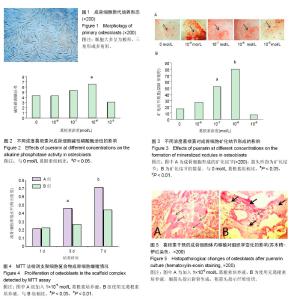
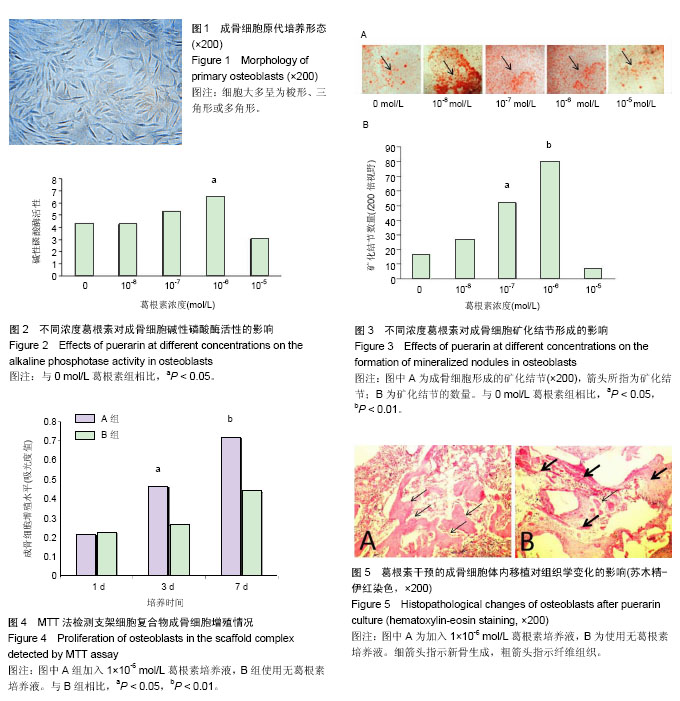
| [1] Krishnan L, Willett NJ, Guldberg RE. Vascularization strategies for bone regeneration. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(2):432-444. [2] Bhattacharya I, Ghayor C, Weber FE. The Use of Adipose Tissue-Derived Progenitors in Bone Tissue Engineering - a Review. Transfus Med Hemother. 2016;43(5):336-343.[3] Tang W, Lin D, Yu Y, et al. Bioinspired trimodal macro/micro/nano-porous scaffolds loading rhBMP-2 for complete regeneration of critical size bone defect. Acta Biomater. 2016;32: 309-323.[4] Baino F, Fiorilli S, Vitale-Brovarone C. Bioactive glass-based materials with hierarchical porosity for medical applications: Review of recent advances. Acta Biomater. 2016;42:18-32.[5] Baino F, Fiorilli S, Vitale-Brovarone C. Composite Biomaterials Based on Sol-Gel Mesoporous Silicate Glasses: A Review. Bioengineering (Basel). 2017;4(1):E15. [6] 孙娟,葛声.大豆异黄酮与围绝经期骨质疏松的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(10):2209-2212.[7] 唐文斌, 屠蕊沁.葛根素抗凋亡作用的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2014,8(11):2146-2149.[8] 杨勇晖, 陈平洋.葛根素防治骨质疏松的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(3):376-378.[9] Tang XL, Liu XJ, Tian Q, et al. Dynamic oxidative stress and DNA damage induced by oestrogen deficiency and protective effects of puerarin and 17β-oestradiol in ovariectomized rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2012;111(2):87-91. [10] 王晓晖,罗向霞,史晓伟,等.葛根素对高糖培养成骨细胞增殖?矿化及凋亡的影响[J].中国中医药科技,2017, 24(11):733-735.[11] Wang C, Meng MX, Tang XL, et al. The proliferation, differentiation, and mineralization effects of puerarin on osteoblasts in vitro. Chin J Nat Med. 2014;12(6):436-442. [12] Wang Y, Wang WL, Xie WL, et al. Puerarin stimulates proliferation and differentiation and protects against cell death in human osteoblastic MG-63 cells via ER-dependent MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt activation. Phytomedicine. 2013;20(10):787-796.[13] 王海珍,贠云飞,苗志勃.葛根素对大鼠成骨细胞增殖影响的体外实验研究[J].中医药导报,2017,19(3):77-79.[14] Declercq H, Van den Vreken N, De Maeyer E, et al. Isolation, proliferation and differentiation of osteoblastic cells to study cell/biomaterial interactions: comparison of different isolation techniques and source. Biomaterials. 2004;25(5):757-768.[15] Yuan J, Cui L, Zhang WJ, et al. Repair of canine mandibular bone defects with bone marrow stromal cells and porous beta-tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials. 2007;28(6):1005-1013. [16] Endo I, Mastumoto T. Bone and Stem Cells. Regulatory mechanism of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to osteoblasts. Clin Calcium. 2014;24(4):555-564.[17] Baum R, Gravallese EM. Bone as a Target Organ in Rheumatic Disease: Impact on Osteoclasts and Osteoblasts. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016;51(1):1-15.[18] 张莹莹,周建斌,曾祥伟,等.葛根素对成骨细胞增殖能力及靶向Runx2的miRNA的影响[J].中国药理学通报, 2016,32(10):1457-1462.[19] 孙玉敏,许晓琳,杨怡,等.葛根素可促进老年女性骨质疏松症患者成骨细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(29):4593-4597.[20] 钱康琦,孙玉明,詹秀琴.实时荧光定量PCR法研究葛根素对成骨细胞TGF-β1及Smad 2/3mRNA表达的影响[J].辽宁中医学院学报,2013, 15(9):46-49.[21] 路立花,杨莉,徐玉荣.葛根素对成骨细胞增殖及骨形态发生蛋白的影响[J].世界中医药,2017,12(9):2139-2142.[22] Whyte MP. Hypophosphatasia and the role of alkaline phosphatase in skeletal mineralization. Endocr Rev. 1994;15(4): 439-461.[23] Addison WN, Azari F, Sørensen ES, et al. Pyrophosphate inhibits mineralization of osteoblast cultures by binding to mineral, up-regulating osteopontin, and inhibiting alkaline phosphatase activity. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(21):15872-15883.[24] Maeno S, Niki Y, Matsumoto H, et al. The effect of calcium ion concentration on osteoblast viability, proliferation and differentiation in monolayer and 3D culture. Biomaterials. 2005; 26(23):4847-4855.[25] Maeno S, Niki Y, Matsumoto H, et al. The effect of calcium ion concentration on osteoblast viability, proliferation and differentiation in monolayer and 3D culture. Biomaterials. 2005; 26(23):4847-4855.[26] Sweet L, Kang Y, Czisch C, et al. Geometrical versus Random β-TCP Scaffolds: Exploring the Effects on Schwann Cell Growth and Behavior. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0139820. [27] Siqueira L, Passador FR, Costa MM, et al. Influence of the addition of β-TCP on the morphology, thermal properties and cell viability of poly (lactic acid) fibers obtained by electrospinning. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;52:135-143. [28] Xu S, Li D, Xie Y, et al. The growth of stem cells within β-TCP scaffolds in a fluid-dynamic environment. Mater Sci Eng C. 2008;28(1):164-170.[29] Lin S, Cui L, Chen G, et al. PLGA/β-TCP composite scaffold incorporating salvianolic acid B promotes bone fusion by angiogenesis and osteogenesis in a rat spinal fusion model. Biomaterials. 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.04.004. [30] Maji K, Dasgupta S, Pramanik K, et al. Preparation and characterization of gelatin-chitosan-nanoβ-TCP based scaffold for orthopaedic application. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018; 86:83-94. |