Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (6): 978-984.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1571
Development of everolimus-eluting stents
Ling Hao1, Wang Bao2, Wu Lixia1, Yan Hui1, Song Chunli1
- 1Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130012, Jilin Province, China; 2Department of Internal Medicine, Dongliao People’s Hospital, Liaoyuan 136600, Jilin Province, China
-
Received:2018-11-05Online:2019-02-28Published:2019-02-28 -
Contact:Song Chunli, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130012, Jilin Province, China -
About author:Ling Hao, Master candidate, Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130012, Jilin Province, China -
Supported by:the Industrial Technology Research and Development Project of Jilin Provincial Development and Reform Commission, No. 2016C044-2 (to SCL); the 13th Five-Year Scientific and Technological Research Project of Jilin Provincial Education Department, No. JJKH20180104KJ (to SCL); the Special Health Project of Jilin Provincial Finance Department in 2018 (to SCL); a grant from Jilin Provincial New Coronary Stent Technology Innovation Center, No. JKFC2017250 (to SCL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ling Hao, Wang Bao, Wu Lixia, Yan Hui, Song Chunli. Development of everolimus-eluting stents[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 978-984.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 依维莫司药物洗脱支架 依维莫司是哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶信号转导途径的蛋白激酶抑制剂[7]。mTOR途径在调节细胞生长、增殖和存活中可发挥重要的作用。Martinet等[8]的体外细胞及动物模型实验发现,依维莫司能够选择性清除血管壁巨噬细胞,而不改变平滑肌细胞的数量和活性。Lebwohl等[9]的临床研究也发现依维莫司可通过抑制mTOR途径,抑制内膜增生及炎症反应的发生,因此依维莫司是支架药物涂层的理想材料。基于合成聚合物的依维莫司药物洗脱支架可有效预防和治疗主要由于平滑肌细胞过度增生引起的支架内再狭窄、支架内血栓和病变部位的血运重建[10-11],已被广泛用于阻塞性冠状动脉疾病的治疗[12]。 2.2 钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架 2.2.1 钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架的有效性 目前临床上最常用的依维莫司药物洗脱支架是钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架,见图2。钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架是第2代药物洗脱支架,是由具有生物相容性含氟聚合物的薄支柱(74-81 μm)钴铬合金平台及洗脱依维莫司(100 μg/cm2)组成的支架[13-14]。Morino等[15]在支架内血栓段抬高性心肌梗死的患者支架植入2周后进行光学相干断层扫描,发现钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架和裸金属支架治疗的患者的心肌梗死面积均有明显改善,而与裸金属支架相比,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架纵向长度、最大面积及平均管腔面积明显增大。Buszman等[16]研究也表明,与裸金属支架相比,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架治疗的患者的发生炎症反应的概率和严重程度降低(P < 0.01)。组织病理学分析结果也显示,与裸金属支架处理的斑块相比,依维莫司药物洗脱支架处理的斑块中新生内膜和支架内侧动脉巨噬细胞及组织蛋白酶B的表达水平明显减少[17]。而炎症反应与支架植入后心血管不良事件有关[18]。Karakulak等[19]研究发现房颤患者和窦性心律患者在钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后手术相关并发症发生率相同,这证实了依维莫司洗脱支架治疗房颤的有效性。"

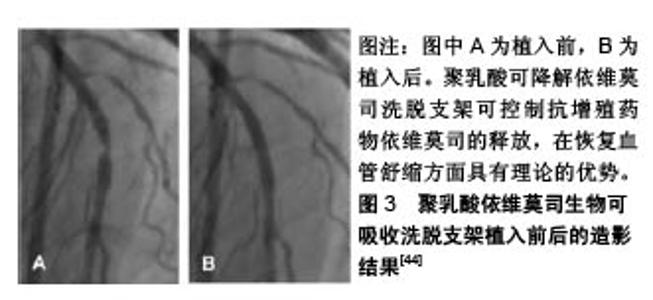
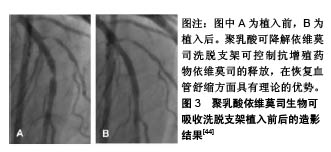
2.2.2 钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入的预后及安全性评估 Aoki等[20]评估了钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后患者的预后及安全性。他们招募了2010年使用钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架进行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗的1 704例患者,共2 649个病灶,并进行了为期5年的随访,发现患者的主要不良心血管事件发生率为10.7%,也仅有9例(0.5%)患者出现支架内血栓。Konishi等[21]针对日本患者的调查也表明,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后3个月血管愈合良好,无内膜增生,且抑制作用持续至少12个月。 支架内血栓形成是支架植入后发生的危及生命的病症[22]。Nakajima等[23]研究发现,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架在所有冠状动脉支架中支架内血栓形成率最低。药物洗脱支架植入后,支架处内皮覆盖的缺失与晚期支架内血栓形成相关。支架处连续药物释放可能会导致诱发内皮覆盖缺失处发生炎症反应,减少血管内一氧化碳的形成,增加活性氧生成,损害血管舒缩机制,诱发冠状动脉斑块的形成[24]。Yano等[25]进行的光学相干断层扫描研究表明,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架支板新生内膜覆盖度达到80%左右,支架支板错位在植入依维莫司药物洗脱支架后4周内完全消失。此外,支架支板的新内膜覆盖几乎在12周内完成。此外,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架的氟化共聚物具有生物相容性,可以减少炎症反应的发生率[26]。Otsuka等[27]研究发现,与西罗莫司洗脱支架和紫杉醇洗脱支架相比,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架的炎症评分更低,纤维蛋白沉积更少。支架周围对比染色是一种相对严重的支架贴壁不良,即1个以上的支架小梁与管壁分离之间有血流信号的情况。与紫杉醇洗脱支架等支架相比,在氟化共聚物处理的依维莫司洗脱支架病灶中支架周围对比染色发生率较低。支架的生物相容性聚合物组成和钴铬设计使得支架具有抗断裂性能[28],这可能时钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后支架内血栓低发生率的原因。 2.2.3 总支杆长度的影响 Hiromasa等[29]试图评估钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后的总支杆长度是否影响患者的临床预后,发现较长的总支杆长度(大于46 mm)的靶病变血运重建率显著高于短总支杆长度组,且长总支杆长度组的靶病变血运重建发生的时间比短总支杆长度组要早。支架内再狭窄是指支架植入后冠状动脉造影发现支架本身及支架边缘5 mm内管腔丢失≥50%的现象[30]。Hoppmann等[31]的研究表明,总支杆长度与钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后3年支架内再狭窄风险增加有关(P < 0.001),且其可能与钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后支架内血栓的发生率无关。Basavarajaiah等[32]研究发现,即使进一步改进金属裸支架技术,采用“全金属护套”的药物洗脱支架进行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗,在复杂病变中靶病变血运重建率的增加也是不可避免的。长期钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后靶病变血运重建的最佳治疗策略仍不清楚,需要进一步研究。 2.2.4 其他 钴铬合金中含有的镍、钴和铬与变态反应有关[33],而依维莫司是一种免疫抑制剂,可抑制接触性变态反应,但在依维莫司释放后可能会引发反应过敏和支架内再狭窄的问题。而Nakajima等[24]研究发现泼尼松龙和抗过敏药物如曲尼司特可改善支架植入后金属过敏患者的预后。此外,Hermiller等[34]研究发现在依维莫司药物洗脱支架治疗的患者中,与单用阿司匹林相比,连续使用噻吩吡啶超过1年者的支架内血栓形成和心肌梗死面积明显减少(P=0.04和P=0.01)。 2.3 依维莫司药物洗脱支架的最新进展 2.3.1 静电纺丝工艺制备的无聚合物依维莫司药物洗脱支架 在聚合物降解过程中产生的酸性产物,即乳酸和乙醇酸,可引起血管壁的炎症反应,而炎症反应在内膜增生和支架再狭窄过程中发挥关键作用[35]。同时,血液-生物材料相互作用首先需要蛋白吸附到支架材料表面。诸如血纤维蛋白原、血管性血友病因子 因子、白蛋白和纤维连接蛋白迅速吸附到支架材料表面,然后是血小板黏附、聚集和凝固,动脉平滑肌细胞迁移和增殖,从而形成支架内再狭窄和血栓。Bae等[36]使用飞秒激光制备一种新型纳米结构的无聚合物依维莫司洗脱支架,金属表面的纳米孔能够将药物储存并输送到目标组织。通过物理方法静电纺丝工艺在药物涂层支架制造期间排除聚合物[37],减少聚合物降解过程中发生的炎症反应,用分层喷射技术对支架进行了依维莫司支架进行涂层,使支架表面呈疏水性,减少了血小板黏附(82.1%)和平滑肌细胞过度增殖。 2.3.2 生物可吸收聚合物依维莫司洗脱支架 生物可降解聚合物药物洗脱支架可以改善生物相容性,降低晚期支架血栓形成的风险[38],而该生物可吸收聚合物由丙交酯乙交酯共聚物代替聚DL-丙交酯组成。与传统生物可吸收支架相比,生物可降解聚合物药物洗脱支架具有较快的生物吸收能力。Arroyo等[39]研究发现该支架可以有效促进动脉血管愈合和预防血管壁慢性炎症反应的发生,生物可吸收聚合物依维莫司药物洗脱支架支架边缘可以看到少量的血管收缩,相对保存的血管内皮功能,降低晚期和极晚期支架血栓的发生率,在植入后15个月动脉愈合良好,生物可吸收聚合物依维莫司药物洗脱支架较生物可吸收血管支架(或持久性聚合物依维莫司洗脱支架更易见到支架处血管舒缩。且有研究显示,生物可吸收聚合物依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后2年的9例患者注射乙酰胆碱后,血管舒缩明显[40]。 2.3.3 环状Arg-Gly-Asp肽的依维莫司涂层冠状动脉支架 内皮化延迟或支架植入后不完全愈合是药物洗脱支架面临的共同问题[41]。Vogt等[42]研究出一种结合环状Arg-Gly-Asp肽的依维莫司药物洗脱支架支架,具有通过内皮祖细胞锚固促进早期和晚期内皮恢复的能力。与依维莫司药物洗脱支架相比,环状Arg-Gly-Asp+依维莫司涂层支架可以减少冠状动脉狭窄,促进支架处内皮细胞恢复活力。通过内皮祖细胞诱导内皮恢复和依维莫司的抗增殖特性协同作用,提高支架的安全性和有效性。在环状Arg-Gly-Asp+依维莫司负载支架中,支架内横截面狭窄减少,支架的再内皮化加速。 2.3.4 其他依维莫司药物洗脱支架 Stone等[43]利用铂-铬依维莫司洗脱支架进行介入治疗,共纳入了1 530例接受冠脉支架植入治疗的患者,12个月的随访发现支架的靶病变失败率、再发心肌梗死、靶病变血运重建较钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架差异无显著性意义。此外,聚乳酸可降解依维莫司洗脱支架具有可吸收的聚合物骨架,涂覆有生物可吸收聚合物聚乳酸,包含并控制抗增殖药物依维莫司的释放,在恢复血管舒缩方面具有理论的优势,见图3 [44],需要更多研究。"
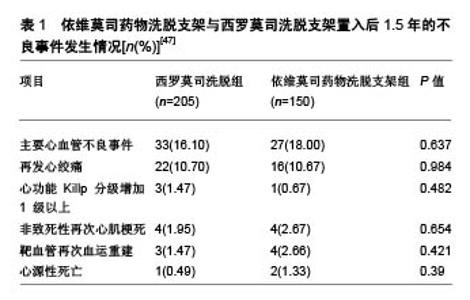
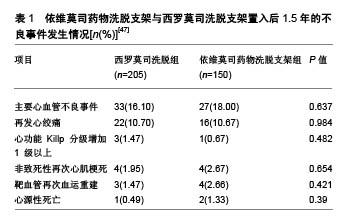
2.4 与其他药物支架比较情况 2.4.1 与西罗莫司洗脱支架的比较 钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架在安全性和疗效方面优于西罗莫司洗脱支架。Otsuka等[25]对149例植入期 > 30 d、≤3年的尸检病例的共204个病灶(依维莫司药物洗脱支架=46;西罗莫司洗脱支架=73)进行病理分析,得出2种支架的晚期支架血栓形成的发生率分别为4%和21%,差异有显著性意义(P=0.008)。与西罗莫司洗脱支架和紫杉醇洗脱支架相比,依维莫司药物洗脱支架表现出较低的炎症反应和较少的生物素沉积。同时,比西罗莫司洗脱支架相比,依维莫司药物洗脱支架变形的发生率较低(P=0.007),支架覆盖面积更大(P=0.004),炎症反应发生率较低(P=0.01)[45]。Choi等[46]的研究也表明支架植入后9个月,光学相干断层扫描检查中未覆盖支架支架和冠状动脉内血栓的发生率显著低于西罗莫司洗脱支架。张娜娜等[47]以旨在评估急性冠脉综合征患者住院期间及出院后长期死亡/心肌梗死再发风险的全球急性冠脉综合征注册(the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events,GRACE)评分较高的患者为研究对象,发现其依维莫司药物洗脱支架比西罗莫司洗脱支架更加获益,主要不良心血管事件发生率较低(P < 0.05),见表1。 2.4.2 与紫杉醇洗脱支架的比较 SPIRIT Ⅱ实验进行了5年随访试图评价XIENCE Ⅴ型洗脱支架(依维莫司药物洗脱支架)与TAXUS紫杉醇洗脱支架(紫杉醇洗脱支架)在支架植入后冠状动脉新生病变情况,结果显示依维莫司药物洗脱支架组心脏死亡率明显低于紫杉醇洗脱支架组(P=0.015)[48]。依维莫司药物洗脱支架中支架血栓形成率低于紫杉醇洗脱支架(P=0.053)。汇总分析SPI-RIT(XIENCE Ⅴ依维莫司洗脱冠状动脉支架系统的临床评估)Ⅱ,Ⅲ和Ⅳ以及COMPARE(第2代依维莫司洗脱和紫杉醇洗脱支架在现实生活中的表现)试验结果表明,钴铬依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后的2年靶病变血运重建率明显低于紫杉醇洗脱支架植入后长期病变和(或)小血管的患者[45,49]。 2.4.3 与佐他莫司洗脱支架比较 阮洁等[50]发现,依维莫司药物洗脱支架组患者靶血管再次血运重建、支架内再狭窄和支架内闭塞发生率均低于 佐他莫司洗脱支架组(P=0.040,P=0.036,P=0.038)。Gu等[51]关于依维莫司药物洗脱支架与佐他莫司洗脱支架的疗效比较的荟萃分析,与佐他莫司洗脱支架相比,依维莫司药物洗脱支架支架内血栓、靶血管血运重建、靶病变血运重建和靶病变失败率显著降低,。 2.4.4 与Biolimus A9洗脱支架比较 Biolimus A9洗脱支架是第3代药物洗脱支架,具有腔内可生物降解聚合物。Sprimont等[52]对植入支架的糖尿病患者进行为期20.8个月的随访,发现Biolimus A9洗脱支架和不可降解聚合依维莫斯洗脱支架的远期疗效和安全性均很接近,2组在心脏死亡、自发性心肌梗死和临床指示靶病灶血运重建的复合初终点发生率方面差异无显著性意义。考虑到所研究的临床事件发生率较低,需要更大样本量的研究来验证这一情况。Smits等[53]研究也发现,Biolimus A9洗脱支架植入后1年的临床和血管造影结果与依维莫司药物洗脱支架植入后接近。Biolimus A9洗脱支架和依维莫司药物洗脱支架均有良好的1年临床疗效,靶病变血运重建发生率低,支架血栓形成率极低。 "
| [1] Lawton J, McGrath J, Jones JS, et al. Treatment of coronary artery disease in an anomalous coronary artery by placement of an intracoronary stent. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1997;41(2): 185-188. [2] Yang JH, Choi SH, Song YB, et al. Long-term outcomes of drug-eluting stent implantation versus coronary artery bypass grafting for patients with coronary artery disease and chronic left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(5): 623-629. [3] Kong KL, Fong AYY, Mejin M, et al. PM222 Early Clinical Outcomes In Patients Electively Implanted With Everolimus And Non-Everolimus Drug Eluting Stents: Impact Of Platelet Function Testing Following Pretreatment With Aspirin And Clopidogrel. Global Heart. 2014;9(1, Supplement):e108. [4] Hayashi T, Kotani J, Ishibashi-Ueda H, et al. Thrombus-related focal in-stent restenosis after everolimus-eluting stent implantation. Heart Vessels. 2014;29(2):273-277. [5] Stone GW, Midei M, Newman W, et al. Comparison of an everolimus-eluting stent and a paclitaxel-eluting stent in patients with coronary artery disease: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2008; 299(16):1903-1913. [6] Palmerini T, Kirtane AJ, Serruys PW, et al. Stent thrombosis with everolimus-eluting stents: meta-analysis of comparative randomized controlled trials. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;5(3): 357-364. [7] Hasskarl J. Everolimus. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014;201: 373-392. [8] Martinet W, Verheye S, De Meyer GR. Everolimus-induced mTOR inhibition selectively depletes macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques by autophagy. Autophagy. 2007;3(3):241-244. [9] Lebwohl D, Anak O, Sahmoud T, et al. Development of everolimus, a novel oral mTOR inhibitor, across a spectrum of diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013;1291:14-32. [10] von Birgelen C, van der Heijden LC, Basalus MW, et al. Five-Year Outcome After Implantation of Zotarolimus- and Everolimus-Eluting Stents in Randomized Trial Participants and Nonenrolled Eligible Patients: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2(3):268-276. [11] Sotomi Y, Suwannasom P, Tenekecioglu E, et al. Differential aspects between cobalt-chromium everolimus drug-eluting stent and Absorb everolimus bioresorbable vascular scaffold: from bench to clinical use. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2015;13(10): 1127-1145. [12] Gatto P, Dumonteil N, Boudou N, et al. Incomplete stent apposition and very late stent thrombosis after everolimus eluting stent implantation and dual antiplatelet therapy interruption. A case of OCT guided therapy. Int J Cardiol. 2015;180:52-54. [13] Ahn JM, Park GM, Cho YR, et al. Comparison of Platinum Chromium Versus Cobalt Chromium Everolimus-eluting Stent in Real World Practice: Outcomes from the Multicenter Prospective IRIS-DES Registry. Am J Cardiol 2013;111(7, Supplement):2B. [14] Barbash IM, Minha S, Torguson R, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of the everolimus-eluting stent compared to first-generation drug-eluting stents in contemporary clinical practice. J Invasive Cardiol. 2014;26(4):154-160. [15] Morino Y, Terashita D, Otake H, et al. Early vascular responses to everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent in the culprit lesions of st-elevation myocardial infarction: results from a multicenter prospective optical coherence tomography study (MECHANISM-AMI 2-week follow-up study). Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2018. doi: 10. 1007/s12928-017-0507-4. [16] Buszman PP, Michalak MJ, Pruski M, et al. Comparable vascular response of a new generation sirolimus eluting stents when compared to fluoropolymer everolimus eluting stents in the porcine coronary restenosis model. Cardiol J. 2016;23(6):657-666. [17] Calfon Press MA, Mallas G, Rosenthal A, et al. Everolimus-eluting stents stabilize plaque inflammation in vivo: assessment by intravascular fluorescence molecular imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;18(5):510-518. [18] Shibata Y, Yano H, Horinaka S, et al. Everolimus-eluting stent suppresses chronic inflammatory reaction compared with bare metal stent in off-label patients. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(Suppl 1): 4807-4817. [19] Karakulak UN, Yorgun H, ?ahiner L, et al. OP-008 Evaluation of Effectiveness and Safety of Everolimus Eluting Stent System (XIENCE V) in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2014; 113(7, Supplement):S3. [20] Aoki J, Kozuma K, Awata M, et al. Five-year clinical outcomes of everolimus-eluting stents from the post marketing study of CoCr-EES (XIENCE V/PROMUS) in Japan. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2018. doi: 10. 1007/s12928-018-0515-z[21] Konishi A, Iwasaki M, Shinke T, et al. Favorable early vessel healing after everolimus-eluting stent implantation: 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-up of optical coherence tomography. J Cardiol. 2018;72(3):193-199. [22] Naito R, Miyauchi K, Konishi H, et al. Early definite stent thrombosis with everolimus-eluting stents. Clin Case Rep. 2015; 3(10):854-857. [23] Nakajima Y, Itoh T, Morino Y. Metal allergy to everolimus-eluting cobalt chromium stents confirmed by positive skin testing as a cause of recurrent multivessel in-stent restenosis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;87(4):E137-142. [24] Giudice P, Attisano T, Di Maio M, et al. Coronary vasomotion dysfunction after everolimus-eluting stent implantation. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2014;6(4):178-182. [25] Yano H, Horinaka S, Ishikawa M, et al. Early vascular responses after everolimus-eluting stent implantation assessed by serial observations of intracoronary optical coherence tomography. Heart Vessels. 2017;32(7):804-812. [26] Sabate M, Cequier A, Iñiguez A, et al. Everolimus-eluting stent versus bare-metal stent in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (EXAMINATION):1 year results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;380(9852):1482-1490. [27] Otsuka F, Vorpahl M, Nakano M, et al. Pathology of second-generation everolimus-eluting stents versus first-generation sirolimus- and paclitaxel-eluting stents in humans. Circulation. 2014;129(2):211-223. [28] Chin-Quee SL, Hsu SH, Nguyen-Ehrenreich KL, et al. Endothelial cell recovery, acute thrombogenicity, and monocyte adhesion and activation on fluorinated copolymer and phosphorylcholine polymer stent coatings. Biomaterials. 2010;31(4):648-657. [29] Hiromasa T, Kuramitsu S, Shinozaki T, et al. Impact of total stent length after cobalt chromium everolimus-eluting stent implantation on 3-year clinical outcomes. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2017; 89(2):207-216. [30] Byrne RA, Joner M, Kastrati A. Stent thrombosis and restenosis: what have we learned and where are we going? The Andreas Grüntzig Lecture ESC 2014. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(47):3320-3331. [31] Hoppmann P, Kufner S, Cassese S, et al. Angiographic and clinical outcomes of patients treated with everolimus-eluting bioresorbable stents in routine clinical practice: Results of the ISAR-ABSORB registry. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2016; 87(5): 822-829. [32] Basavarajaiah S, Naganuma T, Latib A, et al. Extended follow-up following "full-metal jacket" percutaneous coronary interventions with drug-eluting stents. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;84(7): 1042-1050. [33] Honari G, Ellis SG, Wilkoff BL, et al. Hypersensitivity reactions associated with endovascular devices. Contact Dermatitis. 2008; 59(1):7-22. [34] Hermiller JB, Krucoff MW, Kereiakes DJ, et al. Benefits and Risks of Extended Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Everolimus-Eluting Stents. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2016;9(2):138-147. [35] Zamiri P, Kuang Y, Sharma U, et al. The biocompatibility of rapidly degrading polymeric stents in porcine carotid arteries. Biomaterials. 2010;31(31):7847-7855. [36] Bae IH, Jeong MH, Lim KS, et al. Novel Polymer-Free Everolimus-Eluting Stent Fabricated using Femtosecond Laser Improves Re-endothelialization and Anti-inflammation. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7383. [37] Jeon H, Koo S, Reese WM, et al. Directing cell migration and organization via nanocrater-patterned cell-repellent interfaces. Nat Mater. 2015;14(9):918-923. [38] Sprimont P, Pierard S, Vanoverschelde JL, et al. Efficacy and safety of biodegradable polymer biolimus A9-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent in diabetic patients: a prospective non-randomized single-centre long-term comparison. Acta Cardiol. 2014;69(5):523-531. [39] Arroyo DA, Schukraft S, Kallinikou Z, et al. Multianalysis with optical coherence tomography and vasomotion in everolimus-eluting stents and everolimus-eluting biovascular scaffolds: the MOVES trial. Open Heart. 2018;5(1):e000624. [40] Serruys PW, Ormiston JA, Onuma Y, et al. A bioabsorbable everolimus-eluting coronary stent system (ABSORB):2-year outcomes and results from multiple imaging methods. Lancet. 2009;373(9667):897-910. [41] Ota H, Mahmoudi M, Torguson R, et al. Safety and efficacy of everolimus-eluting stents for bare-metal in-stent restenosis. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2015;16(3):151-155. [42] Vogt F, Blindt R, Hoffmann R, et al. TCT-824 Improved Safety And Efficacy Of A Novel Dual cRGD- And Everolimus-coated Coronary Stent Compared To Everolimus-eluting Stents In The Porcine Model. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013;62(18, Supplement 1):B249. [43] Stone GW, Teirstein PS, Meredith IT, et al. A prospective, randomized evaluation of a novel everolimus-eluting coronary stent: the PLATINUM (a Prospective, Randomized, Multicenter Trial to Assess an Everolimus-Eluting Coronary Stent System [PROMUS Element] for the Treatment of Up to Two de Novo Coronary Artery Lesions) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(16): 1700-1708. [44] Ormiston JA, Webster MW, Armstrong G. First-in-human implantation of a fully bioabsorbable drug-eluting stent: the BVS poly-L-lactic acid everolimus-eluting coronary stent. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007;69(1):128-131. [45] Sabaté M, Windecker S, Iñiguez A, et al. Everolimus-eluting bioresorbable stent vs. durable polymer everolimus-eluting metallic stent in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: results of the randomized ABSORB ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction-TROFI II trial. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(3):229-240. [46] Choi HH, Kim JS, Yoon DH, et al. Favorable neointimal coverage in everolimus-eluting stent at 9 months after stent implantation: comparison with sirolimus-eluting stent using optical coherence tomography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012;28(3):491-497. [47] 张娜娜,魏广和,张韶辉,等.西罗莫司与依维莫司药物洗脱支架治疗非ST段抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征的疗效比较[J].中国循环杂志, 2016,31(5):437-441.[48] Onuma Y, Miquel-Hebert K, Serruys PW, et al. Five-year long-term clinical follow-up of the XIENCE V everolimus-eluting coronary stent system in the treatment of patients with de novo coronary artery disease: the SPIRIT II trial. EuroIntervention. 2013;8(9):1047-1051. [49] Claessen BE, Smits PC, Kereiakes DJ, et al. Impact of lesion length and vessel size on clinical outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention with everolimus- versus paclitaxel-eluting stents pooled analysis from the SPIRIT (Clinical Evaluation of the XIENCE V Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System) and COMPARE (Second-generation everolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stents in real-life practice) Randomized Trials. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4(11):1209-1215. [50] 阮洁,蒋萍,苏晞.佐他莫司洗脱支架与依维莫司洗脱支架5年临床疗效比较[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2018,26(6):341-344.[51] Gu H, Hua K, Li W, et al. Safety and efficacy of everolimus-eluting stent versus zotarolimus-eluting stent: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials and observational studies. Int J Cardiol. 2015;201:552-560. [52] Sprimont P, Pierard S, Vanoverschelde JL, et al. Efficacy and safety of biodegradable polymer biolimus A9-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent in diabetic patients: a prospective non-randomized single-centre long-term comparison. Acta Cardiol. 2014;69(5):523-531. [53] Smits PC, Hofma S, Togni M, et al. Abluminal biodegradable polymer biolimus-eluting stent versus durable polymer everolimus-eluting stent (COMPARE II): a randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2013;381(9867):651-660. [54] Connelly M. Cognitive behavioral therapy for treatment of pediatric chronic migraine. JAMA. 2013;310(24):2617-2618. [55] Stone GW, Sabik JF, Serruys PW, et al. Everolimus-Eluting Stents or Bypass Surgery for Left Main Coronary Artery Disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(23):2223-2235. [56] Miura K, Tada T, Kuwayama A, et al. Stent Fracture and Peri-Stent Contrast Staining After Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation - 5-Year Outcomes. Circ J. 2017;81(10):1514-1521. [57] Kuramitsu S, Iwabuchi M, Domei T, et al. Response to letter regarding article, "incidence and clinical impact of stent fracture after everolimus-eluting stent implantation". Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6(1):e10. [58] Ji EY, Park GM, Kim DW, et al. Multiple Stent Fractures After Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation Causing Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Case Report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(6): e2704. [59] Park SJ, Ahn JM, Kim YH, et al. Trial of everolimus-eluting stents or bypass surgery for coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2015;372 (13):1204-1212. [60] Nomura T, Suzuki N, Takamura S, et al. Three-Year Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes After Everolimus-Eluting Stent Implantation in Patients With a History of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. Int Heart J. 2016;57(2):158-166. [61] Kadakia MB, Epps KC, Julien ME, et al. Early aneurysm formation after everolimus-eluting stent implantation. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(2):266-267. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||