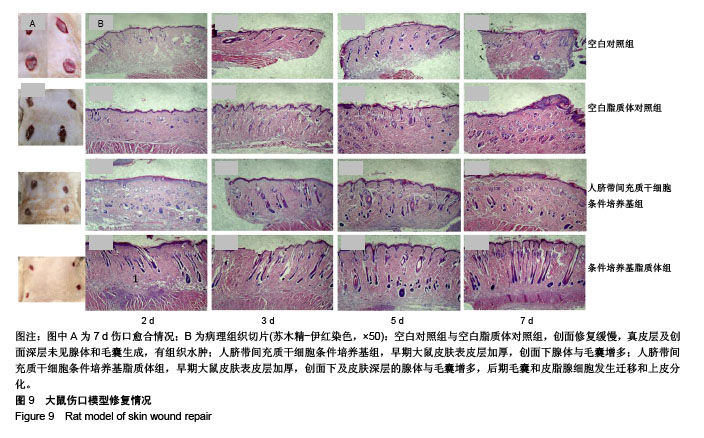
| [1] Dominici M, Le BK, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315. [2] Modo M, Rezaie PP, Patel S, et al. Transplantation of neural stem cells in a rat model of stroke: assessment of short-term graft survival and acute host immunological response. Brain Res. 2002;958(1):70-82. [3] Kucia M, Reca R, Miekus K, et al. Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. Stem Cells. 2005;23(7):879-894. [4] Sell S. On the stem cell origin of cancer. Am J Pathol. 2010; 176(6):2584-2494. [5] Lee M J, Kim J, Lee K I, et al. Enhancement of wound healing by secretory factors of endothelial precursor cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(2): 165-178. [6] Chen L, Tredget EE, Wu PY, et al. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. Plos One. 2008; 3(4):e1886. [7] Kim W S, Park B S, Sung J H. Protective role of adipose-derived stem cells and their soluble factors in photoaging. Arch Dermatol Res. 2009;301(5):329. [8] Larios C, Espina M, Alsina MA, et al. Interaction of three β-interferon domains with liposomes and monolayers as model membranes. Biophys Chem. 2004;111(2):123-133. [9] Proksch E, Brandner JJ. The skin: an indispensable barrier. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17(12):1063-1072. [10] Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321. [11] Wang T, Fang X, Yin ZS.Endothelial progenitor cell-conditioned medium promotes angiogenesis and is neuroprotective after spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(5):887-895.[12] Monteiro N, Martins A, Rui LR, et al. Liposomes in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J R Soc Interface. 2014;11(101):20140459. [13] Xing Y, Wen CY, Li ST, et al.Non-viral liposome-mediated transfer of brain-derived neurotrophic factor across the blood-brain barrier.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(4):617-622.[14] Thomas HE, Zhang Y, Stefely JA, et al. Mitochondrial complex I activity is required for maximal autophagy. Cell Rep. 2018; 24(9):2404-2417. [15] Sapar ML, Ji H, Wang B, et al. Phosphatidylserine externalization results from and causes neurite degeneration in drosophila. Cell Rep. 2018;24(9):2273-2286. [16] Bozzuto G, Molinari A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;2015:975-999. [17] Yingchoncharoen P, Kalinowski DS, Richardson DR. Lipid-based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy: what is available and what is yet to come. Pharmacol Rev. 2016; 68(3):701-787. [18] Irina A, Andrey E, Andrey M, et al. Umbilical cord as prospective source for mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016;. 2016(3):6901286. [19] Davies JE, Walker JT, Keating A. Concise review: wharton's jelly: the rich, but enigmatic, source of mesenchymal stromal cells. stem cells Transl Med. 2017;6(7):1620. [20] Arno AI, Amininik S, Blit PH, et al. Human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells promote skin wound healing through paracrine signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):28. [21] Li, ZY, Paulson AT, Gill T A. Encapsulation of bioactive salmon protein hydrolysates with chitosan-coated liposomes. J Funct Foods. 2015;19:733-743. [22] Jøraholmen MW, Basnet P, Acharya G, et al. PEGylated liposomes for topical vaginal therapy improve delivery of interferon alpha. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2017;113:132-139. [23] Yang L, Yang W, Bi D, et al. A novel method to prepare highly encapsulated interferon-α-2b containing liposomes for intramuscular sustained release. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2006;64(1):9-15. [24] Boulton AJ, Vileikyte L, Ragnarsontennvall G, et al. The global burden of diabetic foot disease. Lancet. 2005;366(9498): 1719-1724. [25] Dominici M, Le BK, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [26] Jayaraman P, Nathan P, Vasanthan P, et al. Stem cells conditioned medium: a new approach to skin wound healing management. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(10):1122-1128. [27] Zhang B, Wang M, Gong A, et al. HucMSC-exosome mediated -Wnt4 signaling is required for cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells. 2015;33(7):2158. [28] Ueda M, Nishino Y. Cell-based cytokine therapy for skin rejuvenation. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21(6):1861-1866. [29] 王黎明.脐带间充质干细胞的分泌蛋白表达谱研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2014.[30] Arno AI, Saeid AN, Blit PH, et al. Effect of human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell paracrine signaling on keloid fibroblasts. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(3):299-307. [31] Shin L, Peterson D A. Human mesenchymal stem cell grafts enhance normal and impaired wound healing by recruiting existing endogenous tissue stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(1):33-42. [32] Talwadekar MD, Kale VP, Limaye LS. Placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells possess better immunoregulatory properties compared to their cord-derived counterparts–a paired sample study. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15784. |