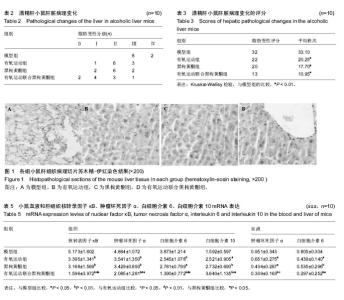
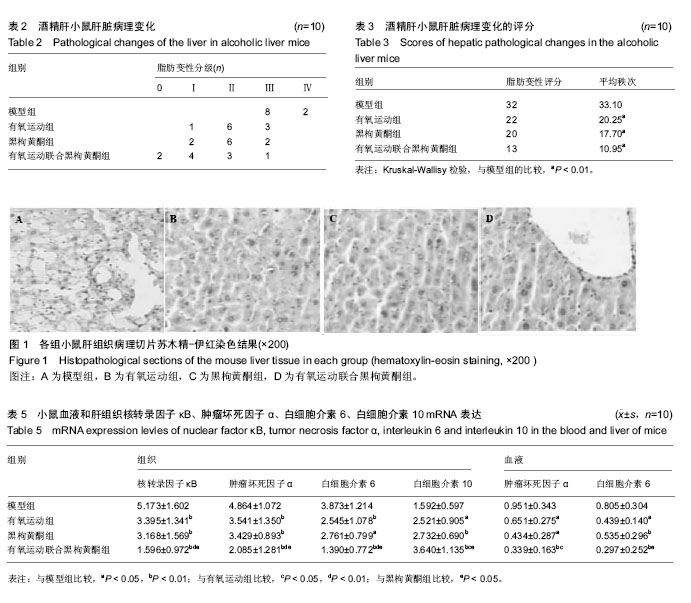
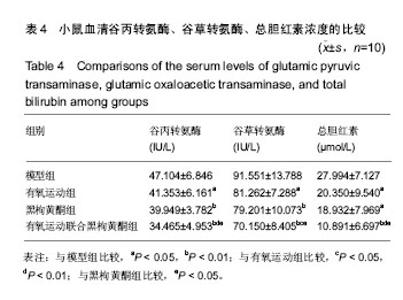
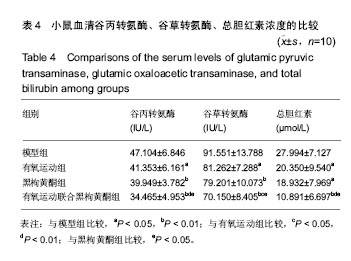
| [1] Wheeler MD. Endotoxin and kupffer cell activation in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res Health. 2003;27(4):300-306.[2] 关光玉,曾家慧,张术斌,等.酒精性脂肪肝小鼠模型的建立[J].宁夏医学杂志,2007,29(11):971-2.[3] 江正菊,宁林玲,胡霞敏,等. 桑叶总黄酮对高脂诱导大鼠高血脂及高血糖的影响[J].中药材,2011,34(1):108-111.[4] Ganesan S, Aggarwal K, Paquette N, et al.NF-κB/Rel Proteins and the Humoral Immune Responses ofDrosophila melanogaster. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011;349:25-60.[5] 周柏存,罗赤苗,陈嘉勤,等.虎纹克胰素与运动干预对阻塞性黄疸肝细胞损伤修复机制的研究[J].生命科学研究, 2017,21(2): 117-124.[6] Zhu L, Wei T, Chang X, et al. Effects of Salidroside on myocardial injury in vivoin vitro via regulation of Nox/NF-κB/AP1 pathway.Inflammation.2015;38: 1589–1598.[7] Preston Campbell J, Mulcrone P, Masood SK, et al.TRIzol and Alu qPCR-based quantification of metastatic seeding within the skeleton. Sci Rep.2015;5:12635.[8] Chang X, Luo F, Jiang W, et al.Protective activity of Salidroside against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer via the MAPK/NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. IntImmunopharmacol. 2015;28: 604-615.[9] 任大宾,孙仁宇. 白介素-10的抗炎功能及其分子机制[J]. 国外医学(呼吸系统分册),2005,25(3):175-178.[10] Bruun JM,Helge JW,Richelsen B,et al. Diet and exercise reduce low-grade in fiammation and macrophage in filtration in adipose tissue but not in skeletal muscle in severely obese subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2006;290: E961-E967.[11] Smith JK,Dykes R,Douglas JE,et al.Long- termexercise and atherogenic activity of blood mononuclear cells in personsat risk of developing ischemic heart disease.JAMA. 1999;281: 1722-1727.[12] Kohut ML,McCann DA,Russell DW,et al.Aerobic exercise,but not fiexibility/resistance exercise,reduces serum IL-18, CRP, and IL-6 independent of betablockers,BMI,and psychosocial factors in older adults.Brain BehavImmun.2006; 20:201-209.[13] Oberbach A,Tonjes A,Kloting N,et al.Effect of a 4 week physicaltraining program on plasma concentrations of in fi ammatory markers inpatientswith abnormal glucose tolerance. Eur J Endocrinol.2006;154:577-585.[14] Thiago Gomes Heck. Pharmacology and exercise: an essentialdiscipline and research area in health courses.J Nov Physiother.2013;3(5):1-2.[15] Gielen S,Adams V,Mobius- Winkler S,et al.Anti- inflammatoryef-fects of exercise training in the skeletal muscle of patients with chronicheartfailure.J Am CollCardiol. 2003;42:861- 868.[16] Colbert LH,Visser M,Simonsick EM,et al.Physical activity, exercise,and in flammatory markers in older adults: findings from the Health,Aging and Body Composition Study. J Am GeriatrSoc.2004;52:1098-1104.[17] 崔纪芳,曹建民,周海涛,等. 黑果枸杞对大鼠运动性心肌损伤的保护作用[J].中国体育科技,2016,52(5):46-51.[18] Islam T, Yu X, Badwal TS, et al. Comparative studies on phenolic profiles,antioxidant capacities and carotenoid contents ofred goji berry (Lycium barbarum) and black goji berry (Lycium ruthenicum). Chem Cent J.2017;11: 59.[19] 张柯,曹建民,郭龙,等.黑果构祀对大鼠运动性肾缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J].首都体育大学学报,2015,27(1):85-89.[20] 朱敬生,陈嘉勤,陈薇薇,等.有氧运动联合雷氏蛛毒对小鼠H_(22)肝肿瘤的干预研究[J].武汉体育学院学报,2014,48(1):96-100.[21] Lin L,Cai WM,Qin CJ,et al.Intervention of TLR4 Signal Pathway Cytokines in Severe Liver Injury with Obstructive Jaundice in Rats.Sports Med.2012;33(7):572-579. |