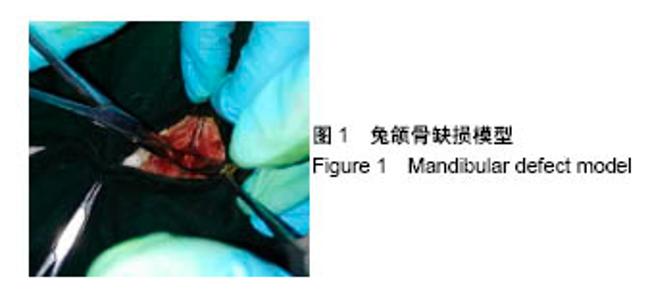
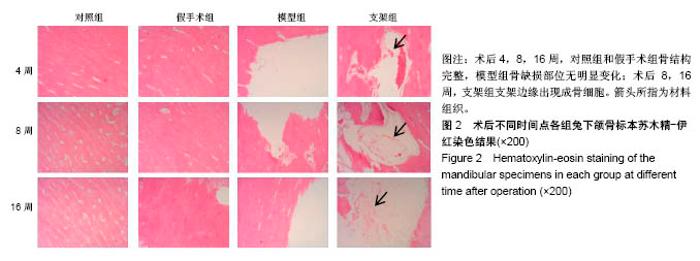
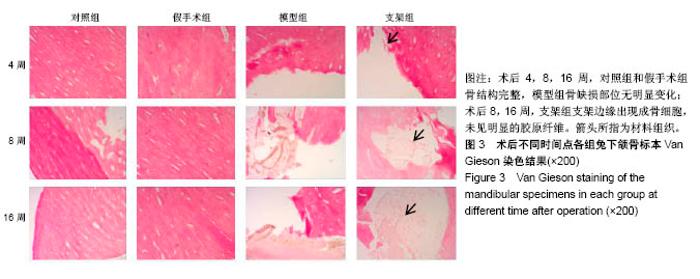
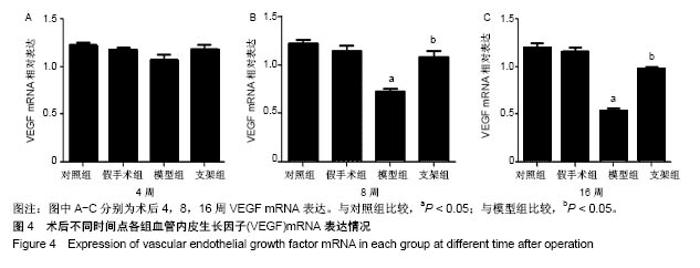
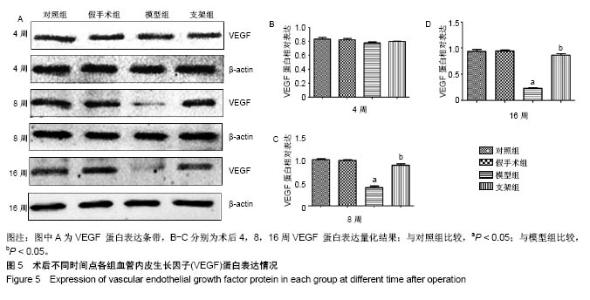
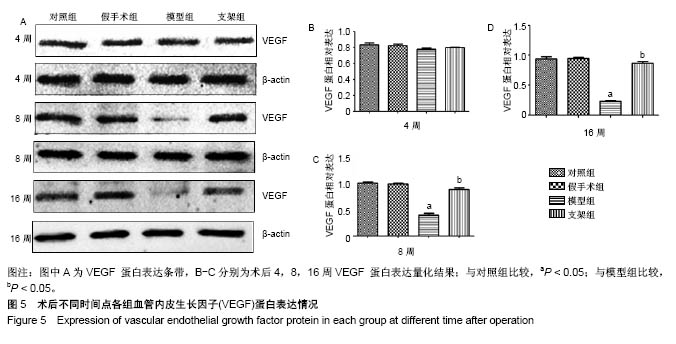
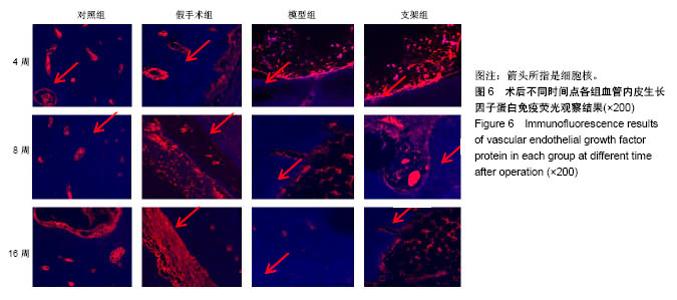
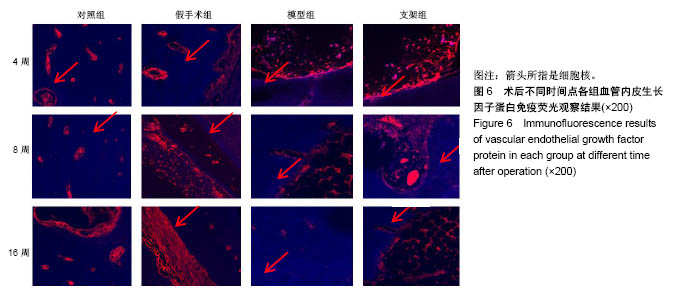
| [1] Briem D, Strametz S, Schröoder K, et al. Response of primary fibroblasts and osteoblasts to plasma treated polyetheretherketone (PEEK) surfaces. J Materi Sci Mater Med. 2005;16(7):671-677. [2] Dorozhkin SV. Calcium Orthophosphates in Nature, Biology and Medicine. Materials. 2009;2(2):399-498. [3] Katzer A, Marquardt H, Westendorf J, et al. Polyetheretherketone--cytotoxicity and mutagenicity in vitro. Biomaterials. 2002;23(8):1749-1759. [4] Converse GL, Conrad TL, Merrill CH, et al. Hydroxyapatite whisker-reinforced polyetherketoneketone bone ingrowth scaffolds. Acta Biomaterialia. 2010;6(3):856-863. [5] Lee JH, Jang HL, Lee KM, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the bioactivity of hydroxyapatite-coated polyetheretherketone biocomposites created by cold spray technology. Acta Biomaterialia. 2013;9(4):6177. [6] Salerno S, Piscioneri A, Laera S, et al. Improved functions of human hepatocytes on NH 3, plasma-grafted PEEK-WC–PU membranes. Biomaterials. 2009;30(26):4348-4356. [7] Dennes TJ, Schwartz J. A Nanoscale Adhesion Layer to Promote Cell Attachment on PEEK. J Am Chem Soc. 2009; 131(10):3456-3457. [8] Marsell R, Einhorn TA. The biology of fracture healing. Injury. 2011;42(6):551-555. [9] Zhao D, Pan C, Sun J, et al. VEGF drives cancer-initiating stem cells through VEGFR-2|[sol]|Stat3 signaling to upregulate Myc and Sox2. Oncogene. 2015;34(24):3107. [10] Bosch C, Melsen B, Vargervik K. Importance of the critical-size bone defect in testing bone-regenerating materials. J Craniofac Surg. 1998;9(4):310-316. [11] Hollinger JO, Kleinschmidt JC. The critical size defect as an experimental model to test bone repair materials. J Craniofac Surg. 1990;1(1):60-68. [12] Aaboe M, Pinholt EM, Hjørting-Hansen E. Unicortical critical size defect of rabbit tibia is larger than 8 mm. J Craniofac Surg. 1994;5(3):201-203. [13] Nyman R, Magnusson M, Sennerby L, et al. Membrane- guided bone regeneration. Segmental radius defects studied in the rabbit. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica. 1995;66(2): 169-173. [14] Chen G, Li W, Yu X, et al. Study of the cohesion of TTCP/DCPA phosphate cement through evolution of cohesion time and remaining percentage. J Mater Sci. 2009;44(3):828. [15] Sayer M, Stratilatov AD, Reid J, et al. Structure and composition of silicon-stabilized tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials. 2003;24(3):369. [16] Reid JW, Pietak A, Sayer M, et al. Phase formation and evolution in the silicon substituted tricalcium phosphate/ apatite system. Biomaterials. 2005;26(16):2887. [17] Jang JH, Castano O, Kim HW. Electrospun materials as potential platforms for bone tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61(12):1065. [18] Arcangeli E, Kon E, Delcogliano M, et al. Nanocomposite biomimetic scaffold in knee osteochondral defect regeneration: an animal study. J Appl Biomater Biomech. 2009;7(1):52-53. [19] Khadka A, Li J, Li Y, et al. Evaluation of hybrid porous biomimetic nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 6 and bone marrow-derived stem cell construct in repair of calvarial critical size defect. J Craniofac Surg. 2011;22(5):1852-1858. [20] Schneider OD, Weber F, Brunner TJ, et al. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of flexible, cottonwool-like nanocomposites as bone substitute material for complex defects. Acta Biomaterialia. 2009;5(5):1775-1784. [21] Chow LC. Next generation calcium phosphate-based biomaterials. Dent Mater J. 2009;28(1):1. [22] 冷卫东,刘彩云,黄翠,等.聚醚醚酮/牙源性双相生物陶瓷复合材料的制备及力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(52): 8418-8422.[23] Fontijn D, Bosch LJ, Duyndam MC, et al. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor-Mediated Overexpression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in 1F6 Human Melanoma Cells is Regulated by Activation of PI-3K and p38 MAPK. Cell Oncol. 2009;31(3):179-190. [24] Park K, Amano H, Ito Y, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (VEGFR-1) signaling enhances angiogenesis in a surgical sponge model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;78:140-149. [25] Horner A, Bishop NJ, Bord S, et al. Immunolocalisation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in human neonatal growth plate cartilage. J Anat. 1999;194(Pt 4):519-524. [26] Becker R, Pufe T, Kulow S, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor during healing of the meniscus in a rabbit model. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004;86(7):1082-1087. [27] Lilley CE, Groutsi F, Han Z, et al. Multiple immediate-early gene-deficient herpes simplex virus vectors allowing efficient gene delivery to neurons in culture and widespread gene delivery to the central nervous system in vivo. J Virol. 2001; 75(9):4343-4356. |